Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell
Cell
Uploaded by
Thilaga SinathuraiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell
Cell
Uploaded by
Thilaga SinathuraiCopyright:
Available Formats
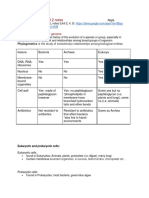
Organelle chloroplast (plastid)
Major eukaryotic organelles Main function Structure Organisms photosynthesis doublemembrane compartment
endoplasmic reticulum
translation and folding of new proteins (rough singleendoplasmic reticulum), membrane expression of lipids compartment (smooth endoplasmic reticulum)
singlesorting and modification Golgi apparatus membrane of proteins compartment
mitochondrion energy production
doublemembrane compartment singlemembrane compartment doublemembrane compartment
Notes plants, protists has some genes; theorized to be engulfed by the (rare kleptoplastic ancestral eukaryotic cell organisms) (endosymbiosis) rough endoplasmic reticulum is covered with ribosomes, has folds that all eukaryotes are flat sacs; smooth endoplasmic reticulum has folds that are tubular cis-face (convex) nearest to rough endoplasmic reticulum; trans-face all eukaryotes (concave) farthest from rough endoplasmic reticulum has some DNA; theorized most to be engulfed by the eukaryotes ancestral eukaryotic cell (endosymbiosis) eukaryotes
vacuole
storage, homeostasis DNA maintenance, RNA transcription
nucleus
all eukaryotes has bulk of genome
Mitochondria and chloroplasts, which have double-membranes and their own DNA, are believed to have originated from incompletely consumed or invading prokaryotic organisms, which were adopted as a part of the invaded cell. This idea is supported in the Endosymbiotic theory.
Organelle/Macromolecule
Main function
Structure
Organisms
acrosome autophagosome centriole cilium
helps spermatoza fuse with ovum vesicle which sequesters cytoplasmic material and organelles for degradation anchor for cytoskeleton movement in or of external medium; "critical developmental signaling pathway"[28]. detects light, allowing phototaxis to take place
single-membrane many animals compartment double-membrane all eukaryotic cells compartment Microtubule protein Microtubule protein animals animals, protists, few plants
eyespot apparatus glycosome glyoxysome hydrogenosome lysosome melanosome mitosome myofibril nucleolus parenthesome peroxisome ribosome vesicle
green algae and other unicellular photosynthetic organisms such as euglenids single-membrane Some protozoa, such as carries out glycolysis compartment Trypanosomes. single-membrane conversion of fat into sugars plants compartment double-membrane energy & hydrogen production a few unicellular eukaryotes compartment breakdown of large molecules (e.g., single-membrane most eukaryotes proteins + polysaccharides) compartment single-membrane pigment storage animals compartment double-membrane not characterized a few unicellular eukaryotes compartment muscular contraction bundled filaments animals protein-DNAribosome production most eukaryotes RNA not characterized not characterized fungi breakdown of metabolic hydrogen single-membrane all eukaryotes peroxide compartment translation of RNA into proteins RNA-protein eukaryotes, prokaryotes single-membrane material transport all eukaryotes compartment
You might also like
- BABS1201 Study Notes at UNSWDocument34 pagesBABS1201 Study Notes at UNSWOliverNo ratings yet
- Biology-Unit 2 Revision Powerpoint (Autosaved)Document153 pagesBiology-Unit 2 Revision Powerpoint (Autosaved)nhmerali786100% (1)
- Swaminee PDFDocument16 pagesSwaminee PDFajay singh67% (21)
- Bioenergetics of Exercise and TrainingDocument62 pagesBioenergetics of Exercise and Trainingswordplay716No ratings yet
- Cells and Microorganisms SM 2021Document4 pagesCells and Microorganisms SM 2021Sami Ali 123No ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Function: Endoplasmic Reticulum ERDocument2 pagesCell Structure & Function: Endoplasmic Reticulum ERLiling CassiopeiaNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument70 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Structure and FunctionDocument2 pagesCell Organelle Structure and FunctionMichu LeclercqNo ratings yet
- Membran Sel Sitoplasma NukleusDocument32 pagesMembran Sel Sitoplasma NukleusAsmaul HusniNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Eukaryotic: SimilaritiesDocument8 pagesProkaryotic Eukaryotic: SimilaritiesnabilahNo ratings yet
- Biochem PrelimDocument42 pagesBiochem PrelimFaith RochaNo ratings yet
- Bio 103 L5 NIADocument31 pagesBio 103 L5 NIAsubrotoghosh2001No ratings yet
- AS Biology: Unit 2 Notes:: The Voice of The GenomeDocument20 pagesAS Biology: Unit 2 Notes:: The Voice of The GenomeAlaska DavisNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1Document12 pagesGeneral Biology 1Samariah Nicole AbajeroNo ratings yet
- Cells: Characteristics of The CellDocument4 pagesCells: Characteristics of The CellRashidah R. DisomaNo ratings yet
- BIO 001 6th LectureDocument37 pagesBIO 001 6th LectureManuelNo ratings yet
- Lec-8,9 CellsDocument30 pagesLec-8,9 CellsAbdullah-Al-mehedi HiraNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 8th Edition Lauralee Sherwood Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 8th Edition Lauralee Sherwood Solutions Manual PDFwoodrowbutleroev8100% (11)
- Full Download Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 8th Edition Lauralee Sherwood Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFull Download Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 8th Edition Lauralee Sherwood Solutions Manualgambolrapinous.ggqcdr100% (42)
- Structure and FunctionsDocument72 pagesStructure and FunctionsSha AkoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: MLT/FN Class Dr. Wanjiku Ndung'uDocument22 pagesCell Structure: MLT/FN Class Dr. Wanjiku Ndung'uGrace NdutaNo ratings yet
- Biology FGS 0044: Mr. Khairul Hafezad Bin AbdullahDocument52 pagesBiology FGS 0044: Mr. Khairul Hafezad Bin AbdullahSophea Mercer AnaisNo ratings yet
- LESSONS in BIOCHEMDocument39 pagesLESSONS in BIOCHEMMikhael Jay IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Biology FGS 0044: Mr. Khairul Hafezad Bin AbdullahDocument52 pagesBiology FGS 0044: Mr. Khairul Hafezad Bin AbdullahSophea Mercer AnaisNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Document8 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 8Saurav SoniNo ratings yet
- BTN-345 L1 Cell StructureDocument30 pagesBTN-345 L1 Cell StructureAditya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument17 pagesThe CelluissojohnyzNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument39 pagesProkaryotic Cell Structure and Functionsabida waryamNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument51 pages2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionNigel Subhash BakkerNo ratings yet
- BiochemDocument108 pagesBiochemJangNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument146 pagesCell TheoryGynewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document29 pagesChapter 4skywalkerNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument6 pagesAnimal Cellmiss_cuteeNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 8th Edition Lauralee Sherwood Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesHuman Physiology From Cells To Systems 8th Edition Lauralee Sherwood Solutions ManualLauraMitchellfgie100% (53)
- 1.cell StructureDocument77 pages1.cell StructureSantino MajokNo ratings yet
- Structural and Functional Manifestation of LifeDocument6 pagesStructural and Functional Manifestation of LifeKaila StefanieNo ratings yet
- The Living CellDocument53 pagesThe Living CellDaniele Joseph HizonNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Prokyrotic and Eukyarotic CellDocument8 pagesGrade 12 Prokyrotic and Eukyarotic CellOlayinka SalmonNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure/ Mitosis & Meiosis: SE Shirley Dept of PathologyDocument36 pagesCell Structure/ Mitosis & Meiosis: SE Shirley Dept of PathologyJohn M. HemsworthNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Its EnvironmentDocument50 pagesCell Structure and Its EnvironmentCarol FernandoNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Lecture PDFDocument49 pagesEukaryotic Cell Lecture PDFDaezel Deux100% (1)
- BOT1501 Course WorkDocument24 pagesBOT1501 Course WorkkathleendmobileNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles and Their FunctionsDocument22 pagesCell Organelles and Their FunctionsJoseph Al Bayonas100% (2)
- CellDocument16 pagesCellanantchouhdary1709No ratings yet
- Cells - Structure and Function: Important Events in The Discovery of CellsDocument8 pagesCells - Structure and Function: Important Events in The Discovery of CellsRameesha RanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 CellsDocument34 pagesChapter 6 CellsChaehyoung LimNo ratings yet
- The Basic Unit of Life: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesThe Basic Unit of Life: ObjectiveHershell ContaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology: Cellular Organization & FunctioningDocument24 pagesCell Biology: Cellular Organization & Functioningshaduni deenaNo ratings yet
- BABS1201-Study-Notes UNSWdocDocument28 pagesBABS1201-Study-Notes UNSWdocgiraffequeenNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 9th Edition Sherwood Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesHuman Physiology From Cells To Systems 9th Edition Sherwood Solutions Manualsanjaktouchbox1wfw100% (29)
- Cell Structures and Its Functions Cell WallDocument5 pagesCell Structures and Its Functions Cell WallNorjanah H. M. AmbolaNo ratings yet
- Unit I Cell & Subcellular Organelles, Cell Mem & Transport BDSDocument48 pagesUnit I Cell & Subcellular Organelles, Cell Mem & Transport BDSshafrasimin22No ratings yet
- Chapter 1.3 Structures and Functions of OrganellesDocument35 pagesChapter 1.3 Structures and Functions of OrganellesFairview PenangNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Mitosis and Meiosis 2007 For UPLOADDocument44 pagesCell Structure Mitosis and Meiosis 2007 For UPLOADJason RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument4 pagesCell BiologyasadzamanchathaNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument10 pagesCELLMAAYER MUHAMMADNo ratings yet
- BABS1201 NotesDocument25 pagesBABS1201 NotesgiraffequeenNo ratings yet
- Module IDocument18 pagesModule IAdvith A JNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument22 pagesCell Structure and FunctionRavi DesaiNo ratings yet
- محاضرة 2Document41 pagesمحاضرة 2AbdulNo ratings yet
- Cell StructuresDocument25 pagesCell StructuresAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- MSDS Tetra Hydroxy Methyl Phosphonium sulphate-THPSDocument23 pagesMSDS Tetra Hydroxy Methyl Phosphonium sulphate-THPSHany OsmanNo ratings yet
- Therapy PolarityDocument37 pagesTherapy PolarityNaina RavahitrarivoNo ratings yet
- Benzi+Cipelli+Et+Al +proof+1 14Document60 pagesBenzi+Cipelli+Et+Al +proof+1 14adan_infowars0% (1)
- Blue BrainDocument22 pagesBlue BrainNakul GawandeNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Mother-to-Infant Transmission of Hepatitis C Virus: Quasispecies Nature and BuoyantDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Mother-to-Infant Transmission of Hepatitis C Virus: Quasispecies Nature and BuoyantMaxime PorcoNo ratings yet
- Insert - HGH CalSet - Ms 05390133190.V4.EnDocument2 pagesInsert - HGH CalSet - Ms 05390133190.V4.EnGuneyden Guneyden100% (1)
- GenomicsDocument8 pagesGenomicsPRATAPNo ratings yet
- Banana (Musa Balbisiana) Peels As Alternative Fot The Production of PaperDocument11 pagesBanana (Musa Balbisiana) Peels As Alternative Fot The Production of PaperApril PabloNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Plasmid DNA From Agrobacterium Using The QIAprep® Spin Miniprep Kit Spin ProcedureDocument3 pagesIsolation of Plasmid DNA From Agrobacterium Using The QIAprep® Spin Miniprep Kit Spin Procedure于连升No ratings yet
- List of Licences (Manufacturers, Importers & Distributors) Valid Up To 04-08-2020Document247 pagesList of Licences (Manufacturers, Importers & Distributors) Valid Up To 04-08-2020Muhammad Boota ZahidNo ratings yet
- Best Answer: Question: What Is The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology? Succinctly (ADocument8 pagesBest Answer: Question: What Is The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology? Succinctly (APrincess Lheakyrie CasilaoNo ratings yet
- Protocolo Dra Neciosup CA209 - 901 - SBW - Peru CorregidoDocument2 pagesProtocolo Dra Neciosup CA209 - 901 - SBW - Peru CorregidoJoel DiazNo ratings yet
- Class-12 Phy. Edu. 7-Dec PB (2022-23)Document6 pagesClass-12 Phy. Edu. 7-Dec PB (2022-23)Nitin SinghNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2 CarbohydratesDocument2 pagesExperiment No. 2 CarbohydratesYellow100% (1)
- Biology Project Final Class 12 InversDocument15 pagesBiology Project Final Class 12 InverstaanusarvNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Monster GeneticsDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Monster Geneticsapi-312959802No ratings yet
- Protein Metabolism and Requirements in The ICUDocument6 pagesProtein Metabolism and Requirements in The ICUntnquynhproNo ratings yet
- Stages of MitosisDocument2 pagesStages of MitosisWONGNo ratings yet
- OME Reflections ON THE EGODocument18 pagesOME Reflections ON THE EGOCamilaNo ratings yet
- Exm Sba QuestionsDocument21 pagesExm Sba Questionsأسعد حسنانNo ratings yet
- Biological OxidationDocument51 pagesBiological OxidationGorav Sharma100% (2)
- IntelliegenceDocument31 pagesIntelliegenceasha suratkalNo ratings yet
- Roustem N. Miftahof, Hong Gil Nam - Mathematical Foundations and Biomechanics of The Digestive system-CUP (2010)Document242 pagesRoustem N. Miftahof, Hong Gil Nam - Mathematical Foundations and Biomechanics of The Digestive system-CUP (2010)Serkan AltinNo ratings yet
- Enzymes-Biology PresentationDocument52 pagesEnzymes-Biology PresentationAdeenNo ratings yet
- ClassOf1 - Ecology - Lifecycle - Pfiesteria - 13Document4 pagesClassOf1 - Ecology - Lifecycle - Pfiesteria - 13ClassOf1.comNo ratings yet
- 061 Degree 6 Nos 19-21 1011Document36 pages061 Degree 6 Nos 19-21 1011Esperant KilondaNo ratings yet
- English Full ProjectDocument17 pagesEnglish Full ProjectShyam SundarNo ratings yet
- Annotated List of Spider Families (Araneida) of Trinidad and TobagoDocument6 pagesAnnotated List of Spider Families (Araneida) of Trinidad and TobagoDanny BoysieNo ratings yet