Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Carbohydrates - Key Notes: Asked To Come Up With It All Off The Top of Your Head
Carbohydrates - Key Notes: Asked To Come Up With It All Off The Top of Your Head
Uploaded by
Foong YeeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Carbohydrates - Key NotesDocument3 pagesCarbohydrates - Key NotesSammie PingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 BIOLOGICAL MOLECULESDocument7 pagesChapter 02 BIOLOGICAL MOLECULESAceTheLastFlameNo ratings yet
- Notes Biology Unit 1Document16 pagesNotes Biology Unit 1tammiem 2363No ratings yet
- Chemistry of Carbohydrates: December 2017Document20 pagesChemistry of Carbohydrates: December 2017yashNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes 2Document32 pagesBio Notes 2Sinin VegaNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes 2Document32 pagesBio Notes 2Sinin VegaNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument48 pagesBiomoleculesalikhantech786No ratings yet
- Biology FSC Chapter 2Document15 pagesBiology FSC Chapter 2Diana PriyaNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument14 pagesBio MoleculessvjbxgjNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates 131204014552 Phpapp02 PDFDocument27 pagesCarbohydrates 131204014552 Phpapp02 PDFTweenie Dalumpines100% (4)
- Chapter 4 Chemical Composition of The CellDocument12 pagesChapter 4 Chemical Composition of The CellBROther RelaxNo ratings yet
- Chapter No.02 Carbohydrates IIDocument56 pagesChapter No.02 Carbohydrates IIsolutionsexpert70059165No ratings yet
- Chapter-Iii:Biomolecules: CarbohydratesDocument12 pagesChapter-Iii:Biomolecules: Carbohydratesbereket gashuNo ratings yet
- STPM BIOLOGY SEMESTER 1 Chapter 1 CarbohydratesDocument9 pagesSTPM BIOLOGY SEMESTER 1 Chapter 1 CarbohydratesMabel Lee Shan Shan100% (3)
- BIOCHEMISTRYDocument105 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYVai SanNo ratings yet
- 2B BiochemistryDocument53 pages2B BiochemistryYashNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - CarbohydratesDocument91 pagesLecture 3 - CarbohydratesAsyraf Arshat0% (1)
- CarbohydratesDocument48 pagesCarbohydratesTrescia Mae EstilloreNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument8 pagesCarbohydratesCyrus Flores,No ratings yet
- 1 A (11) CarbohydratesDocument12 pages1 A (11) Carbohydratesenakshi perusingheNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesCarbohydratesvanshkashp8272No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 CarbohydratesDocument10 pagesChapter 4 CarbohydratesFendy HamidNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates OutlineDocument3 pagesCarbohydrates OutlineKalka BoroNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument26 pagesUntitledSaba ShahazadiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - 1Document35 pagesUnit 2 - 1Sunita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Biology: Carbohydrates Lipids & ProteinsDocument15 pagesBiology: Carbohydrates Lipids & ProteinsDr.CharinNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument8 pagesCarbohydratesNarasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- CarbohyratesDocument47 pagesCarbohyratesEdward SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 Biomolecules: CarbohydratesDocument20 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 Biomolecules: CarbohydratesSOUMYODEEP NAYAKNo ratings yet
- NOTES - PPT - CH 5 Polymers-Carbs-Lipids - NEWDocument59 pagesNOTES - PPT - CH 5 Polymers-Carbs-Lipids - NEWjagadish dasariNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesCarbohydratesNarasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- OOD Echnology: CarbohydratesDocument26 pagesOOD Echnology: CarbohydrateslelascepanovicNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument8 pagesBiological MoleculesQaran PrintingNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Jaymark D. SamsonDocument23 pagesCarbohydrates: Jaymark D. Samson둡챙브로No ratings yet
- Biological MoleculeDocument3 pagesBiological Moleculesna240839No ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Biological MoleculesDocument18 pagesBiochemistry: Biological MoleculesAnup Singh TanwarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 BiomoleculesDocument13 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 Biomoleculesrathi rupaNo ratings yet
- Elementry Plant Bio Chemistery: Carbohydrat ESDocument40 pagesElementry Plant Bio Chemistery: Carbohydrat ESdenolap242No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Practical ReportDocument9 pagesCarbohydrates Practical ReportshubaNo ratings yet
- Genetics and EvolutionDocument5 pagesGenetics and Evolutionmahreen akramNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules Summary SheetsDocument6 pagesBiological Molecules Summary SheetsdanyalbhaijiNo ratings yet
- Home Economics NotesDocument11 pagesHome Economics Noteslone obonetseNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates and Related CompoundsDocument56 pagesCarbohydrates and Related CompoundsMani JeeNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument3 pagesCARBOHYDRATESvyn bringinoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Book - Grade 12 SE-1Document28 pagesChemistry Book - Grade 12 SE-1Abed KaremNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Green Plants Turn H O, Co, and Sunlight Into CarbohydratesDocument121 pagesCarbohydrates: Green Plants Turn H O, Co, and Sunlight Into CarbohydratesRalph Ian CaingcoyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CarbohydratesDocument20 pagesIntroduction To CarbohydratesJason TulipatNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument8 pagesBiomoleculesOM SableNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate ChemistryDocument46 pagesCarbohydrate Chemistryrishibiswas18052001No ratings yet
- A Level BiologyDocument522 pagesA Level BiologyJAMESNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesCarbohydratesEncik AfiqNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 CarbohydratesDocument71 pagesUnit-1 Carbohydratesdasiwev112No ratings yet
- BBC1 K14 K15 KarbohidratDocument31 pagesBBC1 K14 K15 Karbohidratbrigita charvioNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument112 pagesCarbohydratesmaryam ijazNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATES ChemDocument8 pagesCARBOHYDRATES ChemPriyesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Revision Notes in Accordance With Syllabus SpecificationsDocument50 pagesUnit 1. Revision Notes in Accordance With Syllabus SpecificationslucyNo ratings yet
- General and Specific Test For Carbohydrates BioChemDocument15 pagesGeneral and Specific Test For Carbohydrates BioChemwynNo ratings yet
- Aadil BioChemistryDocument3 pagesAadil BioChemistrySaira Falak SherNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Applied to Beer Brewing - General Chemistry of the Raw Materials of Malting and BrewingFrom EverandBiochemistry Applied to Beer Brewing - General Chemistry of the Raw Materials of Malting and BrewingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
Carbohydrates - Key Notes: Asked To Come Up With It All Off The Top of Your Head
Carbohydrates - Key Notes: Asked To Come Up With It All Off The Top of Your Head
Uploaded by
Foong YeeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Carbohydrates - Key Notes: Asked To Come Up With It All Off The Top of Your Head
Carbohydrates - Key Notes: Asked To Come Up With It All Off The Top of Your Head
Uploaded by
Foong YeeCopyright:
Available Formats
CARBOHYDRATES - KEY NOTES
Contain Elements: Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen. Biological Importance Energy Source Structural Compounds Storage Compounds
Carbohydrates are principal respiratory substrates Cellulose (CW of all plant cells) & Lignin Plants, Starch (common plant storage never in animals) Animals. Glycogen (e.g. mammalian liver)
CLASSIFICATION: The basic sugar unit = the saccharide 1 sugar unit = Monosaccaride 2 sugar units = Disaccharide Many sugar units = Polysaccharide
MONOSACCHARIDES Examples of Monosaccharides: Glucose, Ribose General There are the building blocks of other important C/Hs Monosaccharides are: Sweet tasting Soluble in water Reducing sugars (see below)
Reducing Sugar Properties (all monosaccharides are reducing sugars). M/S are capable of REDUCING benedicts solution. When this reduction occurs benedicts solution changes from blue to orange/red.
DISACCHARIDES Examples of D/S: Maltose (Malt sugar), Lactose (milk sugar) Maltose formed by CONDENSATION of 2 units of glucose, the bond is called a glycosidic bond. Note: In the exam you could be given half of the reaction below and asked to fill in the other half - you wouldn't be asked to come up with it all off the top of your head 2 molecules of glucose
Undergo a condensation reaction to form
+ H2O Maltose and Water General Summary of disaccharides May be non-reducing Sweet tasting Water soluble
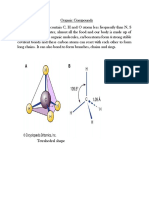
POLYSACCHARIDES Examples of P/S: Starch, Glycogen, Cellulose These are an important group of carbohydrates. Two main divisions: Structural Polysaccharides e.g. Cellulose, Chitin, Lignin (wood) Storage Polysaccharides e.g. Starch and Glycogen
General Properties of P/S Non sweet tasting Non truly soluble in H2O
Structural P/S In these polysaccharides the sugar unit residues present in long chain molecules of the polymer are straight, and cross-linkages between chains occur giving the material its strength. back home
You might also like
- Carbohydrates - Key NotesDocument3 pagesCarbohydrates - Key NotesSammie PingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 BIOLOGICAL MOLECULESDocument7 pagesChapter 02 BIOLOGICAL MOLECULESAceTheLastFlameNo ratings yet
- Notes Biology Unit 1Document16 pagesNotes Biology Unit 1tammiem 2363No ratings yet
- Chemistry of Carbohydrates: December 2017Document20 pagesChemistry of Carbohydrates: December 2017yashNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes 2Document32 pagesBio Notes 2Sinin VegaNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes 2Document32 pagesBio Notes 2Sinin VegaNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument48 pagesBiomoleculesalikhantech786No ratings yet
- Biology FSC Chapter 2Document15 pagesBiology FSC Chapter 2Diana PriyaNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument14 pagesBio MoleculessvjbxgjNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates 131204014552 Phpapp02 PDFDocument27 pagesCarbohydrates 131204014552 Phpapp02 PDFTweenie Dalumpines100% (4)
- Chapter 4 Chemical Composition of The CellDocument12 pagesChapter 4 Chemical Composition of The CellBROther RelaxNo ratings yet
- Chapter No.02 Carbohydrates IIDocument56 pagesChapter No.02 Carbohydrates IIsolutionsexpert70059165No ratings yet
- Chapter-Iii:Biomolecules: CarbohydratesDocument12 pagesChapter-Iii:Biomolecules: Carbohydratesbereket gashuNo ratings yet
- STPM BIOLOGY SEMESTER 1 Chapter 1 CarbohydratesDocument9 pagesSTPM BIOLOGY SEMESTER 1 Chapter 1 CarbohydratesMabel Lee Shan Shan100% (3)
- BIOCHEMISTRYDocument105 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYVai SanNo ratings yet
- 2B BiochemistryDocument53 pages2B BiochemistryYashNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - CarbohydratesDocument91 pagesLecture 3 - CarbohydratesAsyraf Arshat0% (1)
- CarbohydratesDocument48 pagesCarbohydratesTrescia Mae EstilloreNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument8 pagesCarbohydratesCyrus Flores,No ratings yet
- 1 A (11) CarbohydratesDocument12 pages1 A (11) Carbohydratesenakshi perusingheNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesCarbohydratesvanshkashp8272No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 CarbohydratesDocument10 pagesChapter 4 CarbohydratesFendy HamidNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates OutlineDocument3 pagesCarbohydrates OutlineKalka BoroNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument26 pagesUntitledSaba ShahazadiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - 1Document35 pagesUnit 2 - 1Sunita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Biology: Carbohydrates Lipids & ProteinsDocument15 pagesBiology: Carbohydrates Lipids & ProteinsDr.CharinNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument8 pagesCarbohydratesNarasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- CarbohyratesDocument47 pagesCarbohyratesEdward SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 Biomolecules: CarbohydratesDocument20 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 Biomolecules: CarbohydratesSOUMYODEEP NAYAKNo ratings yet
- NOTES - PPT - CH 5 Polymers-Carbs-Lipids - NEWDocument59 pagesNOTES - PPT - CH 5 Polymers-Carbs-Lipids - NEWjagadish dasariNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesCarbohydratesNarasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- OOD Echnology: CarbohydratesDocument26 pagesOOD Echnology: CarbohydrateslelascepanovicNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument8 pagesBiological MoleculesQaran PrintingNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Jaymark D. SamsonDocument23 pagesCarbohydrates: Jaymark D. Samson둡챙브로No ratings yet
- Biological MoleculeDocument3 pagesBiological Moleculesna240839No ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Biological MoleculesDocument18 pagesBiochemistry: Biological MoleculesAnup Singh TanwarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 BiomoleculesDocument13 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 Biomoleculesrathi rupaNo ratings yet
- Elementry Plant Bio Chemistery: Carbohydrat ESDocument40 pagesElementry Plant Bio Chemistery: Carbohydrat ESdenolap242No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Practical ReportDocument9 pagesCarbohydrates Practical ReportshubaNo ratings yet
- Genetics and EvolutionDocument5 pagesGenetics and Evolutionmahreen akramNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules Summary SheetsDocument6 pagesBiological Molecules Summary SheetsdanyalbhaijiNo ratings yet
- Home Economics NotesDocument11 pagesHome Economics Noteslone obonetseNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates and Related CompoundsDocument56 pagesCarbohydrates and Related CompoundsMani JeeNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument3 pagesCARBOHYDRATESvyn bringinoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Book - Grade 12 SE-1Document28 pagesChemistry Book - Grade 12 SE-1Abed KaremNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Green Plants Turn H O, Co, and Sunlight Into CarbohydratesDocument121 pagesCarbohydrates: Green Plants Turn H O, Co, and Sunlight Into CarbohydratesRalph Ian CaingcoyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CarbohydratesDocument20 pagesIntroduction To CarbohydratesJason TulipatNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument8 pagesBiomoleculesOM SableNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate ChemistryDocument46 pagesCarbohydrate Chemistryrishibiswas18052001No ratings yet
- A Level BiologyDocument522 pagesA Level BiologyJAMESNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesCarbohydratesEncik AfiqNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 CarbohydratesDocument71 pagesUnit-1 Carbohydratesdasiwev112No ratings yet
- BBC1 K14 K15 KarbohidratDocument31 pagesBBC1 K14 K15 Karbohidratbrigita charvioNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument112 pagesCarbohydratesmaryam ijazNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATES ChemDocument8 pagesCARBOHYDRATES ChemPriyesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Revision Notes in Accordance With Syllabus SpecificationsDocument50 pagesUnit 1. Revision Notes in Accordance With Syllabus SpecificationslucyNo ratings yet
- General and Specific Test For Carbohydrates BioChemDocument15 pagesGeneral and Specific Test For Carbohydrates BioChemwynNo ratings yet
- Aadil BioChemistryDocument3 pagesAadil BioChemistrySaira Falak SherNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Applied to Beer Brewing - General Chemistry of the Raw Materials of Malting and BrewingFrom EverandBiochemistry Applied to Beer Brewing - General Chemistry of the Raw Materials of Malting and BrewingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)