Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PMP Formulas
PMP Formulas
Uploaded by
ravikumar_sqaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- PMP FormulasDocument5 pagesPMP Formulasbhaveshkumar78100% (8)
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)From EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (17)
- Integrated Cost and Schedule Control in Project ManagementFrom EverandIntegrated Cost and Schedule Control in Project ManagementRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- PMstudyprocesschart Formula V5Document2 pagesPMstudyprocesschart Formula V5786tip786No ratings yet
- PMP Formulas - Cheat Sheet v0.6 PDFDocument2 pagesPMP Formulas - Cheat Sheet v0.6 PDFDildar Saini100% (1)
- Acronym Meaning Description Formula AC: PMP Math FormulasDocument2 pagesAcronym Meaning Description Formula AC: PMP Math FormulasupendrasNo ratings yet
- PMP Formulas - Cheat Sheet v0.6Document2 pagesPMP Formulas - Cheat Sheet v0.6Don GiovzNo ratings yet
- Practical Earned Value Analysis: 25 Project Indicators from 5 MeasurementsFrom EverandPractical Earned Value Analysis: 25 Project Indicators from 5 MeasurementsNo ratings yet
- PmpformulasDocument2 pagesPmpformulasDurga Prasad CuddapahNo ratings yet
- PMP Formula CompilationDocument3 pagesPMP Formula CompilationJRNo ratings yet
- 17 PMP Formulas Mentioned in The PMBOK GuideDocument14 pages17 PMP Formulas Mentioned in The PMBOK GuideStéphane SmetsNo ratings yet
- My Notes On PMP FormulasDocument2 pagesMy Notes On PMP Formulasshakeelkhn18No ratings yet
- My Notes On PMP (Formulas) : Earned Value AnalysisDocument3 pagesMy Notes On PMP (Formulas) : Earned Value AnalysisshanmugaNo ratings yet
- PMP FormulasDocument2 pagesPMP Formulasvnethi9317100% (2)
- PMP Formulae: Earned Value ManagementDocument4 pagesPMP Formulae: Earned Value ManagementOmerZiaNo ratings yet
- PMP FormulasDocument2 pagesPMP FormulasShawn JarrettNo ratings yet
- PMP Formula Pocket GuideDocument1 pagePMP Formula Pocket Guidesunil_v5No ratings yet
- Formulas / Math For PMP: AtypicalDocument3 pagesFormulas / Math For PMP: AtypicalSudhakar Lakshmana RajNo ratings yet
- Formulae To RememberDocument2 pagesFormulae To RemembertutikaNo ratings yet
- Fórmulas: PMBOK - PMI: Cod. Nombre Descripción EVDocument4 pagesFórmulas: PMBOK - PMI: Cod. Nombre Descripción EVWilliam Rojas MoralesNo ratings yet
- Visit For Exam Resources For Disclaimer See PMP® Formula Study GuideDocument2 pagesVisit For Exam Resources For Disclaimer See PMP® Formula Study GuideNeeraj ShuklaNo ratings yet
- PMP FormulasDocument2 pagesPMP FormulasSuranjan Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- Formulas Math For PMPDocument3 pagesFormulas Math For PMPramorclNo ratings yet
- PMP FormulasDocument2 pagesPMP FormulasANNo ratings yet
- Formulas - Math For PMPDocument2 pagesFormulas - Math For PMPabhi10augNo ratings yet
- VI VI - PMP Formula Pocket GuideDocument1 pageVI VI - PMP Formula Pocket GuideSMAKNo ratings yet
- My Notes On PMP (Formulas) : Earned Value AnalysisDocument2 pagesMy Notes On PMP (Formulas) : Earned Value Analysisprerna93No ratings yet
- Project Tracking in SPMDocument18 pagesProject Tracking in SPMjohn millersNo ratings yet
- CMQ-OE FormulasDocument2 pagesCMQ-OE FormulasMusman SattarNo ratings yet
- NonLinear ScaleDocument4 pagesNonLinear ScaleSid KrishNo ratings yet
- EVMS Gold CardDocument1 pageEVMS Gold CardHaneefa ChNo ratings yet
- Formula AC: (Return To Top)Document5 pagesFormula AC: (Return To Top)ranjit12345No ratings yet
- 1 Gold Card 2 Sided June 2012Document2 pages1 Gold Card 2 Sided June 2012sayafrands6252No ratings yet
- Project Management Professional (PMP) - Sample ExamDocument1 pageProject Management Professional (PMP) - Sample ExamAlish ChelackalNo ratings yet
- EVMDocument4 pagesEVMSimNo ratings yet
- Gold Card 2 Sided Jun 2015Document2 pagesGold Card 2 Sided Jun 2015sandi123inNo ratings yet
- PMP Formula Pocket GuideDocument1 pagePMP Formula Pocket Guidenanaba06No ratings yet
- PMP Formula Pocket GuideDocument1 pagePMP Formula Pocket Guidejindalyash1234100% (2)
- Software Project ManagementDocument12 pagesSoftware Project ManagementHarsh Vardhan SinghNo ratings yet
- PMP Formulas Notes PDFDocument2 pagesPMP Formulas Notes PDFDildar SainiNo ratings yet
- Formulas Notes PDFDocument2 pagesFormulas Notes PDFDildar SainiNo ratings yet
- Formulas To Know For ExamDocument5 pagesFormulas To Know For ExamMohsin RazaNo ratings yet
- Gold Card One Sided 8 Jan 2009Document1 pageGold Card One Sided 8 Jan 2009rivera.ivanNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Management Gold CardDocument2 pagesEarned Value Management Gold CardDaniel Rué MayolasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-1Document18 pagesChapter 4-1fentawmelaku1993No ratings yet
- Project Earned Value Analysis1Document4 pagesProject Earned Value Analysis1Anonymous UArnIExNo ratings yet
- PMP Formulas by EdwardDocument3 pagesPMP Formulas by Edwardmask81No ratings yet
- EVM Gold CardDocument1 pageEVM Gold Cardwalmart007No ratings yet
- Brain DumpDocument4 pagesBrain DumpDaniel LeeNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam-Testing Concept-PERT/CPM/Gantt Chart/FPA/EVA/Timebox (Chapter-3)From EverandCISA Exam-Testing Concept-PERT/CPM/Gantt Chart/FPA/EVA/Timebox (Chapter-3)Rating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (3)
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)From EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Earned Value Management for the PMP Certification ExamFrom EverandEarned Value Management for the PMP Certification ExamRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Applied Corporate Finance. What is a Company worth?From EverandApplied Corporate Finance. What is a Company worth?Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Management Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesFrom EverandManagement Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandCorporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
PMP Formulas
PMP Formulas
Uploaded by
ravikumar_sqaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PMP Formulas
PMP Formulas
Uploaded by
ravikumar_sqaCopyright:
Available Formats
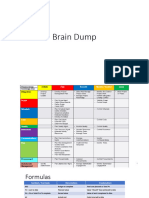
Term
Explanation
IRR
Internal rate of return, higher is better
Payback period
Lower is better
BCR
Benefit/cost ratio, higher is better
CBR
Cost/benefit ratio (switched), lower is better
Number of communication channels n(n-1)/2
Expected Monetary Probability * impact or value Value
Program Evaluation and Review Technique is equal to (Pessimistic +(4*Most PERT Likely)+(Optimistic))/6
PV
Planned Value = BCWS (budgeted cost of work scheduled)
AC
Actual Cost = ACWP (actual cost of work performed)
EV
Earned Value = BCWP (budgeted cost of work performed)
CV
Cost Variance = EV - AC
SV
Schedule Variance = EV - PV
CPI
EV/AC
SPI
EV/PV
EAC (assume AC + BAC - EV budgeted rate)
EAC (using past BAC/cumulative CPI performance)
VAC
BAC - EAC
TCPI (to complete present index)
(BAC-EV)/(BAC-AC) Less than 1 is good as it means you can perform at lower efficiency
Cash flow
Cash inflow - Cash outflow
PV
Present value = FV/(1+r)^n
Sigma values
1 = 68.26 2 = 95.46 3 = 99.73 6 = 99.99
Precedence diagramming method
Activities are nodes and in boxes linked to one another. Has 4 relationships: Finish-start, S-S, F-F, S-F
Arrow diagramming Activity on arrow, only have one relationship, Finish to start. method
1. Achievement 2. Recognition 3. Challenge of the work itself 4. Herzberg's Motivators Responsibility 5. Growth and advancement
Maslow's Needs (lowest first)
1. Physical needs 2. Safety and Security 3. Social 4. Self-esteem 5. Selfactualization
1. Expert: Best, you earn it 2. Reward: Ability to reward. Based on your Powers of PMP position 3. Formal: Power given to your position 4. Referent: Referring to others 5. Penalty: Worst, based off ability to punish
You might also like
- PMP FormulasDocument5 pagesPMP Formulasbhaveshkumar78100% (8)
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)From EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (17)
- Integrated Cost and Schedule Control in Project ManagementFrom EverandIntegrated Cost and Schedule Control in Project ManagementRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- PMstudyprocesschart Formula V5Document2 pagesPMstudyprocesschart Formula V5786tip786No ratings yet
- PMP Formulas - Cheat Sheet v0.6 PDFDocument2 pagesPMP Formulas - Cheat Sheet v0.6 PDFDildar Saini100% (1)
- Acronym Meaning Description Formula AC: PMP Math FormulasDocument2 pagesAcronym Meaning Description Formula AC: PMP Math FormulasupendrasNo ratings yet
- PMP Formulas - Cheat Sheet v0.6Document2 pagesPMP Formulas - Cheat Sheet v0.6Don GiovzNo ratings yet
- Practical Earned Value Analysis: 25 Project Indicators from 5 MeasurementsFrom EverandPractical Earned Value Analysis: 25 Project Indicators from 5 MeasurementsNo ratings yet
- PmpformulasDocument2 pagesPmpformulasDurga Prasad CuddapahNo ratings yet
- PMP Formula CompilationDocument3 pagesPMP Formula CompilationJRNo ratings yet
- 17 PMP Formulas Mentioned in The PMBOK GuideDocument14 pages17 PMP Formulas Mentioned in The PMBOK GuideStéphane SmetsNo ratings yet
- My Notes On PMP FormulasDocument2 pagesMy Notes On PMP Formulasshakeelkhn18No ratings yet
- My Notes On PMP (Formulas) : Earned Value AnalysisDocument3 pagesMy Notes On PMP (Formulas) : Earned Value AnalysisshanmugaNo ratings yet
- PMP FormulasDocument2 pagesPMP Formulasvnethi9317100% (2)
- PMP Formulae: Earned Value ManagementDocument4 pagesPMP Formulae: Earned Value ManagementOmerZiaNo ratings yet
- PMP FormulasDocument2 pagesPMP FormulasShawn JarrettNo ratings yet
- PMP Formula Pocket GuideDocument1 pagePMP Formula Pocket Guidesunil_v5No ratings yet
- Formulas / Math For PMP: AtypicalDocument3 pagesFormulas / Math For PMP: AtypicalSudhakar Lakshmana RajNo ratings yet
- Formulae To RememberDocument2 pagesFormulae To RemembertutikaNo ratings yet
- Fórmulas: PMBOK - PMI: Cod. Nombre Descripción EVDocument4 pagesFórmulas: PMBOK - PMI: Cod. Nombre Descripción EVWilliam Rojas MoralesNo ratings yet
- Visit For Exam Resources For Disclaimer See PMP® Formula Study GuideDocument2 pagesVisit For Exam Resources For Disclaimer See PMP® Formula Study GuideNeeraj ShuklaNo ratings yet
- PMP FormulasDocument2 pagesPMP FormulasSuranjan Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- Formulas Math For PMPDocument3 pagesFormulas Math For PMPramorclNo ratings yet
- PMP FormulasDocument2 pagesPMP FormulasANNo ratings yet
- Formulas - Math For PMPDocument2 pagesFormulas - Math For PMPabhi10augNo ratings yet
- VI VI - PMP Formula Pocket GuideDocument1 pageVI VI - PMP Formula Pocket GuideSMAKNo ratings yet
- My Notes On PMP (Formulas) : Earned Value AnalysisDocument2 pagesMy Notes On PMP (Formulas) : Earned Value Analysisprerna93No ratings yet
- Project Tracking in SPMDocument18 pagesProject Tracking in SPMjohn millersNo ratings yet
- CMQ-OE FormulasDocument2 pagesCMQ-OE FormulasMusman SattarNo ratings yet
- NonLinear ScaleDocument4 pagesNonLinear ScaleSid KrishNo ratings yet
- EVMS Gold CardDocument1 pageEVMS Gold CardHaneefa ChNo ratings yet
- Formula AC: (Return To Top)Document5 pagesFormula AC: (Return To Top)ranjit12345No ratings yet
- 1 Gold Card 2 Sided June 2012Document2 pages1 Gold Card 2 Sided June 2012sayafrands6252No ratings yet
- Project Management Professional (PMP) - Sample ExamDocument1 pageProject Management Professional (PMP) - Sample ExamAlish ChelackalNo ratings yet
- EVMDocument4 pagesEVMSimNo ratings yet
- Gold Card 2 Sided Jun 2015Document2 pagesGold Card 2 Sided Jun 2015sandi123inNo ratings yet
- PMP Formula Pocket GuideDocument1 pagePMP Formula Pocket Guidenanaba06No ratings yet
- PMP Formula Pocket GuideDocument1 pagePMP Formula Pocket Guidejindalyash1234100% (2)
- Software Project ManagementDocument12 pagesSoftware Project ManagementHarsh Vardhan SinghNo ratings yet
- PMP Formulas Notes PDFDocument2 pagesPMP Formulas Notes PDFDildar SainiNo ratings yet
- Formulas Notes PDFDocument2 pagesFormulas Notes PDFDildar SainiNo ratings yet
- Formulas To Know For ExamDocument5 pagesFormulas To Know For ExamMohsin RazaNo ratings yet
- Gold Card One Sided 8 Jan 2009Document1 pageGold Card One Sided 8 Jan 2009rivera.ivanNo ratings yet
- Earned Value Management Gold CardDocument2 pagesEarned Value Management Gold CardDaniel Rué MayolasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-1Document18 pagesChapter 4-1fentawmelaku1993No ratings yet
- Project Earned Value Analysis1Document4 pagesProject Earned Value Analysis1Anonymous UArnIExNo ratings yet
- PMP Formulas by EdwardDocument3 pagesPMP Formulas by Edwardmask81No ratings yet
- EVM Gold CardDocument1 pageEVM Gold Cardwalmart007No ratings yet
- Brain DumpDocument4 pagesBrain DumpDaniel LeeNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam-Testing Concept-PERT/CPM/Gantt Chart/FPA/EVA/Timebox (Chapter-3)From EverandCISA Exam-Testing Concept-PERT/CPM/Gantt Chart/FPA/EVA/Timebox (Chapter-3)Rating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (3)
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)From EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Earned Value Management for the PMP Certification ExamFrom EverandEarned Value Management for the PMP Certification ExamRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Applied Corporate Finance. What is a Company worth?From EverandApplied Corporate Finance. What is a Company worth?Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Management Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesFrom EverandManagement Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandCorporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)