Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Daemon Threads
Daemon Threads
Uploaded by
Pramod PolamuriOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Daemon Threads
Daemon Threads
Uploaded by
Pramod PolamuriCopyright:
Available Formats
Daemon Threads
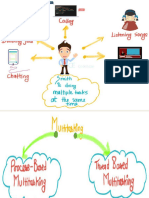
In Java, any thread can be a Daemon thread. Daemon threads are like a service providers for other threads or objects running in the same process as the daemon thread. Daemon threads are used for background supporting tasks and are only needed while normal threads are executing. If normal threads are not running and remaining threads are daemon threads then the interpreter exits. setDaemon(true/false) ? This method is used to specify that a thread is daemon thread. public boolean isDaemon() ? This method is used to determine the thread is daemon thread or not. The following program demonstrates the Daemon Thread:
public class DaemonThread extends Thread { public void run() { System.out.println("Entering run method"); try { System.out.println("In run Method: currentThread() is" + Thread.currentThread()); while (true) { try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException x) { } System.out.println("In run method: woke up again"); } } finally { System.out.println("Leaving run Method"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Entering main Method"); DaemonThread t = new DaemonThread(); t.setDaemon(true); t.start(); try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException x) { } System.out.println("Leaving main method"); } }
The run() method for a daemon thread is typically an infinite loop that waits for a service request.
When the only remaining threads in a process are daemon threads, the interpreter exits. This makes sense because when only daemon threads remain, there is no other thread for which a daemon thread can provide a service. To specify that a thread is a daemon thread, call the setDaemon method with the argument true. To determine if a thread is a daemon thread, use the accessor method isDaemon.
You might also like
- Daemon ThreadDocument2 pagesDaemon ThreadAbdul GafurNo ratings yet
- Multi ThreadingDocument17 pagesMulti ThreadingMadhu SudhanNo ratings yet
- 27-Daemon ThreadDocument2 pages27-Daemon Threadpratigya gNo ratings yet
- Threads in JavaDocument23 pagesThreads in JavaAndrew MutungaNo ratings yet
- 4-Multithreading 1.4-17-01-2022 (17-Jan-2022) Material - I - 17-01-2022 - MDocument20 pages4-Multithreading 1.4-17-01-2022 (17-Jan-2022) Material - I - 17-01-2022 - MRockstar GmailNo ratings yet
- Multi Threading Notes and Interview QuestionsDocument28 pagesMulti Threading Notes and Interview QuestionsCherry Charan TejNo ratings yet
- JAVA_UNIT_4Document39 pagesJAVA_UNIT_4ga568798No ratings yet
- Java - Multithreading: Life Cycle of A ThreadDocument7 pagesJava - Multithreading: Life Cycle of A ThreadRahul GuptaNo ratings yet
- Creating A ThreadDocument4 pagesCreating A ThreadShanmuka SreenivasNo ratings yet
- Multi Threaded Programming: Megha Aggarwal IGIT, GGSIP University, Delhi EmailDocument30 pagesMulti Threaded Programming: Megha Aggarwal IGIT, GGSIP University, Delhi EmailJamuna Prasad GuptaNo ratings yet
- ConcurrencyDocument42 pagesConcurrencySebastian RomaniucNo ratings yet
- Threads in JavaDocument6 pagesThreads in JavaNandana BobanNo ratings yet
- Multithreading in JavaDocument30 pagesMultithreading in JavaSwaragyam PalakuraNo ratings yet
- Multi Threading in Java by Durga SirDocument68 pagesMulti Threading in Java by Durga SirLalitNo ratings yet
- Multi Threading in Java by Durga SirDocument75 pagesMulti Threading in Java by Durga SirLalitNo ratings yet
- Advanced JavaDocument50 pagesAdvanced JavaEntertainment TimeNo ratings yet
- Java Threads and MoreDocument17 pagesJava Threads and MoreArindam BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Java ThreadsDocument85 pagesJava ThreadsabhishekkumarjhafbgNo ratings yet
- Rohan Pahwa Roll No-A17 Reg No-10809673 Mca (Hons) .: Modern Programming Tools & Techniques I For Honors Homework 3Document15 pagesRohan Pahwa Roll No-A17 Reg No-10809673 Mca (Hons) .: Modern Programming Tools & Techniques I For Honors Homework 3vivek19354No ratings yet
- Multi Threading ShrikantDocument106 pagesMulti Threading ShrikantKomal RansingNo ratings yet
- Multithreading in JavaDocument23 pagesMultithreading in Javadagar.shilpa36No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Multi-Threading in JavaDocument29 pagesChapter 10 - Multi-Threading in JavaTanveer Ahmed HakroNo ratings yet
- Java Multithreading PDFDocument9 pagesJava Multithreading PDFPhanidhar S GadiyaramNo ratings yet
- 0b6at Wuxbp6ldWN1RWt6ZS1oWnZvbk5qTFYwdHVSSGxWYkV3Document40 pages0b6at Wuxbp6ldWN1RWt6ZS1oWnZvbk5qTFYwdHVSSGxWYkV3ArinjayKumarNo ratings yet
- MultithreadingDocument2 pagesMultithreadingprasadgr931No ratings yet
- Java Module 5 Chapter 11Document26 pagesJava Module 5 Chapter 112022becs190No ratings yet
- Oops PPT B7Document14 pagesOops PPT B7Ravi teja NalamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Threads 1.1 Non Threaded ApplicationsDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Threads 1.1 Non Threaded ApplicationsB RameshNo ratings yet
- Multithread ProgrammingDocument42 pagesMultithread ProgrammingDevesh SuranaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One MotiDocument32 pagesChapter One MotiBeka BekoNo ratings yet
- Java Programming UNIT-4: ThreadDocument22 pagesJava Programming UNIT-4: Threaduddagiri sirishaNo ratings yet
- Java Programming UNIT-4: ThreadDocument22 pagesJava Programming UNIT-4: Threaduddagiri sirishaNo ratings yet
- Thread: Thread. Even If You Don't Create Any New Threads in Your Program, Threads Are BackDocument28 pagesThread: Thread. Even If You Don't Create Any New Threads in Your Program, Threads Are BackKuldeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Java - MultithreadingDocument8 pagesJava - MultithreadingKoushik Sinha100% (1)
- Multithreading in Java With ExamplesDocument7 pagesMultithreading in Java With ExamplesMANOJ KUMAR D SNo ratings yet
- Multi ThreadingDocument65 pagesMulti Threadingcontact.me90No ratings yet
- Java MultithreadingDocument21 pagesJava MultithreadingKuldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Java MultithreadingDocument25 pagesJava MultithreadingSabyasachi MoitraNo ratings yet
- Threads: Life Cycle of A ThreadDocument18 pagesThreads: Life Cycle of A ThreadPraneeth MutnuruNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document18 pagesUnit 5yicet13049No ratings yet
- OOPJ MultiThreading NJB PDFDocument27 pagesOOPJ MultiThreading NJB PDFRaj ShahNo ratings yet
- CS8392 Oop Unit 4 NotesDocument25 pagesCS8392 Oop Unit 4 NotesChakkarawarthiNo ratings yet
- MultithreadingDocument4 pagesMultithreadingR RNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Multithreadingappletsnetworking - RemovedDocument14 pagesUnit IV Multithreadingappletsnetworking - Removeddarshankumar59429No ratings yet
- Java ThreadsDocument15 pagesJava ThreadsKISHOREMUTCHARLA100% (1)
- Multithreading Class Notes JavaDocument65 pagesMultithreading Class Notes Javadaniel007workNo ratings yet
- Daemon Thread in Java With Example: Properties of Daemon ThreadsDocument2 pagesDaemon Thread in Java With Example: Properties of Daemon ThreadsNAKKA PUNEETHNo ratings yet
- Process Based - Executing Several Tasks Simultaneously - Each Task Is A Separate Independent Process. ThisDocument13 pagesProcess Based - Executing Several Tasks Simultaneously - Each Task Is A Separate Independent Process. ThisWeecky HunterNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Multithreading and Generic ProgrammingDocument24 pagesUnit Iv Multithreading and Generic Programming03 Anton P JacksonNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document16 pagesPresentation 1Deekshitha MarripudiNo ratings yet
- PROGRAMMING PARADIGMS - Unit VDocument33 pagesPROGRAMMING PARADIGMS - Unit VKanthimathi SureshNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Concurrent ProgrammingDocument31 pagesUnit 5 Concurrent ProgrammingMathesh ParamasivamNo ratings yet
- Chapter11 MultithreadingDocument6 pagesChapter11 Multithreadingvoila.albertoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Multithreading - 015357Document34 pagesChapter 5 - Multithreading - 015357adugna gutemaNo ratings yet
- Unit4 Java FullDocument21 pagesUnit4 Java Fullmadani hussainNo ratings yet
- Multithreaded ProgrammingDocument19 pagesMultithreaded ProgrammingNepal Mens TechNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - MultiThreadingDocument36 pagesChapter 5 - MultiThreadingnoahmullerNo ratings yet
- Thread and Design Pattern Lab in JavaDocument17 pagesThread and Design Pattern Lab in JavatinsaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document65 pagesChapter 3Amar EliasNo ratings yet