Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 8 Answers
CH 8 Answers
Uploaded by
Mark Anthony25%(4)25% found this document useful (4 votes)
8K views5 pagesChapter 8: THE ENHANCED ENTITY-RELATIONSHIP (EER) MODEL Answers to Selected Exercises. Consider the BANK ER schema of Figure 7.21 and Modify it. Answer: 8. - no solution provided.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentChapter 8: THE ENHANCED ENTITY-RELATIONSHIP (EER) MODEL Answers to Selected Exercises. Consider the BANK ER schema of Figure 7.21 and Modify it. Answer: 8. - no solution provided.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
25%(4)25% found this document useful (4 votes)
8K views5 pagesCH 8 Answers
CH 8 Answers
Uploaded by
Mark AnthonyChapter 8: THE ENHANCED ENTITY-RELATIONSHIP (EER) MODEL Answers to Selected Exercises. Consider the BANK ER schema of Figure 7.21 and Modify it. Answer: 8. - no solution provided.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
Chapter 8: The Enhanced Entity-Relationship (EER) Model
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley.
1
CHAPTER 8: THE ENHANCED ENTITY-RELATIONSHIP (EER) MODEL
Answers to Selected Exercises
8.16 No solution provided.
8.17 - Consider the BANK ER schema of Figure 7.21, and suppose that it is necessary to
keep track of different types of ACCOUNTS (SAVINGS_ACCTS, CHECKING_ACCTS,
...) and LOANS (CAR_LOANS, HOME_LOANS, ...). Suppose that it is also desirable to keep
track of each account's TRANSACTIONs (deposits, withdrawals, checks, ...) and each loan's
PAYMENTs; both of these include the amount, date, time, ... Modify the BANK schema,
using ER and EER concepts of specialization and generalization. State any assumptions you
make about the additional requirements.
Answer:
8.18 - No solution provided.
8.19 - Identify all the important concepts represented in the library database case study
described here. In particular, identify the abstraction of classification (entity types and
relationship types), aggregation, identification, and specialization/generalization. Specify
(min, max) cardinality constraints whenever possible. List details that will affect the eventual
design but which have no bearing on the conceptual design. List the semantic separately.
Draw an EER diagram of the library database.
Answer:
Chapter 8: The Enhanced Entity-Relationship (EER) Model
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley.
2
8.20 - No solution provided.
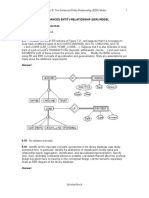
8.21 - Figure 8.12 shows an example of an EER diagram for a small private airport database
that is used to keep track of airplanes, their owners, airport employees, and pilots. From the
requirements for this database, the following information was collected: Each airplane has a
registration number [Reg#], is of a particular plane type [of_type], and is stored in a particular
hangar [stored_in]. Each plane_type has a model number [Model], a capacity [Capacity], and
a weight [Weight]. Each hangar has a number [Number], a capacity [Capacity], and a
location [Location]. The database also keeps track of the owners of each plane [owns] and
the employees who have maintained the plane [maintain]. Each relationship instance in owns
relates an airplane to an owner and includes the purchase date [Pdate]. Each relationship
instance in maintain relates to an employee to a service record [service]. Each plane
undergoes service many times; hence, it is related by [plane_service] o a number of service
records. A service record includes as attributes the date of maintenance [Date], the number
of hours spent on the work [Hours], and the type of work done [Workcode]. We use a weak
entity type [service] to represent airplane service, because the airplane registration number
is used to identify a service record. An owner is either a person or a corporation. Hence, we
use a union type (category) [owner] that is a subset of the union of corporation [Corporation]
and person [Person] entity types. Both pilots {Pilot] and employees [Employee] are
subclasses of person. Each pilot has specific attributes license number [Lic_Num] and
restrictions [Restr]; each employee has specific attributes salary [Salary] and shift {Shift]. All
person entities in the database have data kept on their social security number [Ssn], name
Chapter 8: The Enhanced Entity-Relationship (EER) Model
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley.
3
[Name], address [Address], and telephone number [Phone]. For corporation entities, the data
kept includes name [Name], address [Address], and telephone number [Phone]. The
database also keeps track of the types of planes each pilot is authorized to fly [Flies] and the
types of planes each employee can do maintenance work on [Works_on]. Show how the
small airport EER schema of Figure 8.12 may be represented in UML notation. (Note: We
have not discussed how to represent categories (union types) in UML, so you do not have to
map the categories in this and the following question.)
Answer:
8.22 8.23 No solutions provided.
8.24 - Draw a UML diagram for storing a played game of chess in a database. You may look
at http://www.chessgames.com for an application similar to what you are designing. State
clearly any assumptions you make in your UML diagram. A sample of assumptions you can
Chapter 8: The Enhanced Entity-Relationship (EER) Model
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley.
4
make about the scope is a follows:
1.1. The game of chess is played between two players.
2.2. The game is played on an 8x8 board like the one shown below:
3.3. The players are assigned a color of black or white at the start of the game.
4.4. Each player starts with the following pieces (traditionally called chessmen):
a.a. 1 king
b.b. 1 queen
c.c. 2 rooks
d.d. 2 bishops
e.e. 2 knights
f.f. 8 pawns
5.5. Every piece has its own initial position.
6.6. Every piece has its own set of legal moves based on the state of the game. You do not
need to worry about which moves are legal and which are not other than the following
issues:
a.a. A piece may move to an empty square or capture an opposing piece.
b.b. If a piece is captured, it is removed from the board.
c.c. f a pawn moves to the last row, it is "promoted but converting it into another
piece (a queen, a rook, a bishop, or a knight).
Note: Some of these functions may be spread over multiple classes.
8.25 No solution provided.
8.26 - Which of the following EER diagram(s) is/are incorrect and why? State clearly any
assumptions you make.
a)
1
N
R
A
E
E3
B
o
E1
E2
Formatted: Bullets and Numbering
Formatted: Bullets and Numbering
Formatted: Bullets and Numbering
Formatted: Bullets and Numbering
Formatted: Bullets and Numbering
Formatted: Bullets and Numbering
Formatted: Bullets and Numbering
Chapter 8: The Enhanced Entity-Relationship (EER) Model
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley.
5
Answer:
Only (c) is incorrect.
8.27 - Consider the following EER diagram that describes computer systems at a company.
Provide your own attributes and key for each entity type. Supply max cardinality constraints
justifying your choice. Write a complete narrative description of what this EER diagram
represents.
N M
1
1
b)
A
E
c)
R
A
E1
E2
C
E3
d
E1
o
R
Computer
Laptop Desktop
Accessory
Keyboard
Monitor
Mouse
Software
Operating
System
Component
Memory
Sound card
Video card
d
d d
U U
U
U U
U
U U
U
SoldWith
Options
Options
Supports
Installed
InstalledOS
You might also like
- ER Diagram Question and AnswerDocument2 pagesER Diagram Question and Answerbuddhi11167% (12)
- Solutions CHAPTER 3Document6 pagesSolutions CHAPTER 3Mohammad Abu Moqadam100% (2)
- Ge Lightspeed 16 Brochure PDFDocument8 pagesGe Lightspeed 16 Brochure PDFJairo ManzanedaNo ratings yet
- Navathe Chapter3solutionDocument5 pagesNavathe Chapter3solutionNidhi Bharatiya93% (15)
- ER Diagram ExamplesDocument4 pagesER Diagram ExamplesS Sarkar75% (4)
- NRM 3 Building Maintenance Works 1st Edition PGguidance 2013 PDFDocument554 pagesNRM 3 Building Maintenance Works 1st Edition PGguidance 2013 PDFSonny M. Obdin100% (3)
- ER Diagram ExampleDocument2 pagesER Diagram Exampleruvkeg50% (2)
- Chapter 4 Foundations of Organization DevelopmentDocument49 pagesChapter 4 Foundations of Organization DevelopmentMoses Avinash Andrews0% (1)
- Investigating The Inverse Square Law For A Radioactive SourceDocument7 pagesInvestigating The Inverse Square Law For A Radioactive SourceMarc Wierzbitzki100% (2)
- The Spiritual-Industrial Complex - America's Religious Battle (DR - Soc) PDFDocument286 pagesThe Spiritual-Industrial Complex - America's Religious Battle (DR - Soc) PDFyarghoNo ratings yet
- Books Mechanical EngineeringDocument19 pagesBooks Mechanical Engineeringnavaneeth32450% (8)
- Updated DBMS Question Bank Unit1-2Document14 pagesUpdated DBMS Question Bank Unit1-2Himanshu BhanNo ratings yet
- NormalizationDocument16 pagesNormalizationFenil Desai100% (2)
- Assignment#1 Dbms ErdDocument2 pagesAssignment#1 Dbms ErdSaima Malik60% (5)
- ERD Lab ManualDocument6 pagesERD Lab ManualDua Abu HamdiNo ratings yet
- Create ER DiagramsDocument8 pagesCreate ER DiagramsPremNo ratings yet
- Expanded Pine Valley Furniture Company Database: BackgroundDocument31 pagesExpanded Pine Valley Furniture Company Database: BackgroundKanita Besirevic100% (1)
- Er Diagram SolutionsDocument11 pagesEr Diagram Solutionsbipin bamNo ratings yet
- ER Diagram Question (Section-10)Document4 pagesER Diagram Question (Section-10)Aryaman TiwariNo ratings yet
- DBMS Important Questions Unit WiseDocument4 pagesDBMS Important Questions Unit Wiseprasadghari100% (1)
- Er AnswerDocument13 pagesEr AnswerNicholas Porter100% (1)
- Draw An ER Diagram For The Given ScenarioDocument2 pagesDraw An ER Diagram For The Given Scenarioleninisha100% (1)
- Bahir Dar University Institute of TechnologyDocument5 pagesBahir Dar University Institute of TechnologyAlex TebkewNo ratings yet
- Dbms Practical FileDocument20 pagesDbms Practical FilearjunNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 4.2 ERDDocument2 pagesLab Exercise 4.2 ERDtahirihranimNo ratings yet
- DBMS Unit-1 PPT 1.1 (Introduction, Drawback of File Sysstem, View of Data)Document4 pagesDBMS Unit-1 PPT 1.1 (Introduction, Drawback of File Sysstem, View of Data)lightNo ratings yet
- Answer 9Document8 pagesAnswer 9postscript50% (2)
- Dbms MCQDocument3 pagesDbms MCQBrinda BMNo ratings yet
- Entity Relationship Diagram - ER DiagramDocument10 pagesEntity Relationship Diagram - ER DiagramSwati HansNo ratings yet
- Unit II Database DesignDocument53 pagesUnit II Database DesignCptc CtNo ratings yet
- ER Diagram ExercisesDocument4 pagesER Diagram ExercisesPerry Solano100% (1)
- Question Bank ASQLDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank ASQLMeenakshi Vaylure PaulNo ratings yet
- DBMS AssignmentDocument11 pagesDBMS Assignmentveeru19verma4418100% (1)
- Question 1: Suppose You Are Given The Following Requirements For A SimpleDocument13 pagesQuestion 1: Suppose You Are Given The Following Requirements For A SimpleMehsara IrfanNo ratings yet
- DBMS Univ Question With AnswerDocument20 pagesDBMS Univ Question With AnsweractvenkatesanNo ratings yet
- Database Engineering (EC-240) : Lab Manual # 04Document9 pagesDatabase Engineering (EC-240) : Lab Manual # 04AMINA QADEERNo ratings yet
- CSC 371 DB-I Ver3.6Document3 pagesCSC 371 DB-I Ver3.6Ihtesham MansoorNo ratings yet
- SQL Practical-Question PaperDocument10 pagesSQL Practical-Question PaperSandesh100% (1)
- Tutorial 3Document2 pagesTutorial 3santanuNo ratings yet
- ICT COC DBA Level 4Document4 pagesICT COC DBA Level 4simachew takeleNo ratings yet
- Class Diagram Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesClass Diagram Practice QuestionsSaabNo ratings yet
- Operator Overloading Practice QuestionsDocument3 pagesOperator Overloading Practice QuestionsGODWIN TOMNo ratings yet
- ER Diagram AssignmentDocument1 pageER Diagram Assignmentpuvi ththira100% (2)
- Question Bank System Analysis and Design MCA 205Document5 pagesQuestion Bank System Analysis and Design MCA 205Aftab KhanNo ratings yet
- Oracle AssignmentDocument31 pagesOracle AssignmentComfort JohnsonNo ratings yet
- SPPU Web Technology Lab Questions For EndSemDocument2 pagesSPPU Web Technology Lab Questions For EndSemAneerban ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Cps Module 3Document27 pagesCps Module 3Radhika AjadkaNo ratings yet
- Final ProjDocument80 pagesFinal ProjAnthony BeltranNo ratings yet
- M.C.A. SyllabusDocument17 pagesM.C.A. SyllabusGauravNo ratings yet
- Entity Relationship ExamplesDocument3 pagesEntity Relationship ExamplesbhaskarNo ratings yet
- DBMS QP Set3 To StudentsDocument4 pagesDBMS QP Set3 To StudentsSneha Ignatious0% (1)
- Data Warehousing and Data Mining JNTU Previous Years Question PapersDocument4 pagesData Warehousing and Data Mining JNTU Previous Years Question PapersRakesh VarmaNo ratings yet
- Class Diagram ExamplesDocument3 pagesClass Diagram Examplessharmila_yusofNo ratings yet
- Review Questions - ER ModelDocument57 pagesReview Questions - ER Modelsambashivarao100% (4)
- DBMS Lab Question BankDocument3 pagesDBMS Lab Question BankASHISH KUMAR KEWAT Vel Tech, Chennai100% (1)
- Computer Fundamentals Lab FileDocument27 pagesComputer Fundamentals Lab FileNischay DhimanNo ratings yet
- CS8481 DBMS Lab QNDocument9 pagesCS8481 DBMS Lab QNancyNo ratings yet
- Entity Relationship (ER) Modeling - Learn With A Complete ExampleDocument2 pagesEntity Relationship (ER) Modeling - Learn With A Complete ExampleSafije Sadiki ShainiNo ratings yet
- Sir Syed University of Engineering and TechnologyDocument4 pagesSir Syed University of Engineering and TechnologyFahad SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Practical Assignment For DBMSDocument2 pagesPractical Assignment For DBMSHeta Desai100% (2)
- Dbms Question PaperDocument4 pagesDbms Question PaperSasi PlacementsNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Fundamentals of Database Systems 6E Chapter 01Document3 pagesSolution Manual For Fundamentals of Database Systems 6E Chapter 01Danial Saeed100% (2)
- Solution Manual For Fundamentals of Database Systems 6 e 6th Edition 0136086209Document6 pagesSolution Manual For Fundamentals of Database Systems 6 e 6th Edition 0136086209MarcoJenkinsxzwk100% (45)
- 08Document6 pages08Malik AwaisNo ratings yet
- Elmasri 6e - ISM 07Document14 pagesElmasri 6e - ISM 07Leo Pamungkas NasutionNo ratings yet
- hw1 SolDocument11 pageshw1 Solsolanki_558No ratings yet
- Career Change CV TemplateDocument1 pageCareer Change CV TemplateRachelia FiolinNo ratings yet
- Brij KishorDocument102 pagesBrij KishorShahbaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Writing For Instructional Design - The Elearning CoachDocument25 pagesWriting For Instructional Design - The Elearning CoachComunicar e VencerNo ratings yet
- RelationshipDocument3 pagesRelationshipAkim LncpNo ratings yet
- SBA Guideline Task 5Document3 pagesSBA Guideline Task 5DEVONTE YTNo ratings yet
- Certification ProcessDocument7 pagesCertification ProcessGolden RosesNo ratings yet
- Salming Running WB 2015 LRDocument39 pagesSalming Running WB 2015 LRHoracio SandNo ratings yet
- Effect of CompensationDocument5 pagesEffect of CompensationKomal MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Oracle R12 P2P by Dinesh Kumar SDocument158 pagesOracle R12 P2P by Dinesh Kumar SHarimakeshwaran Rengaraju100% (1)
- Law of Freedom Bond 00 HurdDocument676 pagesLaw of Freedom Bond 00 HurdJesse Faulkner100% (1)
- Oracle Apps DBA QaDocument32 pagesOracle Apps DBA QaImran siddiqueNo ratings yet
- AGS Guideline 2019Document35 pagesAGS Guideline 2019Yudha EnglishNo ratings yet
- Elective ReportDocument3 pagesElective ReportBanu ThuraisingamNo ratings yet
- LIEBHERR R966 980B EN PreviewDocument51 pagesLIEBHERR R966 980B EN PreviewFernando AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- On Isothermal Flow of Viscous Liquids Thorugh Screw PumpsDocument218 pagesOn Isothermal Flow of Viscous Liquids Thorugh Screw PumpsRicardo BarrosNo ratings yet
- Verbal CommunicationDocument16 pagesVerbal CommunicationCamaradrieNo ratings yet
- Burgio, L. Lustre Ceramics Analysis. 2005Document2 pagesBurgio, L. Lustre Ceramics Analysis. 2005Trinidad Pasíes Arqueología-ConservaciónNo ratings yet
- Memory and LearningDocument5 pagesMemory and LearningJananee RajagopalanNo ratings yet
- MangrovesDocument47 pagesMangrovesBhe Bhe Ran100% (1)
- Strategie de Prevenie A SinucideriiDocument206 pagesStrategie de Prevenie A SinucideriiMihai VasileNo ratings yet
- A Passage To India ThemesDocument23 pagesA Passage To India ThemesJitkar HembramNo ratings yet
- Engineering HydrologyDocument2 pagesEngineering Hydrology11520035100% (1)
- Accuplacer Writeplacer Sample EssaysDocument32 pagesAccuplacer Writeplacer Sample EssaysLuisAranaNo ratings yet
- Thinking: (It's Not As Easy As It Looks!)Document23 pagesThinking: (It's Not As Easy As It Looks!)Iain Cook-Bonney100% (2)