Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Enoxaparin (Lovenox)
Enoxaparin (Lovenox)
Uploaded by
Cassie0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
336 views1 pageOriginal Title
Enoxaparin(Lovenox)
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
336 views1 pageEnoxaparin (Lovenox)
Enoxaparin (Lovenox)
Uploaded by
CassieCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
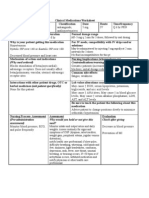
NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications Worksheets
(You will need to make additional copies of these forms)
Generic Name Trade Name Classification Dose Route Time/frequency
Enoxaparin Lovenox Low molecular 40 mg SQ Daily
weight heparins
Peak Onset Duration Normal dosage range
Unknown Unknown 12 hrs Medical patients with acute illness--40 mg once daily
Why is your patient getting this medication For IV meds, compatibility with IV drips and/or solutions
Prevention of DVT/Pulmonary Embolism N/A
Mechanism of action and indications Nursing Implications (what to focus on)
(Why med ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactions
Potentiates the inhibitory effect of antithrombin on factor Xa Contraindicated in: Hypersensitivity, active major bleed. Use
and thrombin. Indicated for prevention and treatment of DVT cautiously in severe kidney or liver disease, untreated hypertention,
and Pulmonary Embolism recent history of ulcer disease. Interacts with other blood thinning agents
and drugs and foods with anticoagulant effects.
Common side effects
Bleeding, anemia
Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal Lab value alterations caused by medicine
medicines (ask patient specifically) Monitor CBC, platelet count, and stools for occult blood periodically
Increased risk for bleeding if used with asparin during therapy. If thrombocytopenia occurs, monitor closely. If
hematocrit decreases unexpectedly, assess patient for potential bleeding
sites. Special monitoring of clotting times (aPTT) is not necessary in
most patients. Monitoring of the aPTT may be considered in certain
patient populations (such as obese patients or patients with renal
insufficiency)
Be sure to teach the patient the following about this
medication
Advise patient to report any symptoms of unusual bleeding or bruising,
dizziness, itching, rash, fever, swelling, or difficulty breathing to health
care professional immediately
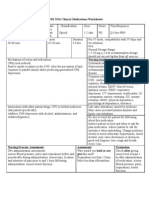
Nursing Process- Assessment Assessment Evaluation
(Pre-administration assessment) Why would you hold or not give this Check after giving
Assess for signs of bleeding and hemorrhage med? Signs of bleeding and hemorrhage.
(bleeding gums; nosebleed; unusual bruising; If signs of bleeding and hemorrhage Monitor patient for hypersensitivity
black, tarry stools; hematuria; fall in hematocrit or reactions (chills, fever, urticaria).
blood pressure; guaiac-positive stools); bleeding
are present. Report signs to physician or other
from surgical site. Notify physician or other health health care professional. Observe
care professional if these occur injection sites for hematomas,
ecchymosis, or inflammation. For
overdose protamine sulfate, 1mg for
each mg of enoxaparin should be
administered by slow IV injection.
You might also like
- Full Download Human Biology 11th Edition Starr Test BankDocument35 pagesFull Download Human Biology 11th Edition Starr Test Banksheathe.zebrinny.53vubg100% (47)
- Warfarin CoumadinDocument1 pageWarfarin CoumadinE100% (5)
- NarcanDocument1 pageNarcanKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Lopressor (Metoprolol) IVDocument2 pagesLopressor (Metoprolol) IVAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Drug Card ToradolDocument2 pagesDrug Card ToradolAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- CholestyramineDocument1 pageCholestyramineKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Drug Card Motrin 800mgDocument2 pagesDrug Card Motrin 800mgAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Drug BisacodylDocument1 pageDrug BisacodylSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Lanoxin (Digoxin)Document3 pagesLanoxin (Digoxin)E100% (5)
- Drug Card BenadrylDocument1 pageDrug Card BenadrylAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Drug Potassium ChlorideDocument1 pageDrug Potassium ChlorideSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Lovenox (Enoxaparin)Document1 pageLovenox (Enoxaparin)E100% (1)
- Lovenox (Enoxaparin)Document1 pageLovenox (Enoxaparin)E100% (5)
- Plavix ClopidogrelDocument2 pagesPlavix ClopidogrelAdrianne Bazo50% (2)
- Irbesartan (Avapro)Document1 pageIrbesartan (Avapro)ENo ratings yet
- LisinoprilDocument1 pageLisinoprilKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Lopressor (Metoprolol) 100mgDocument2 pagesLopressor (Metoprolol) 100mgAdrianne Bazo100% (2)
- Plavix Clopidogrel Drug CardDocument1 pagePlavix Clopidogrel Drug CardSheri490100% (1)
- Drug LovenoxDocument2 pagesDrug LovenoxSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Insulin, Regular (Humulin R)Document1 pageInsulin, Regular (Humulin R)ENo ratings yet
- Plavix (Clopidogrel)Document1 pagePlavix (Clopidogrel)E50% (2)
- ClindamycinDocument3 pagesClindamycinShaira TanNo ratings yet
- Levaquin Drug CardDocument1 pageLevaquin Drug CardSheri490100% (1)
- LevaquinDocument1 pageLevaquinKatie McPeek100% (1)
- AtenololDocument2 pagesAtenololMichael Kuzbyt100% (1)
- Drug AtivanDocument1 pageDrug AtivanSrkocherNo ratings yet
- CarafateDocument1 pageCarafateAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Ativan (Lorazepam) 08Document1 pageAtivan (Lorazepam) 08CassieNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide (Reglan)Document1 pageMetoclopramide (Reglan)ENo ratings yet
- Drug OmeprazoleDocument1 pageDrug OmeprazoleSrkocherNo ratings yet
- DiflucanDocument1 pageDiflucanSheri490No ratings yet
- MupirocinDocument13 pagesMupirocinkurutalaNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDocument1 pageCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- MorphineDocument1 pageMorphineCassie100% (3)
- Drug Card Tricyclic DepressantsDocument2 pagesDrug Card Tricyclic DepressantsAaLona RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Digoxin Drug CardDocument1 pageDigoxin Drug CardMahsa Ahmadzadeh100% (2)
- Huma Log Drug CardDocument1 pageHuma Log Drug CardJanet SheldonNo ratings yet
- VasopressinDocument2 pagesVasopressinKim LompotNo ratings yet
- CiprofloxacinDocument1 pageCiprofloxacinENo ratings yet
- Drug CardDocument2 pagesDrug CardHannahNo ratings yet
- Darvocet N Drug CardDocument1 pageDarvocet N Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- Infective Endocarditis CaseDocument3 pagesInfective Endocarditis CaseMershen GaniaNo ratings yet
- Metformin GlucophageDocument1 pageMetformin GlucophageENo ratings yet
- Galvus (Vildagliptin) : How Does It Work?Document5 pagesGalvus (Vildagliptin) : How Does It Work?Radhakrishna KurupNo ratings yet
- Drug CardsDocument2 pagesDrug CardsMichael LongsNo ratings yet
- Generic Name T Rade Name Classification Minitran Anti Angina NitroglycerinDocument1 pageGeneric Name T Rade Name Classification Minitran Anti Angina NitroglycerinChristopher LeeNo ratings yet
- AmiodaroneDocument2 pagesAmiodaronekumaninaNo ratings yet
- PrevacidDocument1 pagePrevacidAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- LopressorDocument1 pageLopressorSheri490100% (1)
- Activated CharcoalDocument1 pageActivated CharcoalSupreeth PrasadNo ratings yet
- Generic Name FurosemideDocument1 pageGeneric Name FurosemideChristopher LeeNo ratings yet
- Ondansetron (Zofran)Document1 pageOndansetron (Zofran)Michele Gilbert BlumNo ratings yet
- RocephinDocument1 pageRocephinCassieNo ratings yet
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Myocarditis, (Inflamed Heart Muscles) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandMyocarditis, (Inflamed Heart Muscles) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Lovenox (Enoxaparin) 80mgDocument1 pageLovenox (Enoxaparin) 80mgAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- LovenoxDocument1 pageLovenoxAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- LovenoxDocument1 pageLovenoxSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Rathna Drug Card in (Lovenox)Document1 pageRathna Drug Card in (Lovenox)erdos13No ratings yet
- Enoxaparin (Lovenox)Document1 pageEnoxaparin (Lovenox)ENo ratings yet
- Lovenox 40 MLDocument1 pageLovenox 40 MLfaithsamp6No ratings yet
- Tag A MetDocument1 pageTag A MetKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- HaldolDocument2 pagesHaldolKatie McPeek100% (2)
- Re Me RonDocument2 pagesRe Me RonKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- ZofranDocument1 pageZofranKatie McPeek0% (1)
- VigamoxDocument1 pageVigamoxKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Toprol XLDocument2 pagesToprol XLKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- XopenexDocument1 pageXopenexKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- ValiumDocument1 pageValiumKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- PrazosinDocument1 pagePrazosinKatie McPeek0% (1)
- SenokotDocument1 pageSenokotKatie McPeek100% (1)
- RestorilDocument1 pageRestorilKatie McPeek100% (1)
- SynthroidDocument3 pagesSynthroidKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Pro To NixDocument2 pagesPro To NixKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- PrednisoloneDocument2 pagesPrednisoloneKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- ZofranDocument1 pageZofranKatie McPeek0% (1)
- Re QuipDocument1 pageRe QuipKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- LortabDocument2 pagesLortabKatie McPeek100% (1)
- Pep CidDocument1 pagePep CidKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Lo Press orDocument1 pageLo Press orKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- PhenerganDocument2 pagesPhenerganKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- MultivitaminDocument1 pageMultivitaminKatie McPeek88% (8)
- MorphineDocument2 pagesMorphineKatie McPeek100% (2)
- LevofloxacinDocument2 pagesLevofloxacinKatie McPeek100% (3)
- NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications Worksheets: Medical Patients With Acute Illness - 40 MG Once DailyDocument3 pagesNURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications Worksheets: Medical Patients With Acute Illness - 40 MG Once DailyKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- HydrochlorothiazideDocument1 pageHydrochlorothiazideKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- LevaquinDocument1 pageLevaquinKatie McPeek100% (1)
- LasixDocument1 pageLasixKatie McPeek100% (2)
- Influenza VaccineDocument1 pageInfluenza VaccineKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Azazel's Astrology (Part 2)Document51 pagesAzazel's Astrology (Part 2)John Sebastian0% (2)
- Hirsch, Edward - Poet's Choice (2007, Mariner Books) - Libgen - LiDocument227 pagesHirsch, Edward - Poet's Choice (2007, Mariner Books) - Libgen - Litrue dreamNo ratings yet
- The Role of Religion On Purchase Behavior of MusliDocument15 pagesThe Role of Religion On Purchase Behavior of MusliMd. Ariful Haque ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Private Criminal Complaint v. Eric Calhoun & Alley Kat Bar With Lancaster City Police Response To Scene - September 22, 2007Document6 pagesPrivate Criminal Complaint v. Eric Calhoun & Alley Kat Bar With Lancaster City Police Response To Scene - September 22, 2007Stan J. CaterboneNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Review Article PDFDocument10 pagesGuidelines Review Article PDFDelinaBehNo ratings yet
- GG October 2023 FinalDocument3 pagesGG October 2023 Finalapi-250691083No ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: Developments in The Built EnvironmentDocument25 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: Developments in The Built EnvironmentPutri DartamanNo ratings yet
- Currency Trading in Networth Stock Broking LTDDocument67 pagesCurrency Trading in Networth Stock Broking LTDRajesh BathulaNo ratings yet
- EconomyTOEIC RC 1 PDFDocument274 pagesEconomyTOEIC RC 1 PDFTranThuHa162No ratings yet
- Mathematical Induction (John A Bather)Document8 pagesMathematical Induction (John A Bather)NuranaNo ratings yet
- Le CorbusierDocument21 pagesLe CorbusierAbhishek GandhiNo ratings yet
- Organization Culture-Nikhil Peshawaria - Mohit WattsDocument32 pagesOrganization Culture-Nikhil Peshawaria - Mohit WattsAmit Anand KumarNo ratings yet
- Handbook 2022-2023Document120 pagesHandbook 2022-2023pranseiyarNo ratings yet
- Municipal Solid Waste ManagementDocument100 pagesMunicipal Solid Waste ManagementPremkumar T100% (1)
- Once Upon The Time in America - Google Search PDFDocument1 pageOnce Upon The Time in America - Google Search PDFDiana KarchavaNo ratings yet
- Customary Law Take Home TestDocument10 pagesCustomary Law Take Home TestGcina MaqoqaNo ratings yet
- Ucl Thesis Citation StyleDocument6 pagesUcl Thesis Citation Stylemaryburgsiouxfalls100% (1)
- INCREASE CARDIAC OUTPUT Related To Altered Heart Rate RythmDocument3 pagesINCREASE CARDIAC OUTPUT Related To Altered Heart Rate RythmSenyorita KHayeNo ratings yet
- AJ401 MDocument75 pagesAJ401 MJorgeCastillaNo ratings yet
- Family MembersDocument2 pagesFamily MembersCecilia Scarlett Arriagada SanchezNo ratings yet
- Adler Chapter01Document41 pagesAdler Chapter01Rishabh Zak100% (1)
- LAKAS NG MANGGAGAWANG MAKABAYAN (LAKAS), vs. MARCELO ENTERPRISESDocument6 pagesLAKAS NG MANGGAGAWANG MAKABAYAN (LAKAS), vs. MARCELO ENTERPRISESRudith ann QuiachonNo ratings yet
- CTI VCS CONTRL K9 - DatasheetDocument7 pagesCTI VCS CONTRL K9 - Datasheetnihadabed77No ratings yet
- ChecklistDocument2 pagesChecklistLuisNo ratings yet
- Discovery Products (BD) Ltd-ConsDocument1 pageDiscovery Products (BD) Ltd-ConsUnimart DhanmondiNo ratings yet
- Glp1ra SteatohepatitisDocument16 pagesGlp1ra Steatohepatitislakshminivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology and Disease An Interactive Journey For Health Professions 2Nd Edition Colbert Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument8 pagesAnatomy Physiology and Disease An Interactive Journey For Health Professions 2Nd Edition Colbert Test Bank Full Chapter PDFcatherine.hanson719100% (15)
- Compounding Self AssessmentDocument15 pagesCompounding Self AssessmentLara LaiNo ratings yet
- Dat AssDocument19 pagesDat AssMa k Kk60% (15)