Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Resenter: Mbili P K
Resenter: Mbili P K
Uploaded by
Balaram Papana0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views37 pagesA prototype is a model that demonstrates the key features of a product to gather requirements from customers. The prototyping process involves customers and developers defining initial requirements, building a prototype, getting customer feedback, refining the prototype, and either extending it into a product or rebuilding the product. The spiral model is an iterative development process where each iteration involves planning, evaluating risks, building the product, and getting customer feedback to refine the product until it is accepted.
Original Description:
Original Title
Sdlc
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA prototype is a model that demonstrates the key features of a product to gather requirements from customers. The prototyping process involves customers and developers defining initial requirements, building a prototype, getting customer feedback, refining the prototype, and either extending it into a product or rebuilding the product. The spiral model is an iterative development process where each iteration involves planning, evaluating risks, building the product, and getting customer feedback to refine the product until it is accepted.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views37 pagesResenter: Mbili P K
Resenter: Mbili P K
Uploaded by
Balaram PapanaA prototype is a model that demonstrates the key features of a product to gather requirements from customers. The prototyping process involves customers and developers defining initial requirements, building a prototype, getting customer feedback, refining the prototype, and either extending it into a product or rebuilding the product. The spiral model is an iterative development process where each iteration involves planning, evaluating risks, building the product, and getting customer feedback to refine the product until it is accepted.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 37
Presenter: Ambili P K
WHAT IS A PROTOTYPE?
A prototype is a model of the salient features of a product. It helps in gathering and refining the product requirements. For a software product, a prototype may help the customer understand the user interface of the system and how data will be gathered and presented. It is important to note that the prototype is not the actual product. It may be nothing more than a shell or an external layer containing very little computing capability.
STEPS INVOLVED IN PROTOTYPING
Step 1: The customer and the developer meet to define the basic requirements. These requirements are assumed to be incomplete but sufficient to build a prototype. Step 2: The developer builds a prototype of the actual software product to give the customer a feel of the functionality of the product.
STEPS INVOLVED IN PROTOTYPING
Step 3: The customer evaluates the prototype to check which features and functionalities meet the requirements, which are incomplete or inappropriate, and which are missing. Step 4: The customer provides feedback to the developer based on the evaluation of the prototype. .
STEPS INVOLVED IN PROTOTYPING
Step 5: The developer refines the prototype based on the customer feedback by incorporating the changes suggested by the customer. Step 6: The actual product is built after the prototype is found to be satisfactory by either extending the prototype into an operational product or 'throwing away' the prototype and rebuilding the product.
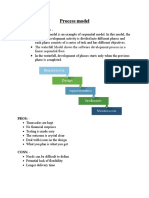
SPIRAL PROCESS MODEL
Each iteration is one circuit around the spiral that results in an end product for evaluation. Every iteration comprises: Planning the iteration, including the estimation of the cost and the schedule. Customer feedback from the previous iteration, if any, is also taken into account Evaluating the risks to arrive at a 'go/no-go' decision
SPIRAL PROCESS MODEL
Engineering or building the product based on the end product of the iteration Customer evaluating the end product built during the iteration These iterations continue until either the final product is accepted or it is decided to stop further work on the product.
A REFINED VERSION OF THE SPIRAL PROCESS MODEL
Customer communication Planning Risk analysis Engineering Integration support Customer evaluation
You might also like
- Sop 4Document2 pagesSop 4Leon Hong83% (6)
- Generic Product Development ProcessDocument3 pagesGeneric Product Development Processhannah_clarice0% (1)
- Agile ModelDocument5 pagesAgile ModelRaghavendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 RAD NotesDocument7 pagesChapter 3 RAD NotesPatricia Agüero FloresNo ratings yet
- Prototype ModelDocument4 pagesPrototype ModelAnurag SinghNo ratings yet
- 142 Assignment 2Document3 pages142 Assignment 2Mohit SoniNo ratings yet
- Prototype ModelDocument17 pagesPrototype ModelKaoboy Nawa LwdeNo ratings yet
- Steps in Protyping: Espedillon, Marigold May L. BSECE 5-1Document9 pagesSteps in Protyping: Espedillon, Marigold May L. BSECE 5-1mgoldiieeeeNo ratings yet
- Fomic Polytechnic University: MBA 1 in Accounting and FinanceDocument6 pagesFomic Polytechnic University: MBA 1 in Accounting and FinancetchoumbaprincessNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering - Prototyping ModelDocument5 pagesSoftware Engineering - Prototyping ModelShoeb Akibul IslamNo ratings yet
- SDLCunit 1Document7 pagesSDLCunit 1Divyadeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Refining Prototypes PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 9 Refining Prototypes PDFAngeline Lagmay VisayaNo ratings yet
- 3-Evolutionary Models - Prototype, Spiral and Concurrent Models-09!01!2024Document21 pages3-Evolutionary Models - Prototype, Spiral and Concurrent Models-09!01!2024asif.sheriff77No ratings yet
- SE Unit - I NotesDocument71 pagesSE Unit - I Notesokchaitanya568No ratings yet
- UNIT 2 - Software Lifecycle ModelsDocument5 pagesUNIT 2 - Software Lifecycle ModelsJames DinoyNo ratings yet
- Prototyping ModelDocument8 pagesPrototyping ModelAbdi GaromaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Spiral Development Model?Document12 pagesWhat Is The Spiral Development Model?Madhur KhannaNo ratings yet
- Prototyping Model - Evolution and Spiral ModelsDocument5 pagesPrototyping Model - Evolution and Spiral ModelsVijay KrishnaNo ratings yet
- What Is Agile TestingDocument17 pagesWhat Is Agile TestingDredz27No ratings yet
- SDLCDocument8 pagesSDLCSourabh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Basic of Software ModellingDocument19 pagesIntroduction and Basic of Software ModellingtruptiNo ratings yet
- Evolutionary Software Process ModelDocument5 pagesEvolutionary Software Process ModelRakesh InjamNo ratings yet
- Hamza Imran (R36) - IT Project Management (Software Process Model)Document13 pagesHamza Imran (R36) - IT Project Management (Software Process Model)Jiya AlamNo ratings yet
- SDLCDocument11 pagesSDLCHrishita MavaniNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-1Document12 pagesUnit 2-1hk979324No ratings yet
- Unit Ii - Project Life Cycle and Effort Estimation 2.1 Software Process and Process ModelsDocument19 pagesUnit Ii - Project Life Cycle and Effort Estimation 2.1 Software Process and Process Models123No ratings yet
- Spiral Model Is A Software Development Model Introduced by Barry Boehm To Decrease TheDocument7 pagesSpiral Model Is A Software Development Model Introduced by Barry Boehm To Decrease TheMitesh ChoubeyNo ratings yet
- Software EngineeringDocument25 pagesSoftware Engineeringmarv hartiganNo ratings yet
- Software Development Life: Cycle (SDLC)Document34 pagesSoftware Development Life: Cycle (SDLC)JohnNo ratings yet
- MKT 508 Cat AnswersDocument14 pagesMKT 508 Cat AnswersJustin mugendiNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Software Process ModelsDocument7 pagesModule 1 - Software Process ModelsfebinstNo ratings yet
- Software Project Management Unit - 2 NotesDocument20 pagesSoftware Project Management Unit - 2 Notesshrey.bhaskar.it.2021No ratings yet
- Week 03Document6 pagesWeek 03O.M. CreationsNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering SummaryDocument9 pagesSoftware Engineering SummaryEmmanuel BongayNo ratings yet
- IE-451 (Lect-2)Document26 pagesIE-451 (Lect-2)Zeeshan JavedNo ratings yet
- SDLC QuestionsDocument2 pagesSDLC QuestionsGadadhar Tiwary100% (1)
- General - Software Development Life Cycle - Prototype Model - CodecademyDocument3 pagesGeneral - Software Development Life Cycle - Prototype Model - CodecademyBloody GamingNo ratings yet
- Process ModelDocument4 pagesProcess ModelParvathi GoudNo ratings yet
- Product DevtDocument26 pagesProduct DevtRalph Gene Trabasas FloraNo ratings yet
- Prototype ModelDocument13 pagesPrototype Modelitspracin750No ratings yet
- SPM NotesDocument131 pagesSPM Notesp rajeshwariNo ratings yet
- EvolutionDocument12 pagesEvolutionswamikollapudi7No ratings yet
- Software Testing-1 PDFDocument75 pagesSoftware Testing-1 PDFSai PinakiNo ratings yet
- Spiral and Evolutionary ModelDocument12 pagesSpiral and Evolutionary ModelSidharath PathaniaNo ratings yet
- A Case ReportDocument14 pagesA Case ReportSandesh GurungNo ratings yet
- SDLC Lab2Document16 pagesSDLC Lab2Chauhan AkanshaNo ratings yet
- PrototypingDocument10 pagesPrototypingNdumisoSitholeNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document19 pagesUnit 2mastersin2022No ratings yet
- SPM Unit 2 NotesDocument19 pagesSPM Unit 2 NotesPrateek SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Product Design - BasicsDocument18 pagesProduct Design - BasicsVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Group A SEDocument13 pagesGroup A SEAmina TariqNo ratings yet
- AgilemodelDocument2 pagesAgilemodelvamsi4929jNo ratings yet
- Process Mode1Document9 pagesProcess Mode1PRINCE HINGRAJIYANo ratings yet
- Assignment No.1: Advance Software EngineeringDocument6 pagesAssignment No.1: Advance Software Engineering韩远No ratings yet
- 4 SDLC Model Iterative Model Incremental ModelDocument22 pages4 SDLC Model Iterative Model Incremental Modelmanjiri510No ratings yet
- 8 Agile ModelDocument2 pages8 Agile Modelraajpout.343No ratings yet
- SPM Unit 2 NotesDocument19 pagesSPM Unit 2 NotesMAYANK RAGHAVNo ratings yet
- All in One AssignmentDocument46 pagesAll in One AssignmentNirmalNo ratings yet
- Ra2011026010080 Week1 AssignmentDocument8 pagesRa2011026010080 Week1 AssignmentShaik IrfanNo ratings yet
- Real-World Solutions for Developing High-Quality PHP Frameworks and ApplicationsFrom EverandReal-World Solutions for Developing High-Quality PHP Frameworks and ApplicationsRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Software TestingDocument28 pagesSoftware TestingBalaram Papana100% (2)
- An Introduction To Software Engineering: Presenter Ambili P KDocument23 pagesAn Introduction To Software Engineering: Presenter Ambili P KBalaram PapanaNo ratings yet
- Software Testing: Presenter: Ambili P KDocument19 pagesSoftware Testing: Presenter: Ambili P KBalaram Papana100% (1)
- Basic Concepts of Software QualityDocument41 pagesBasic Concepts of Software QualityBalaram PapanaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Software Project ManagementDocument83 pagesBasic Concepts of Software Project ManagementBalaram PapanaNo ratings yet