Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physical Const
Physical Const
Uploaded by
ahmetselimdurnaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- IB Physics Tsokos Solution Version 6 EditionDocument9 pagesIB Physics Tsokos Solution Version 6 Editionsatellite40611030% (10)
- Reviewer For Chemical Engineering Licensure Examination 3 Edition Solutions ManualDocument56 pagesReviewer For Chemical Engineering Licensure Examination 3 Edition Solutions ManualSherry Anne Ynciong Panganiban100% (4)
- Fundamental Physical Constants - Physico-Chemical ConstantsDocument1 pageFundamental Physical Constants - Physico-Chemical ConstantsmexcesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 and 3Document50 pagesChapter 2 and 3Christian Peterson75% (8)
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- Constants CombinedDocument5 pagesConstants CombinedAlejandro Matías AstorgaNo ratings yet
- ConstantsDocument2 pagesConstantssolutionerNo ratings yet
- AppendixI PDFDocument2 pagesAppendixI PDFexaguamhNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Conversion Tables For Units: Chapter 1 - 1Document9 pages1.6 Conversion Tables For Units: Chapter 1 - 1Yamel MorenoNo ratings yet
- Physical Constants PDFDocument4 pagesPhysical Constants PDFOscar JiménezNo ratings yet
- Complementary Notes: Prof. Dr. Şenol BAŞKAYADocument28 pagesComplementary Notes: Prof. Dr. Şenol BAŞKAYABarışPulatNo ratings yet
- Basic Unit ConvertionDocument30 pagesBasic Unit ConvertionADIPESHNo ratings yet
- Physical Constant in CGS UnitsDocument2 pagesPhysical Constant in CGS Unitsoberoiryan33No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Section B - Non-Numerical Solutions: 1.1 This System of Units Is The English-System Equivalent of SI. ThusDocument2 pagesChapter 1 - Section B - Non-Numerical Solutions: 1.1 This System of Units Is The English-System Equivalent of SI. ThusFaris NaufalNo ratings yet
- جابتر 1 ,, الدكتور اياد سعد الدين ,,, مهندسون نلتقي فنرتقي ,,S.k.A.H PDFDocument9 pagesجابتر 1 ,, الدكتور اياد سعد الدين ,,, مهندسون نلتقي فنرتقي ,,S.k.A.H PDFAmal Al SayyedNo ratings yet
- Ans Q1. The Vibrational Frequency ofDocument4 pagesAns Q1. The Vibrational Frequency ofKarthik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fenomenos 2Document4 pagesFenomenos 2Paula Andrea Viviescas AyalaNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2024 Solution Paper Feb 1 Shift 1Document17 pagesJEE Main 2024 Solution Paper Feb 1 Shift 1niharika.alakuntaNo ratings yet
- CH 04Document73 pagesCH 04Amilcar Pereira CardosoNo ratings yet
- Conversion TabletDocument2 pagesConversion TabletGreg CollinsNo ratings yet
- Dyn AssignmentDocument8 pagesDyn AssignmentTekle AschuNo ratings yet
- Unit ConversionDocument21 pagesUnit ConversioninsidereaderNo ratings yet
- Interaction DiagramDocument15 pagesInteraction DiagramjungzkiNo ratings yet
- The Handbook of Groundwater EngineeringDocument11 pagesThe Handbook of Groundwater EngineeringminashahabNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 ADocument21 pagesChapter5 ANic BlandoNo ratings yet
- Tugas Termodinamika 2 (Viodita Rizki Tek - Kimia S1 C - 14)Document5 pagesTugas Termodinamika 2 (Viodita Rizki Tek - Kimia S1 C - 14)Viodita RizkiNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions Physics Chapter 13 NucleiDocument16 pagesNCERT Solutions Physics Chapter 13 NucleiVidyakulNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemistry Faculty of Mathematics and Science State University of Padang 2014Document9 pagesDepartment of Chemistry Faculty of Mathematics and Science State University of Padang 2014Anelin OsiriknaNo ratings yet
- Teodor Ognean 1809.0446v1Document8 pagesTeodor Ognean 1809.0446v1arg0nautNo ratings yet
- Table I. Basic Units: Quantity Unit Symbol DefinitionDocument10 pagesTable I. Basic Units: Quantity Unit Symbol DefinitionAnonymous bRf25N8VcSNo ratings yet
- Rating of An Existing Absorption TowerDocument9 pagesRating of An Existing Absorption TowerKvspavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Back of NLC Periodic Table 2020-01-26Document1 pageBack of NLC Periodic Table 2020-01-26Thalia Rose B. RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Ipe JR PhysicsDocument144 pagesIpe JR PhysicsSai Varun KruthiventiNo ratings yet
- Units, Dimensions Error AnalysisDocument25 pagesUnits, Dimensions Error AnalysisVishal KumarNo ratings yet
- LHHW KineticsDocument3 pagesLHHW KineticsDanny Nguyen67% (3)
- 2134 Lab NishantDocument9 pages2134 Lab NishantNishant JalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- EMSOQuickRef PDFDocument6 pagesEMSOQuickRef PDFHRC8055No ratings yet
- Conversões No SIDocument4 pagesConversões No SIRaphael AlencarNo ratings yet
- CHM 111-Introductory Physical Chemistry-1-1Document74 pagesCHM 111-Introductory Physical Chemistry-1-1meamatafarms KennethNo ratings yet
- Atomic Rydberg UnitsDocument2 pagesAtomic Rydberg UnitsQiushi ZhuNo ratings yet
- Mr. Faisal Ikram Bin Abd SamadDocument29 pagesMr. Faisal Ikram Bin Abd SamadAmir HazimNo ratings yet
- Selected Key Equations Conversion Factors and Relationships: (Linearized Form)Document1 pageSelected Key Equations Conversion Factors and Relationships: (Linearized Form)iwannac0okieNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - InPEX Masela FLNG Korea-Batam (Calm)Document5 pagesMathcad - InPEX Masela FLNG Korea-Batam (Calm)fahmyits100% (1)
- 2017-02-08Document7 pages2017-02-08Chris KangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Jawaban TermoDocument50 pagesChapter 1 Jawaban TermoHabib Maulana Yasminto50% (2)
- GIECK Formula Ire Technique ADocument5 pagesGIECK Formula Ire Technique ABENOVERONo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFormula SheetSowkarthiga BaluNo ratings yet
- SI Base UnitsDocument20 pagesSI Base UnitsSatish Kumar MauryaNo ratings yet
- N CH - 19Document7 pagesN CH - 19asif_zehravi8048No ratings yet
- Chem II AP PacketDocument4 pagesChem II AP PacketAmanda Rose DalyNo ratings yet
- Electric Field and Potential: Chapter - 29 ExercisesDocument14 pagesElectric Field and Potential: Chapter - 29 ExercisesKanishk MehtaNo ratings yet
- Generalization of Ideal Gas Behavior - 2Document27 pagesGeneralization of Ideal Gas Behavior - 2Husnil KhatimahNo ratings yet
- Aula 2 Sistema SI NovoDocument17 pagesAula 2 Sistema SI NovoIuri ChavesNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Notes Nucl UnitsDocument2 pages1.3 Notes Nucl UnitsJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- A - Conversion FactorsDocument14 pagesA - Conversion Factorssaeed65No ratings yet
- Field MeasurementsDocument25 pagesField Measurementsrick123No ratings yet
- Physics Assigment 1Document14 pagesPhysics Assigment 1maroofjahanaziziNo ratings yet
- MM FormulaeDocument2 pagesMM FormulaeReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
Physical Const
Physical Const
Uploaded by
ahmetselimdurnaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physical Const
Physical Const
Uploaded by
ahmetselimdurnaCopyright:
Available Formats
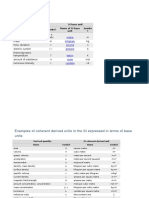
Avogadro's number: Planck's constant: Boltzmann's constant:
Physical constants 1 1 23 26 = 6.02252 10 N = 6.02252 10 gmole kgmole 27 34 h = 6.6256 10 erg sec = 6.6256 10 J sec ergs J cm 1 = 1.38054 10 23 = 0.69503 K K K 1 (where cm is a wave number unit) erg J 7 R = 8.3143 10 = 8314.3 K kgmole K gmole 31 me = 9.1095 10 kg k = 1.38054 10 16 Conversion Factors 1erg = 1 10 7 J = 5.0345 1015 cm 1 (where cm 1 is a wave number unit) 3 1 gmole = 1 10 kgmole kg kg g g 1 =1 (e.g. M O = 32 = 32 ) gmole gmole kgmole kgmole 6 dyne 5 N 1 atm = 1.01325 10 2 = 1.01325 10 2 cm m
2
Universal gas constant: Mass of an electron:
Energy: Moles: Molecular Weight: Pressure:
Wave Number Units [ cm 1 ]
In gas dynamics, "frequency" is sometimes expressed in Wave Number units [ cm 1 ] This "frequency [ cm 1 ]" is actually the true frequency normalized by the light speed in cgs units: [sec 1 ] frequency [sec 1 ] " frequency [cm 1 ]" = = light speed [cm / sec] c [cm / sec] Wave Number units [ cm 1 ] may also be thought of as a unit of energy: energy per molecule = h where h is Planck's constant. Thus, we may compute a Characteristic Temperature: energy per molecule [ J or ergs ] " frequency [cm 1 ]" [K] = = Boltzmann' s constant [ J/K or ergs/K ] Boltzmann' s constant [cm 1 /K] where Boltzmann's constant in terms of wave number units is shown above.
You might also like
- IB Physics Tsokos Solution Version 6 EditionDocument9 pagesIB Physics Tsokos Solution Version 6 Editionsatellite40611030% (10)
- Reviewer For Chemical Engineering Licensure Examination 3 Edition Solutions ManualDocument56 pagesReviewer For Chemical Engineering Licensure Examination 3 Edition Solutions ManualSherry Anne Ynciong Panganiban100% (4)
- Fundamental Physical Constants - Physico-Chemical ConstantsDocument1 pageFundamental Physical Constants - Physico-Chemical ConstantsmexcesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 and 3Document50 pagesChapter 2 and 3Christian Peterson75% (8)
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- Constants CombinedDocument5 pagesConstants CombinedAlejandro Matías AstorgaNo ratings yet
- ConstantsDocument2 pagesConstantssolutionerNo ratings yet
- AppendixI PDFDocument2 pagesAppendixI PDFexaguamhNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Conversion Tables For Units: Chapter 1 - 1Document9 pages1.6 Conversion Tables For Units: Chapter 1 - 1Yamel MorenoNo ratings yet
- Physical Constants PDFDocument4 pagesPhysical Constants PDFOscar JiménezNo ratings yet
- Complementary Notes: Prof. Dr. Şenol BAŞKAYADocument28 pagesComplementary Notes: Prof. Dr. Şenol BAŞKAYABarışPulatNo ratings yet
- Basic Unit ConvertionDocument30 pagesBasic Unit ConvertionADIPESHNo ratings yet
- Physical Constant in CGS UnitsDocument2 pagesPhysical Constant in CGS Unitsoberoiryan33No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Section B - Non-Numerical Solutions: 1.1 This System of Units Is The English-System Equivalent of SI. ThusDocument2 pagesChapter 1 - Section B - Non-Numerical Solutions: 1.1 This System of Units Is The English-System Equivalent of SI. ThusFaris NaufalNo ratings yet
- جابتر 1 ,, الدكتور اياد سعد الدين ,,, مهندسون نلتقي فنرتقي ,,S.k.A.H PDFDocument9 pagesجابتر 1 ,, الدكتور اياد سعد الدين ,,, مهندسون نلتقي فنرتقي ,,S.k.A.H PDFAmal Al SayyedNo ratings yet
- Ans Q1. The Vibrational Frequency ofDocument4 pagesAns Q1. The Vibrational Frequency ofKarthik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fenomenos 2Document4 pagesFenomenos 2Paula Andrea Viviescas AyalaNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2024 Solution Paper Feb 1 Shift 1Document17 pagesJEE Main 2024 Solution Paper Feb 1 Shift 1niharika.alakuntaNo ratings yet
- CH 04Document73 pagesCH 04Amilcar Pereira CardosoNo ratings yet
- Conversion TabletDocument2 pagesConversion TabletGreg CollinsNo ratings yet
- Dyn AssignmentDocument8 pagesDyn AssignmentTekle AschuNo ratings yet
- Unit ConversionDocument21 pagesUnit ConversioninsidereaderNo ratings yet
- Interaction DiagramDocument15 pagesInteraction DiagramjungzkiNo ratings yet
- The Handbook of Groundwater EngineeringDocument11 pagesThe Handbook of Groundwater EngineeringminashahabNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 ADocument21 pagesChapter5 ANic BlandoNo ratings yet
- Tugas Termodinamika 2 (Viodita Rizki Tek - Kimia S1 C - 14)Document5 pagesTugas Termodinamika 2 (Viodita Rizki Tek - Kimia S1 C - 14)Viodita RizkiNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions Physics Chapter 13 NucleiDocument16 pagesNCERT Solutions Physics Chapter 13 NucleiVidyakulNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemistry Faculty of Mathematics and Science State University of Padang 2014Document9 pagesDepartment of Chemistry Faculty of Mathematics and Science State University of Padang 2014Anelin OsiriknaNo ratings yet
- Teodor Ognean 1809.0446v1Document8 pagesTeodor Ognean 1809.0446v1arg0nautNo ratings yet
- Table I. Basic Units: Quantity Unit Symbol DefinitionDocument10 pagesTable I. Basic Units: Quantity Unit Symbol DefinitionAnonymous bRf25N8VcSNo ratings yet
- Rating of An Existing Absorption TowerDocument9 pagesRating of An Existing Absorption TowerKvspavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Back of NLC Periodic Table 2020-01-26Document1 pageBack of NLC Periodic Table 2020-01-26Thalia Rose B. RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Ipe JR PhysicsDocument144 pagesIpe JR PhysicsSai Varun KruthiventiNo ratings yet
- Units, Dimensions Error AnalysisDocument25 pagesUnits, Dimensions Error AnalysisVishal KumarNo ratings yet
- LHHW KineticsDocument3 pagesLHHW KineticsDanny Nguyen67% (3)
- 2134 Lab NishantDocument9 pages2134 Lab NishantNishant JalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- EMSOQuickRef PDFDocument6 pagesEMSOQuickRef PDFHRC8055No ratings yet
- Conversões No SIDocument4 pagesConversões No SIRaphael AlencarNo ratings yet
- CHM 111-Introductory Physical Chemistry-1-1Document74 pagesCHM 111-Introductory Physical Chemistry-1-1meamatafarms KennethNo ratings yet
- Atomic Rydberg UnitsDocument2 pagesAtomic Rydberg UnitsQiushi ZhuNo ratings yet
- Mr. Faisal Ikram Bin Abd SamadDocument29 pagesMr. Faisal Ikram Bin Abd SamadAmir HazimNo ratings yet
- Selected Key Equations Conversion Factors and Relationships: (Linearized Form)Document1 pageSelected Key Equations Conversion Factors and Relationships: (Linearized Form)iwannac0okieNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - InPEX Masela FLNG Korea-Batam (Calm)Document5 pagesMathcad - InPEX Masela FLNG Korea-Batam (Calm)fahmyits100% (1)
- 2017-02-08Document7 pages2017-02-08Chris KangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Jawaban TermoDocument50 pagesChapter 1 Jawaban TermoHabib Maulana Yasminto50% (2)
- GIECK Formula Ire Technique ADocument5 pagesGIECK Formula Ire Technique ABENOVERONo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFormula SheetSowkarthiga BaluNo ratings yet
- SI Base UnitsDocument20 pagesSI Base UnitsSatish Kumar MauryaNo ratings yet
- N CH - 19Document7 pagesN CH - 19asif_zehravi8048No ratings yet
- Chem II AP PacketDocument4 pagesChem II AP PacketAmanda Rose DalyNo ratings yet
- Electric Field and Potential: Chapter - 29 ExercisesDocument14 pagesElectric Field and Potential: Chapter - 29 ExercisesKanishk MehtaNo ratings yet
- Generalization of Ideal Gas Behavior - 2Document27 pagesGeneralization of Ideal Gas Behavior - 2Husnil KhatimahNo ratings yet
- Aula 2 Sistema SI NovoDocument17 pagesAula 2 Sistema SI NovoIuri ChavesNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Notes Nucl UnitsDocument2 pages1.3 Notes Nucl UnitsJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- A - Conversion FactorsDocument14 pagesA - Conversion Factorssaeed65No ratings yet
- Field MeasurementsDocument25 pagesField Measurementsrick123No ratings yet
- Physics Assigment 1Document14 pagesPhysics Assigment 1maroofjahanaziziNo ratings yet
- MM FormulaeDocument2 pagesMM FormulaeReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet