Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AMA Phatophysiology
AMA Phatophysiology
Uploaded by
namonneCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Nutrition Case StudyDocument17 pagesNutrition Case Studymacedon14100% (18)
- (Cor Pulmonale) PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pages(Cor Pulmonale) PATHOPHYSIOLOGYmilayango67% (3)
- Cerebrovascular Accident PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCerebrovascular Accident PathophysiologyBerde KangleonNo ratings yet
- NSTEMI - PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesNSTEMI - PathophysiologyDivyesh DholariyaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CVADocument2 pagesPathophysiology CVATerence Valdehueza67% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Breast CancerDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Breast Cancerpauline mangadaNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis and Ischaemic Heart DiseaseDocument13 pagesAtherosclerosis and Ischaemic Heart DiseaseAkshaya Mistry100% (1)
- Pathophysiology: - Patho - Physiology of Ischemic StrokeDocument5 pagesPathophysiology: - Patho - Physiology of Ischemic StrokeAarti KashyapNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis: School of Veterinary Medicine-UbDocument55 pagesAtherosclerosis: School of Veterinary Medicine-UbBimaldy Purwa KaruniaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument1 pagePathophysiology of CVAYoussry JaranillaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysilogy Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument3 pagesPathophysilogy Acute Myocardial InfarctionronvhadzNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesPathophysiologyzvfvr95hrkNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsDocument166 pagesPharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsEvgeny BadmaevNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure, Cardiomyopathy and Myocarditis I. Congestive Heart FailureDocument23 pagesCongestive Heart Failure, Cardiomyopathy and Myocarditis I. Congestive Heart Failurelovelyc95No ratings yet
- Stroke: By: Serlinawati PakpahanDocument11 pagesStroke: By: Serlinawati PakpahanSaurlina GultomNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis Sanzhar ZhetkenevDocument9 pagesAtherosclerosis Sanzhar ZhetkenevSanzhar AbenovNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DentDocument92 pagesCardiovascular DentVincent De AsisNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure & Circulatory ShockDocument34 pagesHeart Failure & Circulatory ShockMuskaan ZaharaNo ratings yet
- Original StrokeDocument130 pagesOriginal StrokeGafencu SergiuNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesDocument3 pagesSchematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesJosett RomanoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Diet Sedentary Lifestyle Familial History of Hypertension Age - Common in 40 and AboveDocument4 pagesPathophysiology: Diet Sedentary Lifestyle Familial History of Hypertension Age - Common in 40 and AboveJohn AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument118 pagesHeart FailureAli Murtaza AbbasNo ratings yet
- Clase Cardiopatia IsquémicaDocument132 pagesClase Cardiopatia IsquémicaSusy OcampoNo ratings yet
- Management of PediatricDocument48 pagesManagement of PediatricIbrahimNo ratings yet
- AtherosclerosisDocument23 pagesAtherosclerosisPoonam soniNo ratings yet
- 1 Henry McCraeDocument4 pages1 Henry McCraeAbdullah RajaNo ratings yet
- Shock: DefinitionDocument18 pagesShock: DefinitionGaurav ChauhanNo ratings yet
- AtherosclerosisDocument41 pagesAtherosclerosisSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Angina PectorisDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Angina PectorisChristine Elaine Batusin IlaganNo ratings yet
- AtherosclerosisDocument13 pagesAtherosclerosisabanoub khalaf 22No ratings yet
- General Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesGeneral Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsIrish Nicole DCNo ratings yet
- AterosklerosisDocument40 pagesAterosklerosisIda Benecia DeseNo ratings yet
- The Heart-1Document30 pagesThe Heart-1Ebuka AniNo ratings yet
- 1cardiovascular System DisordersDocument13 pages1cardiovascular System DisordersArvin MalondrasNo ratings yet
- ATHEROSCLEROSISDocument41 pagesATHEROSCLEROSISDoc On CallNo ratings yet
- Cerebro Vascular AccidentDocument19 pagesCerebro Vascular AccidentanshitaNo ratings yet
- Diseases and Disorders of The Human Circulatory SystemDocument18 pagesDiseases and Disorders of The Human Circulatory SystemvvNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Patient With CCFDocument34 pagesNursing Management of Patient With CCFJayarani Ashok100% (1)
- Cagayan State University College of Medicine and Surgery SY: 2009-2010Document41 pagesCagayan State University College of Medicine and Surgery SY: 2009-2010ahmad usmanNo ratings yet
- Group 4 ProjectDocument40 pagesGroup 4 Projectlaiba.akhtarNo ratings yet
- PerfusionDocument9 pagesPerfusionAmanda Brittain100% (2)
- Lecture 30 - Pathology of AtherosclerosisDocument43 pagesLecture 30 - Pathology of Atherosclerosisapi-3703352100% (6)
- 3 PathophysiologyDocument4 pages3 PathophysiologySherlyn KirisakiNo ratings yet
- AHN II Serkes PresentationDocument75 pagesAHN II Serkes PresentationSaniNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular DiseaseDocument4 pagesCerebrovascular DiseasekathyfacaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsLilot Antonio Rodriguez Vinarao100% (5)
- CVD InfactionDocument3 pagesCVD InfactionDaryl James MedilloNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Shock: Recognition and ClassificationDocument39 pagesPediatric Shock: Recognition and ClassificationRaghavendra DoddamaniNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pathology 2024Document132 pagesCardiovascular Pathology 2024Chen HouyuNo ratings yet
- Genetic and Chromosomal Abnormalities 1Document10 pagesGenetic and Chromosomal Abnormalities 1arcjendelaclanNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident ReportDocument16 pagesCerebrovascular Accident ReportAngelu Gabrielle CastroNo ratings yet
- Stroke Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument2 pagesStroke Pa Tho PhysiologyBrandoSantosNo ratings yet
- 2013 BAA - Glossary of Common Medical Prefixes and Suffixes For BAA and BLSDocument5 pages2013 BAA - Glossary of Common Medical Prefixes and Suffixes For BAA and BLSM GavinNo ratings yet
- Stages of ShockDocument13 pagesStages of ShockA. P.No ratings yet
- Disorders of Arterial Circulation - 8Document42 pagesDisorders of Arterial Circulation - 8Cres Padua QuinzonNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CVADocument11 pagesPathophysiology CVAallyana kim figueroa lavarias100% (1)
- Learning Objectives in Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument13 pagesLearning Objectives in Cardiovascular DiseaseZul Azim AnuarNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis, (Vascular Thickening) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAtherosclerosis, (Vascular Thickening) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Reverse and Prevent Heart Disease: Natural Ways to Stop and Prevent Heart Disease, Using Plant-Based Oil-Free Diets (Cure Congestive Heart Failure)From EverandReverse and Prevent Heart Disease: Natural Ways to Stop and Prevent Heart Disease, Using Plant-Based Oil-Free Diets (Cure Congestive Heart Failure)No ratings yet
AMA Phatophysiology
AMA Phatophysiology
Uploaded by
namonneOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AMA Phatophysiology
AMA Phatophysiology
Uploaded by
namonneCopyright:
Available Formats
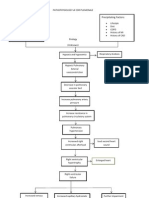
II.
PHATOPHYSIOLOGY
Predisposing Factors: 1) Age: 48 y/o 2) Heredity: Mother died because of stroke 3) Sex: Male 4) Prior Stroke, TIA or heart attack Precipitating Factors: 1) Hypertension 2) Cigarette Smoking 3) Atrial Fibrillation 4) Poor diet 5) Alcohol Intake
Atherosclerosis Formation of Plaque deposits Thrombosis Occlusion by major vessel
Hypertensi on
Lysed or moved thrombus from the vessel
Vascular wall becomes weakened and fragile
Leaking of blood from the fragile vessel wall Sx:, headache, unconsciousness, nausea/vomiting, visual disturbances
Cerebral Hemorrhage Mass of blood forms and grows
Vasospasm of tissue and arteries
Sx: dizziness, confusion, headache
CEREBRAL HYPOPERFUSION
Impaired distribution of oxygen and glucose
Blood seeps into th e ventricles Obstruction of CSF passageway
Formation of small and large clots
Impaired distribution of oxygen and glucose
Tissue hypoxia and cellular starvation
Cerebral Ischemia Accumulation of CSF in the ventricles Lodges unto other cerebral arteries
Initiation of ischemic cascade
Ventricles dilate behind the point of obstruction
Increased ICP Unrelieved obstruction
Anaerobic metabolism by mitochondria
Vertebrobasilar System
Damage to the blood vessel endothelium
Transient Ischemic Attack Structural integrity loss of brain tissue and blood vessels Brain sustains an irreversible cerebral damage
Breakdown of the protective Blood Brain Barrier
Cerebral edema
Compression of tissue
Vascular Congestion
Increased intracranial pressure Impaired perfusion and function
Sx: Alternating motor weaknesses, contralateral hemisensory impairments, double vision, homonymous hemianopsia, nystagmus, conjugate gaze, paralysis, dysphagia, coma
Vertebrobasilar System Cerebellum and brain stem
Continued insufficiency of blood flow
Further compression of tissues
Coma
Cerebral Death
Loss of neural feedback mechanisms
Cessation of physiologic functions
Altered body temperature
Systemic Failure
Impaired Gas exchange
Risk for aspiration r/t NGT use
In Severe Cases
DEATH
You might also like
- Nutrition Case StudyDocument17 pagesNutrition Case Studymacedon14100% (18)
- (Cor Pulmonale) PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pages(Cor Pulmonale) PATHOPHYSIOLOGYmilayango67% (3)
- Cerebrovascular Accident PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCerebrovascular Accident PathophysiologyBerde KangleonNo ratings yet
- NSTEMI - PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesNSTEMI - PathophysiologyDivyesh DholariyaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CVADocument2 pagesPathophysiology CVATerence Valdehueza67% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Breast CancerDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Breast Cancerpauline mangadaNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis and Ischaemic Heart DiseaseDocument13 pagesAtherosclerosis and Ischaemic Heart DiseaseAkshaya Mistry100% (1)
- Pathophysiology: - Patho - Physiology of Ischemic StrokeDocument5 pagesPathophysiology: - Patho - Physiology of Ischemic StrokeAarti KashyapNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis: School of Veterinary Medicine-UbDocument55 pagesAtherosclerosis: School of Veterinary Medicine-UbBimaldy Purwa KaruniaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument1 pagePathophysiology of CVAYoussry JaranillaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysilogy Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument3 pagesPathophysilogy Acute Myocardial InfarctionronvhadzNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesPathophysiologyzvfvr95hrkNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsDocument166 pagesPharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsEvgeny BadmaevNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure, Cardiomyopathy and Myocarditis I. Congestive Heart FailureDocument23 pagesCongestive Heart Failure, Cardiomyopathy and Myocarditis I. Congestive Heart Failurelovelyc95No ratings yet
- Stroke: By: Serlinawati PakpahanDocument11 pagesStroke: By: Serlinawati PakpahanSaurlina GultomNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis Sanzhar ZhetkenevDocument9 pagesAtherosclerosis Sanzhar ZhetkenevSanzhar AbenovNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DentDocument92 pagesCardiovascular DentVincent De AsisNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure & Circulatory ShockDocument34 pagesHeart Failure & Circulatory ShockMuskaan ZaharaNo ratings yet
- Original StrokeDocument130 pagesOriginal StrokeGafencu SergiuNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesDocument3 pagesSchematic Diagram: Signs and Symptoms: Headache, Unconsciousness, Nausea and Vomiting, Visual DisturbancesJosett RomanoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Diet Sedentary Lifestyle Familial History of Hypertension Age - Common in 40 and AboveDocument4 pagesPathophysiology: Diet Sedentary Lifestyle Familial History of Hypertension Age - Common in 40 and AboveJohn AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Heart FailureDocument118 pagesHeart FailureAli Murtaza AbbasNo ratings yet
- Clase Cardiopatia IsquémicaDocument132 pagesClase Cardiopatia IsquémicaSusy OcampoNo ratings yet
- Management of PediatricDocument48 pagesManagement of PediatricIbrahimNo ratings yet
- AtherosclerosisDocument23 pagesAtherosclerosisPoonam soniNo ratings yet
- 1 Henry McCraeDocument4 pages1 Henry McCraeAbdullah RajaNo ratings yet
- Shock: DefinitionDocument18 pagesShock: DefinitionGaurav ChauhanNo ratings yet
- AtherosclerosisDocument41 pagesAtherosclerosisSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Angina PectorisDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Angina PectorisChristine Elaine Batusin IlaganNo ratings yet
- AtherosclerosisDocument13 pagesAtherosclerosisabanoub khalaf 22No ratings yet
- General Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesGeneral Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsIrish Nicole DCNo ratings yet
- AterosklerosisDocument40 pagesAterosklerosisIda Benecia DeseNo ratings yet
- The Heart-1Document30 pagesThe Heart-1Ebuka AniNo ratings yet
- 1cardiovascular System DisordersDocument13 pages1cardiovascular System DisordersArvin MalondrasNo ratings yet
- ATHEROSCLEROSISDocument41 pagesATHEROSCLEROSISDoc On CallNo ratings yet
- Cerebro Vascular AccidentDocument19 pagesCerebro Vascular AccidentanshitaNo ratings yet
- Diseases and Disorders of The Human Circulatory SystemDocument18 pagesDiseases and Disorders of The Human Circulatory SystemvvNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Patient With CCFDocument34 pagesNursing Management of Patient With CCFJayarani Ashok100% (1)
- Cagayan State University College of Medicine and Surgery SY: 2009-2010Document41 pagesCagayan State University College of Medicine and Surgery SY: 2009-2010ahmad usmanNo ratings yet
- Group 4 ProjectDocument40 pagesGroup 4 Projectlaiba.akhtarNo ratings yet
- PerfusionDocument9 pagesPerfusionAmanda Brittain100% (2)
- Lecture 30 - Pathology of AtherosclerosisDocument43 pagesLecture 30 - Pathology of Atherosclerosisapi-3703352100% (6)
- 3 PathophysiologyDocument4 pages3 PathophysiologySherlyn KirisakiNo ratings yet
- AHN II Serkes PresentationDocument75 pagesAHN II Serkes PresentationSaniNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular DiseaseDocument4 pagesCerebrovascular DiseasekathyfacaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsLilot Antonio Rodriguez Vinarao100% (5)
- CVD InfactionDocument3 pagesCVD InfactionDaryl James MedilloNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Shock: Recognition and ClassificationDocument39 pagesPediatric Shock: Recognition and ClassificationRaghavendra DoddamaniNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pathology 2024Document132 pagesCardiovascular Pathology 2024Chen HouyuNo ratings yet
- Genetic and Chromosomal Abnormalities 1Document10 pagesGenetic and Chromosomal Abnormalities 1arcjendelaclanNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident ReportDocument16 pagesCerebrovascular Accident ReportAngelu Gabrielle CastroNo ratings yet
- Stroke Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument2 pagesStroke Pa Tho PhysiologyBrandoSantosNo ratings yet
- 2013 BAA - Glossary of Common Medical Prefixes and Suffixes For BAA and BLSDocument5 pages2013 BAA - Glossary of Common Medical Prefixes and Suffixes For BAA and BLSM GavinNo ratings yet
- Stages of ShockDocument13 pagesStages of ShockA. P.No ratings yet
- Disorders of Arterial Circulation - 8Document42 pagesDisorders of Arterial Circulation - 8Cres Padua QuinzonNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CVADocument11 pagesPathophysiology CVAallyana kim figueroa lavarias100% (1)
- Learning Objectives in Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument13 pagesLearning Objectives in Cardiovascular DiseaseZul Azim AnuarNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis, (Vascular Thickening) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandAtherosclerosis, (Vascular Thickening) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Reverse and Prevent Heart Disease: Natural Ways to Stop and Prevent Heart Disease, Using Plant-Based Oil-Free Diets (Cure Congestive Heart Failure)From EverandReverse and Prevent Heart Disease: Natural Ways to Stop and Prevent Heart Disease, Using Plant-Based Oil-Free Diets (Cure Congestive Heart Failure)No ratings yet