Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pa Tho Physiology
Pa Tho Physiology
Uploaded by
ella joyce0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageMechanical stress, aging, and decreased fluid levels weaken the annulus of the disk, making it prone to tearing and the bulging of disk material which can erode the vertebral body. This causes increased pressure within the nucleus pulposus and irritation of pain fibers, leading to local tenderness and stimulation of bone growth with muscle spasm. Pain occurs due to compression of spinal nerves from disk material protruding from the annulus, decreasing blood flow and mobility in the affected area and causing numbness.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMechanical stress, aging, and decreased fluid levels weaken the annulus of the disk, making it prone to tearing and the bulging of disk material which can erode the vertebral body. This causes increased pressure within the nucleus pulposus and irritation of pain fibers, leading to local tenderness and stimulation of bone growth with muscle spasm. Pain occurs due to compression of spinal nerves from disk material protruding from the annulus, decreasing blood flow and mobility in the affected area and causing numbness.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pagePa Tho Physiology
Pa Tho Physiology
Uploaded by
ella joyceMechanical stress, aging, and decreased fluid levels weaken the annulus of the disk, making it prone to tearing and the bulging of disk material which can erode the vertebral body. This causes increased pressure within the nucleus pulposus and irritation of pain fibers, leading to local tenderness and stimulation of bone growth with muscle spasm. Pain occurs due to compression of spinal nerves from disk material protruding from the annulus, decreasing blood flow and mobility in the affected area and causing numbness.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
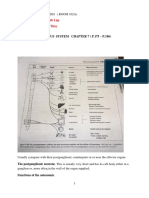
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Mechanical stress (compression, fusion, HPN, rational forces) Male gender is more prone
Aggravated by age due to degenerative changes thus results to muscle weakness
Decreased in protein content (oncotic agents)
-Dehydration and decreased fluid in the annulus. -weakening of the annulus, thus less elastic, thus prone to tearing.
Erosion of vertebral body by bulging disk teared annulus.
Increased pressure and uptake of fluid in the nucleus pulposus.
Irritated pain fibris
Local tenderness
Stimulation of new bone growth accompanied by vertebral spasm.
PAIN
Accompanied by:
Increased tension
Ligament thicken Calcification
Autonomic responses: Papillary dilatation diaphoresis
Replacement of nucleus Results in neutral obstruction
Compression of spinal nerve
Decreased flow of blood in the affected area
Impaired mobility
Numbness occurs
You might also like
- Pathophysiology of FractureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of FractureAnne Lorraine Bringas93% (27)
- Pathophysiology of FractureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of FractureVenus Tagaan UcatNo ratings yet
- 2 NCM114Document24 pages2 NCM114Adrian SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Neurological Disorders Like Lumbago & Sciatica Etc. With Management by HomoeopathyDocument15 pagesNeurological Disorders Like Lumbago & Sciatica Etc. With Management by HomoeopathyChetanNo ratings yet
- Herniated Nucleus PulposusDocument3 pagesHerniated Nucleus PulposusroselleanneNo ratings yet
- Ankylosing SpondylitisDocument23 pagesAnkylosing Spondylitispatel divya100% (1)
- Visceral Pain: Nausea, Vomiting, and Increased Heart Rate May Accompany Visceral PainDocument3 pagesVisceral Pain: Nausea, Vomiting, and Increased Heart Rate May Accompany Visceral PainRubie Ann TillorNo ratings yet
- Legg Calve PerthesDocument7 pagesLegg Calve PerthesNelhbenson LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument28 pagesOsteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritislovelyc95No ratings yet
- Complications of Bed Rest 1Document4 pagesComplications of Bed Rest 1Geetha Bhavani100% (2)
- Immobilisation ConsequencesDocument5 pagesImmobilisation ConsequencesJade BouchardNo ratings yet
- TCM and Cervical Sponylosis 22Document21 pagesTCM and Cervical Sponylosis 22wr48f26rjmNo ratings yet
- Muscular DiseasesDocument24 pagesMuscular DiseasesMaria Theresa FortunaNo ratings yet
- Nhóm 2.2Document52 pagesNhóm 2.2thai luan nguyenNo ratings yet
- Dr. Mona Hasan El Lathy Lecturer in The Department of PT For Musculoskeletal DisordersDocument40 pagesDr. Mona Hasan El Lathy Lecturer in The Department of PT For Musculoskeletal Disordersفاطمه مباركيNo ratings yet
- Compartement Syndrom (21 Juni 2012)Document12 pagesCompartement Syndrom (21 Juni 2012)Tommy HardiantoNo ratings yet
- Refrat Remato LBPDocument33 pagesRefrat Remato LBPwulanNo ratings yet
- Muscle Skeletal Trauma For EMSDocument79 pagesMuscle Skeletal Trauma For EMSPaulhotvw67100% (4)
- Pathophysiology of Spinal Cord InjuryDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Spinal Cord InjuryLouie AdorNo ratings yet
- Planter Fasciitis: Biomechanical AetiologyDocument7 pagesPlanter Fasciitis: Biomechanical AetiologyMohan JoshiNo ratings yet
- LBM 4 SarafDocument16 pagesLBM 4 SarafRahmayuni FItriantiNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain: Respectfully Submitted By: Princess Edelweiss M. Corpuz Wendy Pearn F. Castañeda Andre Kaien S. CorpuzDocument14 pagesLow Back Pain: Respectfully Submitted By: Princess Edelweiss M. Corpuz Wendy Pearn F. Castañeda Andre Kaien S. CorpuzJusthine Mhay BalanceNo ratings yet
- How Pemf Therapy Affects The Body ?Document2 pagesHow Pemf Therapy Affects The Body ?Num NutzNo ratings yet
- Physiologic Changes Associated With Ageing Module 2Document2 pagesPhysiologic Changes Associated With Ageing Module 2Meryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Canal Stenosis - ERHDocument56 pagesCanal Stenosis - ERHAries RHNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis: Arranged byDocument12 pagesOsteoarthritis: Arranged byEdwin DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Imobilisasi Lama: (Prolonged Immobilization)Document45 pagesImobilisasi Lama: (Prolonged Immobilization)jhnaidillaNo ratings yet
- Complications of Bed RestDocument51 pagesComplications of Bed Restsuderson100% (1)
- Backpain Prof KwanDocument7 pagesBackpain Prof KwanNurul Fahmiza TumiranNo ratings yet
- Osteochondrosis of The SpineDocument94 pagesOsteochondrosis of The SpineMoroccan Girl In UkraineNo ratings yet
- Low Back PainDocument100 pagesLow Back Painchandrusai100% (1)
- NP Outreach Curriculum in Rheumatology St. Joseph's Health Care, London, ON Dr. Sherry Rohekar November 12, 2009Document50 pagesNP Outreach Curriculum in Rheumatology St. Joseph's Health Care, London, ON Dr. Sherry Rohekar November 12, 2009lynkx864100% (1)
- Spondylosis, Cervical and LumbarDocument1 pageSpondylosis, Cervical and LumbarLuis HerreraNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: Evaluation and ManagementDocument9 pagesDegenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: Evaluation and ManagementVy Phạm Thị TrúcNo ratings yet
- Ankylosing Spondylitis and Other Seronegative ArthritisDocument20 pagesAnkylosing Spondylitis and Other Seronegative ArthritisAkash ShillNo ratings yet
- Lower Leg Pain Differential Diagnosis - NeuromuscularDocument14 pagesLower Leg Pain Differential Diagnosis - Neuromuscularapi-619359087No ratings yet
- Herniated Nucleus PulposusDocument5 pagesHerniated Nucleus PulposusPeterzen ManaigNo ratings yet
- Physiological Aging: Artizuela, Marisol O'Dell, Andrea Romero, Erra Lee Sese, Kameron Gayla Pangilinan, Kenneth ChristianDocument12 pagesPhysiological Aging: Artizuela, Marisol O'Dell, Andrea Romero, Erra Lee Sese, Kameron Gayla Pangilinan, Kenneth ChristianAndrea Isabel U. O'DellNo ratings yet
- Cikini Pengelolaan Nyeri FinalDocument85 pagesCikini Pengelolaan Nyeri FinalisabellaruthhhNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGYAnne SedanzaNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain: Dr. Doha RasheedyDocument40 pagesLow Back Pain: Dr. Doha RasheedyDoha EbedNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain: Dr. Andi Dhedie P. Sam, M.Kes, SP - OTDocument41 pagesLow Back Pain: Dr. Andi Dhedie P. Sam, M.Kes, SP - OTNia Anggreni100% (1)
- Day 4 Special NeedsDocument8 pagesDay 4 Special NeedsRidwan OlivaNo ratings yet
- Lumbardiscprolapse3 130219095421 Phpapp01Document141 pagesLumbardiscprolapse3 130219095421 Phpapp01Sri Ram 07No ratings yet
- Ortho PAthoDocument4 pagesOrtho PAthoCheriz LukbanNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument2 pagesPa Tho PhysiologyCarla Bianchi Pineda GaananNo ratings yet
- Section of Rheumatology, Internal Medicine Department Faculty of Medicine GMU / Dr. Sardjito General HospitalDocument47 pagesSection of Rheumatology, Internal Medicine Department Faculty of Medicine GMU / Dr. Sardjito General HospitalYane Aulia YasminNo ratings yet
- Pagetsdiseaseofthebone 180107110929Document28 pagesPagetsdiseaseofthebone 180107110929Lolo TotoNo ratings yet
- Discuss Nursing Interventions That Prevent Complications of ImmobilityDocument19 pagesDiscuss Nursing Interventions That Prevent Complications of ImmobilityLilly Ann Vaughan50% (2)
- Herniated DiscDocument5 pagesHerniated Disc4gen_7No ratings yet
- Ankylosing SpondylitisDocument4 pagesAnkylosing SpondylitisHenry TirtosuhartoNo ratings yet
- Illness ScriptsDocument3 pagesIllness Scriptsapi-461267075No ratings yet
- Year 2 Semester 2Document88 pagesYear 2 Semester 2JSeasharkNo ratings yet
- Herniated Nucleus Pulposus (HNP)Document4 pagesHerniated Nucleus Pulposus (HNP)Kevin CamilozaNo ratings yet
- Nyeri Punggung Bawah (Low Back Pain) : DefinisiDocument10 pagesNyeri Punggung Bawah (Low Back Pain) : DefinisiheruNo ratings yet
- Low Back Pain: Aldy S. RambeDocument40 pagesLow Back Pain: Aldy S. RambeHatta Diana TariganNo ratings yet
- Spondylosis: Vertebral ColumnDocument12 pagesSpondylosis: Vertebral ColumnVdct MglNo ratings yet
- CervicalDocument13 pagesCervicalSanjay SoniNo ratings yet
- Clinical Signs in Humans and Animals Associated with Minerals, Trace Elements and Rare Earth ElementsFrom EverandClinical Signs in Humans and Animals Associated with Minerals, Trace Elements and Rare Earth ElementsNo ratings yet
- PantoprazoleDocument1 pagePantoprazoleella joyceNo ratings yet
- TramadolDocument1 pageTramadolella joyceNo ratings yet
- MeropenemDocument2 pagesMeropenemella joyceNo ratings yet
- Methyl DopaDocument1 pageMethyl Dopaella joyceNo ratings yet
- MannitolDocument1 pageMannitolella joyceNo ratings yet
- Stress Management TechniquesDocument29 pagesStress Management Techniquesella joyce100% (3)
- UTI in A Pregnant Woman - NCPDocument6 pagesUTI in A Pregnant Woman - NCPella joyce75% (4)