Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9032 Experiment 01
9032 Experiment 01
Uploaded by
Satish KaradeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9032 Experiment 01
9032 Experiment 01
Uploaded by
Satish KaradeCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical Measurements (9032)
Experiment No. 1
EXPERIMENT NO. 1
1.0 TITLE :
a) b) Preparation for laboratory work . To study the constructional details of Permanent Magnet Moving Coil and Moving iron instruments. Part a) Preparation for laboratory work. Before coming in the laboratory for performing the practicals, please do the following 1. Study the symbols and units.
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
Electrical Measurements (9032)
Experiment No. 1
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
Electrical Measurements (9032)
Experiment No. 1
2.
Answer the questions on basic knowledge
Questions : Write answers to QQQQ (Question numbers to be allotted by the teacher)
1) 2)
Why symbols are necessary in electrical engineering? What information is obtained from the meter marked with following symbols? Write it in two lines.
3) 4) 5) 6)
Draw a circuit to indicate use of Auto - transformer, A. C. Voltmeter, A. C. Ammeter and load. Draw a circuit to indicate use of potential divider, D.C. Voltmeter, D. C. Ammeter and Rheostat. Draw symbols for P.M.M.C. and M. I. Type instruments. List the ranges of voltmeters, ammeters and wattmeters in your laboratory.
(Space for answers)
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
Electrical Measurements (9032)
Experiment No. 1
(Space for answers)
Signature of Teacher
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
Electrical Measurements (9032)
Experiment No. 1
Part B :To study the constructional details of Permanent Magnet Moving Coil and Moving Iron Instruments.
2.0
PRIOR CONCEPTS:
Deflecting torque, Controlling torque, Damping torque. Force on a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field Magnetic repulsion.
3.0
NEW CONCEPTS
Proposition 1 : P.M.M.C. instrument (construction). The instrument has Deflecting system, Controlling system and Damping system. Deflecting system consists of a permanent magnet made of Alnico, a core of soft iron and moving coil of enameled copper wire. The moving coil has a thin cross-section and about 50 - 100 turns. It is wound on a rectangular aluminium former. The former is pivoted on a spindle. The moving coil is free to rotate in the gap of permanent magnet and fixed core. Controlling system consists of springs, called control springs, made of phosphor bronze. (springs also act as the leads for the current). Damping system is based on principle of eddy current. Eddy current damping system generates eddy currents in the permanent magnet and damps the oscillations of indicating pointer by providing force in the opposite direction. Concept Structure 1 :
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
Electrical Measurements (9032)
Experiment No. 1
Proposition 2 : P.M.M.C. instrument (operation). When the moving coil in the field of permanent magnet caries current, a deflecting torque is produced which is proportional to current through the moving coil. Control springs produce the controlling torque which is proportional to angle of deflection. Eddy currents circulating in the aluminium former produce damping torque. Which is proportional to eddy emf induced in it. Concept Structure 2 :
Proposition 3 : P.M.M.C. instrument (scale and use) In PMMC instrument, the scale is uniform as the deflecting torque is linearly proportional to current flowing through the coil. Direction of deflection depends on the direction of current through the moving coil, so the instrument is used for DC measurement only and polarities must be observed while connecting the instrument.
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
Electrical Measurements (9032)
Experiment No. 1
Concept Structure 3 :
Proposition 3 : P.M.M.C. instrument (used for AC measurements). With rectifier, a P.M.M.C. instrument can be connected to AC supply, and the instrument is called as Rectifier type instrument. The rectifier type instrument measures average or r. m. s. AC value depending upon calibration of its scale. Concept Structure 4 :
Part II : Moving Iron Instrument Proposition 5 : Repulsion type MI instrument (construction). The instrument has Deflecting system, Controlling system and Damping system. Deflecting system consists of a circular coil. A soft iron piece called fixed iron is attached to the coil from inside. Spindle is along the axis of coil. Another soft iron piece called as moving iron is attached to the spindle. Controlling system consists of springs, called control springs made of phosphor bronze. Damping system consists of air friction damping.
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
Electrical Measurements (9032)
Experiment No. 1
Concept Structure 5 :
Proposition 6 : Repulsion M. I. Instrument (operation). While coil carries current, the soft iron pieces gets magnetized. Similar poles are formed on the nearer faces of soft iron pieces and they repeal each other. Thus the deflecting torque is due to the repulsion and it is proportional to square of the current through the coil. Control spring provide the controlling torque which is proportional to angle of deflection. Air friction damping is provided to the instrument. So damping torque is proportional to movement of piston in air chamber.
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
Electrical Measurements (9032)
Experiment No. 1
Concept Structure 6 :
Proposition 7 : M. I. Instrument (Scale and Use). In M. I. Instruments, the deflecting torque i.e. the magnitude of deflection is proportional to square of the current (I) so the scale of the instrument is non - uniform and cramped at the beginning. The direction of deflection does not depend on the direction of the current through the coil so the instrument can be used for DC as well as AC measurements and polarities need not be observed while connecting the instrument. (P.M.M.C. instruments being more accurate, they are preferred for DC measurements).
4.0
LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
Intellectual skills: To understand the concept of P.M.M.C. instrument. To understand the concept of M. I. instrument. Motor skills: Ability to use P.M.M.C. instrument. Ability to use M. I. instrument
5.0
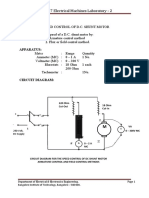
APPARATUS :
Part A : P.M.M.C. instruments (Ammeter, Voltmeter, - any range). Part B : M. I. Instruments (Ammeter, Voltmeter, - any range). o
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
Electrical Measurements (9032)
Experiment No. 1
6.0
STEPWISE PROCEDURE :
Part A : Open a given P.M.M.C. instrument. Observe Deflecting, Controlling and Damping systems. Draw sketch showing all parts of the instrument and label them. (Space for sketch)
Part B : Open a given M. I. instrument. Observe Deflecting, Controlling and Damping systems. Draw sketch showing all parts of the instrument and label them. (Space for sketch)
10
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
Electrical Measurements (9032)
Experiment No. 1
7.0
QUESTIONS :
Write answers to Q. 1, 2 and 15. Write four answers from remaining questions to QQQQ (Question numbers to be allotted by the teacher). 1. Identify the instrument shown below and label the marked components of it Instrument _____________________
Components : 1. __________________ 2. __________________ 3. __________________ 4. __________________ 5. __________________
Instrument _____________________ Components : 1. __________________ 2. __________________ 3. __________________ 4. __________________ 5. __________________
Instrument _____________________
2.
Identify the instrument and label the components marked with arrow Instrument _____________________
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
11
Electrical Measurements (9032)
Experiment No. 1
Complete the following table :
3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13.
Draw sectional view of PMMC and MI instruments to scale. What type of damping is provided in PMMC and MI instruments? Give applications of PMMC and MI instruments. What are the functions of deflecting, controlling and damping torques? Why PMMC instrument is used for d.c. only? State the advantages and limitations of PMMC instrument. State the advantages and limitations of MI instrument. Which meter will you use for measuring 7.5 amp DC? Which type of meter will you use for measuring 6 A a.c.? Is it possible to measure 6A a.c. with a PMMC instrument? Give reason. Identify the type of meter. Draw its IS symbol.
14.
State the material used for PMMC and MI instruments in their constructional parts.
12
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
Electrical Measurements (9032)
Experiment No. 1
(Space for answer)
Signature of Teacher
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
13
You might also like
- Industrial Automation 314 Laboratory ManualDocument11 pagesIndustrial Automation 314 Laboratory Manualkatjinomasa kavetuNo ratings yet
- Storey: Electrical & Electronic Systems © Pearson Education Limited 2004Document15 pagesStorey: Electrical & Electronic Systems © Pearson Education Limited 2004slg2010kvlNo ratings yet
- Measuring InstrumentsDocument36 pagesMeasuring InstrumentsGurram Jithin100% (1)
- Government Polytechnic, Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Electrical Workshop LabDocument15 pagesGovernment Polytechnic, Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Electrical Workshop LabTapobroto Chatterjee100% (1)
- Commutation in DC Machine or Commutation in DC Generator or Motor - Electrical4uDocument6 pagesCommutation in DC Machine or Commutation in DC Generator or Motor - Electrical4uM Kumar MarimuthuNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument43 pagesInduction MotorAshvani ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Experiment-3Document6 pagesLab Report: Experiment-3ayash mohantyNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics 1st ExamDocument34 pagesIndustrial Electronics 1st ExamJomar Bonje100% (1)
- Unit 35 Portfolio Answer 2018Document22 pagesUnit 35 Portfolio Answer 2018Hatem HusseinNo ratings yet
- Plant Engineering 2006sepDocument5 pagesPlant Engineering 2006sepRamco33No ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document15 pagesPresentation 1Ajay Talajiya0% (1)
- Experiment 4 - Three Phase Uncontrolled RectifierDocument13 pagesExperiment 4 - Three Phase Uncontrolled RectifierAaaa DdddNo ratings yet
- Magenetic Chip Collector New 2Document27 pagesMagenetic Chip Collector New 2Hemasundar Reddy JolluNo ratings yet
- Diac CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesDiac CharacteristicsSourabh100% (1)
- .NG EEC115 Electrical Engineering Science 1Document29 pages.NG EEC115 Electrical Engineering Science 1archibong dominicNo ratings yet
- 1 - Insulators String Efficiency ProblemDocument71 pages1 - Insulators String Efficiency ProblemVeera Vamsi Yejju100% (1)
- DC Motor - PPTDocument41 pagesDC Motor - PPTali abdel hadiNo ratings yet
- (Always Learning) Bali, S.P - Electrical Technology-Dorling Kindersley (India) (2013)Document605 pages(Always Learning) Bali, S.P - Electrical Technology-Dorling Kindersley (India) (2013)theking Cor100% (1)
- Basic Electrical and Instrumentation Engineering - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersDocument25 pagesBasic Electrical and Instrumentation Engineering - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersM.V. TVNo ratings yet
- AC PotentiometerDocument3 pagesAC PotentiometerNh Chuminda Yapa100% (1)
- Phasor Representation of ACDocument21 pagesPhasor Representation of ACKavitha NaikNo ratings yet
- Cluster 2 Study GuideDocument17 pagesCluster 2 Study GuideShavoy RichardsonNo ratings yet
- PE Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesPE Lesson PlanAnbalagan GuruNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 - DC Machines PDFDocument123 pagesUnit-2 - DC Machines PDFsujithNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical: Basic Electricity and ElectronicsDocument12 pagesBasic Electrical: Basic Electricity and ElectronicsHadi RusmantoNo ratings yet
- EMMI Lab PDFDocument31 pagesEMMI Lab PDFSarithareddy AvuluriNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Alternating CurrentDocument42 pagesSingle Phase Alternating CurrentMuhammad Waqiuddin Bin Shamsul NizamNo ratings yet
- Electric Machine DesignDocument2 pagesElectric Machine DesignSaman Tofighi0% (1)
- Assignment Questions - Part 1Document2 pagesAssignment Questions - Part 1AnupriyaSaxenaNo ratings yet
- EIE Lecture Notes (6th Semester Electrical)Document84 pagesEIE Lecture Notes (6th Semester Electrical)asli almu0% (1)
- Single Line Diagram of Power System - Circuit GlobeDocument7 pagesSingle Line Diagram of Power System - Circuit GlobeMohammad HamamdNo ratings yet
- Ee8015-Unit-2-Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument30 pagesEe8015-Unit-2-Refrigeration and Air ConditioningS Jey RhajenNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Rectifiers (Chapter 3) by BakshiDocument99 pagesPower Electronics Rectifiers (Chapter 3) by BakshiTariq Khan100% (2)
- Classification of Transmission LinesDocument15 pagesClassification of Transmission LinesJim Erol BancoroNo ratings yet
- "DOL Starter": Submitted byDocument10 pages"DOL Starter": Submitted byKartik InamdarNo ratings yet
- Automatic Control of Street LightDocument63 pagesAutomatic Control of Street LightMani RaoNo ratings yet
- Project PPT 1Document11 pagesProject PPT 1Mahesh ShendeNo ratings yet
- Objectives: at The End of Practical Laboratory, Students Should Be AbleDocument4 pagesObjectives: at The End of Practical Laboratory, Students Should Be Ablecla ren rajNo ratings yet
- DC Machines: Parts of DC MachineDocument51 pagesDC Machines: Parts of DC MachineKUMARNo ratings yet
- Moving Iron InsturmentsDocument3 pagesMoving Iron InsturmentsYash BansalNo ratings yet
- Brake Load Test of Squirel Cage Induction Motor 3 PhaseDocument7 pagesBrake Load Test of Squirel Cage Induction Motor 3 Phasejassisc100% (1)
- Practical No 1 Name M.Jawad Roll No 21Bsc01 Semester 4 Sir Bilal HussainDocument5 pagesPractical No 1 Name M.Jawad Roll No 21Bsc01 Semester 4 Sir Bilal HussainZAIN UL ABIDENNo ratings yet
- Psoc Course FileDocument14 pagesPsoc Course Filecholleti sriramNo ratings yet
- Ec1 Lab Manual PDFDocument44 pagesEc1 Lab Manual PDFpardhu_y4No ratings yet
- EE306 Power System Analysis Hadi SaadatDocument18 pagesEE306 Power System Analysis Hadi SaadatGayathri S. NairNo ratings yet
- Power System FaualtDocument32 pagesPower System Faualtmedanite ashebirNo ratings yet
- Meter Reading ExerciseDocument4 pagesMeter Reading ExerciseGino PaduaNo ratings yet
- Tube Light ManualDocument2 pagesTube Light ManualSwaroop MallickNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 PPT MasterDocument57 pagesUnit 4 PPT MasterRamNo ratings yet
- HRC Fuse: Working & Its ApplicationsDocument3 pagesHRC Fuse: Working & Its ApplicationsPandurang PisalNo ratings yet
- Lec9 - Basics of Electric Drives - IMDocument10 pagesLec9 - Basics of Electric Drives - IMTeofilo DedietroNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of DC MotorDocument4 pagesSpeed Control of DC MotorsanjuNo ratings yet
- A.C. Series MotorDocument16 pagesA.C. Series MotorM BNo ratings yet
- A Report On The "3-Phase Line Fault Detector" Ee344 Minor Project - IDocument34 pagesA Report On The "3-Phase Line Fault Detector" Ee344 Minor Project - IDhruv PatelNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide to International Standardization for Electrical Engineers: Impact on Smart Grid and e-Mobility MarketsFrom EverandPractical Guide to International Standardization for Electrical Engineers: Impact on Smart Grid and e-Mobility MarketsNo ratings yet