Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lipideos: Classificação Dos Lipídeos
Lipideos: Classificação Dos Lipídeos
Uploaded by
Rafael PiccoliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lipideos: Classificação Dos Lipídeos
Lipideos: Classificação Dos Lipídeos
Uploaded by
Rafael PiccoliCopyright:
Available Formats
17/09/2012
Lipideos
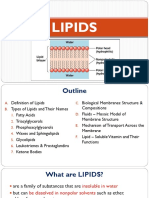
Lipids are organic compounds, found in living organisms, that are soluble in nonpolar organic solvents Organic Compounds are classified as lipids on the basis of a physical property: their solubility in an organic solvent Lipids have a variety of structures and functions
Classificao dos Lipdeos Classificao por funo:
- Estocagem: Triglicerdeos - Reserva de Energia - Componentes de membrana: Lipdeos biliares - Mensageiros: - mensageiros primrios:hormonios esteroidais - Mensageiros secundrios: prostaglandinas e tromboxanas mediadores da resposta hormonal
- Vitaminas lipoflicas - Xenobioticos
Classificao pelas propriedades fsicas: - Ceras esteres de cadeia longa - Graxas triglicerdeos slidos e semislidos - leos triglicerdeos lquidos Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with long hydrocarbon chains
Classificao por estrutura: - Lipideos simples - cidos graxos - leos e gordeuras - Ceras - Lipidedos complexos - Fosfolipideos - Glicolipideos - Esterois - Prostaglandinas, tromboxanas e leucotrienos
17/09/2012
Propriedades Fsicas: Ponto de fuso 13 C
saturated 18-carbon fatty acid melts at 69 C
The physical properties of the fatty acids, and of compounds that contain them, are largely determined by the length and degree of unsaturation of the hydrocarbon chain. The carboxylic acid group is polar (and ionized at neutral pH) and
-5 C
-11 C
accounts for the slight solubility of short-chain fatty acids in water Melting points are also strongly influenced by the length and degree of unsaturation of the hydrocarbon chain. At room temperature (25 C), the saturated fatty acids from 12:0 to 24:0 have a waxy consistency, whereas unsaturated fatty acids of these lengths are oily liquids.
Waxes are esters formed from long-chain carboxylic acids and long-chain alcohols
water repellent
Biological wax. (a) Triacontanoylpalmitate, the major component of beeswax, is an ester of palmitic acid with the alcohol triacontanol.
Pingos de chuva em uma pena
17/09/2012
Triacylglycerols
Triacylglycerols
Triacylglycerols that are solids or semisolids at room temperature are called fats Triacylglycerols that are liquid at room temperature are called oils Organisms store energy in the form of triacylglycerols
Animals products
Plant products
Propriedades dos triglicerdeos: Estado fsico Hidrogenao Oxidao Saponificao
Hidrogenao
17/09/2012
Efeito do calor
slido Gordura Hidrogenada
Produto secundrio da hidrogenao
Oxidao Polyunsaturated fats and oils are easily oxidized by by means of a radical chain reaction
The reaction of fatty acids with causes them to become rancid. The unpleasant taste and smell associated with rancidity are the results of further oxidation of the alkyl hydroperoxide to shorter chain carboxylic acids such as butyric acid that have strong odors
17/09/2012
Saponificao
Detergentes sintticos
Amphipathic lipid aggregates that form in water.
Aplicaes:
(a) In micelles, the hydrophobic chains of the fatty acids are sequestered at the core of the sphere. There is virtually no water in the hydrophobic interior. (b) In an open bilayer, all acyl side chains except those at the edges of the sheet are protected from interaction with water. (c) When a two-dimensional bilayer folds on itself, it forms a closed bilayer, a three-dimensional hollow vesicle (liposome) enclosing an aqueous cavity.
17/09/2012
Phosphoacylglycerols (also called phosphoglycerides) are the major components of cell membranes
The fluidity of a membrane is controlled by the fatty acid components of the phosphoacylglycerols and cholesterol
Phosphoacylglycerols (also called phosphoglycerides) are the major components of cell membranes
Sphingolipids are also found in membranes. They are the major lipid components in the myelin sheaths of nerve fibers.
lipid bilayer
Two of the most common kinds of sphingolipids are sphingomyelins and cerebrosides
17/09/2012
Structural Lipids in Membranes Glicolipideos
The central architectural feature of biological membranes is a double layer of lipids, which acts as a barrier to the passage of polar molecules and ions. Membrane lipids are amphipathic: one end of the molecule is hydrophobic, the other hydrophilic.
Some common types of storage and membrane lipids
The unsaturated fatty acid chains of phosphoacylglycerols are susceptible to oxidation reaction leading to the degradation of membranes. Vitamin E (-tocopherol) is an important antioxidant that protects fatty acid chains from degradation via oxidation
Molculas sinalizadores na comunicao qumica
17/09/2012
You might also like
- Lipid & Membranes - BKSDocument76 pagesLipid & Membranes - BKSAjmain ShakibNo ratings yet
- 03 Lipids StudentsDocument40 pages03 Lipids Studentsmakabigail7No ratings yet
- Lipids - BCSC-BNDocument25 pagesLipids - BCSC-BNJudithNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument53 pagesLipidsGlen Mangali100% (1)
- MC2 Biochemistry Lecture Notes For BSN First Semester, 2019-2020 Prepared By: SALINA OSIAL - ALFADDocument5 pagesMC2 Biochemistry Lecture Notes For BSN First Semester, 2019-2020 Prepared By: SALINA OSIAL - ALFADAl-waleed JulkanainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Lipids Part 2Document22 pagesChapter 6 Lipids Part 2Arissa Jamelia Lofranco AldeanoNo ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument13 pagesLIPIDSSupreeth SPNo ratings yet
- LipidDocument59 pagesLipidlidia maharani100% (1)
- Lecture 8 PDFDocument21 pagesLecture 8 PDFNazir KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Molecular Biology IDocument26 pagesLecture Molecular Biology ImartinmulingeNo ratings yet
- Structure and Classification of Lipids: Lipids Are Naturally Occurring MoleculesDocument19 pagesStructure and Classification of Lipids: Lipids Are Naturally Occurring MoleculesKomic WebtoonNo ratings yet
- CHEM 140 Unit 8 Lec 1 LipidsDocument93 pagesCHEM 140 Unit 8 Lec 1 LipidsMevil Jane MabrasNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Biochemistry 1 - LIPIDSDocument62 pagesNutritional Biochemistry 1 - LIPIDSSalah AlsafiNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Lipids: Saturated Fatty Acid Unsaturated Fatty AcidsDocument53 pagesCarbohydrate Lipids: Saturated Fatty Acid Unsaturated Fatty AcidsSyamila YusofNo ratings yet
- Subject: Biochemistry Assignment On: LipidsDocument8 pagesSubject: Biochemistry Assignment On: LipidsMehran AhmadNo ratings yet
- PertemuanDocument32 pagesPertemuanHaikal FMNo ratings yet
- Biochem SummaryDocument20 pagesBiochem SummaryJAREL ALBERT PASCASIONo ratings yet
- Biomolecules 1Document29 pagesBiomolecules 1jefrillevaldezNo ratings yet
- Lipids and Lipid Metabolism ReviewerDocument14 pagesLipids and Lipid Metabolism ReviewerKiela Therese LabroNo ratings yet
- Membranes and Solute Transport Lecture 1Document32 pagesMembranes and Solute Transport Lecture 1Graphitti Koncepts and DesignsNo ratings yet
- Lipids & Biological MembranesDocument54 pagesLipids & Biological MembranesvictoriousNo ratings yet
- Lipids Friends or Foes-1121Document57 pagesLipids Friends or Foes-1121ywnrmgp9fxNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument44 pagesLipidsMilena De CresentNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Biochemistry 1 - LIPIDSDocument62 pagesNutritional Biochemistry 1 - LIPIDSAdnan AhmedNo ratings yet
- L8 - Structure Functions of Various LipidsDocument23 pagesL8 - Structure Functions of Various Lipidsbilawal khanNo ratings yet
- Lipids and Fats MSCDocument47 pagesLipids and Fats MSCm bilalNo ratings yet
- New Lipid PowerpointDocument113 pagesNew Lipid PowerpointMadane Jamila Amerol SaminNo ratings yet
- 1.4-Carbohydrates and LipidsDocument39 pages1.4-Carbohydrates and LipidsmichaelmarshallNo ratings yet
- MACROmoleculesDocument80 pagesMACROmoleculesMaKenJi EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiochemistryDocument51 pagesIntroduction To BiochemistryAnonymous e0TdsoxUNo ratings yet
- Lipid MetabolismDocument32 pagesLipid MetabolismNahid HasanNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES NOTE 11aaDocument9 pagesBIOMOLECULES NOTE 11aaGyaniNo ratings yet
- HMB 100 Lect. 4Document78 pagesHMB 100 Lect. 4Sylvia NjauNo ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument33 pagesLIPIDSMaria Conxedes GudesNo ratings yet
- 5 LipidDocument32 pages5 LipidAli HusseinNo ratings yet
- Medical Biochemistry - 5Document31 pagesMedical Biochemistry - 5dmutethia68No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: Lecture 11: LipidsDocument34 pagesOrganic Chemistry: Lecture 11: LipidsDương Hà Trúc TâmNo ratings yet
- Biology Lipids PresentationDocument5 pagesBiology Lipids Presentationkaycee charlesNo ratings yet
- Biology Remedial - 2Document54 pagesBiology Remedial - 2Rediat GossayeNo ratings yet
- The Molecules of LifeDocument175 pagesThe Molecules of LifeTiffany BheaNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Class Of: LipidsDocument53 pagesWelcome To Class Of: LipidsMarinela DaumarNo ratings yet
- Biology UNIT 2Document72 pagesBiology UNIT 2suba052k09No ratings yet
- Lehninger Ch10 LipidsDocument36 pagesLehninger Ch10 LipidsAbood alfshekatNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument3 pagesBiological Moleculeslaraking6060No ratings yet
- Biological Molecules - For K-12 TrainingDocument187 pagesBiological Molecules - For K-12 TrainingAlicia CatalanNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument39 pagesBiological MoleculesJennifer Fabia100% (1)
- Che 473 Presented by - Nishatanjum (0802005) Seefat Farzin (0802011) Turna Barua (0802016)Document30 pagesChe 473 Presented by - Nishatanjum (0802005) Seefat Farzin (0802011) Turna Barua (0802016)asha196No ratings yet
- LipidsDocument29 pagesLipidszubairahmed27272No ratings yet
- BTBC209IU Biochemistry 1: International UniversityDocument33 pagesBTBC209IU Biochemistry 1: International UniversityLinhNguyeNo ratings yet
- CNP 3 LipidsDocument49 pagesCNP 3 LipidsKepa KepaNo ratings yet
- SESE 115 Biochemistry: Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University La Union PhilippinesDocument13 pagesSESE 115 Biochemistry: Don Mariano Marcos Memorial State University La Union PhilippinesVhenz MapiliNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 LipidsDocument13 pagesExperiment 5 LipidsClemence Marie FuentesNo ratings yet
- 10.2 Lipids IntroductionDocument55 pages10.2 Lipids Introductionperssivesimangavwa2002No ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument8 pagesBIOMOLECULESjorel marcoNo ratings yet
- Lipids: Bettelheim / Brown / Campbell / Farrell / TorresDocument43 pagesLipids: Bettelheim / Brown / Campbell / Farrell / TorresKatriceNo ratings yet
- Nonpolar.: Dissolve in Non-Polar Solvents Such As Ether, Chloroform, and Acetone But Not Considerably in WaterDocument31 pagesNonpolar.: Dissolve in Non-Polar Solvents Such As Ether, Chloroform, and Acetone But Not Considerably in WaterNejib ReshadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document60 pagesChapter 5EhazNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument10 pagesLipidsapi-233981625No ratings yet
- Lipids (Jigsaw)Document33 pagesLipids (Jigsaw)Milimo JingsawNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 17 - Nutrition, Metabolism, & Body Temperature Regulation)Document17 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 17 - Nutrition, Metabolism, & Body Temperature Regulation)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 LipidsDocument43 pagesChapter 21 Lipidsdaoud sarrawyNo ratings yet
- Injection Molding Resin Shrink and Vents PDFDocument1 pageInjection Molding Resin Shrink and Vents PDFEco TefuNo ratings yet
- Ikon Rare Produt Price List 2019-20 PDFDocument5 pagesIkon Rare Produt Price List 2019-20 PDFAbhishek AvadhaniNo ratings yet
- Aromaticity BknmuDocument24 pagesAromaticity BknmuTrivedi JayNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculeDocument15 pagesBio MoleculeManish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesOrganic ChemistryAshutosh paniNo ratings yet
- List Pesanan Obat: NO Nama Produk Kemasan Komposisi Sediaan Harga Antibiotik Jumlah PesananDocument2 pagesList Pesanan Obat: NO Nama Produk Kemasan Komposisi Sediaan Harga Antibiotik Jumlah PesananRandy JufrilNo ratings yet
- Sodium Bis (2-Methoxyethoxy) Aluminum HydrideDocument8 pagesSodium Bis (2-Methoxyethoxy) Aluminum HydridejavasoloNo ratings yet
- Data StockDocument396 pagesData StockJuriadi PaddoNo ratings yet
- Pump Size Calculation (1.1.17)Document90 pagesPump Size Calculation (1.1.17)Ahmed HassanNo ratings yet
- Reducing Sugars Non-Reducing Sugars: Background Information For TeachersDocument3 pagesReducing Sugars Non-Reducing Sugars: Background Information For TeachersChonie VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Why Is Carbon So Important in Spite of It Being Present in A Very Small QuantityDocument2 pagesWhy Is Carbon So Important in Spite of It Being Present in A Very Small QuantitySuman DasNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis and TCA Cycle - ShuttlesDocument1 pageGlycolysis and TCA Cycle - ShuttlesDr. SHIVA AITHALNo ratings yet
- Oman - Drug - Prices - 06 - 04 - 2013Document488 pagesOman - Drug - Prices - 06 - 04 - 2013Anuj Mairh73% (11)
- Polyester Resin, Resin CompositionDocument11 pagesPolyester Resin, Resin Compositionalfi alfathanaNo ratings yet
- Rubber Products SairamDocument24 pagesRubber Products SairamHina Thetenders.comNo ratings yet
- PediamedsDocument9 pagesPediamedssven stantonNo ratings yet
- Bottle Gourd Nutritional and Medicinal PotentialDocument11 pagesBottle Gourd Nutritional and Medicinal PotentialSafe Solution NepalNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde PDFDocument32 pagesAldehyde PDFMalti GuptaNo ratings yet
- Named ReactionsDocument81 pagesNamed ReactionsH Ramesh KumarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4-Carboxylic Acids DerivativesDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 4-Carboxylic Acids Derivativesshahera rosdiNo ratings yet
- Alkaloids, Biosynthesis and Their ApplicationsDocument16 pagesAlkaloids, Biosynthesis and Their ApplicationsResearch ParkNo ratings yet
- Antoine's ConstantsDocument109 pagesAntoine's ConstantsKeyang Sun100% (1)
- Full Download Test Bank Essential Biochemistry 3rd Edition Pratt Cornely PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank Essential Biochemistry 3rd Edition Pratt Cornely PDF Full Chaptercassatemesoseme7m8v100% (23)
- Citric Acid CycleDocument21 pagesCitric Acid CycleKunda JosephNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination at The Acyl CarbonDocument46 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination at The Acyl CarbonChandraNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit Guides 2020Document135 pagesAP Biology Unit Guides 2020Amy LouNo ratings yet
- List of Hazardous Air Pollutants:: 75070 AcetaldehydeDocument5 pagesList of Hazardous Air Pollutants:: 75070 AcetaldehydeUmit SavasNo ratings yet
- Price List NovemberDocument280 pagesPrice List NovemberEvans SobbaNo ratings yet