Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mid Term Form 1 2004
Mid Term Form 1 2004
Uploaded by
Ct HusnaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mid Term Form 1 2004
Mid Term Form 1 2004
Uploaded by
Ct HusnaCopyright:
Available Formats
SMK. St.
Anthony, Sarikei
FIRST MID TERM EXAMINATION 2004
Name: _______________________ Form 1: ______________________
SCIENCE FORM 1
Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
YOU ARE NOT ALLOWED TO OPEN THE QUESTION PAPER UNTIL YOU HAVE THE PERMISSION. 1. This question paper is bilingual 2. The questions at the right hand side of the pages are in Malay language. The questions at the left hand side of the pages are equivalent in English language. 3. This question paper contains 11 printed pages 4. Answer all questions. 5. Answer each question by blackening the correct space on the answer sheet. 6. Blacken only one space for each question 7. If you wish to change your answer, erase the blackened mark that you have made. Then blacken the space for your new answer. 8. The figures provided are not drawn to scale unless stated.
Prepared by: (Cikgu Norzehan Zakaria) Checked by: . . (Cikgu Hii Su Hee) Head of Science (LF) Unit Department Verified by: (Cikgu Kang Hong Hie) Head of Mathematics & Science 1
Answer all the questions. Section A. 1. What statement about science is incorrect? A Science teaches human how to reach the moon B Science can make dead come alive again C Science teaches human to invent instruments and machines D Science is the understanding about the environment 2. A person who study the medicine is called A a teacher C a scientist B a geologist D a doctor 3. Which of the following is not a natural phenomenon? A Hot spring C Volcanic eruptions B Earthquakes D Pollution 4. Scientific and technological contributions in the field of communication include the following except the A telephone C fax machine B telecommunicati D camera on 5. The scientific methods used by scientist include the following except A observation C. analyzing B recording D. cheating 6. While carrying out an experiment, observations that we record are known as A data C. proposals B notes D. reports 7. Laboratory rules are important because they help safeguard A our belongings C. school furniture B chemical D. our safety 8. Which of the following pair is true of basic quantities and their S.I. units? A Mass gram (g) C. Length centimeter (cm) B Volume litre (l) D. Time second (s) 9. A piece of paper of 0.12 cm thickness is equivalent to A 1200 m C. 0.0012 m B 12 m D. 0.00012 m 10. The degree of hotness of an object is known as A temperature C. length
heat
D. cold
11. 2.15 kg is equivalent to A 0.215 g C. 215 g B 21.5 g D. 2150 g
Jawab semua soalan Bahagian A 1. Yang manakah pernyataan berikut salah mengenai sains? A Sains mengajar manusia cara untuk sampai ke bulan B Sains boleh menyebabkan benda mati hidup semula 2. Seseorang yang mempelajari bidang perubatan dipanggil A guru C saintis B geologi D doktor 3. Manakah di antara berikut bukan fenomena semulajadi? A Kolam air panas C Letupan gunung berapi B Gempa bumi D Pencemaran 4. Peranan teknologi dan saintifik komunikasi termasuk berikut kecuali A telefon C mesin fax B telekomunikasi D kamera 5. Kaedah saintifik yang digunakan oleh saintis termasuk berikut kecuali A membuat pemerhatian C. menganalisa B merekod D. menipu 6. Ketika menjalankan eksperimen, pemerhatian yang kita rekodkan dikenali sebagai A data C. cadangan B nota D. laporan 7. Peraturan-peraturan makmal adalah penting kerana ia merupakan panduan keselamatan untuk A barang kepunyaan C. perabot sekolah kita B bahan kimia D. keselamatan diri kita 8. Yang manakah antara beriku benar mengenai kuantiti asas dan unit S.I. nya? A Jisim gram (g) C. Panjang sentimeter (cm) B Isipadu liter (l) D. Masa saat (s) 9. Sehelai kertas yang ketebalannya 0.12 cm adalah sama dengan A 1200 m C. 0.0012 m B 12 m D. 0.00012 dikenali 10. Darjah kepanasan sesuatu objek m sebagai A suhu B panas C. panjang D. sejuk
11. 2.15 kg adalah sama dengan A 0.215 g C. 215 g B 21.5 g D. 2150 g
15. Albert wants to measure the length of a road on a map. Which of the following instrument will give the most accurate result? A An opisometer B A meter rule C A thread and a ruler D A pair of external calipers and a ruler
0 1 cm Questions 12 and 13 are based on Figure 1
9 10
Figure 2 16. Diagram 2 shows a method to determine the size of a ping pong ball. What is its diameter? A 5 cm C. 6 cm B 2 cm D. 4 cm 17. A clinical thermometer can measure temperature ranges from A 30OC to 40 OC C 0OC to100 OC O O B 32 C to 42 C D 35OC to 100 OC
Figure 1 12. Figure 1 shows an experiment which was conducted by a group of students to measure the time taken by pendulum to make 10 complete swings. The data collected was shown below Experim Time ent taken 1 20 seconds 2 18 seconds 3 19 seconds Calculate the average time taken by the pendulum to make one complete swing. A 1.8 seconds C 2.0 seconds . . B 1.9 seconds D 20 seconds . .
Soalan 12 dan 13 adalah berdasarkan Rajah 1
tali Kaki retot ladung
13. Which of the following variables cannot be controlled in the experiment above? A The length of the string of the pendulum B The weight of pendulum C The height of pendulum D The time of oscillation 14. The mass of an object can be determined by using a/an A beam balance C. measuring cylinder B buret D. eureka tin
Figure 1 12. Rajah 1 menunjukkan satu eksperimen yang dijalankan oleh sekumpulan pelajar untuk menentukan masa yang diambil oleh ladung untuk membuat 10 ayunan lengkap. Data yang dikumpulkan adalah seperti jadual di bawah Eksperi Masa yang men diambil 1 20 saat 2 18 saat 3 19 saat Kirakan masa purata yang diambil oleh ladung untuk membuat satu ayunan lengkap. A 1.8 saat C 2.0 saat 13. Yang manakah antara berikut merupakan pembolehubah yang boleh boleh dimanipulasikan dalam eksperimen di atas? A Panjang tali pendulum B Berat pendulum C Ketinggian pendulum D Tempoh ayunan ayunan
14. Jisim sesuatu objek boleh ditentukan dengan menggunakan A neraca palang C. silinder penyukat B buret D. tin eureka 15. Albert mahu mengukur panjang jalanraya di atas peta. Yang manakah antara peralatan berikut akan memberi keputusan yang paling tepat? A Opisometer B Pembaris meter C benang dan pembaris D Sepasang angkup dan pembaris
Figure 4 19. Which is the correct eye position when reading the volume of the liquid in the measuring cylinder as shown in Figure 4. 80
0 1 cm
9 10 70
Rajah 2 16. Rajah 2 menunjukkan kaedah untuk mengenalpasti saiz sebiji bola ping pong. Apakah diameternya? A 5 cm C. 6 cm B 2 cm D. 4 cm 17. Termometer klinik boleh mengukur suhu berjulat dari A 30OC hingga 40 C 0OC hingga 100 OC O C B 32OC hingga 42 D 35OC hingga 100 OC O C
60
Figure 5 20. Based on Figure 5, what is the reading on the measuring cylinder? A 75 cm3 C 77 cm3 3 B 76 cm D 78 cm3
54 cm3 Measuring cylinder 54 cm3 marbles 22 cm3 water Figure 3 18. Figure 3 shows an experiment conducted to determine the volume of a piece of marble, 10 pieces of marbles are immersed into a measuring cylinder containing some water. Calculate the volume of a piece of marble. A 2.4 cm3 C 3.1 cm3 3 B 2.6 cm D 3.2 cm3 22 cm3 guli air Rajah 3 18. Rajah 3 menunjukkan satu eksperimen yang dijalankan untuk menentukan isipadu sebiji guli, 10 biji guli telah ditenggelamkan ke dalam silinder penyukat yang mengandungi air. Kirakan isipadu sebiji guli. A 2.4 cm3 C 3.1 cm3 B 2.6 cm3 D 3.2 cm3 silinder penyukat
40.6 cm3. What is the volume of the water collected in a beaker? A 30 cm3 C 51.2 cm3 3 B 60 cm D 40 cm3
C
1 cm 1 cm
Rajah 4 19. Yang manakah menunjukkan kedudukan mata yang betul apabila membaca isipadu cecair di dalam silinder penyukat seperti di dalam Rajah 4. 80 70
Figure 7 22. Estimate the area of the irregular shape shown in Figure 7. A 23 cm2 C 25 cm2 2 B 24 cm D 26 cm2 23. The basic unit of an animal or plant is called a/an A Tissue C cell B Organ D system 4
60
Rajah 5 20. Berdasarkan Rajah 5, berapakah bacaan pada silinder penyukat? A 75 cm3 C 77 cm3 3 B 76 cm D 78 cm3
1 1
2 2
Retort Stand Burette
Figure 8 24. Figure 8 shows an amoeba that has been sliced into four parts. Which part still can live and reproduce? A 1 C 3 B 2 D 4 25. Which of the following statements is not true about cells? A Onion cells are plant cells B Animal cells do not have definite shape C Cells can only be seen under a microscope D Animal cells have chloroplast
Water
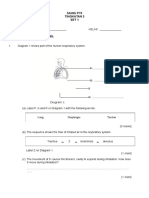
Beaker
Figure 6 21. The apparatus shown in Figure 6 is used to measure the volume of water delivered out. The first reading is 10.6 cm3 and the final reading is
Kaki retot Buret
24. Rajah 8 menunjukkan seekor ameba yang telah dikerat kepada empat bahagian. Bahagian manakah yang akan terus hidup dan membiak? A 1 C 3 B 2 D 4 25. Yang manakah antara kenyataan berikut tidak benar tentang sel? A Sel bawang adalah sel tumbuhan B Sel haiwan tidak mempunyai bentuk yang tetap C Sel hanya boleh dilihat di bawah mikroskop D Sel haiwan mempunyai kloroplas . 26. P
air
Bikar
Rajah 6 21. Radas pada Rajah 6 digunakan untuk mengukur isipadu air yang dikeluarkan. Bacaan pertama ialah 10.6 cm3 dan bacaan akhir ialah 40.6 cm3. Berapakah isipadu air yang dikumpulkan di dalam bikar? A 30 cm3 C 51.2 cm3 3 B 60 cm D 40 cm3 1 cm 1 cm
Figure 9 Figure 9 shows the structure of a plant cell. What is the function of P? A To remove waste products from the cell B To carry out photosynthesis C To protect the cell D To maintain the shape of the cell 27. When focusing a microscope specimen, it is not advisable to lower the objective lens because it may A Damage your eyes C. Break the glass slide B touch the D. Produce a blurred specimen image
Rajah 7 Instruction Summary A B C D I, II and III I and II II and III I only 22. Anggarkan luas bagi bentuk tidak sekata yang ditunjukkan pada Rajah 7. A 23 cm2 C 25 cm2 2 B 24 cm D 26 cm2 23. Unit asas bagi haiwan dan tumbuhan dipanggil A tisu C sel B organ D sistem 4
28. Which of the following is not
correctly
matched.
Animal cell No definite shape No vacuole/very small vacuole C No chloroplast D Has nucleus A B Plant cell Definite shape Big vacuole Has chloroplast Has no nucleus
29. A plant cell has definite shape because it has A Vacuoles C a cell wall B a cell membrane D a nucleus 30. What is the magnifying power of a microscope when the power of its eye piece is x10 and the power of objective lens is x10? A 10x C 1000x B 100x D 10000x
2 1
Rajah 8
Answer for questions 31 to 50 are based on the instruction 31. Select the correct statement/s. I A spring balance is used to measure mass II External calipers are used to measure external diameters of an object. II Internal calipers are used to measure internal I diameter of an object 32. In an experiment, a ball is left to roll freely on an uneven surface. Which of the following methods can be used to obtain results about the movement of the ball? I Measuring II Observing II Testing I 33. The unit/s used for measuring time include I Hour II Minute II second I 26. P Rajah 9 Figure 9 menunjukkan struktur bagi sel tumbuhan. Apakah fungsi bagi bahagian P? A Untuk membuang hasil kumbahan daripada sel B Untuk menjalankan fotosintesis C Untuk melindungi sel D Untuk mengekalkan bentuk sel 27. Apabila memfokus spesimen pada mikroskop, adalah tidak digalakkan untuk menurunkan kanta objektif sebab ia boleh A merosakkan mata C. memecahkah sisip kaca B menyentuh D. menghasilkan imej spesimen yang kabur 28. Manakah antara berikut tidak
29. Sel tumbuhan mempunyai bentuk yang tetap kerana ia mempunyai A vakuol C dinding sel B membran sel D nukleus 30. Apakah kuasa pembesaran mikroskop apabila kuasa kanta mata ialah 10x dan kuasa kanta objektif ialah 10x? A 10x C 1000x B 100x D 10000x
Jawapan bagi soalan 31 to 50 adalah seperti arahan di bawah Ringkasan arahan A B C D I, II dan III I dan II II dan III I sahaja 31. Pilih kenyataan yang betul. I Neraca spring digunakan untuk mengukur jisim II Angkup luar digunakan untuk mengukur diameter luar objek II Angkup dalam digunakan untuk mengukur I diameter dalam objek
32. Dalam satu eksperimen, sebiji bola dibiarkan bergolek di atas permukaan yang tidak rata. Manakah antara kaedah berikut boleh digunakan untuk mendapatkan keputusan tentang pergerakan bola tersebut? I Mengukur II Memerhati II Menguji I 33. Unit yang digunakan untuk mengukur masa termasuk I jam II minit II saat I 34. The length of a piece of chalk is 3.9 cm. This value is equivalent to I 390 m II 39 mm II 0.039 m I 35. Aina wants to be a chemical engineer, so she must study I physics II chemistry II biology I
dipadankan
dengan betul?.
A B C Sel haiwan Tiada bentuk tetap Tiada vakuol/vakuol kecil Tiada kloroplas Sel tumbuhan Berbentuk tetap Vakuol besar Mempunyai kloroplas Tiada nucleus
D Mempunyai nucleus
Z Y
Figure 10 36. Figure 10 shows a swinging pendulum in a plane, from X to Z. Which of the following sequences represent a complete oscillation? I X Y Z Y II X Y Z Y X II Y Z Y X I Y 37. A parallax error must be avoided when using I II II I a thermometer a ruler vernier calipers
34. Panjang sebatang kapur ialah 3.9 cm. Nilai ini sama dengan I 390 m II 39 mm II 0.039 m I 35. Aina mahu menjadi seorang jurutera kimia, jadi dia mesti belajar I fizik II kimia II biologi I .
Z X Y
38. You are asked to measure 20.5 cm3 of sulfuric acid. Which of the following can be used for the purpose? I A measuring cylinder II A burette II A pipette I P
Rajah 10 36. Rajah 10 menunjukkan ayunan ladung dari X ke Z. Yang manakah antara berikut menunjukkan satu ayunan yang lengkap? I X Y Z Y II X Y Z Y X II Y Z Y X Y I 37. Ralat paralaks mestilah dielakkan apabila menggunakan I termometer II pembaris II angkup vernier I 38. Kamu dikehendaki untuk megukur 60.5 cm3 asid sulfurik. Yang manakah antara berikut boleh digunakan untuk tujuan tersebut? I Silinder penyukat II Buret II Pipet I
Figure 11 39. Figure 11 shows a curve line PQ. Its length can be measured by using I thread and ruler II micrometer II ruler and internal calipers I 40. Why is it important to have standard units for international communications? I To facilitate communication among scientist II To standardize quantities in measurement worldwide II To facilitate international trade I 41. Which of the following parts of a plant cell cannot be found in an animal cell? I Vacuole II Cell wall II Cytoplasm I
Rajah 11 39. Rajah 11 menunjukkan satu garis lengkung PQ. Panjang garis itu boleh diukur dengan menggunakan I benang dan pembaris II mikrometer II pembaris dan angkup dalam
I 40. Mengapakah penting untuk kita mempunyai keselarasan unit-unit untuk perhubungan antarabangsa? I Untuk memudahkan komunikasi dikalangan saintis II Untuk menyelaraskan kuantiti di dalam pengukuran antarabangsa II Untuk memudahkan perdagangan I antarabangsa 41. Yang manakah antara berikut pada sel tumbuhan tidak terdapat di dalam sel haiwan? I Vakuol II Dinding sel II Sitoplasma I
I W X Figure 12 48. Figure 12 shows a human check cell. Protoplasm consists of I W II X II Y I 49. Some microorganisms are useful because they help in the process of I making bread II the decomposition of dead material II making cheese I 50. Which of the following can be found in the cytoplasm of a cell? I Water II Salt II Urea I Y
42. The basic structure(s) found in an animal cell is/are I nucleus II cytoplasm II cell membrane I 43. Which of the following is/are true about chloroplast? I Made of cellulose II Contains chlorophyll II Center for making food I 44. Select the correct procedure for using a microscope. I Using both hand to handle the microscope II Placing the microscope in a dark place II Not clipping the slide on the platform I 45. Euglena is a type of organism that cannot be seen with the naked eye. This organism I is a type of animal II has chlorophyll II is a type of plant I 46. The nucleus genes I contains genes II controls the activities in the cell II absorb sunlight in plants to carry out I photosynthesis 47. Choose the correct statement(s). I Animal cell has no fixed shape II Nucleus controls all cell activities II All plant cells have chloroplast
42. Struktur asas yang didapati pada sel haiwan ialah I nukleus II sitoplasma II membran sel I 43. Yang manakah antara berikut benar mengenai kloroplas? I Diperbuat daripada selulosa II Mengandungi klorofil II Tempat membuat makanan I 44. Pilih prosedur yang betul semasa menggunakan mikroskop. I Gunakan kedua-dua belah tangan untuk memegang mikroskop II Simpankan mikroskop di tempat yang gelap II Jangan klipkan sisip kaca di pentas. I
45. Euglena adalah organisma yang tidak boleh dilihat dengan mata kasar. Organisma ini I adalah sejenis haiwan II Mengandungi klorofil II adalah sejenis tumbuhan I 46. Gen nukleus mengandungi I II II I gen-gen mengawal aktiviti di dalam sel menyerap cahaya bagi tumbuhan
48. Rajah 12 menunjukkan sel pipi manusia. Protoplama terdiri daripada I W II X II Y I 49. Terdapat beberapa mikroorganisma yang berfaedah sebab ia membantu dalam proses I pembuatan roti II penguraian bahan mati II pembuatan keju I 50. Yang manakah antara berikut boleh didapati di dalam sitoplasma sel? I Air II Garam II Urea I
47. Pilih kenyataan yang betul. I Sel haiwan tidak mempunyai bentuk yang tetap II Nukleus mengawal semua aktiviti sel II Semua sel tumbuhan mempunyai kloroplas I W X Rajah 12 Y
Answer all the questions (Jawab semua soalan) Section B (Bahagian B) 1. State the function of the following instrument. (Nyatakan fungsi bagi radasradas di bawah) Instrument (Alat)
3 2 1 0
Function (Fungsi) For measuring the ________________ of a straight line. (Untuk mengukur _________________ sesuatu garis lurus.)
A ruler (Pembaris) External calipers (Angkup luar) For measuring the _______________ of a test tube. (Digunakan untuk mengukur _________________ tabung uji.) For measuring the ______________ of a test tube. (Digunakan untuk mengukur _________________ tabung uji.) A graph paper (Kertas graf) For measuring the ______________________ of a liquid. 10 For estimating the _____________________ of an irregular shape. (Untuk menanggarkan ____________________ bentuk tidak sekata)
Internal calipers (Angkup dalam)
(Untuk mengukur ____________________ sesuatu cecair. A measuring cylinder (silinder penyukat) For measuring the _____________ of a liquid in a ___________ amount. For measuring the __________________ of a liquid delivered out. (Untuk mengukur ____________________ sesuatu cecair yang dikeluarkan) For measuring the _____________________ of an object. (Untuk mengukur ________________ sesuatu objek)
A pipette (Pipet) A burrette (Buret)
A beam balance (Neraca palang) For measuring the _______________ of an object. (Untuk mengukur _______________ sesuatu objek) A spring balance (Neraca spring) (10 marks) 2. Complete the following table by using the correct word. (Lengkapkan Jadual berikut) S.I Unit (Unit S.I) meter second Kelvin Celsius gram kilometer galvanometer Symbol (Simbol) A kg s mm mg QUANTITY (KUANTITI) Length (Panjang) Mass (Jisim) Time (Masa) Electric current (Arus elektrik) C mA K centimeter ampere minute kilogram
cm
km
dm
S.I. UNIT (UNIT S.I)
SYMBOL (SIMBOL)
11
Temperature (Suhu) (10 marks) 3.
Figure 1 Figure 1 shows an empty box. (Rajah 1 menunjukkan satu kotak yang kosong) a. By using your own ruler, measure the length, width and height of the box. (Dengan menggunakan pembaris anda, ukurkan panjang, lebar dan tinggi kotak) i. Length (Panjang) : ______________________ cm ii. Width (Lebar) : _____________________ cm iii. Height (Tinggi) : ______________________ cm b. Calculate the volume of the box. (Hitungkan isipadu kotak tersebut) (Given; volume = Length x Width x Height)
c. Why must the eye be positioned vertically above the mark on the ruler while taking the reading? (Mengapakah mata kita mesti berada tepat pada tanda bacaan pada pembaris ketika mengambil bacaan?) _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______. d. What is parallax error? (Apakah ralat paralaks?) ______________________________________________________________________________________ _______. (10 marks) 4. A) Label the parts of the microscope shown in Figure 2. (Labelkan bahagian-bahagian mikroskop yang ditunjukkan di Rajah 2) Objective lens mirror stage piece clip handle eye
Fine-adjustment knob
coarse-adjustment knob 12
(a) ________________________
(b) ________________________
(c) ________________________ (g) _______________ (d) ________________________ (e) ________________________ (f) ________________
Figure 2
B) Give two reasons why you must handle your microscope with care? (Berikan dua alasan mengapakah kamu mesti mengendalikan mikroskop dengan baik? i) _________________________________________________________________________________ ii) _________________________________________________________________________________ C) We use microscope to see __________________________________________________________________) (Kita menggunakan mikroskop untuk melihat ____________________________________________________)
(10 marks)
13
You might also like
- F3 Chapter 7 Energy and PowerDocument13 pagesF3 Chapter 7 Energy and PowerJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 3Document3 pagesForm 2 Chapter 3Ng Imm KhuanNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 2Document2 pagesForm 2 Chapter 2Ng Imm Khuan100% (1)
- Science Answer Scheme Paper 1 and 2 Form1 09Document6 pagesScience Answer Scheme Paper 1 and 2 Form1 09azmijaaffarNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 1 f4Document2 pagesExercise Chapter 1 f4Mohamad Rizal MukhtarNo ratings yet
- SEDEX Mineral SystemDocument18 pagesSEDEX Mineral SystemBenNo ratings yet
- Exercise Introduction To ScienceDocument17 pagesExercise Introduction To Science颜慧嘉No ratings yet
- Section A (20 Marks)Document8 pagesSection A (20 Marks)Elen UningNo ratings yet
- STF Science Module 1 (PMR) Chapter 1: Introduction To Science Section ADocument8 pagesSTF Science Module 1 (PMR) Chapter 1: Introduction To Science Section AzuaihaNo ratings yet
- Sci F1 T1 (E)Document7 pagesSci F1 T1 (E)Sylvia ChinNo ratings yet
- Test 1Document3 pagesTest 1Sutha Tamil Chelvan SuthaNo ratings yet
- f1 Chapter 1Document7 pagesf1 Chapter 1Nurul AzuwinNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 2 Form 1Document23 pagesScience Chapter 2 Form 1Kelvin0% (1)
- Exercise Chapter 5 Form 1 2016Document2 pagesExercise Chapter 5 Form 1 2016Nor Adila100% (1)
- RTS PMR Question Bank Chapter 1 2008Document7 pagesRTS PMR Question Bank Chapter 1 2008FarisaNo ratings yet
- Modul 1 - Form 1 STFDocument31 pagesModul 1 - Form 1 STFmadrosli100% (3)
- Sains Form1 Final ExamDocument10 pagesSains Form1 Final ExamNOR SUAKMA BT JAAFARNo ratings yet
- PMR 2012 Science 108 MantraDocument16 pagesPMR 2012 Science 108 MantraJun MingNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 Chapter-5 - The Air-Around-UsDocument16 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter-5 - The Air-Around-UsLouis Lim0% (1)
- Science Form 1 Chapter 3Document7 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 3huisinNo ratings yet
- Modul SC Chapter 2 - f1Document14 pagesModul SC Chapter 2 - f1Raja InaNo ratings yet
- RTS PMR Question Bank Chapter 3 2008Document7 pagesRTS PMR Question Bank Chapter 3 2008iwan93No ratings yet
- Exercise SC Form 1 Chapter 6Document2 pagesExercise SC Form 1 Chapter 6Nor AdilaNo ratings yet
- F2 Chap 3 MCQDocument5 pagesF2 Chap 3 MCQSuriya GunalanNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Chapter 3 MatterDocument6 pagesForm 1 Chapter 3 Matterjj982150% (2)
- Science Form 1 Chapter 1Document13 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 1huisin100% (1)
- Instruction: Answer All Questions. Each Question Is Followed by Four Choices of Answers. Choose The CorrectDocument11 pagesInstruction: Answer All Questions. Each Question Is Followed by Four Choices of Answers. Choose The CorrectAin AinNo ratings yet
- f2 Chapter 2 PDFDocument9 pagesf2 Chapter 2 PDFNurul Fairuz HusnaNo ratings yet
- Chem Test 1 2018 SECTION BDocument7 pagesChem Test 1 2018 SECTION BAmirah Noor AffandiNo ratings yet
- Latihan Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 4Document11 pagesLatihan Sains Tingkatan 3 Bab 4李友志67% (3)
- KSSM Form 1 Science Chapter 6Document3 pagesKSSM Form 1 Science Chapter 6elizabeth ellsaNo ratings yet
- Soalan Sainsf1Document13 pagesSoalan Sainsf1Husna IzaNo ratings yet
- Ar1 Science Year 4 Paper 1Document16 pagesAr1 Science Year 4 Paper 1Dawson Ador100% (1)
- Answer All Questions.: Sains Pt3 Tingkatan 3 Set 1Document9 pagesAnswer All Questions.: Sains Pt3 Tingkatan 3 Set 1Wan NazrinaNo ratings yet
- Year 6 Paper 1Document12 pagesYear 6 Paper 1Nana AngkingNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Chapter 2Document9 pagesForm 3 Chapter 2Mariana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Form 1 - Chapter 8Document6 pagesForm 1 - Chapter 8Anonymous fhlpbtbXzx67% (3)
- STF Mid Year Science Form 1 2009 Paper2Document12 pagesSTF Mid Year Science Form 1 2009 Paper2Syahrul67% (3)
- Soalansubjektifmidexamt 3Document10 pagesSoalansubjektifmidexamt 3Cikgu Siti RohaizaNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions.: Section ADocument8 pagesAnswer All Questions.: Section ANor AdilaNo ratings yet
- Obj Home WorkDocument9 pagesObj Home WorkYuman WongNo ratings yet
- Peperiksaan Pertengahan TAhun Sains Tingkatan 1Document16 pagesPeperiksaan Pertengahan TAhun Sains Tingkatan 1RosmizaNo ratings yet
- 1 Form 2 Chapter 2 Nutrition Paper 1 Answer All Questions. Each ...Document9 pages1 Form 2 Chapter 2 Nutrition Paper 1 Answer All Questions. Each ...Amira Jasmin JayaNo ratings yet
- Latihan Sains UPSRDocument6 pagesLatihan Sains UPSRAlia AminNo ratings yet
- Science Standard 6 Short TestDocument2 pagesScience Standard 6 Short TestZacky Zack AsfanuddinNo ratings yet
- FORM 2, Chap 03-BiodiversityDocument15 pagesFORM 2, Chap 03-BiodiversitySyahrul100% (11)
- Chapter 7 Linear InequalitiesDocument8 pagesChapter 7 Linear InequalitiesROSMAWATI BINTI MOHAMED -No ratings yet
- MID-TERM EXAMINATION (Chapter 1 To Chapter 4)Document8 pagesMID-TERM EXAMINATION (Chapter 1 To Chapter 4)Shakilla HamzahNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 5Document4 pagesForm 2 Science Exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 5KelvinNo ratings yet
- Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun Matematik Tingkatan 1Document9 pagesPeperiksaan Akhir Tahun Matematik Tingkatan 1Zainal AssaukiNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 1 Form 1Document6 pagesScience Chapter 1 Form 1TAN SHER ENNNo ratings yet
- Exercise Introduction To ScienceDocument17 pagesExercise Introduction To ScienceShu85No ratings yet
- Sains Tingkatan 1Document9 pagesSains Tingkatan 1871226No ratings yet
- Science Form 1Document13 pagesScience Form 1Aziah Husain75% (4)
- Midterm Mathayom 1.2Document12 pagesMidterm Mathayom 1.2AbdullohNo ratings yet
- Soalan Latihan Sains Tahun 4, 5, 6Document28 pagesSoalan Latihan Sains Tahun 4, 5, 6FT Geeyah Tahir100% (1)
- UPT Sains Tahun 4 K1Document14 pagesUPT Sains Tahun 4 K1ROYNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 6: Length and TimeDocument12 pagesWorksheet 6: Length and TimeAnonymous0% (1)
- Question Bank (Chapter 1) Part A: Each Question Is Followed by Four Possible Answers. Choose The Correct Answer or The OneDocument8 pagesQuestion Bank (Chapter 1) Part A: Each Question Is Followed by Four Possible Answers. Choose The Correct Answer or The OneSani IsmailNo ratings yet
- GsDocument5 pagesGssalaandeska2015No ratings yet
- Grade 1 Interdisciplinary UnitDocument21 pagesGrade 1 Interdisciplinary UnitSamantha WilsonNo ratings yet
- Ugc BooksDocument7 pagesUgc BooksNandha KumarNo ratings yet
- PM9820Document2 pagesPM9820akas_yantNo ratings yet
- Barcham DeConstructing The Politics of Indigeneity-With-Cover-Page-V2Document11 pagesBarcham DeConstructing The Politics of Indigeneity-With-Cover-Page-V2Anh Ngữ MercuryNo ratings yet
- 7281 enDocument4 pages7281 enLevent MertNo ratings yet
- ASQ CompleteDocument6 pagesASQ Completeabigailgracesabu00No ratings yet
- Citizen JournalismDocument25 pagesCitizen JournalismRavi VermaNo ratings yet
- 8 BibliographyDocument3 pages8 BibliographyJihan Nadila AsriNo ratings yet
- Cloning and Expression - FLAG and 3xFLAG OverviewDocument3 pagesCloning and Expression - FLAG and 3xFLAG OverviewSigma-Aldrich100% (12)
- Thesis Silpakorn ArchitectureDocument8 pagesThesis Silpakorn Architecturerokafjvcf100% (1)
- Emg Eldro Standard en Rev01!11!2017Document12 pagesEmg Eldro Standard en Rev01!11!2017Pipe RoblesNo ratings yet
- Imalack W 2077 oDocument1 pageImalack W 2077 oahmetNo ratings yet
- Cronus - Deck A: 2X2 MetersDocument4 pagesCronus - Deck A: 2X2 MetersXosé Lois PérezNo ratings yet
- Bois Form Revised 2017 2Document1 pageBois Form Revised 2017 2Regina Amber Dela Cruz100% (5)
- Phonics Planning 3 EditionDocument120 pagesPhonics Planning 3 Editionnatalia violattiNo ratings yet
- Shock Speed ArticleDocument10 pagesShock Speed ArticleKathryn Workman100% (1)
- Rating and Design of Tubular Heat Exchangers Using HTRI PDFDocument4 pagesRating and Design of Tubular Heat Exchangers Using HTRI PDFshridharNo ratings yet
- Acct Statement - XX8434 - 07092022Document7 pagesAcct Statement - XX8434 - 07092022Suhail KhanNo ratings yet
- FTR 900 Singular Cab y Crew Cab Australia PDFDocument4 pagesFTR 900 Singular Cab y Crew Cab Australia PDFdionymackNo ratings yet
- BC Business Case CTOUCHDocument29 pagesBC Business Case CTOUCHMichael J SminiaNo ratings yet
- Mohammad Istiak (CV)Document3 pagesMohammad Istiak (CV)Anonymous bVLovsnNo ratings yet
- 1st Diagnostic Test Pe 7Document2 pages1st Diagnostic Test Pe 7Alona Cajida100% (2)
- English Monologue TopicDocument2 pagesEnglish Monologue TopicVesta GrumadaiteNo ratings yet
- Are We Entering The Age of Involuntary Degrowth? Promethean Technologies and Declining Returns of Innovation (Bonaiuti 2017)Document10 pagesAre We Entering The Age of Involuntary Degrowth? Promethean Technologies and Declining Returns of Innovation (Bonaiuti 2017)CliffhangerNo ratings yet
- Ansys Meshing TutorialDocument9 pagesAnsys Meshing TutorialUppala Krishna ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 6Document4 pagesProblem Set 6ronaldNo ratings yet
- BMC Client ManagementDocument2 pagesBMC Client ManagementAndres OspinaNo ratings yet
- W1-MTB 3rd QuarterDocument5 pagesW1-MTB 3rd QuarterBeatriz CabadingNo ratings yet
- United States Patent (16) Patent N6. US 6,564,491 B2Document5 pagesUnited States Patent (16) Patent N6. US 6,564,491 B2edef345No ratings yet