Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Artificial Insemination
Artificial Insemination
Uploaded by
Shrestha NeharikaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Artificial Insemination
Artificial Insemination
Uploaded by
Shrestha NeharikaCopyright:
Available Formats
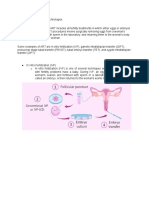
Intrauterine Insemination
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) involves a laboratory procedure to separate fast moving sperm from more sluggish or non-moving sperm. The fast moving sperm are then placed into the woman s womb close to the time of ovulation when the egg is released from the ovary in the middle of the monthly cycle.
Why this technique?
there is unexplained infertility there are ovulation problems the male partner experiences impotence or premature ejaculation you do not have any known fertility problems but may not have a male partner and are trying for a baby using donated sperm.
How does IUI work?
IUI is done between day 12 and day 16 of your monthly cycle. Many clinics will provide you with an ovulation predictor kit to detect the hormone surge that signals imminent ovulation. - or If you use fertility drugs to stimulate ovulation, vaginal ultrasound scans are used to track the development of your eggs. As soon as an egg is mature, you are given a hormone injection to stimulate its release.
The sperm are inserted 36 to 40 hours later. To do this, the doctor first inserts a speculum (a special instrument that keeps your vaginal walls apart) into your vagina (as for a cervical smear test). A small catheter (a soft, flexible tube) is then threaded into your womb via your cervix. The best quality sperm are selected and inserted through the catheter. The whole process takes just a few minutes and is usually a painless procedure but some women may experience a temporary, menstruallike cramping.
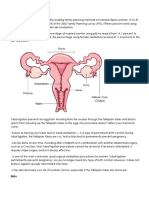
Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer
GIFT is similar to IVF. The woman's ovaries are stimulated to produce more eggs than usual, the eggs are collected, and the man needs to produce sperm (although donor sperm can be used). When egg collection has taken place, two eggs are mixed together with the sperm in a dish.
The main difference from IVF is that with GIFT the gametes (eggs and sperm) are immediately transferred to the woman's fallopian tubes, so fertilization occurs inside, not outside, the woman's body. The embryo can begin its earliest development in natural surroundings rather than in an artificial environment.
How is GIFT performed?
A woman s ovaries are stimulated with medications to increase the probability of producing multiple eggs. Eggs are collected through an aspiration procedure. Three to four eggs are immediately mixed with approximately 200,000 mobile sperm and placed in a special catheter. The mixture of eggs and sperm are transferred to the woman through a laparoscopic procedure by placing a catheter in the fallopian tube and injecting the egg/sperm mixture. The last step is to watch for early pregnancy symptoms. Your fertility specialist will probably use a blood test to determine if pregnancy has occurred.
In general, in vitro fertilization (IVF) is preferable for couples with male factor infertility. GIFT is commonly chosen by couples who have failed to conceive after trying at least one year and who have failed five to six cycles of ovarian stimulation with intrauterine insemination.
Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer
ZIFT is an assisted reproductive procedure similar to in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer, the difference being that the fertilized embryo is transferred into the fallopian tube instead of the uterus. Because the fertilized egg is transferred directly into the tubes, the procedure is also referred to as tubal embryo transfer (TET). This procedure can be more successful than gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT) because your physician has a greater chance of insuring that the egg is fertilized. The woman must have healthy tubes for ZIFT to work.
The main difference between ZIFT and GIFT is that ZIFT transfers a fertilized egg directly into the fallopian tubes while GIFT utilizes a mixture of sperm and eggs.
How is ZIFT performed?
A woman s ovaries are stimulated with medications to increase the probability of producing multiple eggs. Eggs are then collected through an aspiration procedure. Those eggs are fertilized in a laboratory in a procedure identical to IVF. The fertilized eggs are then transferred through a laparoscopic procedure where a catheter is placed deep in the fallopian tube and the fertilized eggs injected. The final step is to watch for early pregnancy symptoms. The fertility specialist will probably use a blood test to determine if pregnancy has occurred.
You might also like
- Health TalkDocument18 pagesHealth TalkMichael Ford77% (30)
- LDS OSCE Guidance For CandidatesDocument4 pagesLDS OSCE Guidance For CandidatesMohamed AlkhafajiNo ratings yet
- In-Vitro Fertilization (Ivf) : Step 1: Stimulation, Also Called Super OvulationDocument5 pagesIn-Vitro Fertilization (Ivf) : Step 1: Stimulation, Also Called Super Ovulationpriyanka100% (1)
- In Vitro Fertilization - Report - g8Document20 pagesIn Vitro Fertilization - Report - g8Maica GeeNo ratings yet
- Assited Reproductive TechnologyDocument40 pagesAssited Reproductive TechnologySanthosh.S.U100% (1)
- CMC Assisted ReproductionDocument3 pagesCMC Assisted Reproductionmavazbo1508No ratings yet
- Why and When Do You Need To Go For IVF?Document2 pagesWhy and When Do You Need To Go For IVF?gbrclinicNo ratings yet
- Procedure: in Vitro Fertilization (Ivf)Document7 pagesProcedure: in Vitro Fertilization (Ivf)Lovely SarangiNo ratings yet
- Assiated Reproductive Technology IpDocument25 pagesAssiated Reproductive Technology IpBharati patil100% (1)
- Bio IvfDocument40 pagesBio IvfkowsikakaruppasamyNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Health Problems and StrategiesDocument12 pagesReproductive Health Problems and StrategiesNirmal ChakravarthyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document19 pagesChapter 3Shelina Elora LiewNo ratings yet
- Technology PsdaDocument8 pagesTechnology PsdaSHREYANo ratings yet
- Artificial Reproductive TechniqueDocument34 pagesArtificial Reproductive TechniqueBhawna JoshiNo ratings yet
- Ivf Clinic at AurangabadDocument7 pagesIvf Clinic at AurangabadSanjay PagareNo ratings yet
- Ivf at Rajul Nursing Home, AligarhDocument2 pagesIvf at Rajul Nursing Home, AligarhAnjulaNo ratings yet
- IVF Step-By-Step - IVF Step-by-Step - FactsheetDocument12 pagesIVF Step-By-Step - IVF Step-by-Step - FactsheetashrafmogyNo ratings yet
- IVF Clinic at BhopalDocument3 pagesIVF Clinic at BhopalViraj JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Technology and Law PsdaDocument15 pagesTechnology and Law PsdaSHREYANo ratings yet
- In Vitro FertilisationDocument5 pagesIn Vitro FertilisationVikram VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Bio Seminar - ARTDocument22 pagesBio Seminar - ARTmanisha.e08No ratings yet
- ZIFTDocument13 pagesZIFT20SUBT22 GOBIKA SNo ratings yet
- Test Tube BabiesDocument1 pageTest Tube BabiesMedikoy HospitalNo ratings yet
- Reproduction ArticialDocument2 pagesReproduction ArticialXpertz PrintingNo ratings yet
- In Vitro FertilizationDocument4 pagesIn Vitro FertilizationFrances Kaye Sta. CruzNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Fertilisation Ivf at Elpis Ivf Center, PuneDocument2 pagesIn Vitro Fertilisation Ivf at Elpis Ivf Center, PuneParag RoteNo ratings yet
- What Medicines Are Used To Treat Infertility in Women?: Clomiphene CitrateDocument3 pagesWhat Medicines Are Used To Treat Infertility in Women?: Clomiphene CitrateLeigh YahNo ratings yet
- Ivf Stepbystep 201802fsivfstDocument3 pagesIvf Stepbystep 201802fsivfstfestusakinloye11No ratings yet
- Test Tube Baby1Document4 pagesTest Tube Baby1kakoliNo ratings yet
- Ivf ENTER - Final FinalDocument15 pagesIvf ENTER - Final FinalsumanavijitNo ratings yet
- 4 atDocument4 pages4 atKawaii NekoNo ratings yet
- Assisted Reproductive TechnologyDocument16 pagesAssisted Reproductive TechnologyQilaNo ratings yet
- In Vitro FertilizationDocument10 pagesIn Vitro Fertilizationbethelhemalemu126No ratings yet
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) at Pratham Aagman IVF Center, RajkotDocument2 pagesIn Vitro Fertilization (IVF) at Pratham Aagman IVF Center, RajkotNita ThakarNo ratings yet
- IN-vitro FertilisationDocument17 pagesIN-vitro FertilisationAbhishek MNo ratings yet
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) : Doaa HegabDocument23 pagesAssisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) : Doaa HegabLinguum100% (1)
- In Vitro Treatment Strategies: Over The Years Charts Have Demonstrated That There HasDocument4 pagesIn Vitro Treatment Strategies: Over The Years Charts Have Demonstrated That There HasBảo Duy Nguyễn HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Artificial Reproductive Technologies: Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer (ZIFT) Is ADocument4 pagesArtificial Reproductive Technologies: Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer (ZIFT) Is AWarp RealityNo ratings yet
- Sem VI IVFDocument5 pagesSem VI IVFFAYYAZ KHANNo ratings yet
- Bio Investigatory ProjectDocument23 pagesBio Investigatory Projectpratim.2006.ghoshNo ratings yet
- Best IVF Centre in Delhi - Best IVF Doctor in DelhiDocument14 pagesBest IVF Centre in Delhi - Best IVF Doctor in Delhiseeds of innocenceNo ratings yet
- Artificial ReproductionDocument9 pagesArtificial ReproductionSagar HanamasagarNo ratings yet
- Assisted Reproductive Technology by Rosemary C. AgboDocument19 pagesAssisted Reproductive Technology by Rosemary C. AgboRosemaryNo ratings yet
- OBGYNFY2024973REIIVFGuide 1-MaleDocument5 pagesOBGYNFY2024973REIIVFGuide 1-MaleashrafmogyNo ratings yet
- In Vitro FertilizationDocument21 pagesIn Vitro FertilizationRahul shyamNo ratings yet
- BioprojectDocument15 pagesBioprojectMohit NayakNo ratings yet
- All You Need To Know About IvfDocument3 pagesAll You Need To Know About Ivfgopika premarajanNo ratings yet
- Project Part-21Document87 pagesProject Part-21Bhimasen PradhanNo ratings yet
- Issues On ArtifDocument7 pagesIssues On ArtifRegene SorianoNo ratings yet
- Best Dr. Seng Shay WayDocument8 pagesBest Dr. Seng Shay Wayhar shishNo ratings yet
- Assisted Reproductive TechnologiesDocument19 pagesAssisted Reproductive TechnologiesGURU ROHIIT KNo ratings yet
- Assisted Reproductive TechnologyDocument16 pagesAssisted Reproductive TechnologyAnanda SadhukhanNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument8 pagesSciencePurpleNo ratings yet
- Invitro FiltrationDocument3 pagesInvitro FiltrationArivarasan SampathNo ratings yet
- Angie Writen ReportDocument3 pagesAngie Writen ReportJhunard Christian O. AsayasNo ratings yet
- 4 Artificial Reproductive Technologies - Science 10Document2 pages4 Artificial Reproductive Technologies - Science 10Czy Anne Nicole IlaganNo ratings yet
- Artificial Insemination, or AI, Is The Process by Which: Citation NeededDocument3 pagesArtificial Insemination, or AI, Is The Process by Which: Citation NeededKathleen Palencia NunezNo ratings yet
- SterilizationDocument6 pagesSterilizationMaria Ella Joanne DapitonNo ratings yet
- Ivf AssignmentDocument4 pagesIvf AssignmentNadiya RashidNo ratings yet
- In-Vitro FertilizationDocument6 pagesIn-Vitro Fertilizationlasaikono_izeNo ratings yet
- Intrauterine Insemination at Elpis IVF Center, PuneDocument3 pagesIntrauterine Insemination at Elpis IVF Center, PuneParag RoteNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer's Association and UT Research CollaborateDocument2 pagesAlzheimer's Association and UT Research CollaborateAbithsuaNo ratings yet
- Cvsi Carfmark Ma Il Service Caremarjc " Invoice/ReceiptDocument5 pagesCvsi Carfmark Ma Il Service Caremarjc " Invoice/Receipthbryant587No ratings yet
- Step 2 CK QuestionsDocument8 pagesStep 2 CK QuestionsIrfan Majeed50% (2)
- Doctor List ReportDocument66 pagesDoctor List ReportKundan KumarNo ratings yet
- Medical Secrets 6Th Edition Mary P Harward Download PDF ChapterDocument38 pagesMedical Secrets 6Th Edition Mary P Harward Download PDF Chaptervicki.krause300100% (20)
- Physical Education 10 Las No.1 Week1 2 Fourth QuarterDocument2 pagesPhysical Education 10 Las No.1 Week1 2 Fourth QuarterTheresa Vasquez Vicente100% (1)
- EpidemiologyDocument10 pagesEpidemiologyMUTHUKUMARANNo ratings yet
- CholelithiasisDocument6 pagesCholelithiasismarkzamNo ratings yet
- CHN FinaleDocument163 pagesCHN FinaleJessa Kris RialubinNo ratings yet
- Hips Back Ankles Buttocks HeelsDocument13 pagesHips Back Ankles Buttocks Heelsفرزدق الحسيناويNo ratings yet
- Husband's Support With The Use of The Iud Contraception in The Acceptors in The Working Area Puskesmas Batu AjiDocument7 pagesHusband's Support With The Use of The Iud Contraception in The Acceptors in The Working Area Puskesmas Batu AjiIntan PramestiNo ratings yet
- Application FormDocument5 pagesApplication Formapi-603319031No ratings yet
- 2023 RestorativesDocument10 pages2023 Restorativesadel abdelmageedNo ratings yet
- List of NMPA Approved Manufactrers of PPE and Medical Devices enDocument29 pagesList of NMPA Approved Manufactrers of PPE and Medical Devices enmomo kiraNo ratings yet
- Study Designs in Epidemiologic Research: Thomas Songer, PHDDocument51 pagesStudy Designs in Epidemiologic Research: Thomas Songer, PHDSaad MotawéaNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Instrumentation Techniques - Dental Ebook & Lecture Notes PDF Download (Studynama - Com - India's Biggest Website For BDS Study Material Downloads)Document23 pagesRecent Advances in Instrumentation Techniques - Dental Ebook & Lecture Notes PDF Download (Studynama - Com - India's Biggest Website For BDS Study Material Downloads)Vinnie SinghNo ratings yet
- Herpesviridae: Prof. Dr. Masood RabbaniDocument28 pagesHerpesviridae: Prof. Dr. Masood RabbaniSadam IrshadNo ratings yet
- PEG Vs Nasogastric Tube FeedingDocument64 pagesPEG Vs Nasogastric Tube FeedingTarek ElsefiNo ratings yet
- VDRL Test and Its InterpretationDocument8 pagesVDRL Test and Its InterpretationThyago SilvaNo ratings yet
- TATHLGP21248V022021Document16 pagesTATHLGP21248V022021vsharma0091No ratings yet
- Cmca2 (Prelim) 1Document10 pagesCmca2 (Prelim) 1NOEL YRIGONNo ratings yet
- KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline Hemodialysis Update - Public Review Draft FINAL - 20150204 PDFDocument78 pagesKDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline Hemodialysis Update - Public Review Draft FINAL - 20150204 PDFศักดิ์ชัย พูนศรีเจริญกุลNo ratings yet
- Workplace Handbook ReportDocument96 pagesWorkplace Handbook ReportKimm Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Coakley Resume2015Document3 pagesCoakley Resume2015api-301353549No ratings yet
- MD Aashiq Alam FileDocument5 pagesMD Aashiq Alam Filekhushi kumariNo ratings yet
- ADAFlossyGenCrossword Eng PDFDocument1 pageADAFlossyGenCrossword Eng PDFlisa.prihastariNo ratings yet
- PR 3Document23 pagesPR 3Jaylanie MabagaNo ratings yet
- Scrub and Circulating Practitioner Simulation Script - Salimbagat, UsmanDocument12 pagesScrub and Circulating Practitioner Simulation Script - Salimbagat, UsmanChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet