Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Isomerism Practice
Isomerism Practice
Uploaded by
jeevan_shankarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Isomerism Practice
Isomerism Practice
Uploaded by
jeevan_shankarCopyright:
Available Formats
Isomerism Practice
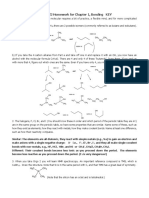
1. Explain briefly with examples: a. Diastereomerism b. Fischer projection c. Delocalisation of electrons d. Resonance energy e. Primary, secondary, tertiary and quarternary carbon atoms 2. Give examples to differentiate between the following: a. Resonance and Tautomerism b. Racemic mixture and meso compound c. Assymmetric and Dissymmetric molecules d. Functional group isomers and Tautomers e. Conformations and Configurational isomers 3. Draw all the possible isomers which bear the name dimethyl naphthalene (one of
them is
4. Draw all possible structural isomers for C6H13Cl and provide their IUPAC names.
Indicate which ones will have enantiomers. 5. In each of the following sets indicate (with explanation) whether they are same compounds or are isomers. In case they are isomers, indicate the type of isomerism
COOH H HOOC OH
CH3
CH3
COOH HO HOOC
and
OH H
H H OH
a.
b.
CH3
and
CH3
O
c. d.
OH H
and and
H3C
H2C
e.
and
6. Draw the Newman projection formula of conformers of 1-chloro propane to illustrate the terms staggered, eclipsed, gauche and anti. Indicate their relative energies. 7. Presence of assymmetric carbon atoms in an organic compound is a necessary and sufficient condition for optical activity - is this statement true or false? Explain with examples. 8. Write down the structures of the following and indicate if any one of them is optically active: (a) n-butyl bromide (b) sec-butyl chloride (c) isobutyl chloride (d) 2-buten-1-ol (e) neopentyl alcohol
You might also like
- Four CornersDocument408 pagesFour CornersBlue82% (11)
- Reading Success 3 - Answer KeyDocument5 pagesReading Success 3 - Answer Keysanti600450% (4)
- Pair and Group ExercisesDocument91 pagesPair and Group Exercisesedgaranaya13No ratings yet
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Saras Project ReportDocument89 pagesSaras Project ReportVikas Choudhary0% (2)
- Lab 7Document7 pagesLab 7Dana Georgiana CrivoiNo ratings yet
- Revised Curriculum DPT-UHS (15!09!15)Document294 pagesRevised Curriculum DPT-UHS (15!09!15)Iqra Iftikhar50% (2)
- JurisprudenceDocument7 pagesJurisprudenceamirakramarainNo ratings yet
- Guide Quiz #1Document3 pagesGuide Quiz #1Rujual BainsNo ratings yet
- CH1O3 Questions PDFDocument52 pagesCH1O3 Questions PDFPrince T MashandaNo ratings yet
- Organicchem ProbsetsDocument132 pagesOrganicchem ProbsetskimyNo ratings yet
- Carbon Compounds: Presenter: Shannon SmithDocument61 pagesCarbon Compounds: Presenter: Shannon SmithShannon SmithNo ratings yet
- 1.10203 Tutorial 1Document2 pages1.10203 Tutorial 1McAdam TULAPINo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Exam 1 (Practice) Chem 237Document3 pagesOrganic Chemistry Exam 1 (Practice) Chem 237Ngoc Minh NgoNo ratings yet
- PG Organic Unit - IDocument13 pagesPG Organic Unit - IElakkiya shankarNo ratings yet
- VSEPRActivity 06Document6 pagesVSEPRActivity 06ᜆᜑᜒᜇᜒᜐ ᜉᜀᜎᜃᜒᜓNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEM CHEMICAL FORMULA and NAMING OF COMPOUNDSDocument35 pagesGEN CHEM CHEMICAL FORMULA and NAMING OF COMPOUNDSKC KayeNo ratings yet
- I PUC Imp Chapterwise Questions - MidtermDocument3 pagesI PUC Imp Chapterwise Questions - Midtermdiyadiya060707No ratings yet
- Isomerism in Organic Chemistry: Number 93 WWW - Curriculum-Press - Co.ukDocument5 pagesIsomerism in Organic Chemistry: Number 93 WWW - Curriculum-Press - Co.ukslixsterNo ratings yet
- Naming Coordination CompoundsDocument8 pagesNaming Coordination CompoundsBLi'H'AbieeNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Workshop Handout - Topic 6 & 7 - SolutionsDocument9 pagesWeek 7 Workshop Handout - Topic 6 & 7 - SolutionsSandesh BNo ratings yet
- Alkenes - ExercisesDocument10 pagesAlkenes - ExercisessrijeetjNo ratings yet
- Fuel MoleculesDocument3 pagesFuel MoleculesPhillip CookNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument49 pagesAcids and BasesapagtemainNo ratings yet
- Class X BAT 1 - CHEM 2ND 50% SLIP TEST-IIDocument2 pagesClass X BAT 1 - CHEM 2ND 50% SLIP TEST-IIphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- CHEM 222 Chap 1 HW F21 KEYDocument3 pagesCHEM 222 Chap 1 HW F21 KEYJessicaNo ratings yet
- StereochemistryDocument19 pagesStereochemistrysophia del rosarioNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument78 pagesChemistryShabnam Fatima SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Questions For Practices: StereochemistryDocument1 pageQuestions For Practices: StereochemistryRohit NewarNo ratings yet
- E4 StereoisomersDocument6 pagesE4 StereoisomersShaun Martel BantuganNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument45 pagesAcids and Basesjordanf48922100% (1)
- CHEM 33 Extra Practice 05 AnswersDocument7 pagesCHEM 33 Extra Practice 05 Answershuang.sundi3134No ratings yet
- Chapter#1.5 Introductory Organic ChemistryyDocument6 pagesChapter#1.5 Introductory Organic ChemistryyMehreenSaeedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 318: Ir, MS, Uv, NMR SpectrosDocument17 pagesChemistry 318: Ir, MS, Uv, NMR Spectrosaamer_shahbaaz0% (4)
- Organic 1 SoruDocument14 pagesOrganic 1 SoruSudeNo ratings yet
- Topic 11 - Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument102 pagesTopic 11 - Introduction To Organic ChemistryMohamad AzzmerNo ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument30 pagesIsomerismNorsyazaEdmiraNo ratings yet
- 11chemistry - Organic chemistry-Notes&VLDocument14 pages11chemistry - Organic chemistry-Notes&VLPrashant SinghNo ratings yet
- Poc Iii QBDocument3 pagesPoc Iii QBrakshitha43dishaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Modeling by Roxie AllenDocument5 pagesMolecular Modeling by Roxie AllenPaul SchumannNo ratings yet
- CH2 FinalDocument10 pagesCH2 Finalreece ramosNo ratings yet
- T6c - Alkenes BookletDocument11 pagesT6c - Alkenes BookletRayhan MessousNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Principles of Organic ChemistryDocument74 pagesSome Basic Principles of Organic ChemistryprateekshadharaniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Question Bank (Final Exam) Class 11Document7 pagesChemistry Question Bank (Final Exam) Class 11Sunit KumarNo ratings yet
- (Part 2) Fundamental Principles of Organic Chemistry Short QuestionsDocument8 pages(Part 2) Fundamental Principles of Organic Chemistry Short QuestionsMohommod Zaman MughalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Related Exam Questions and AnswersDocument11 pagesChemistry Related Exam Questions and AnswersJoseph NyabugaNo ratings yet
- Essay Type QuestionsDocument5 pagesEssay Type QuestionspoorviNo ratings yet
- Bio Organic Chemestry 1Document25 pagesBio Organic Chemestry 1Dharmveer SharmaNo ratings yet
- WorksheetDocument3 pagesWorksheetRana AtaktürkNo ratings yet
- Checklist - Unit 1 AQA Chemistry A-LevelDocument5 pagesChecklist - Unit 1 AQA Chemistry A-LevelChalfin Aitashe MutambwaNo ratings yet
- Chem Exam 4Document30 pagesChem Exam 4TomNo ratings yet
- Chem Covalent Bond 2Document53 pagesChem Covalent Bond 2Erica Joy UngriaNo ratings yet
- Revision Booklet (5, S)Document33 pagesRevision Booklet (5, S)ashokNo ratings yet
- Tutorial # 4 - Chemical Bonding Semester1 2015-16Document2 pagesTutorial # 4 - Chemical Bonding Semester1 2015-16Tericka JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Isomerism PP 4Document12 pagesIsomerism PP 4Aderemi LyndabaeNo ratings yet
- Long Exam 1Document8 pagesLong Exam 1Allan DNo ratings yet
- Test 4Document24 pagesTest 4TomNo ratings yet
- Chemical Graph Theory and The Sherlock Holmes Principle: Alexandru T. BalabanDocument28 pagesChemical Graph Theory and The Sherlock Holmes Principle: Alexandru T. BalabanSimi ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry FHSC1124Document64 pagesOrganic Chemistry FHSC1124Hema Jothy100% (1)
- Robert M. Silverstein - Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds (2005) - 27-28Document2 pagesRobert M. Silverstein - Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds (2005) - 27-28Willmann Antonio Jiménez MoralesNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature & Isomerism (1-77)Document77 pagesNomenclature & Isomerism (1-77)deepakkr08088% (8)
- Chemistry-1st PU: 2&3 Marks Important QuestionsDocument9 pagesChemistry-1st PU: 2&3 Marks Important QuestionsDaksha SubrhamanyaNo ratings yet
- Chem Practice PaperDocument1 pageChem Practice PaperAarush SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Inter First Year Chemistry 4 Marks and 8 Marks Imp Questions.Document4 pagesInter First Year Chemistry 4 Marks and 8 Marks Imp Questions.Koneti Navanth100% (2)
- Activity - Bondi-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesActivity - Bondi-WPS OfficeMarichu VelascoNo ratings yet
- Module 1. The Chemistry of Carbon Compounds TOPIC: Structure and FormulaeDocument38 pagesModule 1. The Chemistry of Carbon Compounds TOPIC: Structure and FormulaeOrlanda EllisNo ratings yet
- Eastern: Unit Northern and IndiaDocument11 pagesEastern: Unit Northern and IndiaPratima MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- When All They Had Was LoveDocument14 pagesWhen All They Had Was LoveRahul Pinnamaneni100% (1)
- Mesopotamian ArchitectureDocument11 pagesMesopotamian ArchitectureMerylle Rose AbejeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 TestDocument10 pagesChapter 6 TestJasonNo ratings yet
- Om Unit IVDocument16 pagesOm Unit IVJagadish MaturuNo ratings yet
- Sumative Test (4TH Quarter) Science 8Document4 pagesSumative Test (4TH Quarter) Science 8Jonel Rule100% (2)
- Puritan LiteratureDocument2 pagesPuritan LiteratureAnat100% (1)
- Diagnostic Test MAPEH 10Document9 pagesDiagnostic Test MAPEH 10Oliver LauretaNo ratings yet
- Ice Breaking AIS655 OCT2020: Ir DR Mohd Badrulhisham IsmailDocument10 pagesIce Breaking AIS655 OCT2020: Ir DR Mohd Badrulhisham IsmailFirdaus YahyaNo ratings yet
- Session 2-Milk and Milk ProductDocument39 pagesSession 2-Milk and Milk ProductZul Fiqriyani SafitriNo ratings yet
- Racism & ImmigrationDocument21 pagesRacism & Immigrationchelzedecko2146No ratings yet
- Escaler Vs CADocument4 pagesEscaler Vs CAjessapuerinNo ratings yet
- Core - Earth and Life Science Learning GuideDocument3 pagesCore - Earth and Life Science Learning GuideJerico Karlos Logarta CortesNo ratings yet
- Cabri GeometryDocument12 pagesCabri Geometrymazni08No ratings yet
- Isolation, Alkaline Hydrolysis and Neutralization of Casein From Non-Fat Dry MilkDocument6 pagesIsolation, Alkaline Hydrolysis and Neutralization of Casein From Non-Fat Dry MilkJacqueline ToNo ratings yet
- 10 Hadiths On Self-Help PDFDocument28 pages10 Hadiths On Self-Help PDFStudij2011100% (1)
- Assignment 2 (ECN 511)Document5 pagesAssignment 2 (ECN 511)Galina FateevaNo ratings yet
- This Paper Addresses Three Leadership Challenges Associated With Effective Management of The PolytechnicDocument11 pagesThis Paper Addresses Three Leadership Challenges Associated With Effective Management of The PolytechnicEESUOLANo ratings yet
- Application of Epidemiology in CHNDocument72 pagesApplication of Epidemiology in CHNAnon Nimos100% (1)
- Fever - PilotDocument4 pagesFever - PilotAlex MurchisonNo ratings yet
- Animal Behavior: BiologyDocument32 pagesAnimal Behavior: BiologySamNo ratings yet
- Estino, Et Al V People PDFDocument14 pagesEstino, Et Al V People PDFrmelizagaNo ratings yet
- 914 GROUP A (Part 1 - Cinderella)Document5 pages914 GROUP A (Part 1 - Cinderella)Esther Joy HugoNo ratings yet
- Native Americans - Artifacts IIIDocument38 pagesNative Americans - Artifacts IIIThe 18th Century Material Culture Resource Center100% (2)