Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math 8 Chapter 8 Notes
Math 8 Chapter 8 Notes
Uploaded by
api-114939020Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math 8 Chapter 8 Notes
Math 8 Chapter 8 Notes
Uploaded by
api-114939020Copyright:
Available Formats
8.
Sketching views of Objects
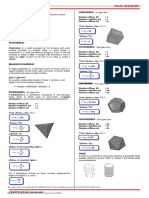
Isometric Drawing is a drawing of a 3D object on triangular dot paper. Drawing different views of an object: When given an isometric drawing, you should create the model using linking blocks. Then rotate the object to look at the all the views. You will be expected to draw the front, left, right and top views of an object. Draw the front view first. Place the top view above the front view and the side views beside the front views. All views should be lined up. You can use dotted lines to show this alignment. Internal line segments are used to show changes in depth. Ex) Sketch the front, top and side views of the following object:
Top
Left Side
Front
Right Side
Do Workbook page 192 with students Assign pages 437-439 #s 4-5, 7-9, 12-14, 16
8.2 Drawing views of rotated objects An object can be rotated: Horizontally about Vertical axis or Vertically about horizontal axis
Rotation may be clockwise Or counterclockwise You will do rotations of 90, 180, and 270
Rotation may be away from you or towards you
When objects are rotated, the shape may stay the same but the views will be different. Some views may interchange, depending on the rotation. Ex) A) Sketch the front, side and top views of the following object
Top
Left Side
Front
Right Side
B)
Sketch the views of the object after a vertical rotation 90 away from you.
Top
Left Side
Front
Right Side
C)
What happened with the views? Left & Right stayed the same but flipped Front changed completely Top - Original front view
Assign pages 444-446 #s 3-12
8.4 Identifying Transformations Three types of Transformations: 1. Translation Known as a slide A translation arrow shows movement along a straight line The original and the image has the same shape and orientation
2.
Reflection Known as a flip A reflection line is used to flip the shape The original and the image have the same shape but the orientation is reversed.
line of reflection
3.
Rotation Known as a turn A turn center is used to rotate an object so many degrees clockwise or counterclockwise. The original and the image have the same shape and orientation but may face different ways.
A Rotate 90' cw about A
Work through investigation 8.4 on page 456 with students. Also have students play the transformers game (BLM 8a & 8b) to review these transformations. Assign pages 460-461 #s 5-12
Investigation 8.4 Page 456 Tia used this design when she laid interlocking paving stones in her driveway.
To create the design, she translated, rotated and reflected the shaded space. Each labeled shape is the image after a transformation. Identify a transformation that produced each image by completing the table below.
Image
Transformation
Explanation
8.5 Constructing Tessellations When congruent copies of a shape cover a plane with no overlaps or gaps the shape tessellates. The design created is called a tessellation. Ex) The diamond shape tessellates since there are no overlaps or gaps. The decagon shape does not tessellate since there are gaps.
A regular polygon is a simple closed figure that has all sides and all angles congruent. Which regular polygons tessellate? Do Activity with Students Using shapes to Tessellate: The sum of the angles at any point where the vertices meets must be 360. All triangles and quadrilaterals tessellate since their interior angles add up to 360. You can also make composite shapes that tessellate by combining shapes. (See Examples 1&2 on pages 464-467) Assign pages 467-469 #s 6-18
You might also like
- Draw Better: Learn To Draw With ConfidenceDocument26 pagesDraw Better: Learn To Draw With ConfidencebackitNo ratings yet
- Turn, Flip Slide Resize: RotationDocument8 pagesTurn, Flip Slide Resize: Rotationpatric bethelNo ratings yet
- Draw Better SampleDocument26 pagesDraw Better SampleSimona DumitruNo ratings yet
- Geometric Designs - SymmetryDocument13 pagesGeometric Designs - Symmetrymeth lazaroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Illustrated VocabularyDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Illustrated Vocabularyapi-308135634No ratings yet
- Transformation PDFDocument16 pagesTransformation PDFShaikh IradNo ratings yet
- Angles & Straight LinesDocument6 pagesAngles & Straight LinesSylvia WongNo ratings yet
- Transformation ProjectDocument15 pagesTransformation Projectapi-288344834No ratings yet
- Transformations: BTEOTSSSBAT Solve Problems Involving Reflection, Rotation, Translation and EnlargementDocument23 pagesTransformations: BTEOTSSSBAT Solve Problems Involving Reflection, Rotation, Translation and EnlargementmangimanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesAssessment Lesson PlanBrian CampbellNo ratings yet
- Mathematics7 q3 Week8and9 v4Document11 pagesMathematics7 q3 Week8and9 v4Rick Jones Abella BuicoNo ratings yet
- Transformations ProjectDocument15 pagesTransformations Projectapi-360928820No ratings yet
- Notes October 2021 CHAPTER17: Position and Movement Grade: 8 Subject: MathematicsDocument9 pagesNotes October 2021 CHAPTER17: Position and Movement Grade: 8 Subject: MathematicsAkshara ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Notes in RotationsDocument4 pagesNotes in RotationshfejNo ratings yet
- LN003 MN114 Orthographic ProjectionDocument62 pagesLN003 MN114 Orthographic ProjectionLAURENT JIBUNGENo ratings yet
- Junior6 Transformations LessonDocument16 pagesJunior6 Transformations LessonaraymundomNo ratings yet
- Tranformations: Rotations: Name Student Activity ClassDocument4 pagesTranformations: Rotations: Name Student Activity ClassDian RizkyNo ratings yet
- Notes December 2020 Chapter 17: Position and Movement Grade: 8 Subject: MathematicsDocument9 pagesNotes December 2020 Chapter 17: Position and Movement Grade: 8 Subject: Mathematicsanish kanthethi100% (1)
- TransformationsDocument19 pagesTransformationsrandhirsaha2000No ratings yet
- TransformationDocument34 pagesTransformationruv.asn17No ratings yet
- CH 09Document32 pagesCH 09Vincents Genesius EvansNo ratings yet
- 3rd ESO EnglishDocument4 pages3rd ESO EnglishDavid Bellvis EgeaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern World Activity No. 1Document12 pagesMathematics in The Modern World Activity No. 1primusmagnuNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLesson Plansai10111989No ratings yet
- PLATE 5 Week5Document17 pagesPLATE 5 Week5Esona Rachelyn P.No ratings yet
- Class 5Document9 pagesClass 5amrithakhubaNo ratings yet
- Form 1 TransformationsDocument66 pagesForm 1 Transformationsiminathi ndlovuNo ratings yet
- Transformations Packet-GraseckDocument33 pagesTransformations Packet-Graseckapi-316517647No ratings yet
- Chap 10Document42 pagesChap 10nicolas_urdanetaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Orthographic ProjectionDocument61 pages3 - Orthographic ProjectionaliffNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Isometric Projection - IIDocument40 pagesLecture 7 - Isometric Projection - IIPremNo ratings yet
- TransformationsRotations LessonPlanDocument6 pagesTransformationsRotations LessonPlanocsc100% (1)
- Chapter09 Geometric FiguresDocument32 pagesChapter09 Geometric Figureslen16328100% (4)
- Unit 2 - Part - IDocument55 pagesUnit 2 - Part - IVamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Part - IDocument55 pagesUnit 2 - Part - IVamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Transformation Module - TitinDocument28 pagesTransformation Module - TitinPryhant KielhNo ratings yet
- Transformations: Proffessor Petty MATH 1351.301Document15 pagesTransformations: Proffessor Petty MATH 1351.301JulieNo ratings yet
- Axonometric & Oblique Projection With ExampleDocument37 pagesAxonometric & Oblique Projection With ExampleBahar Aktuna100% (1)
- Topic 8 TransformationDocument26 pagesTopic 8 Transformationayie4256017No ratings yet
- Crystal ChemistryDocument6 pagesCrystal ChemistryMithra LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Geometric TransformationsDocument7 pagesGeometric TransformationsSeleneGoberdhanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Design and Graphics: Engineer 1C03Document44 pagesEngineering Design and Graphics: Engineer 1C03lebronNo ratings yet
- Gemp 112Document30 pagesGemp 112Games ZoneNo ratings yet
- G7 Ch11 May27Document86 pagesG7 Ch11 May27Zhihui XieNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Drawing Lect 4 PDFDocument23 pagesCivil Engineering Drawing Lect 4 PDFEngr Muhammad Asif JavaidNo ratings yet
- Notes IsometriesDocument3 pagesNotes IsometriesBoy ShahNo ratings yet
- Title of Assignment: Problem DefinitionDocument3 pagesTitle of Assignment: Problem DefinitionSONAL S.KNo ratings yet
- Transferm AtionsDocument7 pagesTransferm AtionsCHENNAIAH GARI SAI BABUNo ratings yet
- G-CO.A.2 Represent Transformations in The Plane Using, G-CO.A.5 G-CO.D.12Document3 pagesG-CO.A.2 Represent Transformations in The Plane Using, G-CO.A.5 G-CO.D.12api-340613387No ratings yet
- Target: Learning Guide Module Subject Code Math 3 Module Code 2.0 Lesson Code 2.4.1 Time LimitDocument14 pagesTarget: Learning Guide Module Subject Code Math 3 Module Code 2.0 Lesson Code 2.4.1 Time LimitJoh TayagNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing IsometricDocument16 pagesEngineering Drawing Isometricpanashezhou321No ratings yet
- Crystal SymmetryDocument50 pagesCrystal Symmetryfatih muhammadNo ratings yet
- 7 Maths NCERT Exemplar Chapter 12Document30 pages7 Maths NCERT Exemplar Chapter 12Robin SNo ratings yet
- Isometric DrawingDocument38 pagesIsometric DrawingSanthan SalaiNo ratings yet
- Gec104 Module 3Document5 pagesGec104 Module 3MicsjadeCastillo100% (1)
- 7 - Pictorial ProjectionDocument48 pages7 - Pictorial Projectionapi-3815216100% (6)
- Beginner's Guide to Sketching Buildings & Landscapes: Perspective and Proportions for Drawing Architecture, Gardens and More! (With over 500 illustrations)From EverandBeginner's Guide to Sketching Buildings & Landscapes: Perspective and Proportions for Drawing Architecture, Gardens and More! (With over 500 illustrations)No ratings yet
- Two Dimensional Computer Graphics: Exploring the Visual Realm: Two Dimensional Computer Graphics in Computer VisionFrom EverandTwo Dimensional Computer Graphics: Exploring the Visual Realm: Two Dimensional Computer Graphics in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- 2010 Sample Final ExamDocument25 pages2010 Sample Final Examapi-114939020No ratings yet
- 2011 Sample Final ExamDocument25 pages2011 Sample Final Examapi-114939020No ratings yet
- Math 8 Unit 3Document22 pagesMath 8 Unit 3api-114939020No ratings yet
- Math 8 Unit 1Document12 pagesMath 8 Unit 1api-114939020No ratings yet
- Amandas Science Notes Unit 2 FluidsDocument18 pagesAmandas Science Notes Unit 2 Fluidsapi-114939020No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Many Properties of Light Can Be Understood Using A Wave Model of LightDocument17 pagesChapter 4: Many Properties of Light Can Be Understood Using A Wave Model of Lightapi-114939020100% (1)
- Math Unit 6 NotesDocument5 pagesMath Unit 6 Notesapi-114939020No ratings yet
- Math 8 Unit 6Document6 pagesMath 8 Unit 6api-114939020100% (1)
- Year 6 Mathematics Term 2 Unit 1Document5 pagesYear 6 Mathematics Term 2 Unit 1api-267136654No ratings yet
- Kepler Nested Platonic Solids 1Document6 pagesKepler Nested Platonic Solids 1Marius Swart100% (1)
- CBSE Class 8 Maths ActivitiesDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 8 Maths ActivitiesS AdilakshmiNo ratings yet
- 7solid Geometry OC PDFDocument5 pages7solid Geometry OC PDFJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Manpower Activity 11-10-2020Document6 pagesManpower Activity 11-10-2020Joshua MidelNo ratings yet
- CH 16Document29 pagesCH 16Ankita KumariNo ratings yet
- Mat402h Exam U of TDocument2 pagesMat402h Exam U of TCrainlyNo ratings yet
- Math6-Q3M1-Understanding Solid Figures-Roque JADocument32 pagesMath6-Q3M1-Understanding Solid Figures-Roque JAmaster hamster95% (20)
- Geometry and TrigonometryDocument6 pagesGeometry and TrigonometryFranc VenturaNo ratings yet
- Maths Is HellDocument20 pagesMaths Is HellSara AliNo ratings yet
- 8Document5 pages8api-288922072No ratings yet
- Trigon 4to3 SecDocument11 pagesTrigon 4to3 SecmalcommmNo ratings yet
- Math g5 m5 Topic D Lesson 19Document16 pagesMath g5 m5 Topic D Lesson 19Bryan Castrø PingølNo ratings yet
- (Wk3 DLL) 3rd Q Math Nov 21-25Document3 pages(Wk3 DLL) 3rd Q Math Nov 21-25JhuvzCLuna100% (4)
- DLP in Grade 5 - Mathematics (Word)Document5 pagesDLP in Grade 5 - Mathematics (Word)Mariam KarisNo ratings yet
- 7 Triangle Congruence PacketDocument5 pages7 Triangle Congruence Packetapi-243405443No ratings yet
- COT 666 SummaryDocument9 pagesCOT 666 SummaryAdvaith JainkumarNo ratings yet
- Detailed - Lesson - Plan - in - Mathematics - VI - For My COT2Document8 pagesDetailed - Lesson - Plan - in - Mathematics - VI - For My COT2LEOLEN BAGAYANNo ratings yet
- Quadrilateral SDocument5 pagesQuadrilateral SNesimovic SanelaNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mathematics 6 - Q3 - W2Document10 pagesDLL - Mathematics 6 - Q3 - W2May Fatima MingoNo ratings yet
- Solution of Triangles DPPDocument9 pagesSolution of Triangles DPPgandchofNo ratings yet
- Math ProjectDocument9 pagesMath ProjectAlleah GeveroNo ratings yet
- Properties of ParallelogramDocument6 pagesProperties of ParallelogramBABY KONo ratings yet
- MensurationDocument6 pagesMensurationKenneth WongNo ratings yet
- Gse Math Unit 5Document108 pagesGse Math Unit 5api-256719324No ratings yet
- Tessellations: Chaim Goodman-StraussDocument33 pagesTessellations: Chaim Goodman-StraussBunbun 221No ratings yet
- Fraccion Compleja Potencias RaicesDocument7 pagesFraccion Compleja Potencias Raicesnogueraroque7541No ratings yet
- Geometry HistoryDocument2 pagesGeometry HistoryManilyn Requejo ObalNo ratings yet
- Onshape Assignment 12 Transform (You Are Going To Make A Dodecahedron) Part 2 of 3Document26 pagesOnshape Assignment 12 Transform (You Are Going To Make A Dodecahedron) Part 2 of 3api-294653971No ratings yet
- Tessellations CompleteDocument42 pagesTessellations CompleteNinda Dananingrum100% (2)