Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Silicon
Silicon
Uploaded by
Sean OoiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- A Study On Giant Covalent StructuresDocument3 pagesA Study On Giant Covalent StructuresNicholas TeyNo ratings yet
- Structure of Ceramics 2:: MME 295: Engineering Materials - IIDocument8 pagesStructure of Ceramics 2:: MME 295: Engineering Materials - IIFahim Faisal RaunaqNo ratings yet
- Carbon Family PDFDocument2 pagesCarbon Family PDFSankalp MishraNo ratings yet
- Why Is Graphite Soft and SlipperyDocument2 pagesWhy Is Graphite Soft and SlipperyAlejandro Calatayud PisarevskyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 Giant Covalent LatticesDocument8 pagesLesson 10 Giant Covalent Latticesdela2No ratings yet
- Describe The Differences in Volatility, Solubility and Electrical Conductivity Between Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocument6 pagesDescribe The Differences in Volatility, Solubility and Electrical Conductivity Between Ionic and Covalent Compoundsmadhuri pawarNo ratings yet
- Giant Molecular StructureDocument2 pagesGiant Molecular StructureMusa ImranNo ratings yet
- Giant Covalent Bond and Metallic Bond NotesDocument8 pagesGiant Covalent Bond and Metallic Bond Notesnihan.8558No ratings yet
- Ch3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Document11 pagesCh3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Amal HassanNo ratings yet
- GIANT COVALENT STRUCTURES-lizDocument8 pagesGIANT COVALENT STRUCTURES-lizKoluoch JrNo ratings yet
- GLY 206 NOTE 5 - SilicatesDocument4 pagesGLY 206 NOTE 5 - SilicatesOdebunmi PaulNo ratings yet
- Giant Covalent Molecule: Group 3 Chemistry L4.2Document13 pagesGiant Covalent Molecule: Group 3 Chemistry L4.2JunKenNo ratings yet
- Atoms CombiningDocument12 pagesAtoms Combiningshehryar khanNo ratings yet
- Group 14 ElementsDocument20 pagesGroup 14 Elementshernaniabdullah0% (1)
- Compounds - Bonding U1 N U2Document19 pagesCompounds - Bonding U1 N U2muhajireenNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding: AllotropesDocument7 pagesCovalent Bonding: AllotropesFatima ZahraNo ratings yet
- Final PDF For Grade 9 PDFDocument5 pagesFinal PDF For Grade 9 PDFmadhuri pawarNo ratings yet
- Kels Uni WorkDocument2 pagesKels Uni Workanon-351417No ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding LectureDocument33 pagesCovalent Bonding LectureGideon CavidaNo ratings yet
- Case Studies in Bonding and StructureDocument3 pagesCase Studies in Bonding and StructureDoc_CrocNo ratings yet
- Giant Covalent Structures (Macromolecules)Document33 pagesGiant Covalent Structures (Macromolecules)ananya.aNo ratings yet
- Che 90308 TypesofsolidsDocument4 pagesChe 90308 Typesofsolidsapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Materials & Macromolecules-OL-NotesDocument3 pagesMaterials & Macromolecules-OL-Notesshlaibat13No ratings yet
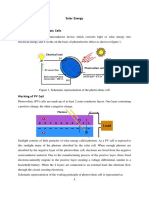
- Solar Energy - FinalDocument5 pagesSolar Energy - FinalRandomNo ratings yet
- Silicates: Which Is More Abundant in The Earth's Crust: Silicates or All The Other Mineral Groups Combined? ExplainDocument2 pagesSilicates: Which Is More Abundant in The Earth's Crust: Silicates or All The Other Mineral Groups Combined? ExplainMiya GatotNo ratings yet
- Giant Covalent Structures (SL)Document5 pagesGiant Covalent Structures (SL)Brooks RalphNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding v1.0Document45 pagesCovalent Bonding v1.0jt100% (1)
- FIGURE 3.1 - Elements in Group Four (IV)Document11 pagesFIGURE 3.1 - Elements in Group Four (IV)RonaldoNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding, Structure Lecture FileDocument17 pagesCovalent Bonding, Structure Lecture FileMahi QuaziNo ratings yet
- Unit1 Mod 3 Group IV ElementsDocument9 pagesUnit1 Mod 3 Group IV ElementsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- AMHOPHOUSDocument8 pagesAMHOPHOUSMohammad Mahmudul HasanNo ratings yet
- Silicon, Silicone and SilicatesDocument17 pagesSilicon, Silicone and SilicatesXue Yi LamNo ratings yet
- The Crystal Structure and Properties of Ionic CompoundsDocument2 pagesThe Crystal Structure and Properties of Ionic CompoundskushanNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Part 2 of 2Document62 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Part 2 of 2Sudhakar ChollangiNo ratings yet
- Comparing Covalent and Ionic Lattices S4Document3 pagesComparing Covalent and Ionic Lattices S4Fatima Ahmed-VeriterNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4: Slag in Steelmaking ContentsDocument5 pagesLecture 4: Slag in Steelmaking ContentsAbhijeet BhagavatulaNo ratings yet
- 2 Cement - Structure and Hydrationby - NADocument34 pages2 Cement - Structure and Hydrationby - NANeelesh ANo ratings yet
- AA IGCSE Unit 1 TESDocument60 pagesAA IGCSE Unit 1 TESSanthiya MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Group 14: By: Shafiq Rasila Mag Nova N HasDocument34 pagesGroup 14: By: Shafiq Rasila Mag Nova N HasShafiq HamzahNo ratings yet
- Properties of Period 3 OxidesDocument21 pagesProperties of Period 3 OxidesJayden Sue100% (1)
- Assignment - 2Document15 pagesAssignment - 2padhiyararpitaNo ratings yet
- Boys' Group 01: Covalent CrystalsDocument14 pagesBoys' Group 01: Covalent Crystalsusman aliNo ratings yet
- Chem PresentationDocument11 pagesChem Presentationsamoya smithNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Properties of Solids StudentDocument7 pages3.2 Properties of Solids StudentZachary Daniel UyNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument25 pagesChemical Bondingjoannavera2020No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding-NotesDocument47 pagesChemical Bonding-NotesHimanshu Meena100% (3)
- Notes On Covalent and Metallic BondingDocument8 pagesNotes On Covalent and Metallic Bondingselma samadNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Silicon and GermaniumDocument4 pagesComparison of Silicon and Germaniumpatrick_carballo78% (9)
- Ionic Bonding and StructureDocument20 pagesIonic Bonding and StructureKaren OrlanskiNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Pigments and GlassesDocument19 pagesCeramic Pigments and GlassesalbaqueNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESODocument6 pagesChemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESOurgazuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Ionic and Covalent BondingDocument2 pagesChemistry-Ionic and Covalent Bondingifaitchwould2No ratings yet
- Name - Bee Bee Iqra Department - Msc. Chemistry: Sem - 2 SemesterDocument15 pagesName - Bee Bee Iqra Department - Msc. Chemistry: Sem - 2 SemesterAna PattinsonNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument11 pagesChemical BondingAsilah AsyiqinNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Period 3Document4 pagesExperiment 1 Period 3Linges LingeswaranNo ratings yet
- Giant Ionic and Giant CovalentDocument8 pagesGiant Ionic and Giant CovalentSamuelNo ratings yet
- L7 - Ionic Compounds PropertiesDocument19 pagesL7 - Ionic Compounds PropertiesKashifNo ratings yet
- Structures of SolidsDocument6 pagesStructures of SolidsAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- Volatile Silicon Compounds: International Series of Monographs on Inorganic ChemistryFrom EverandVolatile Silicon Compounds: International Series of Monographs on Inorganic ChemistryNo ratings yet
Silicon
Silicon
Uploaded by
Sean OoiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Silicon
Silicon
Uploaded by
Sean OoiCopyright:
Available Formats
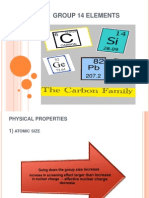
SILICON (IV) OXIDE (SIO2)
Si atom is attached to 4 O atoms.
O atom is attached to 2 Si atoms.
Structure of (SIO2)
Lattice Particles : Silicon atom and oxygen atoms. Lattice Forces : Strong covalent forces.
SILICON (IV) OXIDE (SIO2) has a
GIANT MOLECULAR STRUCTURE like that of a
diamond.
Each silicon is covalently bonded to four oxygen atoms while oxygen is covalently bonded with two silicon atoms. This gives Si/O ratio of 1:2 and therefore, a formula SIO2
Properties of SIO2
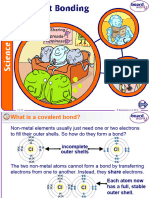
It has a very high melting point (due to strong covalent bond) Therefore, the strong covalent bond needs to be broken down throughout the structure before melting occur. It is also very hard (due to strong
covalent bond)
It doesnt conduct electricity. This is because there is no delocalised electron, and all electrons are held tightly between the atoms, therefore they cannot move freely. It is INSOLUBLE in water and organic solvent. This is because there is no attraction forces that can occur between solvent molecules and the silicon and oxygen atoms which could overcome
You might also like
- A Study On Giant Covalent StructuresDocument3 pagesA Study On Giant Covalent StructuresNicholas TeyNo ratings yet
- Structure of Ceramics 2:: MME 295: Engineering Materials - IIDocument8 pagesStructure of Ceramics 2:: MME 295: Engineering Materials - IIFahim Faisal RaunaqNo ratings yet
- Carbon Family PDFDocument2 pagesCarbon Family PDFSankalp MishraNo ratings yet
- Why Is Graphite Soft and SlipperyDocument2 pagesWhy Is Graphite Soft and SlipperyAlejandro Calatayud PisarevskyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 Giant Covalent LatticesDocument8 pagesLesson 10 Giant Covalent Latticesdela2No ratings yet
- Describe The Differences in Volatility, Solubility and Electrical Conductivity Between Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocument6 pagesDescribe The Differences in Volatility, Solubility and Electrical Conductivity Between Ionic and Covalent Compoundsmadhuri pawarNo ratings yet
- Giant Molecular StructureDocument2 pagesGiant Molecular StructureMusa ImranNo ratings yet
- Giant Covalent Bond and Metallic Bond NotesDocument8 pagesGiant Covalent Bond and Metallic Bond Notesnihan.8558No ratings yet
- Ch3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Document11 pagesCh3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Amal HassanNo ratings yet
- GIANT COVALENT STRUCTURES-lizDocument8 pagesGIANT COVALENT STRUCTURES-lizKoluoch JrNo ratings yet
- GLY 206 NOTE 5 - SilicatesDocument4 pagesGLY 206 NOTE 5 - SilicatesOdebunmi PaulNo ratings yet
- Giant Covalent Molecule: Group 3 Chemistry L4.2Document13 pagesGiant Covalent Molecule: Group 3 Chemistry L4.2JunKenNo ratings yet
- Atoms CombiningDocument12 pagesAtoms Combiningshehryar khanNo ratings yet
- Group 14 ElementsDocument20 pagesGroup 14 Elementshernaniabdullah0% (1)
- Compounds - Bonding U1 N U2Document19 pagesCompounds - Bonding U1 N U2muhajireenNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding: AllotropesDocument7 pagesCovalent Bonding: AllotropesFatima ZahraNo ratings yet
- Final PDF For Grade 9 PDFDocument5 pagesFinal PDF For Grade 9 PDFmadhuri pawarNo ratings yet
- Kels Uni WorkDocument2 pagesKels Uni Workanon-351417No ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding LectureDocument33 pagesCovalent Bonding LectureGideon CavidaNo ratings yet
- Case Studies in Bonding and StructureDocument3 pagesCase Studies in Bonding and StructureDoc_CrocNo ratings yet
- Giant Covalent Structures (Macromolecules)Document33 pagesGiant Covalent Structures (Macromolecules)ananya.aNo ratings yet
- Che 90308 TypesofsolidsDocument4 pagesChe 90308 Typesofsolidsapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Materials & Macromolecules-OL-NotesDocument3 pagesMaterials & Macromolecules-OL-Notesshlaibat13No ratings yet
- Solar Energy - FinalDocument5 pagesSolar Energy - FinalRandomNo ratings yet
- Silicates: Which Is More Abundant in The Earth's Crust: Silicates or All The Other Mineral Groups Combined? ExplainDocument2 pagesSilicates: Which Is More Abundant in The Earth's Crust: Silicates or All The Other Mineral Groups Combined? ExplainMiya GatotNo ratings yet
- Giant Covalent Structures (SL)Document5 pagesGiant Covalent Structures (SL)Brooks RalphNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding v1.0Document45 pagesCovalent Bonding v1.0jt100% (1)
- FIGURE 3.1 - Elements in Group Four (IV)Document11 pagesFIGURE 3.1 - Elements in Group Four (IV)RonaldoNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding, Structure Lecture FileDocument17 pagesCovalent Bonding, Structure Lecture FileMahi QuaziNo ratings yet
- Unit1 Mod 3 Group IV ElementsDocument9 pagesUnit1 Mod 3 Group IV ElementsNkemzi Elias NzetengenleNo ratings yet
- AMHOPHOUSDocument8 pagesAMHOPHOUSMohammad Mahmudul HasanNo ratings yet
- Silicon, Silicone and SilicatesDocument17 pagesSilicon, Silicone and SilicatesXue Yi LamNo ratings yet
- The Crystal Structure and Properties of Ionic CompoundsDocument2 pagesThe Crystal Structure and Properties of Ionic CompoundskushanNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Part 2 of 2Document62 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Part 2 of 2Sudhakar ChollangiNo ratings yet
- Comparing Covalent and Ionic Lattices S4Document3 pagesComparing Covalent and Ionic Lattices S4Fatima Ahmed-VeriterNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4: Slag in Steelmaking ContentsDocument5 pagesLecture 4: Slag in Steelmaking ContentsAbhijeet BhagavatulaNo ratings yet
- 2 Cement - Structure and Hydrationby - NADocument34 pages2 Cement - Structure and Hydrationby - NANeelesh ANo ratings yet
- AA IGCSE Unit 1 TESDocument60 pagesAA IGCSE Unit 1 TESSanthiya MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Group 14: By: Shafiq Rasila Mag Nova N HasDocument34 pagesGroup 14: By: Shafiq Rasila Mag Nova N HasShafiq HamzahNo ratings yet
- Properties of Period 3 OxidesDocument21 pagesProperties of Period 3 OxidesJayden Sue100% (1)
- Assignment - 2Document15 pagesAssignment - 2padhiyararpitaNo ratings yet
- Boys' Group 01: Covalent CrystalsDocument14 pagesBoys' Group 01: Covalent Crystalsusman aliNo ratings yet
- Chem PresentationDocument11 pagesChem Presentationsamoya smithNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Properties of Solids StudentDocument7 pages3.2 Properties of Solids StudentZachary Daniel UyNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument25 pagesChemical Bondingjoannavera2020No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding-NotesDocument47 pagesChemical Bonding-NotesHimanshu Meena100% (3)
- Notes On Covalent and Metallic BondingDocument8 pagesNotes On Covalent and Metallic Bondingselma samadNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Silicon and GermaniumDocument4 pagesComparison of Silicon and Germaniumpatrick_carballo78% (9)
- Ionic Bonding and StructureDocument20 pagesIonic Bonding and StructureKaren OrlanskiNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Pigments and GlassesDocument19 pagesCeramic Pigments and GlassesalbaqueNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESODocument6 pagesChemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESOurgazuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Ionic and Covalent BondingDocument2 pagesChemistry-Ionic and Covalent Bondingifaitchwould2No ratings yet
- Name - Bee Bee Iqra Department - Msc. Chemistry: Sem - 2 SemesterDocument15 pagesName - Bee Bee Iqra Department - Msc. Chemistry: Sem - 2 SemesterAna PattinsonNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument11 pagesChemical BondingAsilah AsyiqinNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Period 3Document4 pagesExperiment 1 Period 3Linges LingeswaranNo ratings yet
- Giant Ionic and Giant CovalentDocument8 pagesGiant Ionic and Giant CovalentSamuelNo ratings yet
- L7 - Ionic Compounds PropertiesDocument19 pagesL7 - Ionic Compounds PropertiesKashifNo ratings yet
- Structures of SolidsDocument6 pagesStructures of SolidsAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- Volatile Silicon Compounds: International Series of Monographs on Inorganic ChemistryFrom EverandVolatile Silicon Compounds: International Series of Monographs on Inorganic ChemistryNo ratings yet