Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reduced Adjective Clause and Reduced Adverb Clause
Reduced Adjective Clause and Reduced Adverb Clause
Uploaded by
Ariza YandwiputraCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- German in Review Answer KeysDocument155 pagesGerman in Review Answer KeysLucas Caruso100% (1)
- Test 4 GrammDocument2 pagesTest 4 GrammДарья Мущак67% (3)
- Su1. TCCDocument10 pagesSu1. TCCDumitrița PopaNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses PDFDocument14 pagesFuture Tenses PDFMAR100% (2)
- Acfrogahakb0a1lw3aokw28nyns7rjowrq FLLH D8lezp6xbclrpjztrb6n15znkdhu9ty7wpdp5pvnqrr 8gl9sasm7om14s1yajuncccci5z3pkc14rhf Tapzsuw Cj3q3d1td254z6pp IgDocument4 pagesAcfrogahakb0a1lw3aokw28nyns7rjowrq FLLH D8lezp6xbclrpjztrb6n15znkdhu9ty7wpdp5pvnqrr 8gl9sasm7om14s1yajuncccci5z3pkc14rhf Tapzsuw Cj3q3d1td254z6pp IgdoniNo ratings yet
- Reduced Relative ClausesDocument7 pagesReduced Relative ClausesAamir100% (2)
- TgsDocument19 pagesTgsShahnaz Putri MaghfirahNo ratings yet
- Work of Syntax2 - 2024Document14 pagesWork of Syntax2 - 2024708242970No ratings yet
- A1 - Lektion 26 - Accusative CaseDocument4 pagesA1 - Lektion 26 - Accusative CaseJoelNo ratings yet
- VerbalsDocument2 pagesVerbalsCalvin MallariNo ratings yet
- Active Vs Passive VoiceDocument10 pagesActive Vs Passive VoiceRozita KamarudinNo ratings yet
- Actv Passive Voice Notes 2Document3 pagesActv Passive Voice Notes 2ainun mardiahNo ratings yet
- Objects As Complements-Lecture NoteDocument21 pagesObjects As Complements-Lecture NoteMun'im MoonNo ratings yet
- AnkitDocument68 pagesAnkitAnkit TiwariNo ratings yet
- Basic DiagrammingDocument4 pagesBasic DiagrammingKezia CanutoNo ratings yet
- Types of Reduced Relative ClausesDocument2 pagesTypes of Reduced Relative ClausesPhát Võ Nguyễn HoàngNo ratings yet
- Vertical Cutout SlideDocument12 pagesVertical Cutout SlideyoonglespianoNo ratings yet
- Dangling Modifiers: Tutoring and Testing CenterDocument2 pagesDangling Modifiers: Tutoring and Testing CenterLuis Fernando Lopez PuenteNo ratings yet
- SubjunctivesDocument19 pagesSubjunctivesFauzi_Kan_Kiku_1510No ratings yet
- Active Vs Passive Voice 25072022 025216pmDocument18 pagesActive Vs Passive Voice 25072022 025216pmh.zaidi569No ratings yet
- Relative ClauseDocument11 pagesRelative ClauseAviva CHANNo ratings yet
- Reduced Relative ClausesDocument8 pagesReduced Relative ClausesGemma PerezNo ratings yet
- Name:jose Juan Feliz Fernandez: Subject Verb ClauseDocument10 pagesName:jose Juan Feliz Fernandez: Subject Verb ClauseAlbert TejedaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 GrammarDocument7 pagesGroup 4 GrammarFadilah Rizqi AmaliahNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 5 - MAKALAH 1 Reduce Adjective Clauses (English Version)Document11 pagesKelompok 5 - MAKALAH 1 Reduce Adjective Clauses (English Version)Tina DiarNo ratings yet
- Learn Korean With Blackpink PDFDocument6 pagesLearn Korean With Blackpink PDFFor JunkNo ratings yet
- Past and Present Passive - Cancould.pastperfectDocument4 pagesPast and Present Passive - Cancould.pastperfectLorena Fernandez RoldanNo ratings yet
- Sentence StructureDocument155 pagesSentence Structureapi-3808291100% (4)
- Diagramming SentencesDocument9 pagesDiagramming SentencesRev Andrew Salinas100% (1)
- Theory N Exercises of Adjective ClauseDocument7 pagesTheory N Exercises of Adjective ClauseJodi AkbarNo ratings yet
- Logical Connectives: Ifsthenb. Not SDocument6 pagesLogical Connectives: Ifsthenb. Not SCdxgugihiNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument18 pagesActive and Passive VoicetanzilanasibzadaNo ratings yet
- Ingles PDFDocument2 pagesIngles PDFBernabe UyuNo ratings yet
- Clause and Its KindsDocument9 pagesClause and Its KindsMuhammad yousafNo ratings yet
- Helping Verbs: Class of VerbDocument11 pagesHelping Verbs: Class of VerbJasmine AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Second PartDocument3 pagesUnit 9 Second PartBrkic EdinNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument8 pagesActive and Passive VoiceEric Arriaga AltamiranoNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument43 pagesPassive VoiceRaquel García Iglesias100% (1)
- Diagramming SentencesDocument3 pagesDiagramming SentencesDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- Subjective and Objective Complements: Chapter ##Document6 pagesSubjective and Objective Complements: Chapter ##Vishnu Ronaldus NarayanNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Morphology and Syntax by Ali Asghar Roll No O11Document6 pagesAssignment of Morphology and Syntax by Ali Asghar Roll No O11Ali Asghar 011100% (1)
- Adjective Clause (Penggunaan Who, Whom, Whose, Which, DLL) : Belajar English Yuk... !!! Iqbal 0 KomentarDocument5 pagesAdjective Clause (Penggunaan Who, Whom, Whose, Which, DLL) : Belajar English Yuk... !!! Iqbal 0 Komentarokik hariNo ratings yet
- Adjective Clause (Penggunaan Who, Whom, Whose, Which, DLL) : Belajar English Yuk... !!! Iqbal 0 KomentarDocument5 pagesAdjective Clause (Penggunaan Who, Whom, Whose, Which, DLL) : Belajar English Yuk... !!! Iqbal 0 Komentarokik hariNo ratings yet
- Reduced Clause 7th GroupDocument5 pagesReduced Clause 7th GroupAfg-Ghynhaalfiyah Chyllowend Arisyhaa KeiinhaLynchNo ratings yet
- Voice (Active and Passive)Document1 pageVoice (Active and Passive)Hans Matthew AntiojoNo ratings yet
- What Is An AdjectiveDocument5 pagesWhat Is An AdjectiveAmirrudin IsmailNo ratings yet
- ClauseDocument2 pagesClauseK͞O͞U͞S͞H͞I͞K͞ K͞A͞R͞M͞A͞K͞A͞R͞No ratings yet
- Majhool SentecnesDocument21 pagesMajhool Sentecnesjonny80% (5)
- Types of InfinitiveDocument21 pagesTypes of InfinitiveМаријана ЦвијетићNo ratings yet
- Modifiers Are Words or Group of Words That Qualify or Describe Other Words in A Sentence. A Modifier Can Be A Single Word, A Phrase, or ADocument6 pagesModifiers Are Words or Group of Words That Qualify or Describe Other Words in A Sentence. A Modifier Can Be A Single Word, A Phrase, or AAbsquatulateNo ratings yet
- Active PassiveDocument8 pagesActive PassiveSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- 2C: Verbs: 17. Keep Subjects Close To Their VerbsDocument11 pages2C: Verbs: 17. Keep Subjects Close To Their VerbsElvin TagalogNo ratings yet
- Grammar GuideDocument9 pagesGrammar Guidestd.majid03No ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris: Adjective ClauseDocument7 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris: Adjective Clauseanon_323638500No ratings yet
- Reduce Adverb and Adjective ClauseDocument11 pagesReduce Adverb and Adjective ClauseIkka ZR IIINo ratings yet
- Assignment of Morphology and Syntax by Ali Asghar Roll No O11Document6 pagesAssignment of Morphology and Syntax by Ali Asghar Roll No O11Shabana AslamNo ratings yet
- What Does Basic Sentence Pattern MeanDocument3 pagesWhat Does Basic Sentence Pattern Meanmcheche12No ratings yet
- selfstudys_com_file (5)Document18 pagesselfstudys_com_file (5)arundhatibhalNo ratings yet
- Final Test Project Active Voice Vs Passive VoiceDocument4 pagesFinal Test Project Active Voice Vs Passive VoicesubhaanNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument13 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechJa Bir Pir ZadNo ratings yet
- New Testament Greek Syntax Laminated SheetFrom EverandNew Testament Greek Syntax Laminated SheetRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cardinal Numbers 0-100Document9 pagesCardinal Numbers 0-100AlberyJosueLoraNo ratings yet
- Inversions Inversions InversionsDocument14 pagesInversions Inversions InversionsJuan TopoNo ratings yet
- NounDocument11 pagesNounAnggi Hardi FauziNo ratings yet
- 4TH Quarter Exam in EnglishDocument4 pages4TH Quarter Exam in EnglishJean HugoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Fundamental Language AbilitiesDocument11 pagesLecture 2 - Fundamental Language AbilitiesЖеня МатееваNo ratings yet
- 2 Лекция. Functional Linguistics.Document47 pages2 Лекция. Functional Linguistics.ZzzKkkNo ratings yet
- German: Paper 3025/01 Translation and CompositionDocument4 pagesGerman: Paper 3025/01 Translation and Compositionmstudy123456No ratings yet
- 2nd Term s3 EnglishDocument35 pages2nd Term s3 EnglishAfolearning EnglishNo ratings yet
- SInclair Corpus Concordance CollocationDocument20 pagesSInclair Corpus Concordance CollocationRuxandra Maria StoicaNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Adjectives Degrees of ComparisonDocument3 pages8.1 Adjectives Degrees of ComparisonLorenzo Catalan Zamudio Jr.No ratings yet
- Second Workshop Review: Simple Past Tense ReviewDocument3 pagesSecond Workshop Review: Simple Past Tense ReviewSILVIA YANETH MORA RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Clause Types Part 2Document4 pagesClause Types Part 2LookAtTheMan 2002No ratings yet
- Graphs and Charts - Introduction. Answer KeyDocument6 pagesGraphs and Charts - Introduction. Answer KeyAna Pociello Samperiz100% (1)
- English For Daily UsageDocument66 pagesEnglish For Daily UsageSoeGi AriFinNo ratings yet
- English at Home BookDocument22 pagesEnglish at Home BookShafique RehmanNo ratings yet
- Would Like, Would Prefer, Would RatherDocument18 pagesWould Like, Would Prefer, Would RatheringridblancoNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice Kelas XiDocument3 pagesPassive Voice Kelas XiAstrinaLNo ratings yet
- Adverbial ClauseDocument11 pagesAdverbial ClauseWahyuni OktaviaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech Lesson and PracticesDocument40 pagesParts of Speech Lesson and PracticesTronblu23No ratings yet
- Structure Skill 3Document3 pagesStructure Skill 3api-262133173No ratings yet
- Final English Grade 5 Week 3 Second QuarterDocument10 pagesFinal English Grade 5 Week 3 Second QuarterEugene PicazoNo ratings yet
- INVERSION ExplainedDocument77 pagesINVERSION Explainedmichele100% (1)
- Materi Itn 2018 PDFDocument113 pagesMateri Itn 2018 PDFdevi karinaNo ratings yet
- Materi Pertemuan 5 - Tenses (Part 2) Perfect Tenses Listening SkillDocument30 pagesMateri Pertemuan 5 - Tenses (Part 2) Perfect Tenses Listening SkillCLOVERNo ratings yet
- Review TestDocument3 pagesReview TestMary Jane SolisNo ratings yet
- Review Sheet Chapter 3-The Language of MedicineDocument3 pagesReview Sheet Chapter 3-The Language of Medicineeddy surielNo ratings yet
- Stage 9 Units 3e4Document13 pagesStage 9 Units 3e4João MarcosNo ratings yet
Reduced Adjective Clause and Reduced Adverb Clause
Reduced Adjective Clause and Reduced Adverb Clause
Uploaded by
Ariza YandwiputraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reduced Adjective Clause and Reduced Adverb Clause
Reduced Adjective Clause and Reduced Adverb Clause
Uploaded by
Ariza YandwiputraCopyright:
Available Formats
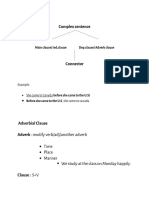
REDUCED ADJECTIVE CLAUSE AND REDUCED ADVERB CLAUSE
THE PRESENT PARTICIPLE
It can replace various the main verb in adjective caluses if it is progressive or in the present tense, or in the past tense of some kind.
EXAMPLE (PRESENT PARTICIPLE)
I saw a man who was carrying an umbrella. Adj. Clause : who was carrying an umbrella Verb in the Adj. Clause : was carrying is active Reduced to : I saw a man carrying an umbrella. Reduced Adj. Clause : carrying an umbrella Participle that starts the reduced clause : carrying We use carrying in the reduced clause because it comes from the active verb in the original clause.
THE PAST PARTICIPLE
It can replace the main verb in adjective clauses if it is passive.
EXAMPLE (PAST PARTICIPLE)
The people who worked there got a raise last year. Adj. Clause : who worked there Verb in the Adj. Clause : worked is active Reduced to : The people working there got a raise last year. Reduced Adj. Clause : working there Participle that starts the reduced clause : working
REDUCED ADJECTIVE CLAUSE
It can be reduced only when the subject of Adverb Clause and the subject of the Main Clause are the same
EXAMPLE (REDUCED ADJECTIVE CLAUSE)
Omit the subject of the clause and the Be from of the verb :
While
i was playing video game, i fell asleep While playing video game, i fell asleep
If there is no Be, omit the subject and change the verb to -ing form :
After
i signed the report, i gave it to the director After signing the report, i gave it to the director
You might also like
- German in Review Answer KeysDocument155 pagesGerman in Review Answer KeysLucas Caruso100% (1)
- Test 4 GrammDocument2 pagesTest 4 GrammДарья Мущак67% (3)
- Su1. TCCDocument10 pagesSu1. TCCDumitrița PopaNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses PDFDocument14 pagesFuture Tenses PDFMAR100% (2)
- Acfrogahakb0a1lw3aokw28nyns7rjowrq FLLH D8lezp6xbclrpjztrb6n15znkdhu9ty7wpdp5pvnqrr 8gl9sasm7om14s1yajuncccci5z3pkc14rhf Tapzsuw Cj3q3d1td254z6pp IgDocument4 pagesAcfrogahakb0a1lw3aokw28nyns7rjowrq FLLH D8lezp6xbclrpjztrb6n15znkdhu9ty7wpdp5pvnqrr 8gl9sasm7om14s1yajuncccci5z3pkc14rhf Tapzsuw Cj3q3d1td254z6pp IgdoniNo ratings yet
- Reduced Relative ClausesDocument7 pagesReduced Relative ClausesAamir100% (2)
- TgsDocument19 pagesTgsShahnaz Putri MaghfirahNo ratings yet
- Work of Syntax2 - 2024Document14 pagesWork of Syntax2 - 2024708242970No ratings yet
- A1 - Lektion 26 - Accusative CaseDocument4 pagesA1 - Lektion 26 - Accusative CaseJoelNo ratings yet
- VerbalsDocument2 pagesVerbalsCalvin MallariNo ratings yet
- Active Vs Passive VoiceDocument10 pagesActive Vs Passive VoiceRozita KamarudinNo ratings yet
- Actv Passive Voice Notes 2Document3 pagesActv Passive Voice Notes 2ainun mardiahNo ratings yet
- Objects As Complements-Lecture NoteDocument21 pagesObjects As Complements-Lecture NoteMun'im MoonNo ratings yet
- AnkitDocument68 pagesAnkitAnkit TiwariNo ratings yet
- Basic DiagrammingDocument4 pagesBasic DiagrammingKezia CanutoNo ratings yet
- Types of Reduced Relative ClausesDocument2 pagesTypes of Reduced Relative ClausesPhát Võ Nguyễn HoàngNo ratings yet
- Vertical Cutout SlideDocument12 pagesVertical Cutout SlideyoonglespianoNo ratings yet
- Dangling Modifiers: Tutoring and Testing CenterDocument2 pagesDangling Modifiers: Tutoring and Testing CenterLuis Fernando Lopez PuenteNo ratings yet
- SubjunctivesDocument19 pagesSubjunctivesFauzi_Kan_Kiku_1510No ratings yet
- Active Vs Passive Voice 25072022 025216pmDocument18 pagesActive Vs Passive Voice 25072022 025216pmh.zaidi569No ratings yet
- Relative ClauseDocument11 pagesRelative ClauseAviva CHANNo ratings yet
- Reduced Relative ClausesDocument8 pagesReduced Relative ClausesGemma PerezNo ratings yet
- Name:jose Juan Feliz Fernandez: Subject Verb ClauseDocument10 pagesName:jose Juan Feliz Fernandez: Subject Verb ClauseAlbert TejedaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 GrammarDocument7 pagesGroup 4 GrammarFadilah Rizqi AmaliahNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 5 - MAKALAH 1 Reduce Adjective Clauses (English Version)Document11 pagesKelompok 5 - MAKALAH 1 Reduce Adjective Clauses (English Version)Tina DiarNo ratings yet
- Learn Korean With Blackpink PDFDocument6 pagesLearn Korean With Blackpink PDFFor JunkNo ratings yet
- Past and Present Passive - Cancould.pastperfectDocument4 pagesPast and Present Passive - Cancould.pastperfectLorena Fernandez RoldanNo ratings yet
- Sentence StructureDocument155 pagesSentence Structureapi-3808291100% (4)
- Diagramming SentencesDocument9 pagesDiagramming SentencesRev Andrew Salinas100% (1)
- Theory N Exercises of Adjective ClauseDocument7 pagesTheory N Exercises of Adjective ClauseJodi AkbarNo ratings yet
- Logical Connectives: Ifsthenb. Not SDocument6 pagesLogical Connectives: Ifsthenb. Not SCdxgugihiNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument18 pagesActive and Passive VoicetanzilanasibzadaNo ratings yet
- Ingles PDFDocument2 pagesIngles PDFBernabe UyuNo ratings yet
- Clause and Its KindsDocument9 pagesClause and Its KindsMuhammad yousafNo ratings yet
- Helping Verbs: Class of VerbDocument11 pagesHelping Verbs: Class of VerbJasmine AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Second PartDocument3 pagesUnit 9 Second PartBrkic EdinNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument8 pagesActive and Passive VoiceEric Arriaga AltamiranoNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument43 pagesPassive VoiceRaquel García Iglesias100% (1)
- Diagramming SentencesDocument3 pagesDiagramming SentencesDharsinero SabandalNo ratings yet
- Subjective and Objective Complements: Chapter ##Document6 pagesSubjective and Objective Complements: Chapter ##Vishnu Ronaldus NarayanNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Morphology and Syntax by Ali Asghar Roll No O11Document6 pagesAssignment of Morphology and Syntax by Ali Asghar Roll No O11Ali Asghar 011100% (1)
- Adjective Clause (Penggunaan Who, Whom, Whose, Which, DLL) : Belajar English Yuk... !!! Iqbal 0 KomentarDocument5 pagesAdjective Clause (Penggunaan Who, Whom, Whose, Which, DLL) : Belajar English Yuk... !!! Iqbal 0 Komentarokik hariNo ratings yet
- Adjective Clause (Penggunaan Who, Whom, Whose, Which, DLL) : Belajar English Yuk... !!! Iqbal 0 KomentarDocument5 pagesAdjective Clause (Penggunaan Who, Whom, Whose, Which, DLL) : Belajar English Yuk... !!! Iqbal 0 Komentarokik hariNo ratings yet
- Reduced Clause 7th GroupDocument5 pagesReduced Clause 7th GroupAfg-Ghynhaalfiyah Chyllowend Arisyhaa KeiinhaLynchNo ratings yet
- Voice (Active and Passive)Document1 pageVoice (Active and Passive)Hans Matthew AntiojoNo ratings yet
- What Is An AdjectiveDocument5 pagesWhat Is An AdjectiveAmirrudin IsmailNo ratings yet
- ClauseDocument2 pagesClauseK͞O͞U͞S͞H͞I͞K͞ K͞A͞R͞M͞A͞K͞A͞R͞No ratings yet
- Majhool SentecnesDocument21 pagesMajhool Sentecnesjonny80% (5)
- Types of InfinitiveDocument21 pagesTypes of InfinitiveМаријана ЦвијетићNo ratings yet
- Modifiers Are Words or Group of Words That Qualify or Describe Other Words in A Sentence. A Modifier Can Be A Single Word, A Phrase, or ADocument6 pagesModifiers Are Words or Group of Words That Qualify or Describe Other Words in A Sentence. A Modifier Can Be A Single Word, A Phrase, or AAbsquatulateNo ratings yet
- Active PassiveDocument8 pagesActive PassiveSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- 2C: Verbs: 17. Keep Subjects Close To Their VerbsDocument11 pages2C: Verbs: 17. Keep Subjects Close To Their VerbsElvin TagalogNo ratings yet
- Grammar GuideDocument9 pagesGrammar Guidestd.majid03No ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris: Adjective ClauseDocument7 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris: Adjective Clauseanon_323638500No ratings yet
- Reduce Adverb and Adjective ClauseDocument11 pagesReduce Adverb and Adjective ClauseIkka ZR IIINo ratings yet
- Assignment of Morphology and Syntax by Ali Asghar Roll No O11Document6 pagesAssignment of Morphology and Syntax by Ali Asghar Roll No O11Shabana AslamNo ratings yet
- What Does Basic Sentence Pattern MeanDocument3 pagesWhat Does Basic Sentence Pattern Meanmcheche12No ratings yet
- selfstudys_com_file (5)Document18 pagesselfstudys_com_file (5)arundhatibhalNo ratings yet
- Final Test Project Active Voice Vs Passive VoiceDocument4 pagesFinal Test Project Active Voice Vs Passive VoicesubhaanNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument13 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechJa Bir Pir ZadNo ratings yet
- New Testament Greek Syntax Laminated SheetFrom EverandNew Testament Greek Syntax Laminated SheetRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cardinal Numbers 0-100Document9 pagesCardinal Numbers 0-100AlberyJosueLoraNo ratings yet
- Inversions Inversions InversionsDocument14 pagesInversions Inversions InversionsJuan TopoNo ratings yet
- NounDocument11 pagesNounAnggi Hardi FauziNo ratings yet
- 4TH Quarter Exam in EnglishDocument4 pages4TH Quarter Exam in EnglishJean HugoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Fundamental Language AbilitiesDocument11 pagesLecture 2 - Fundamental Language AbilitiesЖеня МатееваNo ratings yet
- 2 Лекция. Functional Linguistics.Document47 pages2 Лекция. Functional Linguistics.ZzzKkkNo ratings yet
- German: Paper 3025/01 Translation and CompositionDocument4 pagesGerman: Paper 3025/01 Translation and Compositionmstudy123456No ratings yet
- 2nd Term s3 EnglishDocument35 pages2nd Term s3 EnglishAfolearning EnglishNo ratings yet
- SInclair Corpus Concordance CollocationDocument20 pagesSInclair Corpus Concordance CollocationRuxandra Maria StoicaNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Adjectives Degrees of ComparisonDocument3 pages8.1 Adjectives Degrees of ComparisonLorenzo Catalan Zamudio Jr.No ratings yet
- Second Workshop Review: Simple Past Tense ReviewDocument3 pagesSecond Workshop Review: Simple Past Tense ReviewSILVIA YANETH MORA RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- Clause Types Part 2Document4 pagesClause Types Part 2LookAtTheMan 2002No ratings yet
- Graphs and Charts - Introduction. Answer KeyDocument6 pagesGraphs and Charts - Introduction. Answer KeyAna Pociello Samperiz100% (1)
- English For Daily UsageDocument66 pagesEnglish For Daily UsageSoeGi AriFinNo ratings yet
- English at Home BookDocument22 pagesEnglish at Home BookShafique RehmanNo ratings yet
- Would Like, Would Prefer, Would RatherDocument18 pagesWould Like, Would Prefer, Would RatheringridblancoNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice Kelas XiDocument3 pagesPassive Voice Kelas XiAstrinaLNo ratings yet
- Adverbial ClauseDocument11 pagesAdverbial ClauseWahyuni OktaviaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech Lesson and PracticesDocument40 pagesParts of Speech Lesson and PracticesTronblu23No ratings yet
- Structure Skill 3Document3 pagesStructure Skill 3api-262133173No ratings yet
- Final English Grade 5 Week 3 Second QuarterDocument10 pagesFinal English Grade 5 Week 3 Second QuarterEugene PicazoNo ratings yet
- INVERSION ExplainedDocument77 pagesINVERSION Explainedmichele100% (1)
- Materi Itn 2018 PDFDocument113 pagesMateri Itn 2018 PDFdevi karinaNo ratings yet
- Materi Pertemuan 5 - Tenses (Part 2) Perfect Tenses Listening SkillDocument30 pagesMateri Pertemuan 5 - Tenses (Part 2) Perfect Tenses Listening SkillCLOVERNo ratings yet
- Review TestDocument3 pagesReview TestMary Jane SolisNo ratings yet
- Review Sheet Chapter 3-The Language of MedicineDocument3 pagesReview Sheet Chapter 3-The Language of Medicineeddy surielNo ratings yet
- Stage 9 Units 3e4Document13 pagesStage 9 Units 3e4João MarcosNo ratings yet