Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Enzymes
Enzymes
Uploaded by
Karim El NefeidiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Enzymes
Enzymes
Uploaded by
Karim El NefeidiCopyright:
Available Formats
Enzymes Catalysts Catalysts are chemicals that speed up chemical reactions without being used up or changed in the process.
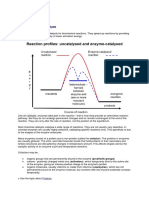
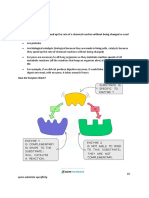
Many of the catalysts used by chemists are inorganic substances such as MnO and iron filings. Such catalysts are very general and catalyse many different reactions. Enzymes: Enzymes are organic catalysts made up protein. They are much more specific, with most enzymes only catalyzing one reaction. This means that the organism has much more control over the reactions taking place, because a general catalyst would affect many reactions that are not required or harmful. Lock and Key Model: Each enzyme has an area know as the active site. The shape and chemistry of this part of the enzyme are such that only one particular substrate can attach. Once, attached there will be a slight change to the shape of the enzyme-substrate complex that results in the reaction occurring (usually breaking down or building up molecules). Once the reaction occurs the products can no longer remain attached, so separate away leaving the active site free to attach to another substrate molecule. Effect of Temperature on Enzymes: All chemical reactions occur more quickly at higher temperatures. This is because particles move faster and make more collisions with sufficient energy for a reaction to occur. This is the same with enzyme-controlled reactions, because faster moving particles collide more with the active sites. However, at a higher temperature (much above 40 C) the enzyme vibrates so much that it starts to lose its shape; we can say it has denatured. The active site is no longer functions correctly as a catalyst. The change is usually permanent, so cooling the enzyme will not repair it. Effect of pH on enzymes Different enzymes work best at different pH, with each having an optimum. If the pH is too far from the optimum, the enzyme will work less efficiently and can become permanently denatured. Amylase works best at a pH of about 8, while pepsin (a protease) works best at about 2 or 3.
You might also like
- Enzyme NotesDocument4 pagesEnzyme NotesMaulana Makhmud100% (2)
- Module 11: EnzymesDocument3 pagesModule 11: EnzymesMariam EskandariNo ratings yet
- Sameer Ahmed Group: GM-01: Function and StructureDocument5 pagesSameer Ahmed Group: GM-01: Function and StructureSameer ButtNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument9 pagesEnzymes42h47n5zvrNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument2 pagesEnzymesbhardwajsaanvi004No ratings yet
- Enzyme StructureDocument17 pagesEnzyme Structureام احمدNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument23 pagesEnzymessamskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- What Are Enzymes?: E E E EDocument15 pagesWhat Are Enzymes?: E E E EFarhana MuradNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Biology Lecture Prepared By: Waleed Zahoor Team Roshni Step-Up PakistanDocument11 pagesEnzymes: Biology Lecture Prepared By: Waleed Zahoor Team Roshni Step-Up PakistanRabia KhalilNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument7 pagesEnzymesMahin TayyabNo ratings yet
- Lesson #8 - EnzymesDocument29 pagesLesson #8 - EnzymesMaya AwadNo ratings yet
- Chapter EnzymesDocument2 pagesChapter EnzymesJaved SohawonNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument22 pagesEnzymesRohan PaneruNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument10 pagesEnzymesSanchit Dhyani100% (1)
- EnzymesDocument40 pagesEnzymesVeronica HanyNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument14 pagesEnzymesshivani.shahNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Function and StructureDocument5 pagesEnzymes: Function and Structuretiyf mojaleedNo ratings yet
- Bio Sem 1Document123 pagesBio Sem 1HALFAH BT HASSANNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Biology Human NutritionDocument7 pagesClass 8 Biology Human NutritionMihika SpamNo ratings yet
- Enzymes PDFDocument4 pagesEnzymes PDFrasha nada100% (1)
- 4-C1.1 Enzymes and MetabolismDocument42 pages4-C1.1 Enzymes and Metabolismmakaya02No ratings yet
- Enzyme NotesDocument4 pagesEnzyme NotesPreethaNo ratings yet
- EnzymeDocument31 pagesEnzymemiriam harriottNo ratings yet
- Genes & Inheritance SeriesDocument58 pagesGenes & Inheritance SeriesKim HoangNo ratings yet
- Enzymatic Test Reaction Biochem Report Group 12Document7 pagesEnzymatic Test Reaction Biochem Report Group 12almira garciaNo ratings yet
- Properties of EnzymesDocument6 pagesProperties of EnzymesNida JavedNo ratings yet
- EnzimasDocument19 pagesEnzimasLuis Alfonso Paez FuentesNo ratings yet
- Ch-5 EnzymesDocument4 pagesCh-5 EnzymesMahamudul HassanNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument12 pagesEnzymesAsima NaqviNo ratings yet
- Enzyme ChemistryDocument9 pagesEnzyme ChemistryVictor OmoloNo ratings yet
- Enzymes - NotesDocument3 pagesEnzymes - Noteshiba.alkubaisyNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Chapter # 1 EnzymesUsman AhmadNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument3 pagesEnzymessashi bNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument4 pagesEnzymesii15021No ratings yet
- Enzymes - Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesEnzymes - Lecture NotesssekitoolekohakimNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Enzyme LabDocument25 pagesGrade 12 Enzyme LabKrystalLovejoyNo ratings yet
- Definitions:: Pakistan International School Jeddah (Es) Biology NotesDocument9 pagesDefinitions:: Pakistan International School Jeddah (Es) Biology NotesMaira. BalsaNo ratings yet
- Bio-Ch 5-EnzymesDocument6 pagesBio-Ch 5-EnzymesHassan RiazNo ratings yet
- Enzyme ChemistryDocument40 pagesEnzyme Chemistryakshif KhanNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Form 3Document4 pagesEnzymes Form 3Ralph MuchingamiNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology (Chapter 5)Document2 pagesIGCSE Biology (Chapter 5)SpablaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Chapter 4 EnzymesDocument18 pagesGrade 8 Chapter 4 EnzymesRaeed FarshidNo ratings yet
- LMRN Molecules of LifeDocument2 pagesLMRN Molecules of LifeVic AuNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument6 pagesEnzymesSarah Farhah2000100% (1)
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 4.5 EnzymesDocument11 pagesBiology Form 4 Chapter 4.5 EnzymesSatpal SinghNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Lab Discussions: Lab #1: Effect of Temperature On EnzymesDocument5 pagesEnzyme Lab Discussions: Lab #1: Effect of Temperature On EnzymesKIARA B SAMUELNo ratings yet
- CH 2306 Lecture Notes Part 2 Enzymology-1Document5 pagesCH 2306 Lecture Notes Part 2 Enzymology-1owegibrian479No ratings yet
- Enzymes - Doc Version 1Document7 pagesEnzymes - Doc Version 1LALITH SAI KNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Bio IgcseDocument7 pagesChap 5 Bio Igcseananya.arumugarajanNo ratings yet
- How Enzymes Work What Are Enzymes?: en Zyme Substrate SpecificityDocument12 pagesHow Enzymes Work What Are Enzymes?: en Zyme Substrate SpecificityRahil BhavanNo ratings yet
- Enzymes (Bio Chem) : Mariano Marcos State University College of Teacher Education Laoag CityDocument34 pagesEnzymes (Bio Chem) : Mariano Marcos State University College of Teacher Education Laoag CityJared TabangcuraNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument5 pagesEnzymeseyosiyas tekleweyinNo ratings yet
- Enzymes 1Document6 pagesEnzymes 1zarszNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 EnzymesDocument23 pagesChapter 16 Enzymesmuhammad.melbNo ratings yet
- Notes #5 - EnzymesKey CleanDocument10 pagesNotes #5 - EnzymesKey CleanLanz MoenNo ratings yet
- 5 - EnzymesDocument5 pages5 - EnzymesIce CoffeeNo ratings yet
- Igcse Biology: EnzymeDocument20 pagesIgcse Biology: EnzymeAliya ShukriNo ratings yet
- Enzyme and Its Substrate and The Formation of A ProductDocument4 pagesEnzyme and Its Substrate and The Formation of A ProductMehul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes:: "Helper" Protein MoleculesDocument26 pagesEnzymes:: "Helper" Protein MoleculesAyesha JamilNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)