Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Grandcase
NCP Grandcase
Uploaded by
Saima BataloOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP Grandcase
NCP Grandcase
Uploaded by
Saima BataloCopyright:
Available Formats
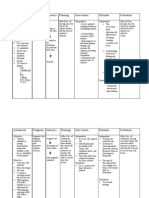
NURSING CARE PLAN ASSESSMENT DATA (Subjective & Objective Cues) NURSING DIAGNOSIS (Problem and Etiology) GOALS
AND OBJECTIVES Short term: After 1 hour of nursing intervention, the patient will verbalize understanding through the use of effective coping behaviors . A Long term: After 2 days of nursing intervention, the patient will display appropriate range of feelings and lessened fear and gain information about the procedure. NURSING INTERVENTIONS AND RATIONALE
Establish patients rapport to gain trust and cooperation. Monitor and record patients vital signs to obtain baseline data. Determine what the patient is fearful of, and thoughtful questioning because patient who find it unacceptable to express fear may find it helpful to know that someone is willing to listen if they do decide to share their feelings at sometimes in the future. Compare verbal and non verbal responses to note congruence or misperceptions in the situation. Assess the degree of fear and the measures patient uses to cope with that fear. This helps determine the effectiveness of coping strategies used by the patient. Maintain a calm and tolerant manner while interacting with patient. The patients feeling of stability increases in a calm and nonthreatening atmosphere and ongoing relationship establishes trust and a basis for communicating fearful feelings. Establish a working relationship through continuity of care. If home environment is unsafe, patients fears are not resolved and fear may become disabling. Encourage rest periods, rest improves ability to cope. Exercise in relaxation, meditation, or guided imagery. Exercise reduces the physiological response to fear.
EVALUATION
Subjective: Anxiety related to deficient nabalaka ko kung unsa knowledge of the procedure. mahitabo sa ako as verbalized. Objective: Fright Fatigue Narrowed focus
Goals met. Short term: Patient was able to demonstrate understanding through the use of effective coping behaviors and resources. Long term: Patient was able to display appropriate range of feelings and lessened fear and gain information about the procedure.
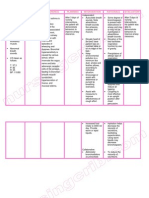
NURSING CARE PLAN ASSESSMENT DATA (Subjective & Objective Cues) Subjective: gitang-tang akong wala nga soso as verbalized. Objective:
NURSING DIAGNOSIS (Problem and Etiology) Impaired tissue integrity related to removal of breast.
GOALS AND OBJECTIVES Short term: After 1 hour of nursing intervention, the patient will participate in prevention measures and treatment program. Long term: After 1-2 days of nursing intervention, the patient will be able to display progressive improvement in wound healing.
NURSING INTERVENTIONS AND RATIONALE
Establish patients rapport to gain trust and cooperation. Monitor and record patients vital signs to obtain baseline data. Assess incision site, take note of size, color, location, temperature, texture, consistency of wound lesion to provide comparative baseline data. Inspect surrounding skin for erythema, induration, maceration to assess extent of involvement. Assess for odors and drains coming out from the skin area of injury to assess early progression of of wound healing, developmental of hemorrhage or infection. Keep the area clean/dry, carefully dress wounds, support incisions and prevent infection to assist bodys natural process of repair. Encourage an increase in protein intake to aid in timely wound healing for the patient. Encourage early ambulation and mobilization to promote circulation and reduce risks associated with immobility. Practice asceptic technique in cleaning/dressing and medicating lesions to reduce risk of cross contamination. Instruct proper disposal of soiled dressing. To prevent spread of infectious agent.
EVALUATION Goals met. Short term: Patient was able to participate in prevention measures and treatment program. Long term: Patient was able to display progressive improvement in wound healing.
Presence of surgical wound in the breast where incision was made. Numbness in the surrounding area redness
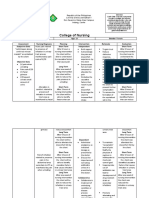
NURSING CARE PLAN ASSESSMENT DATA (Subjective & Objective Cues) Subjective Cues: sakit akong inoperahan as verbalized. Objective Cues: Pain scale of 8/10 facial grimace restlessness guarded behaviour sleep disturbances NURSING DIAGNOSIS (Problem and Etiology) Acute pain related to postoperative incision GOALS AND OBJECTIVES Short term: After 1 hour of nursing intervention patients pain scale will be reduce. Long term: After 2 days of nursing intervention patient will be relieve from pain and will appear more relax. NURSING INTERVENTIONS AND RATIONALE Monitor vital signs to for baseline data. Assess verbal/non-verbal reports of pain, noting location, intensity (0-10 scale), and duration for useful evaluating pain, choice of interventions, effectiveness of therapy. Instruct client to use hands to support neck during movement and to avoid hyperextension of neck for movement restriction is imposed for only a few hours postoperatively to prevent stress on the suture line and reduce muscle tension. Gentle flexing and stretching is then permitted according to pain tolerance to help prevent neck soreness. Encourage patient to use relaxation techniques e.g.,guided imagery, soft music, progressive relaxation to help refocus attention and assist patient to manage more effectively. Instructed to eat soft foods. It may tolerated better than liquids if patient is experienced difficulty of swallowing. EVALUATION Goals partially met. Short term: Patients pain scale was 5/10 from 8/10. Long term: Patient was able to rest at intervals but pain is still felt.
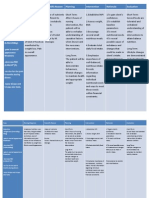
NURSING CARE PLAN ASSESSMENT DATA (Subjective & Objective Cues) Subjective: dili nako mabuhat ang gusto nako buhaton tungod sa akong operasyon as verbalized. Objective: Limited range of motion Immobility Inability to turn sides Inability to change position Inability to transfer from bed to chair NURSING DIAGNOSIS (Problem and Etiology) Activity intolerance related to post operative wound GOALS AND OBJECTIVES Short term: After 1 hour of nursing intervention the patient and the significant others will be able to identify negative factors affecting activity tolerance and eliminate/reduce their effects. Long term: After 2 days of nursing intervention, the patient will be able to improve her activity and perform techniques to enhance activity tolerance. NURSING INTERVENTIONS AND RATIONALE Establish patients rapport to gain trust and cooperation. Monitor and record patients vital signs to obtain baseline data. Assess patients condition, to obtain baseline data to be used in evaluating patients condition. Assess patients level of mobility. This aids in defining what patient is capable of, which is necessary before setting realistic goals. Assess nutritional status. Adequate energy reserves are required for activity. Provide a quite environment and encourage use of stress management. Rest provides time for energy conservation and recovery. Assist client in learning and demonstrating appropriate safety measures. To enhance sense of well being. Encourage client to maintain positive attitudes; suggest use of relaxation techniques such as visualization/guided imagery as appropriate. EVALUATION
Goals met. Sort term: Patient was able to identify negative factors affecting activity tolerance and eliminate/reduce their effects. Long term: Patient was able to improve her activity and perform techniques to enhance activity tolerance.
NURSING CARE PLAN ASSESSMENT DATA (Subjective & Objective Cues) SUBJECTIVE Luya akong lawas as verbalized. OBJECTIVE: Hemoglobin 8.9 g/dl Hemovac drainage 400cc Vital signs: NURSING DIAGNOSIS (Problem and Etiology) Fatigue related to decreased hemoglobin concentration in blood secondary acute blood loss. GOALS AND OBJECTIVES After 2 hours of nursing interventions, the client will manifest the following: Short-term goal: Demonstrate increased perfusion as individually appropriate BP=120/80mmHg RR=18 cpm Capillary refill less than 3 sec Long-term goals: After 4 hours of nursing interventions, the client will manifest the following: Demonstrate behaviors/lifestyle changes to improve circulation. NURSING INTERVENTIONS AND RATIONALE INDEPENDENT 1. Measure capillary refill; palpate for presence/absence and quality of pulses. R: To assess blood flow distributed to extremities. 2. Encourage active or assist with passive leg exercises, with avoidance of isometric exercises. Enhances venous return, reduces venous stasis, and decreases risk of thrombophlebitis. 3. Provide supplemental oxygen as prescribed R: To increase oxygen supply to the myocardium. 4. Monitor vital signs and measure urine output on a regular schedule. R: (Intake may be calculated against output.) 5. Monitor intake and output R: To prevent circulatory overload. DEPENDENT 7. Administer medications with caution as indicated. R: Drug response, half-life, toxic levels may be altered by decreased tissue perfusion. EVALUATION After 2 hours of nursing interventions, the client has manifested the following: Goal met: Demonstrate increased perfusion as individually appropriate BP=120/80mmHg RR=18 cpm Goals partially met: Demonstrate behaviors/ lifestyle changes to improve circulation Capillary refill less than 3 sec
You might also like
- Case Study, Chapter 36Document2 pagesCase Study, Chapter 36Tessa Claire JaranowskiNo ratings yet
- NCP CoughDocument4 pagesNCP CoughKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (Bowel Elemination)Document8 pagesNursing Care Plan (Bowel Elemination)Rijane Tabonoc Omlang100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 2Isabel Barredo Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Desired Outcome Interventions Justification EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Desired Outcome Interventions Justification EvaluationPJNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument9 pagesNursing Care PlanClarisse Anne QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluationria_soriano_2No ratings yet
- Teething:diaper Dermatitis NCPDocument2 pagesTeething:diaper Dermatitis NCPMARK OLVIER E. MELCHORNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument7 pagesNCP FinalRuss RussNo ratings yet
- Pot Term pregnancy-MOMANYIDocument2 pagesPot Term pregnancy-MOMANYISally Gesembe100% (1)
- NCPDocument1 pageNCPAlynna ValbuenaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan: Involution (Bubble He)Document4 pagesTeaching Plan: Involution (Bubble He)Pamela BagabaldoNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainNathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- NCP - EdemaDocument1 pageNCP - Edemavipncpusers100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKath RubioNo ratings yet
- Biopsy: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesBiopsy: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageNursing Care PlanMichael John PaderesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPderic100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Bronchial AsthmaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Bronchial AsthmaSummer Ilu100% (1)
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDocument6 pagesWord Ncp.......... TetanusaianrNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Process (NCP) Stress Overload PrepartumDocument2 pagesNursing Care Process (NCP) Stress Overload PrepartumFrederene JavelonaNo ratings yet
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDocument3 pagesWord Ncp.......... TetanusYvounne Ananias Bautista RNNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nsg. Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument6 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nsg. Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveIngrid Eunice ConcordiaNo ratings yet
- L&D Careplan 1 KarenDocument4 pagesL&D Careplan 1 KarenSimran SandhuNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care Planruggero07100% (2)
- Cutaneous Anthrax Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesCutaneous Anthrax Nursing Care PlanYayin Pestaño100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument7 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternJanmae JivNo ratings yet
- Migraine NCPDocument5 pagesMigraine NCPJohn Dexter FranciscoNo ratings yet
- CHN Family Developmental StagesDocument12 pagesCHN Family Developmental StagesRyll JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Cues/Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goals of Care Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesCues/Data Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goals of Care Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationEjie Boy Isaga100% (1)
- NCP - NewbornDocument1 pageNCP - NewbornChristine Michelle A. BalancadNo ratings yet
- Delayed Growth NCPDocument3 pagesDelayed Growth NCPPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- Deficit)Document2 pagesDeficit)Lee DeeNo ratings yet
- School Age NCPDocument6 pagesSchool Age NCPNikki Coleen SantinNo ratings yet
- S: "Masakit Ang Ulo at Tiyan Niya" As Verbalized byDocument2 pagesS: "Masakit Ang Ulo at Tiyan Niya" As Verbalized bydenise-iceNo ratings yet
- Goboy - Risk For Infection NCPDocument3 pagesGoboy - Risk For Infection NCPLouise GermaineNo ratings yet
- Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding (DUB)Document1 pageDysfunctional Uterine Bleeding (DUB)Bheru LalNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPeun kyung shinNo ratings yet
- NCP OfficialDocument4 pagesNCP Officialapi-310097594No ratings yet
- FATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Document4 pagesFATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Irene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Hypertonic SolutionsDocument4 pagesHypertonic SolutionsVanessa PaguiriganNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPJerome Vergel RubianesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Document1 pageNursing Care Plan: References: Nurse's Pocket Guide Pages 151-155Caroline ChaNo ratings yet
- NCP InfectionDocument3 pagesNCP InfectionPrince AhmirNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPAbbie TantengcoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal & Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal & Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationLP BenozaNo ratings yet
- "Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientDocument2 pages"Hindi Ko Kayo Masyadong Marinig Sa Kanang Tenga Ko, Pwede Bang Sa Kaliwang Side Ko Kayo Magsalita?" As Verbalized by The PatientMussaib Mushtaq100% (1)
- Activity 4.health Education PlanDocument3 pagesActivity 4.health Education Planjoannamae molaga0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Tissue InjuryJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For RabiesDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan For RabiesAngel VillamorNo ratings yet
- Activity IntoleranceDocument2 pagesActivity IntoleranceSenyorita KHaye100% (4)
- NCP Acute Pain FURUNCOLOSISDocument2 pagesNCP Acute Pain FURUNCOLOSISMaria Imogen MilambilingNo ratings yet
- Patty NCP HyperthermiaDocument4 pagesPatty NCP HyperthermiaPatricia Jean FaeldoneaNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument6 pagesNCP Risk For InfectionCazze SunioNo ratings yet
- Risk For Disproportionate GrowthDocument8 pagesRisk For Disproportionate GrowthRahajeng Intan HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanAlvin DagumbalNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasDocument4 pagesNcp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasFran LanNo ratings yet
- PlateletDocument16 pagesPlateletArgene Rose MilletNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKatrina Ponce86% (7)
- NCP Cataract SurgeryDocument5 pagesNCP Cataract SurgeryKristaJaneCelmarBagcatNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument18 pagesNCP FinalJessica Medina100% (1)
- MS Exam 22 Nle StyleDocument9 pagesMS Exam 22 Nle StyleSaima BataloNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals in NursingDocument11 pagesFundamentals in NursingSaima BataloNo ratings yet
- Drug OrderDocument3 pagesDrug OrderSaima BataloNo ratings yet
- Types of SuturesDocument7 pagesTypes of SuturesSaima BataloNo ratings yet
- Case Study F. BaylosisDocument27 pagesCase Study F. BaylosisJenina Rosa P. Llanes100% (1)
- Medonic m20 Blood Cell CounterDocument109 pagesMedonic m20 Blood Cell CounterRupendra SahuNo ratings yet
- Dapsone Lyme DiseaseDocument53 pagesDapsone Lyme DiseasecemalsagmenNo ratings yet
- BELLO DOCsDocument98 pagesBELLO DOCsPia Loraine BacongNo ratings yet
- Pry 6 Phe 3RD TermDocument31 pagesPry 6 Phe 3RD Termsamuel joshuaNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia TechDocument8 pagesAnesthesia TechGloria JaisonNo ratings yet
- MCE IGCSE Biology PPT C10Document53 pagesMCE IGCSE Biology PPT C10Aheer GhoshNo ratings yet
- 4008 B / 4008 H / 4008 S Hemodialysis Device Technical ManualDocument378 pages4008 B / 4008 H / 4008 S Hemodialysis Device Technical ManualAleksei PodkopaevNo ratings yet
- MCQ 3Document21 pagesMCQ 3Robert Edwards100% (1)
- (Ebook PDF) Textbook of Critical Care 7th Edition Jean-Louis Vincent - Ebook PDF All ChapterDocument69 pages(Ebook PDF) Textbook of Critical Care 7th Edition Jean-Louis Vincent - Ebook PDF All Chapterdryndalifasi100% (11)
- CONTAGIOUS DISEASES and The GERM THEORYDocument3 pagesCONTAGIOUS DISEASES and The GERM THEORYWilliam Alejandro Alarcon Lazaro100% (1)
- Postpartum NCPDocument20 pagesPostpartum NCPireneNo ratings yet
- Netter's Internal Medicine 2nd Ed 17Document19 pagesNetter's Internal Medicine 2nd Ed 17Panagiotis SouldatosNo ratings yet
- Dental BiofilmsDocument44 pagesDental BiofilmsRamona MateiNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 8Document4 pagesMapeh 8Hannah Loth ExceliseNo ratings yet
- Insert - Testosterone II CalSet II - Ms - 05202230190.v10.enDocument2 pagesInsert - Testosterone II CalSet II - Ms - 05202230190.v10.enykinomoto5No ratings yet
- Managing Health For Field Operations in Oil and Gas ActivitiesDocument44 pagesManaging Health For Field Operations in Oil and Gas Activitiesadeoye_okunoyeNo ratings yet
- HIV/AIDS Symptoms and SignsDocument3 pagesHIV/AIDS Symptoms and SignsAmin MofrehNo ratings yet
- The Role of Bacterial Biofilm in Persistent Infections and Control StrategiesDocument8 pagesThe Role of Bacterial Biofilm in Persistent Infections and Control StrategiesJenny TaylorNo ratings yet
- Priyanka Pradhan: A Project Work On Study of Pathogenic Bacteria From Brackish Waters of Chilika Lake, OdishaDocument33 pagesPriyanka Pradhan: A Project Work On Study of Pathogenic Bacteria From Brackish Waters of Chilika Lake, Odishapraanya kishoreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Communicable Diseases 2ND Sem 2022 2023Document10 pagesChapter 1 Communicable Diseases 2ND Sem 2022 2023Lovelyn Cantollas EugenioNo ratings yet
- Surgical InterventionDocument27 pagesSurgical Interventionmardsz100% (9)
- Management of Mesenteric Lymphadenopathy by Individualized Homoeopathic Medicine: A Case ReportDocument6 pagesManagement of Mesenteric Lymphadenopathy by Individualized Homoeopathic Medicine: A Case ReportTanisha SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Oakland Athletics V AIGDocument69 pagesOakland Athletics V AIGTHROnlineNo ratings yet
- Đề Cà MauDocument19 pagesĐề Cà Mautuantu_51No ratings yet
- GRAM STAINING AND CLINICAL UTILITY by Dr.T.V.Rao MDDocument2 pagesGRAM STAINING AND CLINICAL UTILITY by Dr.T.V.Rao MDtummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- Q 1MCQs Microbiology For MRCP and MRCPathDocument40 pagesQ 1MCQs Microbiology For MRCP and MRCPathDr Sumant SharmaNo ratings yet
- GTG 64b PDFDocument21 pagesGTG 64b PDFajeng larasati0% (1)
- Coswara - A Database of Breathing, Cough, and Voice Sounds For COVID-19 DiagnosisDocument5 pagesCoswara - A Database of Breathing, Cough, and Voice Sounds For COVID-19 DiagnosisSANJAY S KUMARNo ratings yet