Professional Documents
Culture Documents
O'Neil Clarke Mathematics Institute Circle Theorem Questions
O'Neil Clarke Mathematics Institute Circle Theorem Questions
Uploaded by
alessseCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Applications and Interpretation Standard May 2022 Paper 1 TZ1Document16 pagesApplications and Interpretation Standard May 2022 Paper 1 TZ1Adrianus RioNo ratings yet
- BC - Unit IV - Slope Intercept InvestigationDocument5 pagesBC - Unit IV - Slope Intercept InvestigationMichael ParsonsNo ratings yet
- Symmetry Worksheet 3 2 4Document3 pagesSymmetry Worksheet 3 2 4Rayrc Pvt LtdNo ratings yet
- Maths C Semester 1 Tutorial Book PDFDocument244 pagesMaths C Semester 1 Tutorial Book PDFDefi ChRistiani TNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 11: Pythagoras' Theorem and Similar Shapes: Answers To Core Revision Exercises: Shape, Space and MeasuresDocument1 pageWorksheet 11: Pythagoras' Theorem and Similar Shapes: Answers To Core Revision Exercises: Shape, Space and Measuresmk hatNo ratings yet
- Apsmo 2022Document7 pagesApsmo 2022Haowen XieNo ratings yet
- Ws - Lines and AnglesDocument4 pagesWs - Lines and AnglesManya Elhance100% (1)
- 2013 Amc 6 PDFDocument9 pages2013 Amc 6 PDFmnagireddyNo ratings yet
- DP 1 AA HL Partial FractionsDocument70 pagesDP 1 AA HL Partial FractionsSundarNo ratings yet
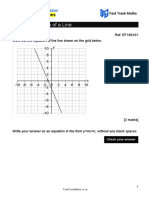
- Midpoint of A Line PDFDocument3 pagesMidpoint of A Line PDFR NovNo ratings yet
- Past Papers 1 1Document8 pagesPast Papers 1 1Sigit Galih NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Kangaroo Math 2019Document8 pagesKangaroo Math 2019ธนเสฐฐ์ กิตติวรรธโนทัยNo ratings yet
- Accuracy and Bounds - Past Paper Questions: Year Series Paper NumberDocument18 pagesAccuracy and Bounds - Past Paper Questions: Year Series Paper Numberislam2059No ratings yet
- ICAS Maths D 2017Document13 pagesICAS Maths D 2017billing63wtNo ratings yet
- 2017 Junior EnglishDocument16 pages2017 Junior EnglishWai MarNo ratings yet
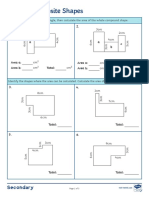
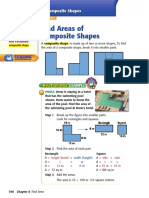
- Area of Composite Shapes Activity SheetDocument3 pagesArea of Composite Shapes Activity SheetgayatriNo ratings yet
- Find Areas of Composite ShapesDocument4 pagesFind Areas of Composite ShapesClemmon HodgesNo ratings yet
- IMC GeometryDocument8 pagesIMC GeometryJane ChangNo ratings yet
- SLMCC 2010 PaperDocument1 pageSLMCC 2010 PaperIshamael Snook100% (1)
- Extended Paper 2 May 00Document12 pagesExtended Paper 2 May 00Mari Carmen Pérez GómezNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 6 Sample Olympiad Paper: For More Such Papers VisitDocument12 pagesMath Grade 6 Sample Olympiad Paper: For More Such Papers VisitdebamalyaNo ratings yet
- Myp QuestionsDocument5 pagesMyp QuestionsnizNo ratings yet
- AMC 8 Problems 1999 2013Document124 pagesAMC 8 Problems 1999 2013Afshiya AnjumNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/52Document12 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/52Sraboni ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Spjet Sample Paper No 2Document16 pagesSpjet Sample Paper No 2MinhChau HoangNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Math Grade 8 Linear Equations 3Document2 pagesWorksheet Math Grade 8 Linear Equations 3Ibrahimli KhadijaNo ratings yet
- ArithmagonDocument2 pagesArithmagonViet Hoang QuocNo ratings yet
- Answers To Checkpoint Mathematics Workbook 1 New Edition - 1 PDFDocument12 pagesAnswers To Checkpoint Mathematics Workbook 1 New Edition - 1 PDFRoqia AbulebbehNo ratings yet
- Elapsed Time Table) )Document2 pagesElapsed Time Table) )lnNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 Maths Sample Paper Set 2 PDFDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 8 Maths Sample Paper Set 2 PDFHRS originalNo ratings yet
- NUS 2018 Math (Ao) (Sample Past Paper)Document11 pagesNUS 2018 Math (Ao) (Sample Past Paper)Shansha DeweNo ratings yet
- Number BasesDocument15 pagesNumber BasesPraveenNo ratings yet
- Geometrical ShapesDocument31 pagesGeometrical ShapesAlanie Grace Beron Trigo100% (1)
- Measurement+ +Area+&+PerimeterDocument12 pagesMeasurement+ +Area+&+PerimeterAnson LinNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Numbers To 1000 - QuestionsDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Numbers To 1000 - QuestionsMarlin XinNo ratings yet
- T - LinesDocument7 pagesT - LinesSifatNo ratings yet
- Australian Mathematics Competition (AMC) Performance ReportDocument51 pagesAustralian Mathematics Competition (AMC) Performance ReportRajuNo ratings yet
- Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 FY 19-20 FY 19-20 Total Total Total Total TotalDocument2 pagesQ1 Q2 Q3 Q4 FY 19-20 FY 19-20 Total Total Total Total Totalraddy13No ratings yet
- HCF LCM Squre RootsDocument0 pagesHCF LCM Squre RootsCh Saqib NazirNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Math Worksheet 15-ADocument4 pagesClass 8 Math Worksheet 15-AHereebNo ratings yet
- ISMO PreviousPaper 5Document13 pagesISMO PreviousPaper 5kalthebal1029No ratings yet
- OCR S1 Notes Permutations and CombinationsDocument8 pagesOCR S1 Notes Permutations and CombinationsJon HadleyNo ratings yet
- SASMO Grade 7 (Secondary 1) Sample QuestionsDocument5 pagesSASMO Grade 7 (Secondary 1) Sample QuestionsYopi TobriyantoNo ratings yet
- 6 Igcse Circle TheoremsDocument18 pages6 Igcse Circle Theorems4sqsmq2856No ratings yet
- Quadratic Sequences Worksheet 1Document3 pagesQuadratic Sequences Worksheet 1PoojaNo ratings yet
- HKDSE Maths Sample Paper 1Document15 pagesHKDSE Maths Sample Paper 1bradNo ratings yet
- GCSE Maths Foundation - Exam-Style QuestionsDocument6 pagesGCSE Maths Foundation - Exam-Style QuestionsFastTrackMathsNo ratings yet
- Secondary 3 Imocsea Sample TestDocument9 pagesSecondary 3 Imocsea Sample TestpriyagvspvNo ratings yet
- Y10 Working With Unfamiliar Problems 1Document1 pageY10 Working With Unfamiliar Problems 1kheyNo ratings yet
- 2014 Intermediate Team Solutions (English)Document9 pages2014 Intermediate Team Solutions (English)alex jobogNo ratings yet
- P4-L Key PDFDocument1 pageP4-L Key PDFendangNo ratings yet
- Pink Kangaroo 2022 SolutionsDocument12 pagesPink Kangaroo 2022 SolutionsSakethNo ratings yet
- P1 Math Workbook 1Document47 pagesP1 Math Workbook 1TO ChauNo ratings yet
- Gauss Contest: Canadian Mathematics CompetitionDocument4 pagesGauss Contest: Canadian Mathematics CompetitionSteven LiNo ratings yet
- WS-Simplifying Surds - With Answers PDFDocument1 pageWS-Simplifying Surds - With Answers PDFAjay PeryaghNo ratings yet
- SASMO 2018 Grade-6Document9 pagesSASMO 2018 Grade-6S1ice manNo ratings yet
- Principles of Math 12 - Permutations and Combinations Lesson 2Document10 pagesPrinciples of Math 12 - Permutations and Combinations Lesson 2abelNo ratings yet
- Class 7 - Mathematics - Yearly - Reena Krishnakumar - Reena KrishnakumarDocument6 pagesClass 7 - Mathematics - Yearly - Reena Krishnakumar - Reena KrishnakumarmuzaffaralhashmimaazmuzaffarNo ratings yet
- 3 RD Preliam 10 TH STDDocument8 pages3 RD Preliam 10 TH STDSneha sonarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5-Consumer ArithmeticDocument12 pagesLesson 5-Consumer Arithmeticalessse100% (1)
- Prime Ministers of Jamaica PDFDocument10 pagesPrime Ministers of Jamaica PDFalessseNo ratings yet
- Algebraic ExpressionsDocument21 pagesAlgebraic ExpressionsalessseNo ratings yet
- Problem Paper QuadraticDocument1 pageProblem Paper QuadraticalessseNo ratings yet
- Chemical InjuryDocument192 pagesChemical InjuryalessseNo ratings yet
O'Neil Clarke Mathematics Institute Circle Theorem Questions
O'Neil Clarke Mathematics Institute Circle Theorem Questions
Uploaded by
alessseOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
O'Neil Clarke Mathematics Institute Circle Theorem Questions
O'Neil Clarke Mathematics Institute Circle Theorem Questions
Uploaded by
alessseCopyright:
Available Formats
ONeil Clarke Mathematics Institute Circle Theorem Questions
1. In the diagram below, Calculate the following angles, giving reasons for your answer. (i) OAE (ii) AOB (iii) ACB (iv) ADB
2.
In the diagram calculate the size of the following angles, giving reasons, (a) GFH (b) GDE (c) DEF
In this diagram below, Calculate, giving reason for each step of your answer, the size of 3. (i) PTR (ii) TPR (iii) TSR
4. Calculate giving reasons (i) VZW (ii) XYZ
CBD
(iii) AED
5. Calculate, giving reasons (i) ACB
(ii)
6. Calculate with reasons the size of BEO BCE BAE BOE
Calculate, giving reasons, the size of 7. Calculate giving reasons, the size of the following (i) OLQ (ii) NQP (iii) NLP (iv) NPL
(i) EDB
(ii) BEC (iii) CBT
8.
(iv) BAE
9.
ONeil Clarke Mathematics Institute Circle Theorems
Number 0. A straight line drawn from the centre of a circle to bisect a chord which is not a diameter is a right angle to the chord. Hence from the diagram AOB is isosceles and hence OAB = OBA
Number 1(a) Angle formed at the centre of a circle is TWICE angle formed at the circumference subtended by the same chord (arc) 1(b) Angle formed in a semi circle opposite diameter is a right angle i.e AXB= 90
Number 2. Angles in the same segment are equal (Angles standing on the same chord are equal)
You might also like
- Applications and Interpretation Standard May 2022 Paper 1 TZ1Document16 pagesApplications and Interpretation Standard May 2022 Paper 1 TZ1Adrianus RioNo ratings yet
- BC - Unit IV - Slope Intercept InvestigationDocument5 pagesBC - Unit IV - Slope Intercept InvestigationMichael ParsonsNo ratings yet
- Symmetry Worksheet 3 2 4Document3 pagesSymmetry Worksheet 3 2 4Rayrc Pvt LtdNo ratings yet
- Maths C Semester 1 Tutorial Book PDFDocument244 pagesMaths C Semester 1 Tutorial Book PDFDefi ChRistiani TNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 11: Pythagoras' Theorem and Similar Shapes: Answers To Core Revision Exercises: Shape, Space and MeasuresDocument1 pageWorksheet 11: Pythagoras' Theorem and Similar Shapes: Answers To Core Revision Exercises: Shape, Space and Measuresmk hatNo ratings yet
- Apsmo 2022Document7 pagesApsmo 2022Haowen XieNo ratings yet
- Ws - Lines and AnglesDocument4 pagesWs - Lines and AnglesManya Elhance100% (1)
- 2013 Amc 6 PDFDocument9 pages2013 Amc 6 PDFmnagireddyNo ratings yet
- DP 1 AA HL Partial FractionsDocument70 pagesDP 1 AA HL Partial FractionsSundarNo ratings yet
- Midpoint of A Line PDFDocument3 pagesMidpoint of A Line PDFR NovNo ratings yet
- Past Papers 1 1Document8 pagesPast Papers 1 1Sigit Galih NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Kangaroo Math 2019Document8 pagesKangaroo Math 2019ธนเสฐฐ์ กิตติวรรธโนทัยNo ratings yet
- Accuracy and Bounds - Past Paper Questions: Year Series Paper NumberDocument18 pagesAccuracy and Bounds - Past Paper Questions: Year Series Paper Numberislam2059No ratings yet
- ICAS Maths D 2017Document13 pagesICAS Maths D 2017billing63wtNo ratings yet
- 2017 Junior EnglishDocument16 pages2017 Junior EnglishWai MarNo ratings yet
- Area of Composite Shapes Activity SheetDocument3 pagesArea of Composite Shapes Activity SheetgayatriNo ratings yet
- Find Areas of Composite ShapesDocument4 pagesFind Areas of Composite ShapesClemmon HodgesNo ratings yet
- IMC GeometryDocument8 pagesIMC GeometryJane ChangNo ratings yet
- SLMCC 2010 PaperDocument1 pageSLMCC 2010 PaperIshamael Snook100% (1)
- Extended Paper 2 May 00Document12 pagesExtended Paper 2 May 00Mari Carmen Pérez GómezNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 6 Sample Olympiad Paper: For More Such Papers VisitDocument12 pagesMath Grade 6 Sample Olympiad Paper: For More Such Papers VisitdebamalyaNo ratings yet
- Myp QuestionsDocument5 pagesMyp QuestionsnizNo ratings yet
- AMC 8 Problems 1999 2013Document124 pagesAMC 8 Problems 1999 2013Afshiya AnjumNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/52Document12 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/52Sraboni ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Spjet Sample Paper No 2Document16 pagesSpjet Sample Paper No 2MinhChau HoangNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Math Grade 8 Linear Equations 3Document2 pagesWorksheet Math Grade 8 Linear Equations 3Ibrahimli KhadijaNo ratings yet
- ArithmagonDocument2 pagesArithmagonViet Hoang QuocNo ratings yet
- Answers To Checkpoint Mathematics Workbook 1 New Edition - 1 PDFDocument12 pagesAnswers To Checkpoint Mathematics Workbook 1 New Edition - 1 PDFRoqia AbulebbehNo ratings yet
- Elapsed Time Table) )Document2 pagesElapsed Time Table) )lnNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 Maths Sample Paper Set 2 PDFDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 8 Maths Sample Paper Set 2 PDFHRS originalNo ratings yet
- NUS 2018 Math (Ao) (Sample Past Paper)Document11 pagesNUS 2018 Math (Ao) (Sample Past Paper)Shansha DeweNo ratings yet
- Number BasesDocument15 pagesNumber BasesPraveenNo ratings yet
- Geometrical ShapesDocument31 pagesGeometrical ShapesAlanie Grace Beron Trigo100% (1)
- Measurement+ +Area+&+PerimeterDocument12 pagesMeasurement+ +Area+&+PerimeterAnson LinNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Numbers To 1000 - QuestionsDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Numbers To 1000 - QuestionsMarlin XinNo ratings yet
- T - LinesDocument7 pagesT - LinesSifatNo ratings yet
- Australian Mathematics Competition (AMC) Performance ReportDocument51 pagesAustralian Mathematics Competition (AMC) Performance ReportRajuNo ratings yet
- Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 FY 19-20 FY 19-20 Total Total Total Total TotalDocument2 pagesQ1 Q2 Q3 Q4 FY 19-20 FY 19-20 Total Total Total Total Totalraddy13No ratings yet
- HCF LCM Squre RootsDocument0 pagesHCF LCM Squre RootsCh Saqib NazirNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Math Worksheet 15-ADocument4 pagesClass 8 Math Worksheet 15-AHereebNo ratings yet
- ISMO PreviousPaper 5Document13 pagesISMO PreviousPaper 5kalthebal1029No ratings yet
- OCR S1 Notes Permutations and CombinationsDocument8 pagesOCR S1 Notes Permutations and CombinationsJon HadleyNo ratings yet
- SASMO Grade 7 (Secondary 1) Sample QuestionsDocument5 pagesSASMO Grade 7 (Secondary 1) Sample QuestionsYopi TobriyantoNo ratings yet
- 6 Igcse Circle TheoremsDocument18 pages6 Igcse Circle Theorems4sqsmq2856No ratings yet
- Quadratic Sequences Worksheet 1Document3 pagesQuadratic Sequences Worksheet 1PoojaNo ratings yet
- HKDSE Maths Sample Paper 1Document15 pagesHKDSE Maths Sample Paper 1bradNo ratings yet
- GCSE Maths Foundation - Exam-Style QuestionsDocument6 pagesGCSE Maths Foundation - Exam-Style QuestionsFastTrackMathsNo ratings yet
- Secondary 3 Imocsea Sample TestDocument9 pagesSecondary 3 Imocsea Sample TestpriyagvspvNo ratings yet
- Y10 Working With Unfamiliar Problems 1Document1 pageY10 Working With Unfamiliar Problems 1kheyNo ratings yet
- 2014 Intermediate Team Solutions (English)Document9 pages2014 Intermediate Team Solutions (English)alex jobogNo ratings yet
- P4-L Key PDFDocument1 pageP4-L Key PDFendangNo ratings yet
- Pink Kangaroo 2022 SolutionsDocument12 pagesPink Kangaroo 2022 SolutionsSakethNo ratings yet
- P1 Math Workbook 1Document47 pagesP1 Math Workbook 1TO ChauNo ratings yet
- Gauss Contest: Canadian Mathematics CompetitionDocument4 pagesGauss Contest: Canadian Mathematics CompetitionSteven LiNo ratings yet
- WS-Simplifying Surds - With Answers PDFDocument1 pageWS-Simplifying Surds - With Answers PDFAjay PeryaghNo ratings yet
- SASMO 2018 Grade-6Document9 pagesSASMO 2018 Grade-6S1ice manNo ratings yet
- Principles of Math 12 - Permutations and Combinations Lesson 2Document10 pagesPrinciples of Math 12 - Permutations and Combinations Lesson 2abelNo ratings yet
- Class 7 - Mathematics - Yearly - Reena Krishnakumar - Reena KrishnakumarDocument6 pagesClass 7 - Mathematics - Yearly - Reena Krishnakumar - Reena KrishnakumarmuzaffaralhashmimaazmuzaffarNo ratings yet
- 3 RD Preliam 10 TH STDDocument8 pages3 RD Preliam 10 TH STDSneha sonarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5-Consumer ArithmeticDocument12 pagesLesson 5-Consumer Arithmeticalessse100% (1)
- Prime Ministers of Jamaica PDFDocument10 pagesPrime Ministers of Jamaica PDFalessseNo ratings yet
- Algebraic ExpressionsDocument21 pagesAlgebraic ExpressionsalessseNo ratings yet
- Problem Paper QuadraticDocument1 pageProblem Paper QuadraticalessseNo ratings yet
- Chemical InjuryDocument192 pagesChemical InjuryalessseNo ratings yet