Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Metals and Nonmetals
Metals and Nonmetals
Uploaded by
Angelica JuneOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Metals and Nonmetals
Metals and Nonmetals
Uploaded by
Angelica JuneCopyright:
Available Formats
METALS and NONMETALS
( Act. # 2.3 )
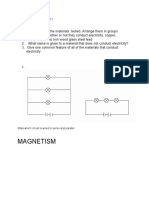
Objectives: To know what are the metals and nonmetals Materials: copper wire, tin, aluminum, sulfur crystals, iodine crystals, hammer, wooden block,
thumb tacks, two batteries, electric bulb, electrical wire (1 m)
Procedure:
A. Electrical Conductivity 1. Set up the conductivity apparatus as shown in Figure 4.10 2. Separately test the conductivity of the copper wire, tin, aluminum, sulfur crystals and iodine crystals by testing each material using the conductivity apparatus. If the bulb connected to the apparatus lights up, the material is a conductor. 3. Record your observations in Data Table 4.4 B. Malleability, Brittleness, and Ductility Place each of the copper wire, tin, aluminum, sulfur crystals, and iodine crystals on a separate piece of paper. Hammer each one at a time. Which is malleable? ductile? brittle? Record your observations in Data Table 4.4 Data Table 4.4 PROPERTY (Malleable, Ductile, Brittle) ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY CLASSIFICATION (Metal or Nonmetal)
SUBSTANCE
Copper Tin Aluminum Sulfur Iodine
Questions
Which elements do you consider metals? Which are nonmetals? Explain why.
Conclusion
You might also like
- Electrical Properties of MaterialsDocument7 pagesElectrical Properties of MaterialsMahrukh JavedNo ratings yet
- Science 5 DLP 32 - Classifying Materials Into Conductors and InsulatorsDocument9 pagesScience 5 DLP 32 - Classifying Materials Into Conductors and InsulatorsMary Jane Elaba100% (1)
- Exp7 Metal CorrosionDocument21 pagesExp7 Metal CorrosionArisha Ruzalani100% (1)
- LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 8: Metals Nonmetals and MetalloidsDocument4 pagesLESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 8: Metals Nonmetals and Metalloidsrigie.divinagraciaNo ratings yet
- The Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred ExperimentsFrom EverandThe Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred ExperimentsNo ratings yet
- The Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred Experiments Performed with Simple, Home-made ApparatusFrom EverandThe Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred Experiments Performed with Simple, Home-made ApparatusNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Conducting Materials NotesDocument21 pagesUNIT-1 Conducting Materials NotesAdarsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2Document8 pagesLab Report 2Turan GuliyevNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 9Document3 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 9ChloeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1A:: Determining The Voltage of The Voltaic CellDocument5 pagesExperiment 1A:: Determining The Voltage of The Voltaic Cellhusna azizanNo ratings yet
- METALSDocument10 pagesMETALSUKAEGBU NADIA NMACHINo ratings yet
- Basic Classification of Engineering MaterialsDocument34 pagesBasic Classification of Engineering MaterialsDiana .0119No ratings yet
- METALS AND NON - METALS STD 7Document9 pagesMETALS AND NON - METALS STD 7Sanhitha RameshNo ratings yet
- Hesc104 PDFDocument12 pagesHesc104 PDFÁđîtýa ĶumaŕNo ratings yet
- BAHAN KULIAH MATERIAL ELEKTROTEKNIK LandscapeDocument54 pagesBAHAN KULIAH MATERIAL ELEKTROTEKNIK LandscapeFrissa Aninditaalan08No ratings yet
- QTR 1 Module 5 Metals & NonmetalsDocument12 pagesQTR 1 Module 5 Metals & NonmetalsNick BantoloNo ratings yet
- Engineering MaterialsDocument9 pagesEngineering MaterialsJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Good Conductors of Heat and Electricity: Lesson 2Document14 pagesCharacteristics of Good Conductors of Heat and Electricity: Lesson 2Teacher JoanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Conductors and InsulatorsDocument17 pagesElectrical Conductors and InsulatorsnlalamNo ratings yet
- Environment Degradation of Materials - 1Document27 pagesEnvironment Degradation of Materials - 1NSHIMIYIMANA Jean d'AmourNo ratings yet
- Conductors and InsulatorsDocument17 pagesConductors and InsulatorsRichard PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Measuringcellpotentiallab BekahkatieoliDocument8 pagesMeasuringcellpotentiallab Bekahkatieoliapi-222447568No ratings yet
- Electroplating of Metals and Its Rate of Rusting Between Electroplated Nail and A Normal Iron NailDocument13 pagesElectroplating of Metals and Its Rate of Rusting Between Electroplated Nail and A Normal Iron NailWILSON LING XING YONG MoeNo ratings yet
- Spark Test of Metals: B B A ADocument4 pagesSpark Test of Metals: B B A ALovely NievesNo ratings yet
- Redox Potential MeasurementsDocument17 pagesRedox Potential Measurementsmosoil100% (1)
- Chapter 1 EemDocument5 pagesChapter 1 EemTanishq MudaliarNo ratings yet
- Electrical PropertiesDocument35 pagesElectrical Propertiesjacklog600No ratings yet
- Sci 5 Q23 WK 2Document24 pagesSci 5 Q23 WK 2ROVELLA AGOHOB100% (1)
- FINAL DEMO - CathDocument9 pagesFINAL DEMO - CathCatherine Pagaling Lucas67% (3)
- Chemicals Effect of CurrentDocument2 pagesChemicals Effect of CurrentRanveer RathiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Grade 11: Topic: Electric Current. Conductors and InsulatorsDocument14 pagesChemistry Grade 11: Topic: Electric Current. Conductors and Insulators7Timothy hnNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Ta Electroplating TembagaDocument7 pagesJurnal Ta Electroplating TembagaRaihan HafizNo ratings yet
- Procesos de Manufactura Materials Report Equipo 1Document17 pagesProcesos de Manufactura Materials Report Equipo 1Eduardo SotoNo ratings yet
- Dielectric EffectDocument27 pagesDielectric Effectsania bibiNo ratings yet
- Playful Colorful Kids Science Class PresentationDocument13 pagesPlayful Colorful Kids Science Class Presentationsamantha2012lopezNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Magnetic MaterialDocument14 pagesElectrical and Magnetic MaterialVishwajeet DhanwadeNo ratings yet
- Name: Pilas, Yory Limar G. Date: September 10, 2021 Course and Yr: 1B BSABEDocument4 pagesName: Pilas, Yory Limar G. Date: September 10, 2021 Course and Yr: 1B BSABEZheanjee CotdiNo ratings yet
- I Will Show You The Diagram TomorrowDocument1 pageI Will Show You The Diagram TomorrowHun TerNo ratings yet
- Presented by SamnSarDocument18 pagesPresented by SamnSarsamantha2012lopezNo ratings yet
- L 1 - Mse628a - 31 7 19Document44 pagesL 1 - Mse628a - 31 7 19Dhanishtha SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture8-Environmental Degradation and Material SelectionDocument29 pagesLecture8-Environmental Degradation and Material SelectionRUGERO KeslyneNo ratings yet
- Chemical Effect and Electric CurrentDocument3 pagesChemical Effect and Electric CurrentRANJIT KUMAR SHAHNo ratings yet
- Science Notes - Lession-3 - Metals & Non-Metals (Chemistry)Document30 pagesScience Notes - Lession-3 - Metals & Non-Metals (Chemistry)Himanshi guptaNo ratings yet
- Study of Electrical Properties of Iron (Iii) Oxide (Fe2o3) Nanopowder by Impedance SpectrosDocument7 pagesStudy of Electrical Properties of Iron (Iii) Oxide (Fe2o3) Nanopowder by Impedance SpectrosIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- A03 - MENDOZA, Alexis L.Document3 pagesA03 - MENDOZA, Alexis L.Alexis MendozaNo ratings yet
- Testing The Conductivity of Various Everyday Objects Can Be A Fun and Educational ExperimentDocument1 pageTesting The Conductivity of Various Everyday Objects Can Be A Fun and Educational ExperimentLAM ENG HO G11L-14No ratings yet
- Unit 8 Metals 1Document11 pagesUnit 8 Metals 1Elaiza Angelene NacarioNo ratings yet
- Case Study For FailureDocument16 pagesCase Study For FailureSaranshChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Magnetism IntroductionDocument4 pagesMagnetism IntroductionKaylon NelsonNo ratings yet
- Amta5 6 Applying Shielded Metal Arc Welding Smaw TechniquesDocument132 pagesAmta5 6 Applying Shielded Metal Arc Welding Smaw TechniquesSaurav Kumaar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Conducting MaterialDocument8 pagesConducting MaterialSaroj KumarNo ratings yet
- AlloysDocument4 pagesAlloysM.zuhair asifNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Metals 8.3Document9 pagesChemistry Notes Metals 8.3Alan DoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 6.1Document1 pageWorksheet 6.1annnyyyaaaaaNo ratings yet
- 7th Chemistry, L-6, Metals and Non-MetalsDocument4 pages7th Chemistry, L-6, Metals and Non-MetalsDEEPAK JAINNo ratings yet
- ResistanceDocument2 pagesResistancelyca apostolNo ratings yet
- Electrical MaterialsDocument2 pagesElectrical MaterialsDarshan Thakar0% (1)
- Discussion Points: Metals Properties ObjectDocument9 pagesDiscussion Points: Metals Properties ObjectSumithra KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Metals and AlloysDocument9 pagesGroup 1 - Metals and AlloysJohn Jim Paul DunesNo ratings yet
- Unit 2B L2 Applied ScienceDocument15 pagesUnit 2B L2 Applied ScienceTracy JonesNo ratings yet