Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Uploaded by
L1verp00lOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Uploaded by
L1verp00lCopyright:
Available Formats
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, a protocol for assigning dynamic IP addresses to devices on a network.
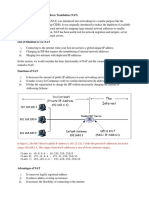
With dynamic addressing, a device can have a different IP address every time it connects to the network. In some systems, the device's IP address can even change while it is still connected. DHCP also supports a mix of static and dynamic IP addresses. Dynamic addressing simplifies network administration because the software keeps track of IP addresses rather than requiring an administrator to manage the task. This means that a new computer can be added to a network without the hassle of manually assigning it a unique IP address. Many ISPs use dynamic IP addressing for dial-up users. DNS The domain name system (DNS) is the way that Internet domain names are located and translated into Internet Protocol addresses. A domain name is a meaningful and easy-toremember "handle" for an Internet address. Because maintaining a central list of domain name/IP address correspondences would be impractical, the lists of domain names and IP addresses are distributed throughout the Internet in a hierarchy of authority. There is probably a DNS server within close A. WINS stands for Windows Internet Name Service. WINS is a NetBIOS Name Server that registers your NetBIOS names and resolves into IP addresses. If you're using NetBIOS over TCP/IP you will need to have WINS running so that each can find out the correct IP address of the other to communicate.
You might also like
- Technical Interview Questions Active Directory and Networking - Part IDocument90 pagesTechnical Interview Questions Active Directory and Networking - Part Iajitskhot108100% (29)
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)Document4 pagesDHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)Qasim CheemaNo ratings yet
- Nomi Lab AssignmentDocument3 pagesNomi Lab AssignmentQasim CheemaNo ratings yet
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) SERVERDocument3 pagesDHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) SERVERnktnikki258No ratings yet
- The Domain Name SystemDocument19 pagesThe Domain Name SystemJordan SpringerNo ratings yet
- Lab Handout 3 DHCP DNS HTTPDocument3 pagesLab Handout 3 DHCP DNS HTTPapi-3739389No ratings yet
- Computer Networks Lab (CL307) Lab Session 06: National University of Computer & Emerging ScienceDocument15 pagesComputer Networks Lab (CL307) Lab Session 06: National University of Computer & Emerging Sciencesnooker masterNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) : DHCP Server Assigns IP Addresses To Multiple ClientsDocument2 pagesDynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) : DHCP Server Assigns IP Addresses To Multiple ClientssrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On DHCP, DNS and APIPADocument5 pagesResearch Paper On DHCP, DNS and APIPAEr Sailesh Paudel100% (1)
- Baheilu SeminaerDocument20 pagesBaheilu SeminaerawokebaheiluNo ratings yet
- Interview QuestionsDocument10 pagesInterview QuestionsshankarguptamNo ratings yet
- IP Address and DNSDocument11 pagesIP Address and DNSAtiqah Rais100% (1)
- DHCP, Telnet, SSHDocument11 pagesDHCP, Telnet, SSHAditya GhuleNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol - DHCP: Feature Overview and Configuration GuideDocument20 pagesDynamic Host Configuration Protocol - DHCP: Feature Overview and Configuration GuideHào VươngNo ratings yet
- 21BCE9257 - CN - Lab Assignment 4Document8 pages21BCE9257 - CN - Lab Assignment 4krishnakishore9347No ratings yet
- Network Address Translation: Presented by Varsha HondeDocument22 pagesNetwork Address Translation: Presented by Varsha HondeTú HoàngNo ratings yet
- 4.7 - IP Addressing ServicesDocument4 pages4.7 - IP Addressing Serviceskrs4kesharaNo ratings yet
- Lab Web TechDocument11 pagesLab Web TechAnonymous RANRem9INo ratings yet
- Unit-1.2 Internet and World Wide WebDocument40 pagesUnit-1.2 Internet and World Wide Webco22352No ratings yet
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol PDFDocument3 pagesDynamic Host Configuration Protocol PDFSaeed AhmadNo ratings yet
- DHCP Feature Overview GuideDocument19 pagesDHCP Feature Overview GuidestianiNo ratings yet
- What Is DHCPDocument7 pagesWhat Is DHCPTeenuJosephNo ratings yet
- DNS, WLC, DHCP, EtcDocument11 pagesDNS, WLC, DHCP, Etcing.daniel.velasquez.g.25No ratings yet
- Briefly Describe What Are Ip Addresses: Cidr Ipv6Document4 pagesBriefly Describe What Are Ip Addresses: Cidr Ipv6Randall CastilloNo ratings yet
- DHCP Feature Overview GuideDocument33 pagesDHCP Feature Overview GuideRajesh BeheraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 CiscoDocument18 pagesChapter 7 CiscoOnakisNo ratings yet
- NetworkDocument4 pagesNetworkArjun SinghNo ratings yet
- DHCP and NAT - Knowledge BaseDocument6 pagesDHCP and NAT - Knowledge BaseHasib Hamidul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Mugiraneza: Window Server AdministratorDocument8 pagesMugiraneza: Window Server AdministratorMugïrañeza JøšhűåNo ratings yet
- 14.3 Networking Features TerminologyDocument9 pages14.3 Networking Features TerminologyPavel VarabyouNo ratings yet
- System and Network Administration AssignmentDocument15 pagesSystem and Network Administration AssignmentShelema KasayeNo ratings yet
- Web Tech (Concept of Ip Address and DNS)Document12 pagesWeb Tech (Concept of Ip Address and DNS)khafaei krikNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument48 pagesUntitledSữa Chua Nếp CẩmNo ratings yet
- Systems Administration and Management Coursework: Group B (Members)Document44 pagesSystems Administration and Management Coursework: Group B (Members)Wekesa DerrickNo ratings yet
- Ip Address and DNSDocument10 pagesIp Address and DNSNor AthirahNo ratings yet
- Client-Server Network: Local Area Networks (Lans) FTP DnsDocument8 pagesClient-Server Network: Local Area Networks (Lans) FTP DnsPopa AlinNo ratings yet
- Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP)Document4 pagesReverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP)Himanshu PatelNo ratings yet
- 1.1 What Is A Computer Network?Document9 pages1.1 What Is A Computer Network?Mmichael123456789No ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument11 pagesLab Reporthr913642No ratings yet
- 3.1 What Is DHCPDocument1 page3.1 What Is DHCPcloud scapeNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Presentation: Name: Kunal Sharma Reg No.: RA1711008010006 Dept.: IT Year: III Semester: VDocument18 pagesIndustrial Training Presentation: Name: Kunal Sharma Reg No.: RA1711008010006 Dept.: IT Year: III Semester: VKunal Sharma100% (1)
- Interview QuestionsDocument85 pagesInterview Questionssimha23No ratings yet
- Understanding TCP/IPDocument9 pagesUnderstanding TCP/IPsputnik_2012No ratings yet
- Tle (Ict) Narra: Mrs. Analyn E. Llaban Second GroupDocument5 pagesTle (Ict) Narra: Mrs. Analyn E. Llaban Second GroupMary Bianca ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Internet Protocol: DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Is A Protocol Used by NetworkedDocument3 pagesInternet Protocol: DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Is A Protocol Used by NetworkedsamirNo ratings yet
- Dns DHCPDocument8 pagesDns DHCPJan DivdNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 CCNDocument7 pagesLab 4 CCNAreeba NoorNo ratings yet
- Dns Dos Attack Protection System Imlpementation Using VerilogDocument3 pagesDns Dos Attack Protection System Imlpementation Using Verilograsheed72No ratings yet
- W2k Net - Chapter1 - Designing A Windows 2000 NetworkDocument19 pagesW2k Net - Chapter1 - Designing A Windows 2000 NetworktheplagueisbackNo ratings yet
- 242641how To Get Hired in The Softether IndustryDocument2 pages242641how To Get Hired in The Softether IndustryvoadilixthNo ratings yet
- DNS Delegations and DHCPDocument12 pagesDNS Delegations and DHCPmanjeet chauhanNo ratings yet
- Modules 9 - 12 Group Exam Answers PART 2Document2 pagesModules 9 - 12 Group Exam Answers PART 2Jhonna Gail EscuadroNo ratings yet
- TCP-IP Networking BasicsDocument73 pagesTCP-IP Networking Basicssaihunter100% (1)
- Introduction To Network Address Translation (NAT)Document4 pagesIntroduction To Network Address Translation (NAT)Firemandeheavenly InamenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - Network SystemsDocument22 pagesLecture 10 - Network Systemsarnold.7800x3dNo ratings yet
- Linux & Windows Short DefinitionsDocument8 pagesLinux & Windows Short DefinitionsMohammad AzamNo ratings yet
- Lmhost WinsDocument1 pageLmhost WinsGioberty TineoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, Email Verification, Header Analysis, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some SMTP Testing, Email Verification, Header Analysis, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WP Email Tools: Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WP Email Tools: Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsNo ratings yet