Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Uploaded by
Rashmi HarneCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- CiscoDocument7 pagesCiscoJill_xyinz14589No ratings yet
- Network Address Translation: Presented by Varsha HondeDocument22 pagesNetwork Address Translation: Presented by Varsha HondeTú HoàngNo ratings yet
- NAT and PATDocument4 pagesNAT and PATAbenezer TarikuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Network Address Translation (NAT)Document4 pagesIntroduction To Network Address Translation (NAT)Firemandeheavenly InamenNo ratings yet
- NAT (Network Address Translation) : Defining NAT Inside and Outside InterfacesDocument6 pagesNAT (Network Address Translation) : Defining NAT Inside and Outside Interfacesimb2No ratings yet
- What Is NATDocument9 pagesWhat Is NATBelete TilahunNo ratings yet
- New Network ProjectDocument13 pagesNew Network ProjectSubham PandeyNo ratings yet
- NAT and PATDocument2 pagesNAT and PATAtik Israk Lemon100% (1)
- Configuring Static NAT in Cisco RouterDocument10 pagesConfiguring Static NAT in Cisco RouterDeepthi. rajshekarNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation NAT TutorialDocument4 pagesNetwork Address Translation NAT Tutorialjorge jaramillo coronellNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NATDocument9 pagesIntroduction To NATShaba MichaelNo ratings yet
- 52 Nat PatDocument5 pages52 Nat PatBHARYNo ratings yet
- NAT PAN TheoryDocument9 pagesNAT PAN TheoryArun SomashekarNo ratings yet
- NAT in DetailDocument12 pagesNAT in DetailRahul MishraNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation: Naveen PatelDocument18 pagesNetwork Address Translation: Naveen PatelNishant MishraNo ratings yet
- 24 Network Address TranslationDocument20 pages24 Network Address TranslationRakesh CharyNo ratings yet
- How Network Address Translation WorksDocument8 pagesHow Network Address Translation WorksPhaniraj LenkalapallyNo ratings yet
- DHCP and NAT - Knowledge BaseDocument6 pagesDHCP and NAT - Knowledge BaseHasib Hamidul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Fatima Jinnah Women University: Items DescriptionDocument5 pagesFatima Jinnah Women University: Items DescriptionfaizaNo ratings yet
- CN LEC Four - 2Document38 pagesCN LEC Four - 2Michael HauleNo ratings yet
- Network Address TranslationDocument86 pagesNetwork Address Translationchauhanbinod24No ratings yet
- CCNA NAT ConfigurationDocument3 pagesCCNA NAT Configurationsneha77No ratings yet
- How NAT WorksDocument10 pagesHow NAT WorksRajNo ratings yet
- Configuration of DHCP & DNS Along With PAT ConfigurationDocument28 pagesConfiguration of DHCP & DNS Along With PAT ConfigurationKoushik Q SarkarNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 NATDocument11 pagesLab 6 NATCharles CarpenterNo ratings yet
- Topology Hiding - Vijay - TopDocument52 pagesTopology Hiding - Vijay - TopnepoznateNo ratings yet
- Nat Basics PDFDocument48 pagesNat Basics PDFeveswan2008No ratings yet
- Network Address Translation (NAT)Document49 pagesNetwork Address Translation (NAT)Kero MaalosaNo ratings yet
- Notes For Lecture-11 MCA 206: Advanced Computer NetworksDocument8 pagesNotes For Lecture-11 MCA 206: Advanced Computer NetworksDilip DubeyNo ratings yet
- Configuring Static and Dynamic Nat TranslationDocument24 pagesConfiguring Static and Dynamic Nat TranslationMiguel Angel FeriaNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation (NAT)Document16 pagesNetwork Address Translation (NAT)Mubarik Ali MuhumedNo ratings yet
- Nat - Overview 8.3 and LaterDocument24 pagesNat - Overview 8.3 and LaterThomas SchmelingNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 5 PDFDocument34 pagesLecture - 5 PDFLatera FekedeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Nat PatDocument21 pagesLecture 9 Nat PatTanvir ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Configuring Static and Dynamic Nat TranslationDocument18 pagesConfiguring Static and Dynamic Nat Translationmanarkim44No ratings yet
- Access The Public Internet Via Network Address Translation (NAT)Document7 pagesAccess The Public Internet Via Network Address Translation (NAT)Hotico CatalinNo ratings yet
- Anshul Gupta Synopsis NatDocument7 pagesAnshul Gupta Synopsis NatKing DigitalNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation (NAT) & Port Address Translation (PAT)Document1 pageNetwork Address Translation (NAT) & Port Address Translation (PAT)devanasontaniya738No ratings yet
- Nat Basics PDFDocument46 pagesNat Basics PDFDorivaldoNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation (NAT) Is A Process in Which One or More Local IP AddressDocument10 pagesNetwork Address Translation (NAT) Is A Process in Which One or More Local IP AddresslijmatiosNo ratings yet
- 4.7 - IP Addressing ServicesDocument4 pages4.7 - IP Addressing Serviceskrs4kesharaNo ratings yet
- NAT WBUT (MAKAUT) Short NoteDocument3 pagesNAT WBUT (MAKAUT) Short NoteSayantan PalNo ratings yet
- Project Report Tim KaddouraDocument7 pagesProject Report Tim KaddouraKHILESHNo ratings yet
- Factsheet IPv6Document2 pagesFactsheet IPv6Daniel ChecchiaNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation NAT For Threat DefenseDocument66 pagesNetwork Address Translation NAT For Threat DefensesaurabhNo ratings yet
- 006 57-NAT On FTDDocument6 pages006 57-NAT On FTDPractical1No ratings yet
- Chapter 4b IPv6 FeaturesDocument18 pagesChapter 4b IPv6 Featuresbettelly84No ratings yet
- TCP/IP Protocol Suite and IP AddressingDocument31 pagesTCP/IP Protocol Suite and IP AddressingHungry LadyNo ratings yet
- Design of IPV6 Enterprise Network With Stateless Address Auto ConfigurationDocument5 pagesDesign of IPV6 Enterprise Network With Stateless Address Auto ConfigurationsaravananaecNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Design of IP Address & RoutingDocument88 pagesTopic 3 - Design of IP Address & Routingfentahunmuluye23No ratings yet
- Information About NATDocument24 pagesInformation About NATsrikanth kNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Network Address TranslationDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Network Address Translationpabup1hebyl2100% (1)
- Nat - 6Document72 pagesNat - 6etiNo ratings yet
- Experiment On Dynamic NATDocument6 pagesExperiment On Dynamic NATpial hasan BornoNo ratings yet
- NAT For FTDDocument108 pagesNAT For FTDTim BurchmoreNo ratings yet
- Nat in Voip: RequirementsDocument19 pagesNat in Voip: Requirementsgarytj21No ratings yet
- NAT and PATDocument17 pagesNAT and PATAbhishrkNo ratings yet
- IP AddressDocument33 pagesIP AddressVikas JatNo ratings yet
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Uploaded by
Rashmi HarneOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Uploaded by
Rashmi HarneCopyright:
Available Formats
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Objectives:
Network Address Translation (NAT) Static NAT Dynamic NAT Port Address Translation (PAT)
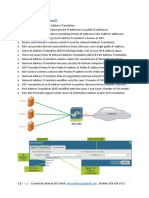
Network Address Translation
Network Address Translation is the translation of public IP address to private IP address or private IP address to public IP address while using the Internet over the Web Server. Characteristics:
Operate at Network Layer of OSI model Overcome the problem of lack of public IP addresses Provide security from hackers by hiding addresses Transparent to the source and destination computers
NAT Implementation
NAT is implemented using two techniques:
Static Address Translation Dynamic Address Translation
Static NAT
It allows you to establish a one-to-one mapping between local and global addresses. Static NAT requires same number of public IP addresses as that of private IP addresses, that's why it is called as one to one mapping. In this technique more number of public IP addresses are required.
Dynamic NAT
It allows you to establish dynamic mapping between local and global addesses. In dynamic mapping, it creates a group of public IP addresses which are to be assigned to private IP addresses. The number of public IP addresses is limited, which is advantage over the Static NAT.
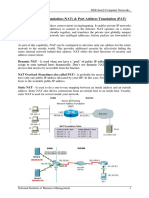
Port Address Translation (PAT)
The Port Address Translation (PAT) is used to translate internal addresses to only one or a few external addresses. In a PAT implemented network, the router assigns same IP address to all the devices, but uses different port numbers The total number of port numbers can theoretically be as high as 65,536 per IP address. It is the most useful technique over the above two as it uses only one public IP address.
You might also like
- CiscoDocument7 pagesCiscoJill_xyinz14589No ratings yet
- Network Address Translation: Presented by Varsha HondeDocument22 pagesNetwork Address Translation: Presented by Varsha HondeTú HoàngNo ratings yet
- NAT and PATDocument4 pagesNAT and PATAbenezer TarikuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Network Address Translation (NAT)Document4 pagesIntroduction To Network Address Translation (NAT)Firemandeheavenly InamenNo ratings yet
- NAT (Network Address Translation) : Defining NAT Inside and Outside InterfacesDocument6 pagesNAT (Network Address Translation) : Defining NAT Inside and Outside Interfacesimb2No ratings yet
- What Is NATDocument9 pagesWhat Is NATBelete TilahunNo ratings yet
- New Network ProjectDocument13 pagesNew Network ProjectSubham PandeyNo ratings yet
- NAT and PATDocument2 pagesNAT and PATAtik Israk Lemon100% (1)
- Configuring Static NAT in Cisco RouterDocument10 pagesConfiguring Static NAT in Cisco RouterDeepthi. rajshekarNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation NAT TutorialDocument4 pagesNetwork Address Translation NAT Tutorialjorge jaramillo coronellNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NATDocument9 pagesIntroduction To NATShaba MichaelNo ratings yet
- 52 Nat PatDocument5 pages52 Nat PatBHARYNo ratings yet
- NAT PAN TheoryDocument9 pagesNAT PAN TheoryArun SomashekarNo ratings yet
- NAT in DetailDocument12 pagesNAT in DetailRahul MishraNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation: Naveen PatelDocument18 pagesNetwork Address Translation: Naveen PatelNishant MishraNo ratings yet
- 24 Network Address TranslationDocument20 pages24 Network Address TranslationRakesh CharyNo ratings yet
- How Network Address Translation WorksDocument8 pagesHow Network Address Translation WorksPhaniraj LenkalapallyNo ratings yet
- DHCP and NAT - Knowledge BaseDocument6 pagesDHCP and NAT - Knowledge BaseHasib Hamidul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Fatima Jinnah Women University: Items DescriptionDocument5 pagesFatima Jinnah Women University: Items DescriptionfaizaNo ratings yet
- CN LEC Four - 2Document38 pagesCN LEC Four - 2Michael HauleNo ratings yet
- Network Address TranslationDocument86 pagesNetwork Address Translationchauhanbinod24No ratings yet
- CCNA NAT ConfigurationDocument3 pagesCCNA NAT Configurationsneha77No ratings yet
- How NAT WorksDocument10 pagesHow NAT WorksRajNo ratings yet
- Configuration of DHCP & DNS Along With PAT ConfigurationDocument28 pagesConfiguration of DHCP & DNS Along With PAT ConfigurationKoushik Q SarkarNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 NATDocument11 pagesLab 6 NATCharles CarpenterNo ratings yet
- Topology Hiding - Vijay - TopDocument52 pagesTopology Hiding - Vijay - TopnepoznateNo ratings yet
- Nat Basics PDFDocument48 pagesNat Basics PDFeveswan2008No ratings yet
- Network Address Translation (NAT)Document49 pagesNetwork Address Translation (NAT)Kero MaalosaNo ratings yet
- Notes For Lecture-11 MCA 206: Advanced Computer NetworksDocument8 pagesNotes For Lecture-11 MCA 206: Advanced Computer NetworksDilip DubeyNo ratings yet
- Configuring Static and Dynamic Nat TranslationDocument24 pagesConfiguring Static and Dynamic Nat TranslationMiguel Angel FeriaNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation (NAT)Document16 pagesNetwork Address Translation (NAT)Mubarik Ali MuhumedNo ratings yet
- Nat - Overview 8.3 and LaterDocument24 pagesNat - Overview 8.3 and LaterThomas SchmelingNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 5 PDFDocument34 pagesLecture - 5 PDFLatera FekedeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Nat PatDocument21 pagesLecture 9 Nat PatTanvir ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Configuring Static and Dynamic Nat TranslationDocument18 pagesConfiguring Static and Dynamic Nat Translationmanarkim44No ratings yet
- Access The Public Internet Via Network Address Translation (NAT)Document7 pagesAccess The Public Internet Via Network Address Translation (NAT)Hotico CatalinNo ratings yet
- Anshul Gupta Synopsis NatDocument7 pagesAnshul Gupta Synopsis NatKing DigitalNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation (NAT) & Port Address Translation (PAT)Document1 pageNetwork Address Translation (NAT) & Port Address Translation (PAT)devanasontaniya738No ratings yet
- Nat Basics PDFDocument46 pagesNat Basics PDFDorivaldoNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation (NAT) Is A Process in Which One or More Local IP AddressDocument10 pagesNetwork Address Translation (NAT) Is A Process in Which One or More Local IP AddresslijmatiosNo ratings yet
- 4.7 - IP Addressing ServicesDocument4 pages4.7 - IP Addressing Serviceskrs4kesharaNo ratings yet
- NAT WBUT (MAKAUT) Short NoteDocument3 pagesNAT WBUT (MAKAUT) Short NoteSayantan PalNo ratings yet
- Project Report Tim KaddouraDocument7 pagesProject Report Tim KaddouraKHILESHNo ratings yet
- Factsheet IPv6Document2 pagesFactsheet IPv6Daniel ChecchiaNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation NAT For Threat DefenseDocument66 pagesNetwork Address Translation NAT For Threat DefensesaurabhNo ratings yet
- 006 57-NAT On FTDDocument6 pages006 57-NAT On FTDPractical1No ratings yet
- Chapter 4b IPv6 FeaturesDocument18 pagesChapter 4b IPv6 Featuresbettelly84No ratings yet
- TCP/IP Protocol Suite and IP AddressingDocument31 pagesTCP/IP Protocol Suite and IP AddressingHungry LadyNo ratings yet
- Design of IPV6 Enterprise Network With Stateless Address Auto ConfigurationDocument5 pagesDesign of IPV6 Enterprise Network With Stateless Address Auto ConfigurationsaravananaecNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Design of IP Address & RoutingDocument88 pagesTopic 3 - Design of IP Address & Routingfentahunmuluye23No ratings yet
- Information About NATDocument24 pagesInformation About NATsrikanth kNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Network Address TranslationDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Network Address Translationpabup1hebyl2100% (1)
- Nat - 6Document72 pagesNat - 6etiNo ratings yet
- Experiment On Dynamic NATDocument6 pagesExperiment On Dynamic NATpial hasan BornoNo ratings yet
- NAT For FTDDocument108 pagesNAT For FTDTim BurchmoreNo ratings yet
- Nat in Voip: RequirementsDocument19 pagesNat in Voip: Requirementsgarytj21No ratings yet
- NAT and PATDocument17 pagesNAT and PATAbhishrkNo ratings yet
- IP AddressDocument33 pagesIP AddressVikas JatNo ratings yet