Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intro To Trig Day 5 Worksheet
Intro To Trig Day 5 Worksheet
Uploaded by
mbpershanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Intro To Trig Day 5 Worksheet
Intro To Trig Day 5 Worksheet
Uploaded by
mbpershanCopyright:
Available Formats
Intro to Trig: Day Five
Important Stuff 1. Complete this table.
Name:________________________
sin( ) =
cos( ) =
= 30 = 45 = 270 = 210 = 0
( sin( ) ) 2 + ( cos( ) ) 2
2. For each quadrant below, determine if the sine and cosine of an angle whose terminal ray falls in the quadrant is positive (+) or negative (-).
3. Suppose that for some angle , we know that sin( ) =
could the angle be in?
2 . What quadrant 3
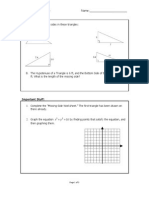
4. Suppose that for some angle , we know that cos( ) = 0.234 and that sin( ) < 0 . What quadrant is the angle in? 5. Were going to prove that sin 2 ( ) + cos 2 ( ) = 1 , always.
a. What is the equation of the unit circle?
b. By definition, x = cos( ) and y = sin( ) . Make a substitution into the
equation of the unit circle that gives you what were trying to prove.
Page 1 of 2
Intro to Trig: Day Five
Name:________________________
6. The theorem that you just proved is often called the Pythagorean Identity.
What does the theorem have to do with the Pythagorean Theorem? Is it similar? Different? Write a sentence or two of your thoughts.
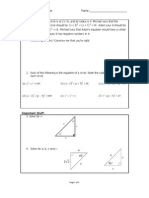
7. Suppose that, for some angle a in the second quadrant, sin( a ) =
figuring out what angle a is equal to, what is cos(a ) ?
3 . Without 5
8. An angle, , has a terminal ray that falls in the first quadrant and cos( ) =
Determine sin( ) , and put your answer in simplest radical form.
1 . 3
Interesting Stuff Here are some next steps to investigate: What does the graph of y = sin(x) look like? What happens if you change a, b or c in y = a sin(bx) + c ? Can you do a trigonometric regression? What sort of data would the trigonometric graphs be a good fit for?
Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Grade 11 Trigonometry TestDocument5 pagesGrade 11 Trigonometry Testingroy75% (8)
- FE Math PracticeDocument8 pagesFE Math PracticeAdam Wilkins71% (7)
- Visual Patterns For Exponentials Period 2Document6 pagesVisual Patterns For Exponentials Period 2mbpershanNo ratings yet
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Trigonometric FunctionsDocument27 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Trigonometric FunctionsPrasanth VarrierNo ratings yet
- Period 1 Patterns PageDocument2 pagesPeriod 1 Patterns PagembpershanNo ratings yet
- Trig SubstitutionDocument13 pagesTrig SubstitutionwillygopeNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions in The Unit CircleDocument10 pagesTrigonometric Functions in The Unit CircleDerick John PalapagNo ratings yet
- Trig Problem SetDocument6 pagesTrig Problem Setshreesha mNo ratings yet
- Algebra Basic Rules in Algebra: M N M+N M N M-N M N MN M M M M M M M/N - M M oDocument61 pagesAlgebra Basic Rules in Algebra: M N M+N M N M-N M N MN M M M M M M M/N - M M oChristian ArloNo ratings yet
- Last TrigDocument18 pagesLast TrigsamjshahNo ratings yet
- NCERT Class 11 Maths Trigonometric Functions QuestionsDocument27 pagesNCERT Class 11 Maths Trigonometric Functions QuestionsDouglas Beach100% (1)
- Lesson Plan: Class: Algebra Grade Level: Freshmen and Sophomores Unit: Introduction To Geometry Teacher: Ms. Carolyn YusaDocument9 pagesLesson Plan: Class: Algebra Grade Level: Freshmen and Sophomores Unit: Introduction To Geometry Teacher: Ms. Carolyn Yusaapi-608246476No ratings yet
- Solutions1 12Document107 pagesSolutions1 12Mario ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Trig TestDocument7 pagesUnit 5 Trig Testarg456No ratings yet
- GRE Mathematics Subject Test GR0568 Solutions: Charles RamboDocument50 pagesGRE Mathematics Subject Test GR0568 Solutions: Charles RambopmhashiNo ratings yet
- 7 The Trigonometric Functions (A.k.a. The Circular Functions)Document8 pages7 The Trigonometric Functions (A.k.a. The Circular Functions)a2hasijaNo ratings yet
- Math9 Q4 Week1 2 Hybrid Version2Document19 pagesMath9 Q4 Week1 2 Hybrid Version2Mystic AungNo ratings yet
- Intermediate GeometryDocument16 pagesIntermediate GeometryD.SREEPRANAD 7a2020No ratings yet
- Trigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument10 pagesTrigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig Functionsmonelmetal100% (1)
- Trigonometric Functions: 3.1 OverviewDocument27 pagesTrigonometric Functions: 3.1 OverviewkennedyNo ratings yet
- Complex NumbersDocument6 pagesComplex NumbersJyiou YimushiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Trigonometry: Section 4.1: AnglesDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Trigonometry: Section 4.1: AnglesMuralikrishna SingamaneniNo ratings yet
- Geometry 1Document11 pagesGeometry 1ayavuyancoko14No ratings yet
- Thumbnail HereDocument115 pagesThumbnail HereFor 3rd Party signupsNo ratings yet
- Inequalities-Olympiad-Method With Partial DifferentiationDocument6 pagesInequalities-Olympiad-Method With Partial Differentiationsanits591No ratings yet
- A Short Introduction To Interval Analysis: Raazesh SainudiinDocument139 pagesA Short Introduction To Interval Analysis: Raazesh SainudiinRufai OlalekanNo ratings yet
- For Math MajorsDocument3 pagesFor Math MajorsMissEu Ferrer Montericz100% (3)
- MATS 4217 Tutorial 1Document4 pagesMATS 4217 Tutorial 1nchangdania05No ratings yet
- The Pythagorean Theorem and The Angle Sum and Difference IdentititesDocument3 pagesThe Pythagorean Theorem and The Angle Sum and Difference IdentititesJUANNo ratings yet
- FHMW Student EditionDocument211 pagesFHMW Student EditionsammycatNo ratings yet
- Math Formulas For Class XDocument6 pagesMath Formulas For Class Xravilakra lakraNo ratings yet
- Elementary MathematicsDocument14 pagesElementary MathematicsViet Quoc Hoang100% (1)
- High School Secrets: 1 Translation and Rotation MatterDocument6 pagesHigh School Secrets: 1 Translation and Rotation MatterViet Quoc Hoang100% (2)
- A Letter To My Algebra 2 Students On Complex NumbersDocument5 pagesA Letter To My Algebra 2 Students On Complex NumbersmbpershanNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - TrigonometryDocument10 pagesTopic 3 - Trigonometryapi-25887606100% (1)
- Cosine of Rational AnglesDocument6 pagesCosine of Rational Anglesjugoo653No ratings yet
- Applications of Number Theory 163: K K K 1 K 1 1 0 0 1 2 KDocument7 pagesApplications of Number Theory 163: K K K 1 K 1 1 0 0 1 2 Ktukicool8892No ratings yet
- Graphing Sine and CosineDocument17 pagesGraphing Sine and CosineNiaNo ratings yet
- Ps 1 SolDocument3 pagesPs 1 SolPang XsNo ratings yet
- Prove Trig IdentitiesDocument2 pagesProve Trig IdentitiesAnas ElgaudNo ratings yet
- FE Math ReviewDocument44 pagesFE Math Reviewskillzxiv100% (1)
- Lesson 4-8 Stem 1BDocument15 pagesLesson 4-8 Stem 1BJune Patricia AraizNo ratings yet
- Class1 WorksheetDocument4 pagesClass1 WorksheetWill SeagravesNo ratings yet
- Bith212 Unit 1 IntegersDocument35 pagesBith212 Unit 1 IntegersAntonateNo ratings yet
- 1 Asymptotic Notation IntroDocument4 pages1 Asymptotic Notation IntroKarin AngelisNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument3 pagesTrigonometryvitalismdriveNo ratings yet
- 2020-21 Unit 1 - Trigonometry Student NotesDocument20 pages2020-21 Unit 1 - Trigonometry Student Notesapi-335847647No ratings yet
- Discrete MathematicsDocument11 pagesDiscrete MathematicsRohit SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 62 Trigonometric Ratio & Identity Part 1 of 2Document12 pages62 Trigonometric Ratio & Identity Part 1 of 2Mayank SainiNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities: Peggy AdamsonDocument17 pagesTrigonometric Identities: Peggy AdamsonAbdul RahimNo ratings yet
- Problems: Ted Eisenberg, Section EditorDocument16 pagesProblems: Ted Eisenberg, Section Editorสฮาบูดีน สาและNo ratings yet
- AP Review Chapter 3Document20 pagesAP Review Chapter 3DSaulBNo ratings yet
- Solved Exercise Boolean Algebra 131004063357 Phpapp02 PDFDocument35 pagesSolved Exercise Boolean Algebra 131004063357 Phpapp02 PDFjamaros0% (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- No Calculators, Please! 1a. Simplify The Expression 2 - 1b. How Sure Are You About Your Answer?Document1 pageNo Calculators, Please! 1a. Simplify The Expression 2 - 1b. How Sure Are You About Your Answer?mbpershanNo ratings yet
- Exponents Survey Part 1Document23 pagesExponents Survey Part 1mbpershanNo ratings yet
- Best Worst ClassroomsDocument4 pagesBest Worst ClassroomsmbpershanNo ratings yet
- Table CardsDocument3 pagesTable CardsmbpershanNo ratings yet
- A Letter To My Algebra 2 Students On Complex NumbersDocument5 pagesA Letter To My Algebra 2 Students On Complex NumbersmbpershanNo ratings yet
- Handout p2d1Document2 pagesHandout p2d1mbpershanNo ratings yet
- Best Worst ClassroomsDocument2 pagesBest Worst ClassroomsmbpershanNo ratings yet
- Handout p2d1Document2 pagesHandout p2d1mbpershanNo ratings yet
- Equations of Circles (11E)Document20 pagesEquations of Circles (11E)mbpershanNo ratings yet
- Plinko HandoutDocument2 pagesPlinko HandoutmbpershanNo ratings yet
- Self and Society - Course Plan v1.9Document5 pagesSelf and Society - Course Plan v1.9mbpershanNo ratings yet
- Intro To Trig P3 Day OneDocument3 pagesIntro To Trig P3 Day OnembpershanNo ratings yet
- Tan Function1Document3 pagesTan Function1mbpershanNo ratings yet
- Intro To Trig P5 Day FourDocument2 pagesIntro To Trig P5 Day FourmbpershanNo ratings yet
- Tan Function1Document3 pagesTan Function1mbpershanNo ratings yet
- Intro To Trig P3 Day TwoDocument3 pagesIntro To Trig P3 Day TwombpershanNo ratings yet
- Intro To Trig P3 Day FourDocument3 pagesIntro To Trig P3 Day FourmbpershanNo ratings yet
- Tan Function1Document3 pagesTan Function1mbpershanNo ratings yet
- Systems Day 2 WorksheetDocument2 pagesSystems Day 2 WorksheetmbpershanNo ratings yet
- Reality CheckDocument1 pageReality CheckmbpershanNo ratings yet
- Quadratics Day 5Document1 pageQuadratics Day 5mbpershanNo ratings yet
- Thin Lens WorksheetDocument2 pagesThin Lens WorksheetmbpershanNo ratings yet