Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sclerenchyma
Sclerenchyma
Uploaded by
Hong Ming0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
222 views6 pagesSclerenchyma is a supporting plant tissue composed of fibers and sclereids with thick secondary cell walls made of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. It consists of dead cells whose thickened walls make up to 90% of the cell volume, providing structure and support to plant parts that stop elongating like stems and leaf veins. Sclerenchyma cells are found bundled together or associated with other cell types to mechanically reinforce plant structures, and also form the hard outer coverings of seeds and nuts.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSclerenchyma is a supporting plant tissue composed of fibers and sclereids with thick secondary cell walls made of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. It consists of dead cells whose thickened walls make up to 90% of the cell volume, providing structure and support to plant parts that stop elongating like stems and leaf veins. Sclerenchyma cells are found bundled together or associated with other cell types to mechanically reinforce plant structures, and also form the hard outer coverings of seeds and nuts.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
222 views6 pagesSclerenchyma
Sclerenchyma
Uploaded by
Hong MingSclerenchyma is a supporting plant tissue composed of fibers and sclereids with thick secondary cell walls made of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. It consists of dead cells whose thickened walls make up to 90% of the cell volume, providing structure and support to plant parts that stop elongating like stems and leaf veins. Sclerenchyma cells are found bundled together or associated with other cell types to mechanically reinforce plant structures, and also form the hard outer coverings of seeds and nuts.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
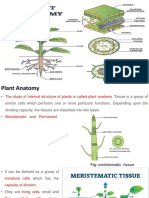
Sclerenchyma
What is sclerenchyma?
Sclerenchyma is a supporting tissue in plants.
There are 2 groups of sclerenchyma:
- Fibres and sclereids
Their walls consist of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin.
Sclerenchyma cells are the principal, supporting cells
in plant tissues that have ceased elongation.
They often occur as bundle cap fibers.
Sclerenchyma cells are characterized by thickenings in their
secondary walls.
Mature sclerenchyma is composed of dead cells with
extremely thick cell walls (secondary walls) that make up to
90% of the whole cell volume.
It is the hard, thick walls that make sclerenchyma cells
important strengthening and supporting elements in plant
parts that have ceased elongation.
The walls of these cells are very thick and built up in a uniform
layer around the entire margin of the cell. Often, the cell dies
after its cell wall is fully formed. Sclerenchyma cells are
usually found associated with other cells types and give them
mechanical support.
Sclerenchyma is found in stems and also in leaf veins.
Sclerenchyma also makes up the hard outer covering of seeds
and nuts.
You might also like
- Botany Lec - Group Work 1Document3 pagesBotany Lec - Group Work 1TJ ArciagaNo ratings yet
- Jerryrose R. Tamayo Bsoa-2BDocument6 pagesJerryrose R. Tamayo Bsoa-2BRobert MaganaNo ratings yet
- Parenchyma: Vulgaris and Other MesophytesDocument3 pagesParenchyma: Vulgaris and Other Mesophytesdamsel in distressNo ratings yet
- SclerenchymaDocument1 pageSclerenchymaMuhammad MustafaNo ratings yet
- Sclerenchyma-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesSclerenchyma-WPS OfficeFawad MalikNo ratings yet
- Class 9th Ch2 Notes-1Document3 pagesClass 9th Ch2 Notes-1jeffreywoods567890No ratings yet
- Biology: 11 OCTOBER, 2021 MondayDocument10 pagesBiology: 11 OCTOBER, 2021 MondayOyasor Ikhapo AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Tissues System FinalDocument9 pagesTissues System FinalSoha Ch100% (1)
- Meristematic TissuesDocument4 pagesMeristematic TissuesNur Syiffa RosmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18Document8 pagesLecture 18Praveen 007No ratings yet
- Simple Permanent TissueDocument9 pagesSimple Permanent Tissueking100% (1)
- Class 9 MT Science Notes TissueDocument12 pagesClass 9 MT Science Notes TissueKhushi Agrawal100% (1)
- Collenchyma-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesCollenchyma-WPS OfficeFawad MalikNo ratings yet
- Anatomy.. Paper ADocument6 pagesAnatomy.. Paper ASoha Ch100% (1)
- Plant PhysiologyDocument11 pagesPlant PhysiologyRonniedz LicotNo ratings yet
- Anatomy in Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesAnatomy in Flowering PlantsDanish UllahNo ratings yet
- Plant Histology and AnatomyDocument39 pagesPlant Histology and AnatomyN Madhusudhan50% (2)
- Plant Tissues: Epidermis Ground Tissue Vascular Tissue Biomass Leaves Xylem Phloem Differentiated PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesPlant Tissues: Epidermis Ground Tissue Vascular Tissue Biomass Leaves Xylem Phloem Differentiated Photosynthesismurari_sahu100% (1)
- Biology Plant TissuesDocument10 pagesBiology Plant TissuesChandrakala K RNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument10 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plantsl8627352No ratings yet
- 1a BIO 002 Lecture, KadiriDocument27 pages1a BIO 002 Lecture, KadiriAikay EmmaNo ratings yet
- Different Kind of Tissues in Plant and AnimalsDocument15 pagesDifferent Kind of Tissues in Plant and AnimalsKeerti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6.anatonomy of Flowering PlantsDocument12 pagesChapter 6.anatonomy of Flowering PlantsKeerthana IX-C [370]No ratings yet
- Ke L-SciDocument5 pagesKe L-SciMaricar BautistaNo ratings yet
- Sistem Peredaran Darah MamaliaDocument6 pagesSistem Peredaran Darah MamaliaAlfian IskandarNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue and Anatomy NotesDocument15 pagesPlant Tissue and Anatomy Noteskhan kashif100% (1)
- ANATOMY Short NotesDocument12 pagesANATOMY Short Notesyuganks2007No ratings yet
- hssb2101t Ir SectionDocument4 pageshssb2101t Ir Sectionfhhgghhg hggghgNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument4 pagesPresentationkaashvi2109No ratings yet
- CH 6Document6 pagesCH 6Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956No ratings yet
- Sa Nka LP: Sankalp EducationDocument3 pagesSa Nka LP: Sankalp Educationshalini priyaNo ratings yet
- 8 July 9am2 l4 ShubhdaDocument12 pages8 July 9am2 l4 ShubhdaEshu JainNo ratings yet
- Plant TissuesDocument1 pagePlant TissuesIJ SeducoNo ratings yet
- Document 35Document25 pagesDocument 35Oyasor Ikhapo AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Tissue - Class 9Document9 pagesTissue - Class 9Rohit Jain100% (1)
- Document 35Document17 pagesDocument 35Oyasor Ikhapo AnthonyNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument35 pagesTissuesAbhi LiteNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument14 pagesAnatomy of Flowering PlantsRaQtrNo ratings yet
- Plant PrintsDocument11 pagesPlant PrintsWARDAH SHOAIBNo ratings yet
- Definition and Overview of A Plant CellDocument19 pagesDefinition and Overview of A Plant CellRica NorcioNo ratings yet
- Plant TissueDocument19 pagesPlant TissueKAMESH .G100% (1)
- Plant TissuesDocument53 pagesPlant TissuesClarissa LaruanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Shobhit NirwanDocument15 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants - Shobhit NirwanPrakhar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- MF009 2B Plant Cells Tissues James L2Document12 pagesMF009 2B Plant Cells Tissues James L2Horng Ke GoNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy Class 12Document63 pagesPlant Anatomy Class 12Ranjeet Pandey100% (1)
- Info Sheets On Plant TissuesDocument6 pagesInfo Sheets On Plant TissuesjasmineecasttNo ratings yet
- The Plant Body: Tissues and MeristemDocument11 pagesThe Plant Body: Tissues and MeristemClarissa CuñaNo ratings yet
- 7.plant TissueDocument3 pages7.plant TissueRAVINDRA PRASADNo ratings yet
- 6.anatomy of Flowering Plants-FDocument28 pages6.anatomy of Flowering Plants-Fshrutianand8915No ratings yet
- Plant TissuesDocument24 pagesPlant TissuesKen Torres Paycana100% (1)
- Central Vacuole: MeristematicDocument4 pagesCentral Vacuole: MeristematicElizabeth Nicole Uy FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Permanent TissuesDocument16 pagesPermanent TissuesRiyashika RNo ratings yet
- General-Biology-2-Plant-Cells 2Document10 pagesGeneral-Biology-2-Plant-Cells 2villasencio.shaneeNo ratings yet
- 6. Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument10 pages6. Anatomy of Flowering PlantsRAJDEEP MUKHERJEENo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plantschandutalawar187No ratings yet
- Plant TissuesDocument11 pagesPlant TissuesrenzropalNo ratings yet
- Plant TissueDocument8 pagesPlant Tissueshaardesh84100% (1)
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants-Class 11Document7 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants-Class 11ICSE BOARDNo ratings yet
- Detailed Tissues Class 9 Notes (NCERT Book Chapter 6)Document12 pagesDetailed Tissues Class 9 Notes (NCERT Book Chapter 6)suman_das1983100% (8)