Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology of Cerebral Schistosomiasis
Pathophysiology of Cerebral Schistosomiasis
Uploaded by
Risa Sol AriasOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pathophysiology of Cerebral Schistosomiasis
Pathophysiology of Cerebral Schistosomiasis
Uploaded by
Risa Sol AriasCopyright:
Available Formats
B.
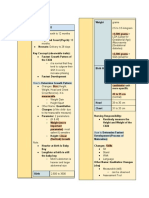
Diagram Predisposing Factors: *Age *Race - Filipino *Gender - common in male
Precipitating Factors: *Occupation - farmer *Poor compliance to treatment *Living in schistosomiasis endemic area *Lifestyle
cercariae penetrate human skin transform into a schistosomulae remain on the skin for 2 days travels into the lungs to mature reaches the liver after 8-10 days to further mature adult worms pair and produce eggs migrate to either intestines or bladder on the bladder Batson veins permits route to the CNS worms and eggs reach the brain they secrete antigens immune response formation of granuloma on the cerebrum increased ICP (intracranial pressure)
S/Sx: 1. seizures 2. headache 3. visual abnormalities 4. Speech disturbances 5. Hemiparesis, hemiplegia, ataxia 6. Nystagmus 7. Sensory impairment
Cerebral Schistosomiasis
If treated: Nursing mgt: 1. Health teachings regarding prevention of reinfection, compliance to treatment, follow-up check-ups, and lifestyle modification.
If not treated: DEATH
Medical mgt: 1. Antischistosomal drugs such as Praziquantel to cause death of the adult worm, resulting in cessation of oviposition and thus a reduction in the inflammatory response. 2. Corticosteroids to diminish granulomatous inflammation and edema, thereby reducing the compression and destruction of the nervous tissue. 3. Anticonvulsant to prevent or stop/control ongoing seizures.
Surgical mgt: Surgical excision is not encouraged.
You might also like
- PnclexDocument3 pagesPnclexPaul Michael BaguhinNo ratings yet
- BioethicsCasesEEI 316232215 PDFDocument38 pagesBioethicsCasesEEI 316232215 PDFAman UllahNo ratings yet
- Case Study GI #4Document5 pagesCase Study GI #4Jenny JendersNo ratings yet
- BulaloDocument7 pagesBulaloRobin HaliliNo ratings yet
- 1.MOD On GERON (1) CommunicationDocument19 pages1.MOD On GERON (1) CommunicationPatricia VasquezNo ratings yet
- Corona RadiataDocument89 pagesCorona RadiataPamela laquindanumNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Neurologic DisordersDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Neurologic DisordersdanceNo ratings yet
- NCM116 Module 3 Cerebrovascular Disease QuizDocument5 pagesNCM116 Module 3 Cerebrovascular Disease QuizIvan FernandezNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: ScenarioDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: ScenarioIrish Jane GalloNo ratings yet
- Cellular AberrationsDocument94 pagesCellular AberrationsridzkhaNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives: Introduction To Gerontological NursingDocument12 pagesLearning Objectives: Introduction To Gerontological NursingArlyn MendenillaNo ratings yet
- 3 Clinical Features of Parkinsons DiseaseDocument5 pages3 Clinical Features of Parkinsons DiseasemuhammadridhwanNo ratings yet
- Path o PhysiologyDocument9 pagesPath o PhysiologyKyle Ü D. CunanersNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument16 pagesHypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseTintin Ponciano100% (1)
- PediaDocument9 pagesPediaNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Quiz 7. NCM 116 For StudentsDocument4 pagesQuiz 7. NCM 116 For StudentsZayne Lucas Gabrielle TadiamonNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing ReviewerDocument10 pagesCommunity Health Nursing ReviewerNicole CastillaNo ratings yet
- Geria Lec Portfolio CasiaDocument9 pagesGeria Lec Portfolio CasiaMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure NCLEX QuestionsDocument5 pagesHeart Failure NCLEX QuestionsMelodia Turqueza GandezaNo ratings yet
- Review MSDocument8 pagesReview MSPatrycyaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute CholecystitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute CholecystitisKush KhannaNo ratings yet
- NCM 116: Care of Clients With Problems in Nutrition and Gastrointestinal, Metabolism and Endocrine,, Acute and ChronicDocument18 pagesNCM 116: Care of Clients With Problems in Nutrition and Gastrointestinal, Metabolism and Endocrine,, Acute and ChronicSIJINo ratings yet
- MS EndoDocument22 pagesMS EndoFrechel Ann Landingin PedrozoNo ratings yet
- Post Test 19Document4 pagesPost Test 19Naomi VirtudazoNo ratings yet
- Cushing's SyndromeDocument5 pagesCushing's SyndromesummerduskNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Nursing: Nursima N. SampangDocument20 pagesGeriatric Nursing: Nursima N. SampangIrwan M. IskoberNo ratings yet
- InTech-Diabetic Foot and GangreneDocument25 pagesInTech-Diabetic Foot and GangrenePutu Reza Sandhya PratamaNo ratings yet
- GerontologyDocument150 pagesGerontologyKakak wawa95No ratings yet
- I. Isbar: I Identity of PatientDocument2 pagesI. Isbar: I Identity of PatientAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Pleural Fluid Analysis: How The Test Is PerformedDocument4 pagesPleural Fluid Analysis: How The Test Is PerformedKevin LlorenteNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam McaDocument7 pagesMidterm Exam McaBeverly DatuNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Case Study Jan 2 101xDocument4 pagesCardiovascular Case Study Jan 2 101xElizabeth SpokoinyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Clients With Altered PerceptionDocument83 pagesNursing Care of Clients With Altered PerceptionDanica Franco100% (1)
- Abnormal Perception PDFDocument5 pagesAbnormal Perception PDFsugarmelodies100% (1)
- Psychosocial Care of Older Adults: Cognition and Perception: Ma. Concepcion A. Maico, RN, MAN, Ed.DDocument35 pagesPsychosocial Care of Older Adults: Cognition and Perception: Ma. Concepcion A. Maico, RN, MAN, Ed.DMEJIE MARL RAVEN INSTRELLANo ratings yet
- IM AdconDocument28 pagesIM AdconCla SantosNo ratings yet
- History of Past IllnessDocument4 pagesHistory of Past IllnessKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis HydrocephalusDocument11 pagesCase Analysis HydrocephalusRaiNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Medsurg LectureDocument9 pagesCardiology Medsurg LectureTine GuibaoNo ratings yet
- Simu 20 Test 2Document108 pagesSimu 20 Test 2Profile Info100% (1)
- Nursing ResearchDocument12 pagesNursing ResearchShane SappayaniNo ratings yet
- Esophageal CancerDocument8 pagesEsophageal CancerSakthiswaran RajaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Myocardial InfarctionDocument5 pagesAnatomy Myocardial InfarctionLyka Milo AvilaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Gemst Assessment PabilloreDocument7 pagesLesson 2 Gemst Assessment PabilloreInward Demons CommunityNo ratings yet
- NCM 417 MODULE I Quiz 1Document3 pagesNCM 417 MODULE I Quiz 1joyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Midterms - Geria LecDocument5 pagesMidterms - Geria LecGiel Margareth LindoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Practice TestDocument4 pagesNursing Practice TestMarianne BaquilalaNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument3 pagesCommunicable Diseasemiss RNNo ratings yet
- A. Cultural Factors/ethnicity Such As Regard To Elders, Perception of HealthDocument3 pagesA. Cultural Factors/ethnicity Such As Regard To Elders, Perception of Healthlouie john abilaNo ratings yet
- I. Multiple Choice: (Type I, Type II)Document2 pagesI. Multiple Choice: (Type I, Type II)greggy_rebel17No ratings yet
- Tut 3Document3 pagesTut 3Bobet ReñaNo ratings yet
- np1 5Document25 pagesnp1 5Sittie Haya LazimNo ratings yet
- Gouty Arthritis: Presented By: Petit Ivy Mae B. NacarioDocument21 pagesGouty Arthritis: Presented By: Petit Ivy Mae B. NacarioMarivic DianoNo ratings yet
- COPARDocument21 pagesCOPAREdra VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Transes EndoDocument20 pagesTranses EndoISABEL REGASPINo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument9 pagesPathophysiologySuzette PipoNo ratings yet
- Physiobiologic Bases and Behavior Neuroscience: Biology and BehaviorDocument25 pagesPhysiobiologic Bases and Behavior Neuroscience: Biology and BehaviorKeith AquinoNo ratings yet
- Operating Room Write UpDocument2 pagesOperating Room Write UpEnrico Sapitula Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)From EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)No ratings yet