Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Electricity
Basic Electricity
Uploaded by
RLcircuitOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Electricity
Basic Electricity
Uploaded by
RLcircuitCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Electricity
Instructor: Date: Jesus Calderon 7/30/12 Lecture 1 In this lecture we are going to cover the following topics: 1. Matter 2. The nature of atoms 3. Conductors 4. Insulators Matter - All physical objects that are composed of matter have mass and occupied space. - All mater can be divided into three categories: Solids Liquids Gases
For Example: The three states of water are: Ice Liquid water Steam Solid State Liquid State Gaseous State
Matter is in a solid state if it retains its shape and volume Matter is in a liquid state if it retains its volume but not its shape. Matter is in a gaseous state if it cannot retain its shape or volume.
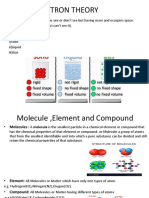
The Atom - Matter is composed of tiny particles called molecules, which are the smallest particles that a substance can be divided and still maintain its physical properties. - Molecules can be divided into smaller particles called atoms. There are 92 different kinds of atoms found in nature including Hydrogen, Calcium, Zinc, Carbon, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and others. Atomic Structure - The atom can be divided into the following three fundamental particles: Electrons Protons Neutrons Electrons have a negative charge Protons have a positive charge Neutrons have no charge
Conductors - Materials that allowed many electrons to move freely from atom to atom are called conductors. Example - Silver - Copper - Gold - Aluminum - Iron - Steel - Brass
Insulators - Materials that allowed few electrons to move freely from one atom to another. Example - Glass - Rubber - Oil - Asphalt - Fiberglass - Porcelain - Ceramic
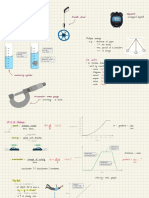
Current - Current is the flow of electrons from one atom to the next atom in the same general direction. The symbol for current is I Current is determined by the number of electrons that pass through a cross section of conductive material in a period of one second. Current is measure in Amperes which is abbreviated as amps. The symbol for amps is A Units of Measuring Current Flow Prefix 1 Kilo ampere 1 milli ampere 1 micro ampere Symbol 1kA 1mA 1A Decimal 1000 A 0.001 A 0.000001 A
Direction of current flow - Current flow from positive to negative
Voltage - Voltage is the force that is required for electrons to flow in a conductive material. The symbol for voltage is V Voltage sources have an excess of electrons at one terminal and a shortage of electrons at the other terminal. Voltage is measure in Volts. The symbol for a voltage source in a circuit is
Units of Measuring Voltage Prefix 1 Kilovolt 1 millivolt 1 microvolt Symbol 1kV 1mV 1V Decimal 1000 V 0.001 V 0.000001 V
Resistance - Resistance impedes the flow of electrons in a conductive material. The symbol for resistance is R The amount of resistance depends on 1. Material properties 2. Length 3. Cross-sectional area 4. Temperature Resistance is measure in Ohms which is abbreviated as . The symbol for resistance in a circuit is
Units of Measuring Voltage Prefix 1 Kilohm 1 Megohm Symbol 1k 1M Decimal 1000 1000000
Name: Date: Subject: Exam 1 1. Name the fundamental particles of an atom and their corresponding electric charge.
2. Name the three states of matter.
3. What is a conductor?
4. What is an insulator?
5. Name three good conductors.
6. Name three good insulators
7. What is current?
8. What is voltage?
9. What is resistance?
10. The force that is applied to a conductor and causes current flow is
You might also like
- Operation Guide - RX Path ImbalanceDocument3 pagesOperation Guide - RX Path ImbalanceBiodun123456775% (4)
- (Alex Ward) Biophysical Bases of ElectrotherapyDocument184 pages(Alex Ward) Biophysical Bases of ElectrotherapyColleen WhiteNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Magnetic Properties of MaterialsDocument32 pagesElectrical and Magnetic Properties of MaterialsArmida Ármídà50% (2)
- EEE 101 To Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument14 pagesEEE 101 To Electrical and Electronics EngineeringArhamNo ratings yet
- Origin of ElectricityDocument36 pagesOrigin of ElectricitySherwin PagpaguitanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 Fundamentals of ElectricityDocument18 pagesChapter 01 Fundamentals of ElectricityPrathamesh KathadeNo ratings yet
- Mod 3 FinalDocument212 pagesMod 3 FinalNavin Ji100% (2)
- Chapter 2 Basic Physics of ElectricityDocument31 pagesChapter 2 Basic Physics of ElectricityMelchor CarabayasNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical TheoryDocument22 pagesBasic Electrical TheoryAnthony MinozaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical TheoryDocument22 pagesBasic Electrical TheoryAnthony MinozaNo ratings yet
- Tieng Anh Chuyen Nganh Dien-Dien TuDocument95 pagesTieng Anh Chuyen Nganh Dien-Dien TuPhong Vũ VănNo ratings yet
- Electronics-NOTES2 1 ZDocument83 pagesElectronics-NOTES2 1 ZDr. Ramchandra Gosavi PatilNo ratings yet
- 3 Electricity Sth20Document3 pages3 Electricity Sth20Abde SlamNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits: Syed Muhammad Rehan Ali Phone No. 03335577508 Whatsapp. 03175115649Document39 pagesElectronic Circuits: Syed Muhammad Rehan Ali Phone No. 03335577508 Whatsapp. 03175115649Syed Mohammad Rehan AliNo ratings yet
- G-10 PhyDocument18 pagesG-10 PhyEl EgnouNo ratings yet
- Tarea 2 IdiomaDocument1 pageTarea 2 IdiomaSofia ReinhardtNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ElectricityDocument22 pagesFundamentals of ElectricityMark PalomaresNo ratings yet
- Electricidad BásicaDocument32 pagesElectricidad BásicaDueñas MartínezNo ratings yet
- Electrical Properties of MaterialsDocument6 pagesElectrical Properties of Materialssabari ramasamyNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 BEDocument39 pagesLec 1 BEalaaelk943No ratings yet
- My Note PDFDocument23 pagesMy Note PDFAswini Kumar PaloNo ratings yet
- Elec Coures Book 2010Document67 pagesElec Coures Book 2010eltonNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectricityDocument6 pagesBasic ElectricityThe Irshaad KhaanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Intro To ElectricityDocument14 pagesChapter 1 Intro To ElectricityRia Bariso100% (1)
- Работа №1 Переведите: The Concept of Electrical CurrentDocument5 pagesРабота №1 Переведите: The Concept of Electrical CurrentлюдмилаNo ratings yet
- Quizzes 1 10112023 CDocument2 pagesQuizzes 1 10112023 Cvodangnhuhoa015No ratings yet
- UNIT 1: Conductors, Insulators and SemiconductorsDocument35 pagesUNIT 1: Conductors, Insulators and SemiconductorscôngNo ratings yet
- Conductors & Insulators-1Document35 pagesConductors & Insulators-1mariam.ahmed03No ratings yet
- Tugas Buku Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pagesTugas Buku Bahasa InggrisFandi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- 2-Konsep Arus Dan TeganganDocument22 pages2-Konsep Arus Dan Teganganoggay94No ratings yet
- Ee 211 Chapter 1Document6 pagesEe 211 Chapter 1RickNo ratings yet
- Duy 2Document11 pagesDuy 2Bieu NayNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument74 pagesBasic Electronicsphilip derit100% (1)
- Electron TheoryDocument21 pagesElectron Theoryjehanzaib albertNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Basic ElectricityDocument18 pagesModule 3: Basic ElectricityApriljoy DannugNo ratings yet
- Applied Electronics I Exit Exam NotesDocument242 pagesApplied Electronics I Exit Exam Notesassefa295No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics BookDocument57 pagesBasic Electronics BookNur Hafizah Kamilah SapawiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document19 pagesChapter 4migadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ElectricityDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Electricityhazreen othman100% (4)
- Basic Electronics: Subcourse Edition OD1633 8Document117 pagesBasic Electronics: Subcourse Edition OD1633 8yuvionfireNo ratings yet
- Electrical Properties of SolidsDocument4 pagesElectrical Properties of Solidsstephen james100% (1)
- ElectricityDocument161 pagesElectricityamanNo ratings yet
- Intro To Semicon MaterialsDocument37 pagesIntro To Semicon MaterialsJerome MacabinquilNo ratings yet
- Chemicals Effect of CurrentDocument2 pagesChemicals Effect of CurrentRanveer RathiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Fundamentals of ElectricityDocument11 pagesChapter 1 Fundamentals of ElectricityTynoh Musuku100% (2)
- Material 2Document22 pagesMaterial 2zeekumNo ratings yet
- Cours 4 Et Exercices Anglais TechDocument5 pagesCours 4 Et Exercices Anglais TechÁł ÃăNo ratings yet
- 2365-202-01 - Electron Theory Day 1.Document4 pages2365-202-01 - Electron Theory Day 1.BillNo ratings yet
- Ulo1aletscheck VillanuevaDocument2 pagesUlo1aletscheck VillanuevaARC VILLANUEVANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Electron TheoryDocument23 pagesChapter 1 Electron TheoryJames Ryan GarmaNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Magnetic Properties of MaterialsDocument71 pagesElectrical and Magnetic Properties of MaterialsArmida ÁrmídàNo ratings yet
- Notes in Che 324 Prepared: Engr. Brenda T. Domingo Coloma, CheDocument8 pagesNotes in Che 324 Prepared: Engr. Brenda T. Domingo Coloma, ChePaul Philip LabitoriaNo ratings yet
- Week 6Document4 pagesWeek 6JUAN CAMILO BRIEZ MONTEALEGRENo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - Chapter Notes - Notes - ICSEDocument8 pagesAtomic Structure - Chapter Notes - Notes - ICSEItu DeyNo ratings yet
- Less 01 & Cont 01 Introduction To Semiconductors PDFDocument2 pagesLess 01 & Cont 01 Introduction To Semiconductors PDFAnusooya VNo ratings yet
- Electron TheoryDocument62 pagesElectron Theoryadancuellar100% (1)
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Concept Paper-Bagasse As FuelDocument12 pagesConcept Paper-Bagasse As FuelDaniel Andre Ocampo PrudencioNo ratings yet
- Rothoblaas - Typ S.certificate Eta - enDocument47 pagesRothoblaas - Typ S.certificate Eta - enAndrei GheorghicaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.1 Linear EquationsDocument24 pagesTopic 1.1 Linear EquationsnshoulyNo ratings yet
- Interpretations and CorrelationsDocument17 pagesInterpretations and CorrelationsMonal Raj100% (2)
- P1. Motion NotesDocument5 pagesP1. Motion NotesShanayaNo ratings yet
- Tarun Summer Internship Report FormattedDocument52 pagesTarun Summer Internship Report FormattedGOVIND SINGHNo ratings yet
- 103-2 ss01 SSDocument49 pages103-2 ss01 SSErin LinNo ratings yet
- Wire Drawing: Group 3Document6 pagesWire Drawing: Group 3Pratik AcharyaNo ratings yet
- PSA Course File - 2016Document2 pagesPSA Course File - 2016Mohammad Tahir Khan NiaziNo ratings yet
- HW 07Document2 pagesHW 07wtcNo ratings yet
- Basics of Foundation DesignDocument454 pagesBasics of Foundation DesignZainebAl-FaeslyNo ratings yet
- Gall5231328512232fip PDFDocument15 pagesGall5231328512232fip PDFAndres CortezNo ratings yet
- DGK Cement Co LTD., Kalar Kahar, Process CT Teatment Compromise Feb 14, 2012Document30 pagesDGK Cement Co LTD., Kalar Kahar, Process CT Teatment Compromise Feb 14, 2012sacopioNo ratings yet
- E255 Standard Practice For Sampling Copper and Copper Alloys For The Determination of Chemical CompositionDocument5 pagesE255 Standard Practice For Sampling Copper and Copper Alloys For The Determination of Chemical CompositionBryan Mesala Rhodas GarciaNo ratings yet
- Mix Proportioning of Bituminous Concrete Grade-1: SL - No Test Test Method Spec. Requireme NT Test Results RemarksDocument6 pagesMix Proportioning of Bituminous Concrete Grade-1: SL - No Test Test Method Spec. Requireme NT Test Results RemarksAbhay kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- FLIR - Mill Ladle Refractory MonitoringDocument2 pagesFLIR - Mill Ladle Refractory MonitoringDavis Cahua100% (1)
- CHM 451 F-12 Exam 3 AnswersDocument10 pagesCHM 451 F-12 Exam 3 AnswersAbdul Mueez Lone100% (1)
- Design of Wireless Power Transfer System For RailwDocument9 pagesDesign of Wireless Power Transfer System For Railw19TK5AO265 V.NavaneethaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27 Suspensions and EmulsionsDocument49 pagesChapter 27 Suspensions and EmulsionsKate Montenegro67% (3)
- Pple Assignment-4Document7 pagesPple Assignment-4Subhangi KashyapNo ratings yet
- General Physics I Chapter 14 Wave MotionDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics I Chapter 14 Wave Motionnomio12No ratings yet
- By The ASCE Task Committee On Design Criteria For Composite Structures in Steel and Concrete ABSTRACT: This Commentary Complements The "Proposed Specification For StrucDocument25 pagesBy The ASCE Task Committee On Design Criteria For Composite Structures in Steel and Concrete ABSTRACT: This Commentary Complements The "Proposed Specification For StrucPrapa KaranNo ratings yet
- Ether Plasma SanandaDocument5 pagesEther Plasma SanandaALCHEMISTT100% (1)
- Trig Exam Example 20-2Document10 pagesTrig Exam Example 20-2api-267824245No ratings yet
- Mathematics 20 2 Quadratic Functions and EquationsDocument96 pagesMathematics 20 2 Quadratic Functions and Equations22-Rawan AdnanNo ratings yet
- Diffraction F. M. Grimaldi: Click On The Image For DetailsDocument5 pagesDiffraction F. M. Grimaldi: Click On The Image For DetailsGxilleNo ratings yet
- Twelve Books That Changed The WorldDocument6 pagesTwelve Books That Changed The Worldapi-19838084No ratings yet
- Chemistry in Microstructured ReactorsDocument41 pagesChemistry in Microstructured ReactorsMatteo RizzottoNo ratings yet
- Continuity Diaphragm For Skewed Continuous Span PrecastDocument2 pagesContinuity Diaphragm For Skewed Continuous Span PrecastDiego Estrada Paz100% (1)