Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Axis Determination
Axis Determination
Uploaded by
anakagungbagusOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Axis Determination
Axis Determination
Uploaded by
anakagungbagusCopyright:
Available Formats
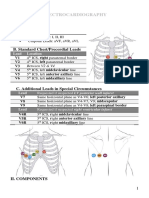
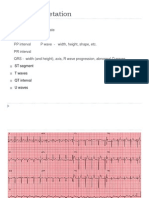
Axis Determination: Method 1 A. Check lead I (0 degrees) 1. QRS positive (predominately up) a. Vector points to patient's Left b.
Correlates with right half of axis circle 2. QRS negative (predominately down) a. Vector points to patient's Right b. Correlates with left half of axis circle B. Check lead aVF (90 degrees) 1. QRS positive (predominately up) a. Vector points to bottom half of axis circle 2. QRS negative (predominately down) a. Vector points to upper half of axis circle C. Interpretation 1. Indeterminate: Extreme Right Axis Deviation a. Lead I: Negative QRS b. Lead aVF: Negative QRS 2. Right Axis Deviation a. Lead I: Negative QRS b. Lead aVF: Positive QRS 3. Normal range a. Lead I: Positive QRS b. Lead aVF: Positive QRS 4. Left Axis Deviation a. Lead I: Positive QRS b. Lead aVF: Negative QRS II. Axis Determination: Method 2 A. Select Isoelectric lead from limb and augmented leads 1. Isoelectric lead averages to baseline 2. Positive deflection equals negative deflection B. Identify isoelectric lead on axis circle C. Choose lead that is perpendicular to isoelectric lead D. Use Lead I and aVF to determine quadrant E. Read perpendicular lead's degrees off axis circle
I.
You might also like
- ECG For MRCP SecondDocument12 pagesECG For MRCP Secondahmedelyousif815974100% (3)
- ElectrocardiogramDocument11 pagesElectrocardiogramAbby BhevNo ratings yet
- Basics of ElectrocardiographyDocument227 pagesBasics of ElectrocardiographyVlad CarabinNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography Basics: Dr. Nagula PraveenDocument90 pagesElectrocardiography Basics: Dr. Nagula PraveenhendranatjNo ratings yet
- Ecg (Ekg) : Dr. Jamal Dabbas Interventional Cardiologist & InternistDocument87 pagesEcg (Ekg) : Dr. Jamal Dabbas Interventional Cardiologist & Internistsara rababahNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiography: I. Leads A. Limb LeadsDocument11 pagesElectrocardiography: I. Leads A. Limb LeadsJoezelle0% (1)
- Conduction Pathways: - Sinoatrial Node - Atrioventricular Node - AV Bundle - Bundle Branches - Purkinje FibersDocument66 pagesConduction Pathways: - Sinoatrial Node - Atrioventricular Node - AV Bundle - Bundle Branches - Purkinje FibersSuhail Ahmed AbbasiNo ratings yet
- A Self-Directed Learning Module: Queen's University Department of Emergency MedicineDocument38 pagesA Self-Directed Learning Module: Queen's University Department of Emergency MedicinerinoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ECG InterpretationDocument99 pagesIntroduction To ECG InterpretationSharushna GokoelmissierNo ratings yet
- Membaca Ekg: Dr. Aritantri Darmayani, M.SC, SPPDDocument76 pagesMembaca Ekg: Dr. Aritantri Darmayani, M.SC, SPPDDekdesNo ratings yet
- Part 02 EP TracingsDocument42 pagesPart 02 EP TracingsHany100% (1)
- Qrs & Voltage: Dr. David D. Ariwibowo SPJP, FihaDocument14 pagesQrs & Voltage: Dr. David D. Ariwibowo SPJP, FihaJevisco LauNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ECG Interpretation January 2023Document101 pagesIntroduction To ECG Interpretation January 2023davidjoejoekidNo ratings yet
- Basic Ecg From FastlanDocument125 pagesBasic Ecg From Fastlanomarfaruque7807No ratings yet
- Interpretion of EcgDocument17 pagesInterpretion of EcgAbdul SamadNo ratings yet
- EKG1 2007 AlmeidaDocument48 pagesEKG1 2007 AlmeidalilymurielNo ratings yet
- (1P) ECG On GoingDocument10 pages(1P) ECG On GoingElmer PatrickNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation UnismaDocument178 pagesECG Interpretation UnismadefinaNo ratings yet
- Pre TestDocument7 pagesPre TestJoudaziz2003No ratings yet
- CURS EkGNR 2Document32 pagesCURS EkGNR 2Ana-Maria Iuliana IlieNo ratings yet
- EKG Common Clinical ArrhythmiasDocument54 pagesEKG Common Clinical ArrhythmiasFaisal AlhasNo ratings yet
- Ecg CookbookDocument2 pagesEcg CookbookCalin Popa100% (1)
- Bimbingan Ekg r1Document76 pagesBimbingan Ekg r1lintang andilaNo ratings yet
- ECG - Module - Printable Analysis and Interpretation of ECGDocument37 pagesECG - Module - Printable Analysis and Interpretation of ECGPankaj PatilNo ratings yet
- Basic ECG ReadingDocument41 pagesBasic ECG ReadingBenj100% (4)
- Interpretasi Elektrokardiografi: Dr. Erlina Marfianti, MSC, SPPD Departemen Ilmu Penyakit Dalam Fakultas Kedokteran UiiDocument60 pagesInterpretasi Elektrokardiografi: Dr. Erlina Marfianti, MSC, SPPD Departemen Ilmu Penyakit Dalam Fakultas Kedokteran UiiArif Zulfian MubarokNo ratings yet
- General: Determination of Heart Rate and Rhythm Determination of The Heart RateDocument14 pagesGeneral: Determination of Heart Rate and Rhythm Determination of The Heart RatedanradulescuNo ratings yet
- DASAR KURSUS EKG - DR WiryawanDocument68 pagesDASAR KURSUS EKG - DR WiryawanElsa TjahyaNo ratings yet
- Didactics ECGDocument87 pagesDidactics ECGGenesis Poblacion100% (1)
- Medicine - EKG - Lab Coat PocketsDocument1 pageMedicine - EKG - Lab Coat Pocketsskeebs23No ratings yet
- EKG Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesEKG Cheat SheetJoNo ratings yet
- ECG Module PrintableDocument39 pagesECG Module PrintableAbu HibbaanNo ratings yet
- CardiologyDocument99 pagesCardiologySimple LyricsNo ratings yet
- C2 Lab 1xbnmvncmxcDocument51 pagesC2 Lab 1xbnmvncmxcanaNo ratings yet
- Normal Ecg ReportDocument27 pagesNormal Ecg ReportMark DycNo ratings yet
- ECG Hipertrofii Atriale Si Ventriculare, Blocuri de Ramura, IschemieDocument60 pagesECG Hipertrofii Atriale Si Ventriculare, Blocuri de Ramura, IschemieAndreea ŞtefănescuNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 - Rectifier CircuitsDocument6 pagesLab 2 - Rectifier CircuitsHemil PatelNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiographic Interpretation of Cardiac MuscleDocument6 pagesElectrocardiographic Interpretation of Cardiac MuscleMahnoor ZafarNo ratings yet
- Ecg 1Document66 pagesEcg 1Joud D.No ratings yet
- Engineering Surveying Unit - 4: TheodoliteDocument17 pagesEngineering Surveying Unit - 4: TheodoliteSumit Kumar SinhaNo ratings yet
- Ecg - Basics For The Anesthesiologists: Dr.K.M.LakshmanarajanDocument145 pagesEcg - Basics For The Anesthesiologists: Dr.K.M.LakshmanarajanKM Lakshmana RajanNo ratings yet
- How To Analyze EkgsDocument40 pagesHow To Analyze EkgsJosh WeisNo ratings yet
- ECGDocument198 pagesECGKatrina Maravilla100% (1)
- Practice. After About 500 ECG's, You Be Able To Do Them Without Forgetting Major DetailsDocument5 pagesPractice. After About 500 ECG's, You Be Able To Do Them Without Forgetting Major DetailsRameezAmerNo ratings yet
- Basics of EKG InterpretationDocument132 pagesBasics of EKG InterpretationSiddhant GautamNo ratings yet
- Department of Cardiology and Vascular Medicine, Padjadjaran University School of Medicine Hasan Sadikin Hospital BandungDocument61 pagesDepartment of Cardiology and Vascular Medicine, Padjadjaran University School of Medicine Hasan Sadikin Hospital BandungMuhammad AmrieNo ratings yet
- ECG Evaluaton PDFDocument2 pagesECG Evaluaton PDFMus'abIdriesAbuzetunNo ratings yet
- 07.01 - 12 Lead ECG Interpretation 2019Document141 pages07.01 - 12 Lead ECG Interpretation 2019Lana LocoNo ratings yet
- A. Van Der Pauw ConductivityDocument10 pagesA. Van Der Pauw ConductivityBobNo ratings yet
- Normal Impulse Conduction: Sinoatrial Node AV Node Bundle of His Bundle Branches Purkinje FibersDocument73 pagesNormal Impulse Conduction: Sinoatrial Node AV Node Bundle of His Bundle Branches Purkinje FibersIndra ToshiwayNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation: RR Interval Heart RateDocument66 pagesECG Interpretation: RR Interval Heart RateRoxana NegureanuNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Clinical ECGDocument40 pagesBasic Concepts of Clinical ECGArslan KhanNo ratings yet
- Normal Impulse Conduction: Sinoatrial Node AV Node Bundle of His Bundle Branches Purkinje FibersDocument73 pagesNormal Impulse Conduction: Sinoatrial Node AV Node Bundle of His Bundle Branches Purkinje FibersIndra ToshiwayNo ratings yet
- Hypertrophy and Enlargement of The HeartDocument23 pagesHypertrophy and Enlargement of The HeartZion_MilgemNo ratings yet
- Intro ECGDocument9 pagesIntro ECGChithra RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- 12-Lead EKG (EMT Presentation)Document168 pages12-Lead EKG (EMT Presentation)Oas OssNo ratings yet
- The Normal Adult ECGDocument84 pagesThe Normal Adult ECGkimiastroNo ratings yet