Professional Documents
Culture Documents
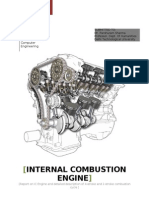
The Internal Combustion Engine Is An Engine in Which The Combustion of A Fuel
The Internal Combustion Engine Is An Engine in Which The Combustion of A Fuel
Uploaded by
Begu CataOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Internal Combustion Engine Is An Engine in Which The Combustion of A Fuel
The Internal Combustion Engine Is An Engine in Which The Combustion of A Fuel
Uploaded by
Begu CataCopyright:
Available Formats
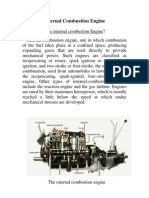
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel (eg.
: fossil fuel) occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine the expansion of the high temperature and pressure gases, which are produced by the combustion, directly applies force to components of the engine, such as the pistons or turbine blades or a nozzle, and by moving it over a distance, generates useful mechanical energy.[7][8][9][10] The term internal combustion engine usually refers to an engine in which combustion is intermittent, such as the more familiar four-stroke and two-stroke piston engines, along with variants, such as the Wankel rotary engine. ICE delivers an excellent power-to-weight ratio with few disadvantages. While there have been and still are many stationary applications, the real strength of internal combustion engines is in mobile applications and they dominate as a power supply for cars, aircraft, and boats, from the smallest to the largest
You might also like
- Gilmore-Isms Season 4Document8 pagesGilmore-Isms Season 4Begu CataNo ratings yet
- EngineDocument2 pagesEnginefirosNo ratings yet
- Assignment AT 112Document4 pagesAssignment AT 112Zamora Enguerra EmmalyneNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine: "ICEV" Redirects Here. For The Form of Water Ice, See - For The High Speed Train, SeeDocument1 pageInternal Combustion Engine: "ICEV" Redirects Here. For The Form of Water Ice, See - For The High Speed Train, SeeSelva KumarNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EngineDocument13 pagesInternal Combustion EngineNAITAJINo ratings yet
- Duke Engine: An Overview of Present State of Art and Future PotentialDocument4 pagesDuke Engine: An Overview of Present State of Art and Future PotentialRitic JainNo ratings yet
- Concept of An Internal Combustion EngineDocument9 pagesConcept of An Internal Combustion EngineDiego Andrée ArmasNo ratings yet
- Seminar Duke EngineDocument4 pagesSeminar Duke EngineMahaManthraNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Jump ToDocument7 pagesInternal Combustion Engine: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia Jump ToAbdullah KhaledNo ratings yet
- The Internal Combustion EngineDocument8 pagesThe Internal Combustion EngineRiko AidaNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine: Delhi Technological UniversityDocument22 pagesInternal Combustion Engine: Delhi Technological UniversityArth AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Intoduction To I..c EngineDocument1 pageIntoduction To I..c EngineThe Lord Nura ANo ratings yet
- Term Paper ON I C Engine ThermodynamicDocument14 pagesTerm Paper ON I C Engine ThermodynamicSuresh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Internal Combustion EngineDocument25 pagesPresentation Internal Combustion EngineAbderrazak ZahirNo ratings yet
- Szorenyi EngineDocument13 pagesSzorenyi EngineLuis EspinosaNo ratings yet
- EngineDocument19 pagesEngineSukumar PaniNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Engines emDocument9 pagesDifferent Types of Engines emJose Albert MacayaNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EngineDocument16 pagesInternal Combustion EngineHamzeh Al-QaisiNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine-2016Document27 pagesInternal Combustion Engine-2016ZerotheoryNo ratings yet
- Engine HistoryDocument38 pagesEngine HistoryNijanthan RNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 01 Air Breathing Propulsion (Ac8501)Document34 pagesAssignment - 01 Air Breathing Propulsion (Ac8501)SUBHASH PNo ratings yet
- C - E - Exhaust I - Inlet P - R - S - V - W-: Gray StructureDocument2 pagesC - E - Exhaust I - Inlet P - R - S - V - W-: Gray StructureNithyanandmNo ratings yet
- SimoleDocument2 pagesSimoleKelantan QawiyNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine - WikipediaDocument23 pagesInternal Combustion Engine - WikipediaDhrubajyotiGuptaNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EngineDocument4 pagesInternal Combustion EngineMugabe GomosNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Two Stroke & Four Stroke EnginesDocument4 pagesA Comparison of Two Stroke & Four Stroke EnginesLubna KhanNo ratings yet
- Petrol Engine: Working CyclesDocument7 pagesPetrol Engine: Working CyclesBrijesh Patel100% (1)
- Ijltest 08140014g.karthickDocument11 pagesIjltest 08140014g.karthickGrace Roxanne Gandia-AlpajoraNo ratings yet
- Engine - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument12 pagesEngine - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShumway GordonNo ratings yet
- Wankel Engine: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument34 pagesWankel Engine: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRajeshwar SinghNo ratings yet
- Wiki Grazing 3Document8 pagesWiki Grazing 3WolfMensch1216No ratings yet
- Ijri Me 01 006Document5 pagesIjri Me 01 006ijripublishersNo ratings yet
- Hand Made CarDocument33 pagesHand Made CarSahil DhirNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine: Navigation SearchDocument21 pagesGas Turbine: Navigation SearchluffydsiniNo ratings yet
- Pimsat Colleges Engineering Materials 1Document8 pagesPimsat Colleges Engineering Materials 1Sev Anne T. GonzalesNo ratings yet
- MOTORESDocument22 pagesMOTORESAry guimaraes netoNo ratings yet
- Project Intro Internal Combustion EngineDocument4 pagesProject Intro Internal Combustion EngineAmit Kumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- NEVA93011FUDocument21 pagesNEVA93011FUvictor.ansartNo ratings yet
- Ajmie 20160101 11Document9 pagesAjmie 20160101 11Deniz AtmacaNo ratings yet
- Engine: Machine Energy Mechanical EnergyDocument79 pagesEngine: Machine Energy Mechanical Energyshubhamvpathade03No ratings yet
- Study On EngineDocument2 pagesStudy On EnginePRIGAHNo ratings yet
- The Case For The Diesel EngineDocument26 pagesThe Case For The Diesel EngineChangsun HwangNo ratings yet
- Wiki Grazing 4Document4 pagesWiki Grazing 4WolfMensch1216No ratings yet
- Ship Machineries: by Group 2Document54 pagesShip Machineries: by Group 2Wilfred Joseph T. Casas100% (1)
- 19me02033 I.C Engines ReportDocument18 pages19me02033 I.C Engines ReportNagapavan MarisettyNo ratings yet
- Four-Stroke and Two-Stroke Marine Engines Comparison and ApplicationDocument8 pagesFour-Stroke and Two-Stroke Marine Engines Comparison and ApplicationAbdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Engines EssayDocument5 pagesEngines EssayValiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-4Document58 pagesChapter 1-4Yousef SalahNo ratings yet
- Jimma University Jimma Institute of Technology Faculty of Mechanical EngineeringDocument52 pagesJimma University Jimma Institute of Technology Faculty of Mechanical EngineeringSofoniyas FeysaNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Flywheel in A Multi Cylinder Petrol EngineDocument10 pagesDesign and Analysis of Flywheel in A Multi Cylinder Petrol Enginesadman.me.20200208042No ratings yet
- Novel Two-Stroke High-Speed Direct-Injection Diesel..mattarelli09Document20 pagesNovel Two-Stroke High-Speed Direct-Injection Diesel..mattarelli09enjpetNo ratings yet
- Energy EducationDocument46 pagesEnergy EducationCharol AoayNo ratings yet
- Two Stroke EngineDocument7 pagesTwo Stroke Engine21AE313 Aman khanNo ratings yet
- Combustion Turbines: Five-Stroke EngineDocument3 pagesCombustion Turbines: Five-Stroke EngineWolfMensch1216No ratings yet
- Design Methodology For Compressed Air EngineDocument7 pagesDesign Methodology For Compressed Air EngineShashank SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Internal CombustionDocument16 pagesInternal CombustionWojtek PolisNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Partie 1Document28 pagesCH 2 Partie 1Ali zitouni MeriemNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbines: HistoryDocument12 pagesGas Turbines: HistorySuresh Kannan PNo ratings yet
- Engine Design-Theory (M-4)Document7 pagesEngine Design-Theory (M-4)AADITYA SAH[UCOE-3692]No ratings yet
- Naval Engineering: Principles and Theory of Gas Turbine EnginesFrom EverandNaval Engineering: Principles and Theory of Gas Turbine EnginesNo ratings yet
- Manual Utilizare Usa MititeluDocument31 pagesManual Utilizare Usa MititeluValentin EneaNo ratings yet
- Scene Study Guidelines: A Handbook For Theater 2668 Acting I Fundamentals of ActingDocument36 pagesScene Study Guidelines: A Handbook For Theater 2668 Acting I Fundamentals of ActingBegu Cata100% (2)
- Uhf Ask Receiver IC U3741BM: FeaturesDocument33 pagesUhf Ask Receiver IC U3741BM: FeaturesBegu CataNo ratings yet
- Air Induction SystemDocument12 pagesAir Induction SystemBegu CataNo ratings yet