Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NabillaJasmine 59081002013
NabillaJasmine 59081002013
Uploaded by
Nabilla JasmineOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NabillaJasmine 59081002013
NabillaJasmine 59081002013
Uploaded by
Nabilla JasmineCopyright:
Available Formats
Nabilla Jasmine 59081002013
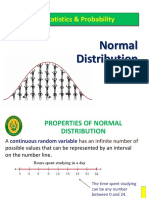
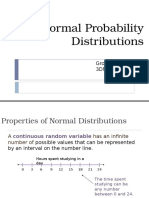
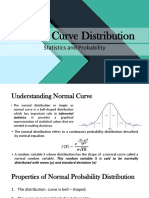
The Normal Distributions A density curve is a curve that Is always on or above the horizontal axis, and Has area exactly 1 underneath it
A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. The area under the curve and above any range of values is the proportion of all observations that fall in the range. There are many types of density curves. We are going to focus on a family of curves called Normal curves. The mean and standard deviation computed from actual observations (data) are denoted by and s, respectively. The mean and standard deviation of the distribution represented by the density curve are denoted by (mu) and (sigma), respectively. Normal curves are: bell-shaped not too steep, not too fat defined means & standard deviations
The Normal Distribution: Mean defines the center of the curve Standard deviation defines the spread Notation is N(,). Symmetrical around Infections points (change in slope, blue arrows) at
Standard Normal (Z) Distribution: The Standard Normal distribution has mean 0 and standard deviation 1 We call this a Z distribution: Z~N(0,1) Any Normal variable x can be turned into a Z variable (standardized) by subtracting and dividing by :
z
Standardized Scores:
How many standard deviations is 68 from on X~N(70,2.8)? z = (x ) / = (68 - 70) / 2.8 = -0.71 The value 68 is 0.71 standard deviations below the mean 70
The standard normal table is table A. Table A is a table of areas under the standard normal curve. The table entry for each value z is the area under the curve to the left of z
You might also like
- Chapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data: Section 2.2Document17 pagesChapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data: Section 2.2张书0% (1)
- Normal DistributionDocument22 pagesNormal Distributionaamirali31No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7Riezel PepitoNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution Part 1Document26 pagesNormal Distribution Part 1Da YongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7Riezel PepitoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03-Normal DistributionsDocument28 pagesChapter 03-Normal DistributionsamandaluvsanimalsNo ratings yet
- Normal Random VariableDocument8 pagesNormal Random VariableLoraine Buen FranciscoNo ratings yet
- NormalDistribution ExamplesDocument45 pagesNormalDistribution ExamplesDeniz ArasNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument32 pagesNormal Distributionmariannchello123No ratings yet
- Week11-Normal Distribution (Ekstra-Week)Document59 pagesWeek11-Normal Distribution (Ekstra-Week)düşünennurNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Normal Distribution PDFDocument24 pages2.3 Normal Distribution PDFChelsea RoqueNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribn TheoryDocument16 pagesNormal Distribn TheoryGuru Ballur0% (1)
- 5 BMGT 220 Normal DistributionDocument10 pages5 BMGT 220 Normal DistributionPamela Chimwani100% (1)
- MS104 March 2 DiscussionDocument36 pagesMS104 March 2 DiscussionEminNo ratings yet
- MASTAT - Ch5 Continuous Distributions - 022518Document7 pagesMASTAT - Ch5 Continuous Distributions - 022518ventus5thNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Report (1) (Autosaved)Document51 pagesGroup 1 Report (1) (Autosaved)Rheanna Nogales BanguilanNo ratings yet
- Ap Stats Chapter 2 Glossary of Important Terms Tps4eDocument2 pagesAp Stats Chapter 2 Glossary of Important Terms Tps4eapi-295686071No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Normal Distribution Z-ScoresDocument33 pagesCHAPTER 4 Normal Distribution Z-Scoresapi-3729261100% (7)
- 2.3 Modelo NormalDocument17 pages2.3 Modelo NormalJESUS RUIZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06Document70 pagesChapter 06Angelo Mikko RosarioNo ratings yet
- Definition:: ParametersDocument3 pagesDefinition:: ParametersEmman TariqNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution & Z-ScoresDocument82 pagesNormal Distribution & Z-Scoresgela tinNo ratings yet
- Group 7Document27 pagesGroup 7HayaNo ratings yet
- Eco 2Document31 pagesEco 2Nebiyu WoldesenbetNo ratings yet
- BS Lect 13Document34 pagesBS Lect 13jasonnumahnalkelNo ratings yet
- CH 6 - CH 8 (Notes)Document42 pagesCH 6 - CH 8 (Notes)Chilombo KelvinNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution - Class1Document29 pagesNormal Distribution - Class1Sameer DohadwallaNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument59 pagesNormal DistributionAkash Katariya100% (1)
- Normal DistributionDocument16 pagesNormal DistributionGilagidkidNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument27 pagesStatisticsBernice Mikaela IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document34 pagesLecture 6Luna eukharisNo ratings yet
- Continuous Probability DistributionDocument60 pagesContinuous Probability DistributionJethro MiñanoNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Standard Normal DistributionsDocument7 pages3.2 Standard Normal DistributionsTheory SummersNo ratings yet
- C - Normal DistributionDocument196 pagesC - Normal DistributionRi chalNo ratings yet
- L3 BMGT 220 Normal Distribution-1Document37 pagesL3 BMGT 220 Normal Distribution-1mwendaflaviushilelmutembeiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 (Normal Probability Distribution)Document39 pagesChapter 5 (Normal Probability Distribution)abcd1234ff44No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 The Normal DistributionDocument12 pagesChapter 4 The Normal Distributionleonessa jorban cortesNo ratings yet
- Chapter Ii. Lesson 1 The Normal Dist. TableDocument3 pagesChapter Ii. Lesson 1 The Normal Dist. Tablealiciatomada123No ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument24 pagesNormal DistributionPam FajardoNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document54 pagesModule 3Alrac Anacta MalaitNo ratings yet
- Chap4 ElsyDocument60 pagesChap4 ElsyKamil IbraNo ratings yet
- 04 NormalDistributionDocument43 pages04 NormalDistributionShane Olen GonzalesNo ratings yet
- The Normal Distribution: ConceptsDocument17 pagesThe Normal Distribution: ConceptsJay Ian GeronaNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument3 pagesNormal DistributionSangeetha SumamNo ratings yet
- Normal Curve Distribution: Statistics and ProbabilityDocument9 pagesNormal Curve Distribution: Statistics and ProbabilityJet Carillo ToledoNo ratings yet
- Normal Probability Curve: By: Keerthi Samuel.K, Lecturer Vijay Marie College of NursingDocument22 pagesNormal Probability Curve: By: Keerthi Samuel.K, Lecturer Vijay Marie College of NursingSree LathaNo ratings yet
- Normal Curve Distribution IIIf-2-3 Chapter 2 Lesson 1Document20 pagesNormal Curve Distribution IIIf-2-3 Chapter 2 Lesson 1CHARLYN JOY SUMALINOGNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution in Mathematical Statistics and FoundationDocument7 pagesNormal Distribution in Mathematical Statistics and Foundationswamylns707No ratings yet
- 02.4 Probability - CPDDocument23 pages02.4 Probability - CPDRomel DecenillaNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution:: - Probability - Characteristics and Application of Normal Probability Curve - Sampling ErrorDocument21 pagesNormal Distribution:: - Probability - Characteristics and Application of Normal Probability Curve - Sampling ErrorsanthiyasandyNo ratings yet
- Normal and Standard Normal DistributionDocument18 pagesNormal and Standard Normal DistributionJDR JDRNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument16 pagesNormal DistributionimtiazNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document61 pagesModule 5HarijaNo ratings yet
- Univariate StatisticsDocument7 pagesUnivariate StatisticsDebmalya DuttaNo ratings yet
- Topic20 8p7 GalvinDocument53 pagesTopic20 8p7 GalvinJude SantosNo ratings yet
- StatsDocument3 pagesStatsdream is my husbandNo ratings yet
- (Lecture 5) Normal DistributionDocument55 pages(Lecture 5) Normal DistributionSabaNo ratings yet
- Standard Normal Distribution and Normal Distribution TableDocument10 pagesStandard Normal Distribution and Normal Distribution TableHanna GalatiNo ratings yet
- The Standard Normal Distribution 2Document50 pagesThe Standard Normal Distribution 2CTD QUIAMCO, JADE MAR PALALON FLIGHT DRILLERNo ratings yet
- Standard-Slope Integration: A New Approach to Numerical IntegrationFrom EverandStandard-Slope Integration: A New Approach to Numerical IntegrationNo ratings yet