Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rathna Drug Card in (Lovenox)
Rathna Drug Card in (Lovenox)
Uploaded by
erdos13Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rathna Drug Card in (Lovenox)
Rathna Drug Card in (Lovenox)
Uploaded by
erdos13Copyright:
Available Formats
COMMUNITY COLLEGE OF ALLEGHENEY COUNTY ALLEGHENY CAMPUS DEPARTMENT OF NURSING NRN 101 AND NRN102 DRUG CARD Directions:
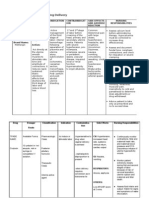
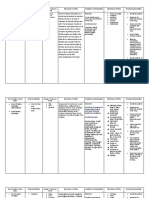
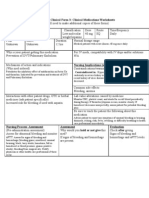
Complete one drug card for each medication Write the rationale for why this patient is getting the prescribed medication. Drug Trade Name: Lovenox Physiological Action: Common Side Effects: Bleeding, (How drug works in the body) anemia Generic Name: Enoxaparin Potentiates the inhibitory effect of Adverse Side Effects: Advise patient antithrombin on factor Xa and to report any symptoms of unusual Classification: Low molecular thrombin. bleeding or bruising, dizziness, weight heparins itching, rash, fever, swelling, or Uses: (Therapeutic) difficulty breathing to health care Usual Ranges: Medical patients It is an anticoagulant used to professional immediately with acute illness--40 mg once prevent and treat deep vein Contraindications with food or other daily thrombosis or pulmonary embolism drugs: Hypersensitivity, active major bleed. Use cautiously in severe Adult: Pediatric kidney or liver disease, untreated hypertention, recent history of ulcer Recommended Frequency of disease. Interacts with other blood Administration: Daily thinning agents and drugs and foods with anticoagulant effects. Recommended Route of Administration: SQ Pregnancy Category: B NURSING CONSIDERATIONS(Before, during or after administration) RATIONALE for this Patient: (Why prescribed for patient)
(Pre-administration assessment) Assess for signs of bleeding and hemorrhage (bleeding gums; nosebleed; unusual bruising; black, tarry stools; hematuria; fall in hematocrit or blood pressure; guaiac-positive stools); bleeding from surgical site. Notify physician or other health care professional if these occur. PRESCRIBED Dosage Route Check after giving Signs of bleeding and hemorrhage. Monitor patient for hypersensitivity reactions (chills, fever, urticaria). Report signs to physician or other health care professional. Observe Times Given injection sites for hematomas, ecchymosis, or inflammation. For overdose protamine sulfate, 1mg for each mg of enoxaparin should be administered by slow IV injection.
Frequency
RT Reviewed 1985/LAB Reviewed June 1989/LAB Reviewed June 1990/KAC Revised July 1991/HPO Revised May 2002/LAC Revised January 2003
You might also like
- Client Profile: Case StudyDocument1 pageClient Profile: Case Studysivakamasundari pichaipillaiNo ratings yet
- Naplex KatDocument21 pagesNaplex KatShan Shani100% (5)
- Steroid Potency ChartDocument3 pagesSteroid Potency ChartGee Thanabhorn100% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyGi Ey ElNo ratings yet
- Ertapenem (Invanz)Document1 pageErtapenem (Invanz)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Urea Cycle Disorders - Management - UpToDateDocument21 pagesUrea Cycle Disorders - Management - UpToDatePIERINANo ratings yet
- Drug Study-Med WardDocument2 pagesDrug Study-Med WardErnest Brian FernandezNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseAli GarciaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan 1gagandipkS100% (1)
- Drug BisacodylDocument1 pageDrug BisacodylSrkocherNo ratings yet
- KetoconazoleDocument2 pagesKetoconazoleMD. DELWAR HOSSAINNo ratings yet
- Lovenox (Enoxaparin)Document1 pageLovenox (Enoxaparin)E100% (5)
- Lovenox (Enoxaparin)Document1 pageLovenox (Enoxaparin)E100% (1)
- Side Effects:: AtropineDocument7 pagesSide Effects:: AtropinekletadaNo ratings yet
- Lui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionDocument1 pageLui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionMagdayao Romamea100% (1)
- KetoconazoleDocument2 pagesKetoconazolenatinlalaNo ratings yet
- Dosage: 50 MG Order: PRN q6h Route: IV (Case Scenario Based)Document3 pagesDosage: 50 MG Order: PRN q6h Route: IV (Case Scenario Based)Edward Luis EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument81 pagesFinal Drug StudyMinaNo ratings yet
- TrazodoneDocument20 pagesTrazodoneAjay MehtaNo ratings yet
- Amikacin 2Document2 pagesAmikacin 2Sian AsadaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PantoprazoleDocument3 pagesDrug Study PantoprazoleIRISH CACAYANNo ratings yet
- Dolan Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDolan Drug StudyLian Robbie BautistaNo ratings yet
- Suxamethonium Chloride Injection Bp-PiDocument8 pagesSuxamethonium Chloride Injection Bp-PinanaNo ratings yet
- PP MecobalaminDocument2 pagesPP MecobalaminshindyNo ratings yet
- Combizar Drug StudyDocument6 pagesCombizar Drug StudymrnmrsllNo ratings yet
- Mitomycin - UsmanDocument3 pagesMitomycin - UsmanSittie Nashieva A. UsmanNo ratings yet
- LovenoxDocument1 pageLovenoxAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- AnastrozoleDocument2 pagesAnastrozoleAnonymous FgT04krgymNo ratings yet
- Case Pre Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCase Pre Drug StudyJoule PeirreNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HydrocodoneDocument1 pageDrug Study HydrocodoneYlrenne DyNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dosa Ge Mechanis Mof Action Indicatio N Contraindic Ation Adverse/Side Effects Nursing InterventionsDocument14 pagesDrug Name Dosa Ge Mechanis Mof Action Indicatio N Contraindic Ation Adverse/Side Effects Nursing InterventionsVin LandichoNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide (Reglan)Document1 pageMetoclopramide (Reglan)ENo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studyanne009No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug Studyabulan100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyChickz HunterNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Administration Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Name Mechanism of Action Administration Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesIvan Liquiran AvenadoNo ratings yet
- Famotidine Drug Card PDFDocument2 pagesFamotidine Drug Card PDFKish AmoreNo ratings yet
- NizoralDocument4 pagesNizoralianecunar100% (2)
- Generic Name Brand Name Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageGeneric Name Brand Name Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilitiesitsmeayaNo ratings yet
- Essential Amino AcidDocument1 pageEssential Amino AcidKayki LouiseNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: MethyldopaDocument1 pageDrug Study: MethyldopaTempoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - IbuprofenDocument3 pagesDrug Study - IbuprofenThalia UyNo ratings yet
- IFOSFAMIDEDocument4 pagesIFOSFAMIDEErza GenatrikaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug Studykennethbote0% (1)
- Tinidazole Is An AntiDocument6 pagesTinidazole Is An AntiNoi Maya Anggrita SariNo ratings yet
- AmloDocument1 pageAmloamy navajaNo ratings yet
- Fluvastatin - Drug StudyDocument1 pageFluvastatin - Drug StudyKevin H. MilanesNo ratings yet
- TumsDocument2 pagesTumsAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY NaproxenDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY NaproxenMargarette Mae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Ketorolac)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Ketorolac)Andrea De RuedaNo ratings yet
- CoversylDocument3 pagesCoversylianecunarNo ratings yet
- Drug Literature For MupirocinDocument3 pagesDrug Literature For MupirocinKate EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyGian Era100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyDavid RefuncionNo ratings yet
- ProgesteroneDocument1 pageProgesteroneAGUIRANG, Crystal Joyce R.No ratings yet
- Transmetil 500mgDocument6 pagesTransmetil 500mgHarisankarthekkethil 26No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Arterial PunctureDocument14 pagesArterial PunctureGstayu WidiastutiNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- LovenoxDocument1 pageLovenoxKatie McPeek100% (2)
- Drug Study Feu NRMF IcuDocument9 pagesDrug Study Feu NRMF IcuAnne Genesis V. PinedaNo ratings yet
- Drug Evaluation MonographDocument12 pagesDrug Evaluation MonographYodaheNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyPang ProjectNo ratings yet
- Montelukast MedicineDocument4 pagesMontelukast MedicineAman ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- List ObatDocument7 pagesList ObatAini Shofa HaniahNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Ocular Pharmacotherapeutics - Nov. 6 - Dr. CastilloDocument6 pages3.2 Ocular Pharmacotherapeutics - Nov. 6 - Dr. CastilloHanako Sasaki AranillaNo ratings yet
- Ncologist: Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents in Renal MedicineDocument6 pagesNcologist: Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents in Renal MedicineSergio RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Marijuana in The United StatesDocument4 pagesMarijuana in The United StatesParas khuranaNo ratings yet
- Drug GuidelinesDocument203 pagesDrug GuidelinesPreth Pal SinghNo ratings yet
- AntihistamineDocument32 pagesAntihistaminenadinek96100% (1)
- OTCtxDocument3 pagesOTCtxlosangelesNo ratings yet
- PL - Retail - 12 - 05 - 2023Document29 pagesPL - Retail - 12 - 05 - 2023DwiNo ratings yet
- Master BpjsDocument9 pagesMaster BpjsHardi OtoyNo ratings yet
- CCO Gastric Cancer LL SlidesDocument63 pagesCCO Gastric Cancer LL SlidesPoncho Silva100% (1)
- Alfaxan CD Rtu Leaflet Australia Feb 06Document2 pagesAlfaxan CD Rtu Leaflet Australia Feb 06spygrlbtrNo ratings yet
- OmalizumabDocument3 pagesOmalizumabapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Hormonal TherapiesDocument39 pagesHormonal TherapiesJalal EltabibNo ratings yet
- Potency Class Topical Corticosteroid FormulationDocument5 pagesPotency Class Topical Corticosteroid FormulationgowindamijayaNo ratings yet
- Sisa Stock 14 SepDocument60 pagesSisa Stock 14 SepmutiaNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary Label - Guiding PrinciplesDocument3 pagesAuxiliary Label - Guiding PrinciplesVanessa EstebanNo ratings yet
- Stock Dma 27 Juli 20Document1,918 pagesStock Dma 27 Juli 20Rila Vita SariNo ratings yet
- Abc Ven FixDocument18 pagesAbc Ven FixTANIA PRIMADARANo ratings yet
- 1 Drugs For HypertensionDocument62 pages1 Drugs For HypertensionSaniNo ratings yet
- Investor Presentation - Update On NCE and NDDS Programs (Company Update)Document61 pagesInvestor Presentation - Update On NCE and NDDS Programs (Company Update)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- Vrinda Life - ProductsDocument10 pagesVrinda Life - ProductsDr. Trilochan satapathyNo ratings yet
- Stok 25mei23Document29 pagesStok 25mei23galihNo ratings yet
- Topical Steroids (Sep 19) PDFDocument7 pagesTopical Steroids (Sep 19) PDF1234chocoNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Laws and RegulationsDocument42 pagesPharmaceutical Laws and RegulationsPreeti KherwaNo ratings yet
- Funtrivia Questions Sci / Tech: Join Funtrivia For FreeDocument5 pagesFuntrivia Questions Sci / Tech: Join Funtrivia For FreeCherry May CandaliaNo ratings yet