Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TD Unit 2
TD Unit 2
Uploaded by
Shine SonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TD Unit 2
TD Unit 2
Uploaded by
Shine SonCopyright:
Available Formats
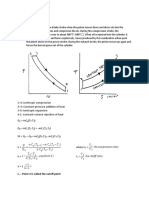
FORMULAE - AIR CYCLES Otto cycle:
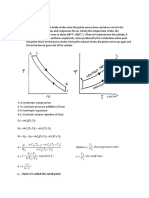
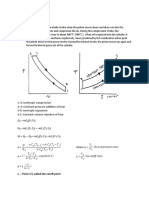
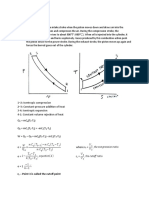
P-V diagram for Otto cycle
T-S diagram for Otto cycle 1-2 Isentropic compression 2-3 Constant-volume heat addition 3-4 Isentropic expansion 4-1 Constant-volume heat rejection Heat supplied qin=mCv(T3-T2) Heat rejected qout=mCv(T4-T1)
Efficiency k==1.4
=(qin-qout) / qin
Mean effective pressure = Pm= P1r (r(k-1)-1)(rp-1) / (kr-1) where r is the compression ratio rp is the pressure ratio Diesel cycle:
1-2- Isentropic compression 2-3-Constant pressure heat addition 3-4-Isentropic expansion 4-1-Constant volume heat rejection Heat supplied qin=mCp(T3-T2) Heat rejected qout=mCv(T4-T1)
k==1.4 rc=Cut off ratio Pm=P1[krk(rc-1)-r(rck-1)] / (k-1)(r-1)
Dual cycle:
P-V and T-S diagrams 1-2-Isentropic compression 2-3-Constant volume heat addition 3-4-Constant pressure heat addition 4-5-Isentropic expansion 5-1-Constant volume heat rejection Heat supplied qin=mCv(T3-T2)+mCp(T4-T3) Heat rejected qout=mCv(T5-T1) = 1 (rprck-1) / rk-1[(rp-1)+rpk(rc-1)] Pm=P1[krprk(rc-1)+rk(rp-1)-r(rprck-1)] / (r-1)(k-1)
Brayton cycle:
1-2 Isentropic compression (in a compressor) 2-3 Constant-pressure heat addition 3-4 Isentropic expansion (in a turbine) 4-1 Constant-pressure heat rejection
rp is the pressure ratio.
You might also like
- Non-Conventional Energy Sources by G D RaiDocument713 pagesNon-Conventional Energy Sources by G D RaiVS Deepak Rajpurohit91% (217)
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- Thermo Cycles 2Document16 pagesThermo Cycles 2cobalt boronNo ratings yet
- Additional ProblemsDocument5 pagesAdditional ProblemsPJ PerezNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Contuity (Tutorial Part 3)Document13 pagesFluid Flow Contuity (Tutorial Part 3)Anne Gabrielle DavidNo ratings yet
- Process Overview (1) - Fpso Ruby IiDocument1 pageProcess Overview (1) - Fpso Ruby IiCao Huu TungNo ratings yet
- Diesel Cycle: R - Point 3 Is Called The Cutoff PointDocument8 pagesDiesel Cycle: R - Point 3 Is Called The Cutoff PointJethro Briza GaneloNo ratings yet
- Prelim Ito Na PreDocument8 pagesPrelim Ito Na PreJethro Briza GaneloNo ratings yet
- Diesel Cycle: R - Point 3 Is Called The Cutoff PointDocument5 pagesDiesel Cycle: R - Point 3 Is Called The Cutoff PointJethro Briza GaneloNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocument13 pagesInternal Combustion EnginesEunice Joy VillegasNo ratings yet
- Diesel Cycle: R - Point 3 Is Called The Cutoff PointDocument7 pagesDiesel Cycle: R - Point 3 Is Called The Cutoff PointJethro Briza GaneloNo ratings yet
- Analisa Siklus OttoDocument9 pagesAnalisa Siklus OttochandraNo ratings yet
- 1 Otto Cycle, Diesel and DualDocument17 pages1 Otto Cycle, Diesel and DualPrincess Mae BalabaNo ratings yet
- Brayton CycleDocument5 pagesBrayton CycleAnonymous yorzHjDBd100% (1)
- Gas Power Cycles: Final State Gaseous State All ThroughtDocument26 pagesGas Power Cycles: Final State Gaseous State All Throughtboj VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Brayton CycleDocument9 pagesBrayton CycleJustino BalaneNo ratings yet
- Web6 Combuction SystemDocument11 pagesWeb6 Combuction SystemeswarbobbyNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer - Unit IDocument37 pagesApplied Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer - Unit IArun ShankarNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engines: LecturDocument32 pagesInternal Combustion Engines: LecturPuneet GargNo ratings yet
- Principle of TurbomachineryDocument159 pagesPrinciple of TurbomachinerySharath ChandraNo ratings yet
- Theoretical CyclesDocument49 pagesTheoretical CyclesMariaEzzaSyUy100% (1)
- Kmme Te101-3Document6 pagesKmme Te101-3ayla sözenNo ratings yet
- Marine Diesel (WEEK - 3) Thermodynamics: Jurusan Teknik Sistem Perkapalan ITS SurabayaDocument38 pagesMarine Diesel (WEEK - 3) Thermodynamics: Jurusan Teknik Sistem Perkapalan ITS SurabayafaridNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document30 pagesLecture 01Diane ClaireNo ratings yet
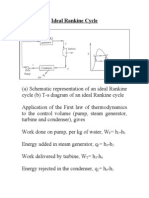
- Ideal Rankine CycleDocument27 pagesIdeal Rankine Cycleslv_prasaadNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic CyclesDocument32 pagesThermodynamic CyclessunitbhaumikNo ratings yet
- IC Engines 2012 Edition Theory & QuestionsDocument178 pagesIC Engines 2012 Edition Theory & Questionskumarrohit91No ratings yet
- Gas Cycles Otto, Diesel, Dual CyclesDocument43 pagesGas Cycles Otto, Diesel, Dual Cyclesprasad5034100% (1)
- Unit-Ii Diesel, Gas Turbine and Combined Cycle Power PlantsDocument71 pagesUnit-Ii Diesel, Gas Turbine and Combined Cycle Power Plantsrsankarganesh MECH-HICETNo ratings yet
- Principle of TurbomachineryDocument159 pagesPrinciple of TurbomachineryWalid MohammedNo ratings yet
- Cycles PDFDocument10 pagesCycles PDFratchagarajaNo ratings yet
- Diesel CycleDocument18 pagesDiesel CycleJustino BalaneNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Gas Power CyclesDocument48 pagesIntroduction To Gas Power CyclesN S SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- Siklus Dual (Dual Cycle) : C C v (T T v T T C T T α=RasiotekananDocument4 pagesSiklus Dual (Dual Cycle) : C C v (T T v T T C T T α=RasiotekananImam FitriadiNo ratings yet
- 4 EngineCyclesAnalysisDocument9 pages4 EngineCyclesAnalysisNatthaphon NaosookNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument79 pagesThermodynamicstixy2013No ratings yet
- Me423 Chapter 2Document76 pagesMe423 Chapter 2ddhiruNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document31 pagesLecture 6Anil BhagureNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Air CyclesDocument32 pagesLecture 3 Air CyclesMemo KhalidNo ratings yet
- Gas Power Cycles Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyDocument68 pagesGas Power Cycles Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyAbraham HutomoNo ratings yet
- Fuel Air and Actual CyclesDocument39 pagesFuel Air and Actual CyclesHrithik SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Engine Cycles 2Document18 pagesChapter 3 - Engine Cycles 2Zaidan AlsallalNo ratings yet
- Diesel Cycle For Mechanical EngineersDocument21 pagesDiesel Cycle For Mechanical Engineerszega5394No ratings yet
- RAC TutorialDocument30 pagesRAC Tutorialkhushal bhanderiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes OnDocument200 pagesLecture Notes Onananth k r100% (3)
- Thermodynamic Cycle PresentationDocument29 pagesThermodynamic Cycle PresentationAnonymous Oh1pxYX30% (1)
- Gas TurbineDocument7 pagesGas TurbineVishal BediNo ratings yet
- Gas Power Cycles Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyDocument68 pagesGas Power Cycles Study Guide in Powerpoint: To AccompanyManjunatha TnNo ratings yet
- 2 Otto Diesel & Dual CyclesDocument39 pages2 Otto Diesel & Dual CyclesFausto ArambuloNo ratings yet
- Vapour Power CycleDocument12 pagesVapour Power Cyclelakshmikanth97No ratings yet
- Topic 8 Gas Turbine Power PlantDocument6 pagesTopic 8 Gas Turbine Power PlantILEENVIRUSNo ratings yet
- Propulsion and Power Formula SheetDocument4 pagesPropulsion and Power Formula SheetArun VinthanNo ratings yet
- Gas Power Cycle - Part 1Document46 pagesGas Power Cycle - Part 1Shahran IezzatNo ratings yet
- Ic Engine Ignou NotesDocument16 pagesIc Engine Ignou NotesRakesh JhaNo ratings yet
- Unit Twelve - Refrigeration and Air Standard Cycles OutlineDocument5 pagesUnit Twelve - Refrigeration and Air Standard Cycles OutlinebarelihbNo ratings yet
- OTTO Cycle Summery (Q - Q) + (W - W) U - U: in Out in Out F IDocument1 pageOTTO Cycle Summery (Q - Q) + (W - W) U - U: in Out in Out F IjehadyamNo ratings yet
- Otto CycleDocument5 pagesOtto CycleSaraju NandiNo ratings yet
- Diesel CycleDocument7 pagesDiesel CycleJayaprakash S MechNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- YhhjjDocument52 pagesYhhjjSam CunananNo ratings yet
- Ash Handling SystemDocument7 pagesAsh Handling SystemrocksNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Performance and Water Consumption of Hybrid Cooling System Configurations For Concentrated Solar Power PlantsDocument19 pagesThermodynamic Performance and Water Consumption of Hybrid Cooling System Configurations For Concentrated Solar Power PlantsALL THE GOOD STUFFNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document15 pagesChapter 1Niña Lyka ComiaNo ratings yet
- Energy Balance On W1Document3 pagesEnergy Balance On W1Kricel MaqueraNo ratings yet
- IRENA RE Capacity Statistics 2021Document64 pagesIRENA RE Capacity Statistics 2021Pedro MentadoNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 1Document8 pagesResearch Paper 1ankitNo ratings yet
- MPOCGT-01-MB-PD-M1200 A HEAT AND MASS BALANCE DIAGRAM (1) RemovedDocument2 pagesMPOCGT-01-MB-PD-M1200 A HEAT AND MASS BALANCE DIAGRAM (1) RemovedTheekshana MalalasekaraNo ratings yet
- Myanmar: Page 1 of 3 - Country FactsheetDocument3 pagesMyanmar: Page 1 of 3 - Country FactsheetArkar SoeNo ratings yet
- Assigment of EnglishDocument3 pagesAssigment of EnglishSafwan BakrmanyNo ratings yet
- Uhde Biomass and Coal Gasification: Fluidized Bed Entrained FlowDocument24 pagesUhde Biomass and Coal Gasification: Fluidized Bed Entrained Flowanshuman432No ratings yet
- Complete ThesisDocument196 pagesComplete ThesisSagar KumarNo ratings yet
- KatalogDocument11 pagesKatalogZarko MikicNo ratings yet
- 2nd Law Analysis of Brayton Rankine CycleDocument19 pages2nd Law Analysis of Brayton Rankine CycleJoao MinhoNo ratings yet
- DOE List of Power ContractsDocument9 pagesDOE List of Power Contractskonverg101No ratings yet
- Techno-Economic Performance Analysis of Energy Production From Biomass at Different Scales in The UK ContextDocument11 pagesTechno-Economic Performance Analysis of Energy Production From Biomass at Different Scales in The UK ContextSyarif HidayatNo ratings yet
- J-1996 Alternative Fuels PDFDocument1 pageJ-1996 Alternative Fuels PDFSarthak GuptaNo ratings yet
- 30.72 KWP SLDDocument1 page30.72 KWP SLDDaniel Gnanaselvam100% (1)
- Adindah Haedriah-Scientist Create Energy-Making Artificial LeafDocument4 pagesAdindah Haedriah-Scientist Create Energy-Making Artificial LeafDinda HaedriahNo ratings yet
- Power Plants, GujaratDocument13 pagesPower Plants, GujaratPrashantsutharNo ratings yet
- Malunggay (Moringa Oleifera) and Malabar Spinach (Basella Alba) Extract For Reducing Salinity Level of Seawater in Watering Tomato (Lycopersicon Esculentum Mill.)Document3 pagesMalunggay (Moringa Oleifera) and Malabar Spinach (Basella Alba) Extract For Reducing Salinity Level of Seawater in Watering Tomato (Lycopersicon Esculentum Mill.)Brian KobeNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Attractiveness of Net Metered Solar Photovoltaic Technology To Member Consumers of Batangas II Electric Cooperative Inc. by J. AriasDocument29 pagesFactors Affecting The Attractiveness of Net Metered Solar Photovoltaic Technology To Member Consumers of Batangas II Electric Cooperative Inc. by J. AriasJoan AriasNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Analysis & Enhancement of Cogeneration PlantDocument17 pagesThermodynamic Analysis & Enhancement of Cogeneration PlantSheri KhosoNo ratings yet
- 6FA DLN 2.6 Extended Interval Combustion System - GEA17898 PDFDocument1 page6FA DLN 2.6 Extended Interval Combustion System - GEA17898 PDFLenin RamonNo ratings yet
- Start Reducing Factory Operating Costs and Carbon Emissions in Just One Month - .Document6 pagesStart Reducing Factory Operating Costs and Carbon Emissions in Just One Month - .ranNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of A Renewable Microgrid FinalDocument46 pagesFundamentals of A Renewable Microgrid FinalFrederick Pantua DolorzoNo ratings yet
- April July LaycansDocument1 pageApril July LaycansKumar Jagannath SNo ratings yet