Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kidney
Kidney
Uploaded by
Ashish PatelOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kidney
Kidney
Uploaded by
Ashish PatelCopyright:
Available Formats
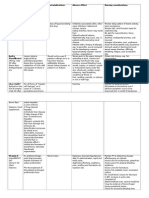
Prednisone 20 mg 1x a day (usual dose of 5 mg Daily) Used for Immunosuppression for Kidney
Myfortic: 720 mg BID
Prophylaxis of organ rejection concomitantly with cyclosporine and corticosteroids in patients receiving allogeneic renal transplant Cautions: Mouth ulceration, gum hyperplasia, gingivitis, dry mouth, dysphagia, oral moniliasis, and stomatitis. Reductions in platelet counts Acyclovir-Valacyclovir: Mycophenolate may increase the serum concentration of Acyclovir-Valacyclovir. Acyclovir-Valacyclovir may increase the serum concentration of Mycophenolate. Risk C: CycloSPORINE (Systemic): May decrease the serum concentration of Mycophenolate. Specifically, cyclosporine may decrease concentrations of the active metabolite mycophenolic acid. Risk D: Consider therapy modification
Cyclosporine: 150 mg po q. am and 125 mg p.o. q.pm
Prophylaxis of organ rejection in kidney transplants, has been used with azathioprine and/or corticosteroids Cautions: Mouth sores, swallowing difficulty, gingivitis, gum hyperplasia, xerostomia (normal salivary flow resumes upon discontinuation), abnormal taste, tongue disorder, tooth disorder, and gingival bleeding. Action: Inhibition of production and release of interleukin II and inhibits interleukin II-induced activation of resting T-lymphocytes. May cause significant hyperkalemia and hyperuricemia. May cause seizures, particularly if used with high-dose corticosteroids. Encephalopathy has been reported, predisposing factors include hypertension, hypomagnesemia, hypocholesterolemia, high-dose corticosteroids, high cyclosporine serum concentration, and graftversus-host disease; may be more common in patients with liver transplant. Antifungal Agents (Azole Derivatives, Systemic): May decrease the metabolism of CycloSPORINE (Systemic). Risk D: Consider therapy modification
Limit Grapefruit Juice: May decrease the metabolism of CycloSPORINE (Systemic). Risk D: Consider therapy modification
Calcitriol 0.25 mcg (MICROGRAMS) p.o. twice weekly, Monday and Thursday
Oral, injection: Management of hypocalcemia in patients on chronic renal dialysis; management of secondary hyperparathyroidism in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) Effects on Dental Tx: Metallic taste and xerostomia (normal salivary flow resumes upon discontinuation). CKD stage 4: Oral: 0.25 mcg/day. Treatment should only be started with serum 25(OH) D >30 ng/mL, serum iPTH >110 pg/mL, serum calcium <9.5 mg/dL and serum phosphorus <4.6 mg/dL
Aspirin 325 mg p.o. daily
Treatment of mild-to-moderate pain, inflammation, and fever; prevention and treatment of myocardial infarction (MI), acute ischemic stroke, and transient ischemic episodes; management of rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatic fever, osteoarthritis; adjunctive therapy in revascularization procedures (coronary artery bypass graft [CABG], percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty [PTCA], carotid endarterectomy), stent implantation Key adverse event(s) related to dental treatment: As with all drugs which may affect hemostasis, bleeding is associated with aspirin. Hemorrhage may occur at virtually any site; risk is dependent on multiple variables including dosage, concurrent use of multiple agents which alter hemostasis, and patient susceptibility. 7-10 day
Lantus: 18 units subcutaneously daily (Long acting insulin analog) MORNING APPOINTMENTS Treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus (insulin dependent, IDDM) to improve glycemic control Humulin sliding scale Tx of Type 1 diabetes mellitus
WARNING: Hypokalemia: Insulin (especially I.V. insulin) causes a shift of potassium from the extracellular space to the intracellular space, possibly producing hypokalemia. If left untreated, hypokalemia may result in respiratory paralysis, ventricular arrhythmia and even death. Use with caution in patients at risk for hypokalemia (eg, loop diuretic use). Monitor serum potassium and supplement potassium when necessary. Hypoglycemia: The most common adverse effect of insulin is hypoglycemia. The timing of hypoglycemia differs among various insulin formulations. Hypoglycemia may result from increased work or exercise without eating; use of long-acting insulin preparations (eg, insulin detemir, insulin glargine) may delay recovery from hypoglycemia. Profound and prolonged episodes of hypoglycemia may result in convulsions, unconsciousness, temporary or permanent brain damage, or even death. Insulin requirements may be altered during illness, emotional disturbances, or other stressors. Patients with type 1 diabetes (insulin dependent) should be appointed for dental treatment in the morning in order to minimize chance of stressinduced hypoglycemia.
Catapres 0.2 mg transdermal patch once weekly (CLONIDINE) Transdermal patch: Management of hypertension (monotherapy or as adjunctive therapy) Significant xerostomia (normal salivary flow resumes upon discontinuation), orthostatic hypotension, and abnormal taste. Ethanol: Avoid ethanol (may increase CNS depression). Herb/Nutraceutical: Avoid dong quai if using for hypertension (has estrogenic activity). Avoid ephedra, yohimbe, ginseng (may worsen hypertension). Avoid valerian, St John's wort, kava kava, gotu kola (may increase CNS depression).
IRON: 325 mg p.o. daily prevention, treatment of iron deficiency anemia Vitamin D 50,000 units po daily
Omeprazole 20 mg p.o. daily (STARTED DURING HOSPITALIZION DUE TO STRESS DOSE STEROIDS)
Short-term (4-8 weeks) treatment of active duodenal ulcer disease or active benign gastric ulcer; treatment of heartburn and other symptoms associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD); short-term (4-8 weeks) treatment of endoscopically-diagnosed erosive esophagitis; maintenance healing of erosive esophagitis; long-term treatment of pathological hypersecretory conditions; as part of a multidrug regimen for H. pylori eradication to reduce the risk of duodenal ulcer recurrence Effect on Dental Tx: Taste perversion, dry mouth, esophageal candidiasis, and mucosal atrophy (tongue). Amphetamines: Proton Pump Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Amphetamines. Specifically, data indicate that Proton Pump Inhibitors may increase the rate at which Amphetamines are absorbed. Total exposure to Amphetamines is not significantly changed. Risk C: Monitor therapy
Oxycodone (5 mg po daily) pain Management of moderate-to-severe pain, normally used in combination with nonopioid analgesics OxyContin is indicated for around-the-clock management of moderate-tosevere pain when an analgesic is needed for an extended period of time. Hypotension: May cause hypotension; use with caution in patients with hypovolemia, cardiovascular disease (including acute MI), or drugs which may exaggerate hypotensive effects (including phenothiazines or general anesthetics). Amphetamines: May enhance the analgesic effect of Analgesics (Opioid). Risk C: Monitor therapy Thiazide Diuretics: Analgesics (Opioid) may enhance the orthostatic hypotensive effect of Thiazide Diuretics. Risk C: Monitor therapy Instruct patient to avoid high-fat meals when taking some products
ALLERGY: VASOTEC - To delay the progression of nephropathy and reduce risks of cardiovascular events in hypertensive patients with type 1 or 2 diabetes mellitus; hypertensive crisis, diabetic nephropathy, hypertension
secondary to scleroderma renal crisis, diagnosis of aldosteronism, idiopathic edema, Bartter's syndrome, postmyocardial infarction for prevention of ventricular failure
You might also like
- Drug Study TramadolDocument14 pagesDrug Study TramadolBianca Freya Porral85% (13)
- Drugs NclexDocument30 pagesDrugs Nclexawuahboh100% (1)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Gout Treatment Medications and Lifestyle Adjustments To Lower Uric AcidDocument16 pagesGout Treatment Medications and Lifestyle Adjustments To Lower Uric AcidnellaNo ratings yet
- 8 Drug StudyDocument19 pages8 Drug StudyLoyloy D ManNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument6 pagesPathophysiology: Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritiscathycolNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFranco ObedozaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug StudyMc Joewell HudencialNo ratings yet
- Farmakoterapi Gout and HipeurisemiaDocument54 pagesFarmakoterapi Gout and HipeurisemiaIrvan Firmansyah Adi SutrisnoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJoan RabeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudiesDocument16 pagesDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- Amphotericin B Deoxycholate (Conventional) - Drug Information - UpToDate-4Document4 pagesAmphotericin B Deoxycholate (Conventional) - Drug Information - UpToDate-4Vh TRNo ratings yet
- Complete Drug StudyDocument239 pagesComplete Drug StudyRPh Krishna Chandra Jagrit0% (1)
- Gout & Hyperuricemia: Bagian Farmasi Klinik & KomunitasDocument39 pagesGout & Hyperuricemia: Bagian Farmasi Klinik & KomunitasizzafrNo ratings yet
- Sialogogues & Anti SailogoguesDocument43 pagesSialogogues & Anti SailogoguesTavleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDocument19 pagesDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Ix. Pharmacologic Management Brand Name Classification Indication Mechanism of Action Dosage and Frequency Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationDocument21 pagesIx. Pharmacologic Management Brand Name Classification Indication Mechanism of Action Dosage and Frequency Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationDizerine Mirafuentes RolidaNo ratings yet
- Management of HyperuricemiaDocument23 pagesManagement of HyperuricemiaSoad ShedeedNo ratings yet
- Docetaxel - 40mg/ml Injection: InstructionDocument11 pagesDocetaxel - 40mg/ml Injection: InstructionywNo ratings yet
- Gout and HyperuricemiaDocument7 pagesGout and HyperuricemiaTaj lamajedNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Indication, Dosage, Side Effect, Precaution MIMS MalaysiaDocument1 pageMefenamic Acid Indication, Dosage, Side Effect, Precaution MIMS MalaysianuruladyanisaifuzzamanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument20 pagesDrug StudyBrylle CapiliNo ratings yet
- Penyakit Tersering Di PuskesmasDocument5 pagesPenyakit Tersering Di PuskesmasRama Al MaduriNo ratings yet
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632No ratings yet
- Drug Study 68-75Document8 pagesDrug Study 68-75joshua_santiago_5No ratings yet
- Nicardipine (: ClassificationDocument14 pagesNicardipine (: ClassificationWilliam CiferNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Document13 pagesCardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Maica EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GDocument9 pagesDrug Analysis: Submitted By: GALICINAO, Gretta Shalou GggalicinaoNo ratings yet
- 4-Gout--1st yearDocument75 pages4-Gout--1st yearAubrey GadorNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studysarah1217No ratings yet
- Drug Study 1Document4 pagesDrug Study 1bibet_martijaNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocument70 pagesNephrotic SyndromeNaz Al-ShahraniNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug ProfileDocument3 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug ProfileAhmad WaliNo ratings yet
- Common Anti-Diabetics and AnticoagulantsDocument14 pagesCommon Anti-Diabetics and AnticoagulantsemmanuelmkibuniNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HydralazineDocument10 pagesDrug Study HydralazineLuige AvilaNo ratings yet
- Complete Albendazole Information From DrugsDocument4 pagesComplete Albendazole Information From DrugselephantynoseNo ratings yet
- AllopurinolDocument48 pagesAllopurinolFarha Elein KukihiNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeDocument9 pagesDrugs Study, Nursing, PreoperativeKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- w15 - Drug StudyDocument4 pagesw15 - Drug StudyGeneva LatorreNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyLovely Saad TubañaNo ratings yet
- Definitions OF DiagnosisDocument25 pagesDefinitions OF DiagnosisGlaire ZarateNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudytrinaLCNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyEzshkha OngueNo ratings yet
- Dosage: Route:: Mycobacterium TuberculosisDocument21 pagesDosage: Route:: Mycobacterium TuberculosisLyn ConsingNo ratings yet
- Drug 25Document17 pagesDrug 25carol_gigliotti24100% (1)
- Endocrine and MetabolicDocument30 pagesEndocrine and Metabolicjamaica faith ramonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShiara Ruth EdrosoloNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study Neh Jai2xDocument10 pagesDrugs Study Neh Jai2xjai2xNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Gouty ArthritisDocument56 pagesKuliah Gouty Arthritischrysandre100% (1)
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAnn Aquino100% (1)
- GOUT PresentationDocument24 pagesGOUT Presentationtasneemsofi100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument28 pagesDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Volume 1 Unit 5 CardioDocument138 pagesPharmacology Volume 1 Unit 5 CardioAkhilesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ProjectDocument7 pagesDrug Study ProjectMaRic Gabutin Guerra100% (1)
- Dental Treatment of Medical Compromised PatientsDocument50 pagesDental Treatment of Medical Compromised PatientssrinivasNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesNursing Care PlanVincent QuitorianoNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument8 pagesPeptic Ulcer Diseasepragna novaNo ratings yet
- Volume 5 Over-the-Counter ProductsDocument478 pagesVolume 5 Over-the-Counter ProductsDikri Fadhlurrohman100% (2)
- The History of Alopecia AreataDocument24 pagesThe History of Alopecia AreatamedifacuNo ratings yet
- ADHD PowerpointDocument93 pagesADHD PowerpointFred LuskNo ratings yet
- 1 - Aripiprazole in The Treatment 52 Minggu AutismDocument8 pages1 - Aripiprazole in The Treatment 52 Minggu AutismmirafauziNo ratings yet
- Utilizing Drug Repurposing Against COVID-19 - EffiDocument9 pagesUtilizing Drug Repurposing Against COVID-19 - EffiDaniel PratamaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1878535221005931 MainDocument15 pages1 s2.0 S1878535221005931 MainFernando NunesNo ratings yet
- Contoh Label Obat 3Document2 pagesContoh Label Obat 3astipranitaNo ratings yet
- Amphetamine Use DisordersDocument22 pagesAmphetamine Use DisordersZaid WaniNo ratings yet
- Clinical Spectrum of Atherosclerotic Heart DiseaseDocument50 pagesClinical Spectrum of Atherosclerotic Heart Diseaseadamu mohammadNo ratings yet
- Obesity and Anticipated Difficult Airway - A Comprehensive Approach With Videolaryngoscopy, Ramp Position, Sevoflurane and Opioid Free AnaesthesiaDocument8 pagesObesity and Anticipated Difficult Airway - A Comprehensive Approach With Videolaryngoscopy, Ramp Position, Sevoflurane and Opioid Free AnaesthesiaIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- 2nd Ed Critical Care Pharmacy Handbook Revised 19th Jan 2021 Final 5.5.21Document186 pages2nd Ed Critical Care Pharmacy Handbook Revised 19th Jan 2021 Final 5.5.21SAUMOJIT MAJUMDERNo ratings yet
- Nebulization TherapyDocument3 pagesNebulization TherapyGemalie KadilNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing: PsychopharmacologyDocument14 pagesPsychiatric Nursing: PsychopharmacologyShandz de RosasNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs and AntidoteDocument114 pagesEmergency Drugs and AntidoteAlexa BelderolNo ratings yet
- Nervoussystemsabbyasachi16vphajj1m-160614092343 (1) 2Document48 pagesNervoussystemsabbyasachi16vphajj1m-160614092343 (1) 2Mary GargarNo ratings yet
- Salivary GlandDocument38 pagesSalivary GlandWasfe BarzaqNo ratings yet
- Pentasa LeafletDocument2 pagesPentasa LeafletreadalotbutnowisdomyetNo ratings yet
- Autohemotherapy in Veterinary FieldDocument4 pagesAutohemotherapy in Veterinary Fieldelhawarykareem3No ratings yet
- US20200360337A1 McCorkle Et Al Cannabinoid Conversion Hemp ExtractsDocument13 pagesUS20200360337A1 McCorkle Et Al Cannabinoid Conversion Hemp ExtractsStephenNo ratings yet
- Standard Assessment Form For Postgraduate Courses: (Anatomy)Document13 pagesStandard Assessment Form For Postgraduate Courses: (Anatomy)Lee NaNo ratings yet
- Calcitriol - Drug InformationDocument13 pagesCalcitriol - Drug InformationNikesh DoshiNo ratings yet
- Makalah Farmasetika Dasar MDRDocument10 pagesMakalah Farmasetika Dasar MDRWinda WindaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Classification & Mechanism - Basic Science - OrthobulletsDocument9 pagesAntibiotic Classification & Mechanism - Basic Science - OrthobulletsHossam Elden Helmy HaridyNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Drug Action and Dose Response Relationship (First Part)Document138 pagesMechanism of Drug Action and Dose Response Relationship (First Part)geniousmasud721No ratings yet
- Functional Psychosis: Characterized by Disturbances in Thinking, EmotionDocument33 pagesFunctional Psychosis: Characterized by Disturbances in Thinking, EmotionPoonam RanaNo ratings yet
- India - Pharmaceuticals MarketDocument14 pagesIndia - Pharmaceuticals MarketNaveena ShreeNo ratings yet
- Systemic Medicines Taken by Adult Special CareDocument10 pagesSystemic Medicines Taken by Adult Special CareAlistair KohNo ratings yet
- DR Kannappan Palaniappan - Fertility, GynaecologyDocument1 pageDR Kannappan Palaniappan - Fertility, GynaecologyKavitha Jeya MoorthiNo ratings yet
- PDF Natural Medicines Clinical Efficacy Safety and Quality 1St Edition Dilip Ghosh Editor Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Natural Medicines Clinical Efficacy Safety and Quality 1St Edition Dilip Ghosh Editor Ebook Full Chapterderek.mitchell839No ratings yet