Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Locomotion
Locomotion
Uploaded by
Nadia NoriezanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Materi Human SkeletonDocument6 pagesMateri Human SkeletonRicky UchihaNo ratings yet
- Human BonesDocument39 pagesHuman Bonesmuhammad ijazNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument31 pagesSkeletal SystemZabeth ZabNo ratings yet
- 2 Skeletal System HandoutDocument8 pages2 Skeletal System Handoutapi-302873465No ratings yet
- 2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsDocument59 pages2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsilyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Module 8aDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Module 8aJayR MendonesNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Berasrama Penuh Integrasi Gopeng Prepared By:Muhd Fazli Bin DollahDocument60 pagesSekolah Berasrama Penuh Integrasi Gopeng Prepared By:Muhd Fazli Bin DollahrameshkasinathanNo ratings yet
- Premedical Biology: Motor MechanismDocument44 pagesPremedical Biology: Motor MechanismsheenaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesSkeletal SystemmikeNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Report PDFDocument86 pagesSkeletal System Report PDFMarian Elaine RufilaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument31 pagesSkeletal SystemMae Antonette OrlinaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Skeletal SystemDocument26 pagesAnatomy - Skeletal SystemShereen AlobinayNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesSkeletal SystemJovi Floresca AberinNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 3 SkeletalDocument9 pagesLaboratory 3 SkeletalKyla InoferioNo ratings yet
- 3 Musculoskeletal System-2020-10132Document11 pages3 Musculoskeletal System-2020-10132Горькое ДноNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument8 pagesDefinitionJamesNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Anatomy: 1.1 The Skeletal SystemDocument110 pagesTopic 1: Anatomy: 1.1 The Skeletal SystemJayden OoiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in SportDocument64 pagesUnit 1 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in Sportdomhughes1093No ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Skeletal SystemDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Human Skeletal SystemKristine DomacenaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System AnatomyDocument6 pagesSkeletal System AnatomymanuelaristotleNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System (Use) - PESWDocument86 pagesSkeletal System (Use) - PESWAudrianna GaddyNo ratings yet
- Midterm TopicDocument5 pagesMidterm Topicjamesbaguia315No ratings yet
- The Skeletal System - PPTX G 6Document30 pagesThe Skeletal System - PPTX G 6JjiscoolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 & 8 Notes - A&PDocument8 pagesChapter 7 & 8 Notes - A&PAshley MarieNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesSkeletal SystemMaureen Tianson DomingoNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesThe Skeletal SystemJessa Mae BanquirigNo ratings yet
- Our Body SystemDocument51 pagesOur Body SystemAlexius BaghiNo ratings yet
- 01 The Human Skeleton 2014 - WebDocument33 pages01 The Human Skeleton 2014 - Webapi-240330821No ratings yet
- Skripta Za Usmeni Iz EngleskogDocument15 pagesSkripta Za Usmeni Iz EngleskogElizabetaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System 1Document31 pagesSkeletal System 1Hannan AliNo ratings yet
- ACE CPT Chapter 9 Part 1 (Edition 6)Document6 pagesACE CPT Chapter 9 Part 1 (Edition 6)alishuuuNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument24 pagesSkeletal Systemrheanna0076No ratings yet
- SKELETAL SYSTEM - OutlineDocument2 pagesSKELETAL SYSTEM - OutlineLind MondanoNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesThe Skeletal SystemShailendra Singh ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Anatomy: Skull Mandible Temporal BoneDocument5 pagesSkeletal System Anatomy: Skull Mandible Temporal BoneMichael Villamor100% (1)
- 2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsDocument61 pages2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & Animalsliming8112No ratings yet
- 3 Musculoskeletal System-21805Document11 pages3 Musculoskeletal System-21805Dan ZagoreanuNo ratings yet
- Movement and Locomotion-23-24Document3 pagesMovement and Locomotion-23-24Chintan ShahNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System: Study: Orthopedics, Rheumatology Physician: Orthopedist, Rheumatologist FunctionsDocument10 pagesMusculoskeletal System: Study: Orthopedics, Rheumatology Physician: Orthopedist, Rheumatologist Functionsamelia niitaNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System Anatomy - ClasspptDocument107 pagesThe Skeletal System Anatomy - ClasspptSy OrdinesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Skeletal To EndoDocument46 pagesReviewer Skeletal To EndoSophia CaisipNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Skeletal System-Notes of LessonDocument4 pagesChapter-6 Skeletal System-Notes of Lessonjothishree24121980No ratings yet
- Introduction To Musculoskeletal System 2012Document18 pagesIntroduction To Musculoskeletal System 2012Mandeep DhillonNo ratings yet
- Osteocytes - Bone Cells Classifications of Bones According To SizeDocument17 pagesOsteocytes - Bone Cells Classifications of Bones According To SizeA CNo ratings yet
- Joints and Movement 1.0Document10 pagesJoints and Movement 1.0gseavillNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument62 pagesSkeletal SystemVincentBauza100% (1)
- Skeletal System 5 Functions of The Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesSkeletal System 5 Functions of The Skeletal SystemShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- BonesDocument2 pagesBonesSherry SinghNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 5 - Chapter 05Document10 pagesExp SC 5 - Chapter 05megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Neither To Be FoundDocument57 pagesNeither To Be FoundKhaelNo ratings yet
- 16 A&p All 3 SystemsDocument76 pages16 A&p All 3 SystemsMalou SanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-6 Lesson Summarty Pe 1Document7 pagesUnit 4-6 Lesson Summarty Pe 1Vergel CallejaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System (2) - 2Document71 pagesSkeletal System (2) - 2alazarademe797No ratings yet
- Reading 3 The Skeletal SystemDocument18 pagesReading 3 The Skeletal Systemlephuongvy1406No ratings yet
- Movement-Rigid Strong Bones Is Well Suited ForDocument7 pagesMovement-Rigid Strong Bones Is Well Suited ForEllah GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System and MuscularDocument4 pagesSkeletal System and MuscularLuz Dianne SoloriaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System On Axial & Appendicular BonesDocument26 pagesSkeletal System On Axial & Appendicular BoneskadyNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal and Muscular System Summary Note 1601471541Document7 pagesThe Skeletal and Muscular System Summary Note 1601471541Uwais AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 AnaphyDocument10 pagesChapter 5 AnaphyKryzell Ann HadcanNo ratings yet
Locomotion
Locomotion
Uploaded by
Nadia NoriezanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Locomotion
Locomotion
Uploaded by
Nadia NoriezanCopyright:
Available Formats
LOCOMOTION & SUPPORT Necessity To search food & shelter Escape from enemies To find mates To search more
more conducive environment
Vertebral column
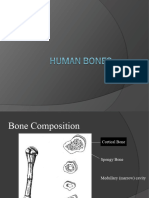
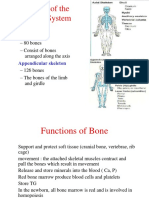
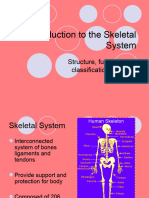
Functions of skeleton Provide shape & support Enable movement Protect internal organs Produce blood cells Store materials (calcium & phosphate)
Structure of typical vertebrae
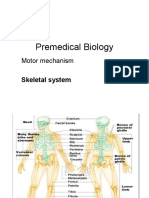
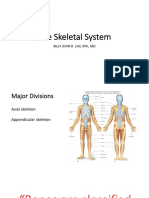
Structure of human skeleton
Ribcage Axial skeleton Skull Cranium - encloses & protect brain (consist 8 pieces of bones) Bone of face (facial bones) protect eyes, ears & nose Upper jaw immovable Lower jaw movable to allow speech & chewing of food Consist 12 ribs Joined to sternum by cartilages Articulate with thoracic vertebrae & sternum First 7 pairs of ribcage = true ribs 8 to 10 = false ribs 11 & 12 = floating ribs
Appendicular skeleton pectoral girdle clavicle & scapula forelimb humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges pelvic girdle ischium, ilium, pubis hind limb femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsal, metatarsal, phalanges
Muscles made up of muscle fibres movement of body brought about by contraction of a pair of antagonistic muscles comes from ATP produced in mitochondria
Functions of synovial fluid Produce by synovial membrane To lubricate joints Preventing friction
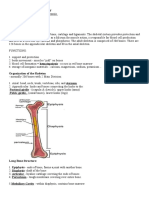
Ligaments flexible, strong & elastic connective tissue connect bone to bone
Tendons dense connective tissues strong & elastic connect muscles to bones
Bending the arm when biceps contracts, triceps relaxes Radius is pulled upwards Arm being bent
Straightening the arm When triceps contracts, biceps relaxes Pulls ulna down Arm is straightened
You might also like
- Materi Human SkeletonDocument6 pagesMateri Human SkeletonRicky UchihaNo ratings yet
- Human BonesDocument39 pagesHuman Bonesmuhammad ijazNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument31 pagesSkeletal SystemZabeth ZabNo ratings yet
- 2 Skeletal System HandoutDocument8 pages2 Skeletal System Handoutapi-302873465No ratings yet
- 2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsDocument59 pages2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsilyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Module 8aDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Module 8aJayR MendonesNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Berasrama Penuh Integrasi Gopeng Prepared By:Muhd Fazli Bin DollahDocument60 pagesSekolah Berasrama Penuh Integrasi Gopeng Prepared By:Muhd Fazli Bin DollahrameshkasinathanNo ratings yet
- Premedical Biology: Motor MechanismDocument44 pagesPremedical Biology: Motor MechanismsheenaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesSkeletal SystemmikeNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Report PDFDocument86 pagesSkeletal System Report PDFMarian Elaine RufilaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument31 pagesSkeletal SystemMae Antonette OrlinaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Skeletal SystemDocument26 pagesAnatomy - Skeletal SystemShereen AlobinayNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesSkeletal SystemJovi Floresca AberinNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 3 SkeletalDocument9 pagesLaboratory 3 SkeletalKyla InoferioNo ratings yet
- 3 Musculoskeletal System-2020-10132Document11 pages3 Musculoskeletal System-2020-10132Горькое ДноNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument8 pagesDefinitionJamesNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Anatomy: 1.1 The Skeletal SystemDocument110 pagesTopic 1: Anatomy: 1.1 The Skeletal SystemJayden OoiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in SportDocument64 pagesUnit 1 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in Sportdomhughes1093No ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Skeletal SystemDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Human Skeletal SystemKristine DomacenaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System AnatomyDocument6 pagesSkeletal System AnatomymanuelaristotleNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System (Use) - PESWDocument86 pagesSkeletal System (Use) - PESWAudrianna GaddyNo ratings yet
- Midterm TopicDocument5 pagesMidterm Topicjamesbaguia315No ratings yet
- The Skeletal System - PPTX G 6Document30 pagesThe Skeletal System - PPTX G 6JjiscoolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 & 8 Notes - A&PDocument8 pagesChapter 7 & 8 Notes - A&PAshley MarieNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesSkeletal SystemMaureen Tianson DomingoNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesThe Skeletal SystemJessa Mae BanquirigNo ratings yet
- Our Body SystemDocument51 pagesOur Body SystemAlexius BaghiNo ratings yet
- 01 The Human Skeleton 2014 - WebDocument33 pages01 The Human Skeleton 2014 - Webapi-240330821No ratings yet
- Skripta Za Usmeni Iz EngleskogDocument15 pagesSkripta Za Usmeni Iz EngleskogElizabetaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System 1Document31 pagesSkeletal System 1Hannan AliNo ratings yet
- ACE CPT Chapter 9 Part 1 (Edition 6)Document6 pagesACE CPT Chapter 9 Part 1 (Edition 6)alishuuuNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument24 pagesSkeletal Systemrheanna0076No ratings yet
- SKELETAL SYSTEM - OutlineDocument2 pagesSKELETAL SYSTEM - OutlineLind MondanoNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesThe Skeletal SystemShailendra Singh ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Anatomy: Skull Mandible Temporal BoneDocument5 pagesSkeletal System Anatomy: Skull Mandible Temporal BoneMichael Villamor100% (1)
- 2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsDocument61 pages2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & Animalsliming8112No ratings yet
- 3 Musculoskeletal System-21805Document11 pages3 Musculoskeletal System-21805Dan ZagoreanuNo ratings yet
- Movement and Locomotion-23-24Document3 pagesMovement and Locomotion-23-24Chintan ShahNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System: Study: Orthopedics, Rheumatology Physician: Orthopedist, Rheumatologist FunctionsDocument10 pagesMusculoskeletal System: Study: Orthopedics, Rheumatology Physician: Orthopedist, Rheumatologist Functionsamelia niitaNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System Anatomy - ClasspptDocument107 pagesThe Skeletal System Anatomy - ClasspptSy OrdinesNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Skeletal To EndoDocument46 pagesReviewer Skeletal To EndoSophia CaisipNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Skeletal System-Notes of LessonDocument4 pagesChapter-6 Skeletal System-Notes of Lessonjothishree24121980No ratings yet
- Introduction To Musculoskeletal System 2012Document18 pagesIntroduction To Musculoskeletal System 2012Mandeep DhillonNo ratings yet
- Osteocytes - Bone Cells Classifications of Bones According To SizeDocument17 pagesOsteocytes - Bone Cells Classifications of Bones According To SizeA CNo ratings yet
- Joints and Movement 1.0Document10 pagesJoints and Movement 1.0gseavillNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument62 pagesSkeletal SystemVincentBauza100% (1)
- Skeletal System 5 Functions of The Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesSkeletal System 5 Functions of The Skeletal SystemShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- BonesDocument2 pagesBonesSherry SinghNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 5 - Chapter 05Document10 pagesExp SC 5 - Chapter 05megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Neither To Be FoundDocument57 pagesNeither To Be FoundKhaelNo ratings yet
- 16 A&p All 3 SystemsDocument76 pages16 A&p All 3 SystemsMalou SanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-6 Lesson Summarty Pe 1Document7 pagesUnit 4-6 Lesson Summarty Pe 1Vergel CallejaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System (2) - 2Document71 pagesSkeletal System (2) - 2alazarademe797No ratings yet
- Reading 3 The Skeletal SystemDocument18 pagesReading 3 The Skeletal Systemlephuongvy1406No ratings yet
- Movement-Rigid Strong Bones Is Well Suited ForDocument7 pagesMovement-Rigid Strong Bones Is Well Suited ForEllah GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System and MuscularDocument4 pagesSkeletal System and MuscularLuz Dianne SoloriaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System On Axial & Appendicular BonesDocument26 pagesSkeletal System On Axial & Appendicular BoneskadyNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal and Muscular System Summary Note 1601471541Document7 pagesThe Skeletal and Muscular System Summary Note 1601471541Uwais AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 AnaphyDocument10 pagesChapter 5 AnaphyKryzell Ann HadcanNo ratings yet