Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Name of The Drug
Name of The Drug
Uploaded by
Christine Joy CamachoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Name of The Drug
Name of The Drug
Uploaded by
Christine Joy CamachoCopyright:
Available Formats
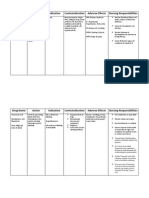
Name of the Drug Mannitol
Dosage and Administration 100cc q4
Indication Adjunct for treatment of tuberculosis with primary and secondary antitubercular drugs when these are not successful
Adverse Effects Common: myalgia, nausea, vomiting, arthralgia, anorexia. Serious: thrombocytopenia, hepatotoxicity, nephritis, porphyria, gout, hypersensitivity reactions.
Contraindication Hypersensitivity to pyrazinamide, severe liver disease, acute gout.
Nursing Implication To minimize possible photosensitivity reaction, apply adequate sunscreen and use proper covering when exposed to strong sunlight. Notify treating physician if symptoms do not improve after several weeks on drug. Do not stop taking medication without consulting treating physician.
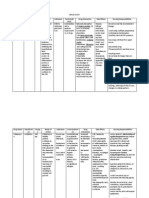
Clarithromycin
125 mg/ml syrup 3.5ml BID
Pharyngitis/tonsillitis Acute maxillary sinusitis Acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis (Streptococcus pneumoniae, Moraxella catarrhalis), pneumonia (S. pneumoniae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae) Acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis (H. influenzae)
Common: diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain. Severe: pseudomembranous colitis, ventricular arrhythmias, nephritis, cholestatic jaundice, angioedema. .
Hypersensitivity to macrolide antibiotics, concomitant administration of pimozide.
Use with caution in patients with liver or kidney dysfunction. Parameters to monitor Signs and symptoms of superinfection, in particular pseudomembranous colitis. Signs and symptoms of renal toxicity. Signs and symptoms of hearing impairment. Patients with Kidney or liver disease is at highest risk.
Uncomplicated skin and skin structure infections
Rifampicin
200mg/ml syrup 3.75 OD before breakfast
Pulmonary tuberculosis: used in conjunction with other agents (combination therapy) Meningococcal prophylaxis Prophylaxis of Hemophilius influenzae type B infections
Common: diarrhea, red discoloration of urine and other body fluids. Serious: acute renal failure, confusion, bone marrow depression, hepatic injury.
Hypersensitivity to rifampin or rifamycins.
Avoid driving or other activities requiring alertness until full response to rifampin or ripampicin is evaluated. Avoid alcohol. Rifampin may stain soft contact lenses permanently. Accordingly, soft contact lenses should not be worn during treatment with this drug. Do not discontinue taking rifampin without approval of treating physician.
Isoniazid
200 mg/ml 2.5 ml p.c 20 min. before breakfast
Primary treatment for active tuberculosis; firstline drug for combination therapy Prophylaxis against TB bacillus, prophylaxis following exposure: Drug of choice
Common: anorexia, nausea, abdominal pain, weakness. Serious: peripheral neuropathy, hepatitis, bone marrow suppression, seizures, depression, optic neuritis, blindness.
Acute liver disease, prior liver toxicity associated with INH therapy, severe hypersensitivity reaction to isoniazid(drug fever, arthritis).
Avoid alcohol. Drink 23 L of fluids/d. Report symptoms of drug side effects such as fatigue, anorexia, weakness (symptoms of hepatitis) to treating physician and stop drug. Continue therapy uninterrupted
to prevent relapse and spread Of infection . Food: Ideally, should be taken on an empty stomach; may administer with food if gastric irritation occurs. There may be a severe reaction if isoniazid is taken along with foods that contain large amounts of tyramine (eg, aged cheese, Chianti wine,pickled herring).
You might also like
- Drug CardsDocument187 pagesDrug Cardsintaaf82% (34)
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument14 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TramadolDocument14 pagesDrug Study TramadolBianca Freya Porral85% (13)
- Rifampicin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesRifampicin Drug StudyMaila Joy Pring Fuentes67% (3)
- Pharma CardsDocument5 pagesPharma CardsazancheNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyDiana Laura LeiNo ratings yet
- Drugs For EmergencyDocument25 pagesDrugs For EmergencyJunathan L. DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Psych Drug StudyDocument5 pagesPsych Drug StudyLorina Lynne Apelacio100% (4)
- Ultimate Reference DocumentDocument29 pagesUltimate Reference DocumentShellyza Moledina SajwaniNo ratings yet
- AntiepilepticDocument4 pagesAntiepilepticWan TokNo ratings yet
- Additional Pharma CardsDocument21 pagesAdditional Pharma CardsBrilie Karl Viray100% (1)
- PhenytoinDocument6 pagesPhenytoinapi-3797941100% (1)
- Ketorolac TromethamineDocument4 pagesKetorolac TromethamineSebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- WEEK2 Course Task (ALFEREZ, DINIELA)Document4 pagesWEEK2 Course Task (ALFEREZ, DINIELA)DINIELA ALLAINE ALFEREZNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyKaloy AnneNo ratings yet
- Medications Sheet PreopDocument37 pagesMedications Sheet Preopapi-503879428No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyMarc AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Session 8Document13 pagesSession 8Elly 94No ratings yet
- EMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyDocument8 pagesEMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyShaine WolfeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocument34 pagesDrug Study On Emergency DrugsMei-mei ZhuangNo ratings yet
- Amphotericin B Deoxycholate (Conventional) - Drug Information - UpToDate-4Document4 pagesAmphotericin B Deoxycholate (Conventional) - Drug Information - UpToDate-4Vh TRNo ratings yet
- Dosage: Route:: Mycobacterium TuberculosisDocument21 pagesDosage: Route:: Mycobacterium TuberculosisLyn ConsingNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studyjanelee2824No ratings yet
- NizoralDocument4 pagesNizoralianecunar100% (2)
- Drug Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDrug Name Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJanry-Mae Escobar TumanengNo ratings yet
- Anti TB DrugsDocument22 pagesAnti TB DrugsIsmael JaaniNo ratings yet
- CeftriaxoneDocument2 pagesCeftriaxoneArianne Rose100% (2)
- Generic: Acetazolamide Brand: DiamoxDocument33 pagesGeneric: Acetazolamide Brand: DiamoxAshley Topp100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMiru มิริวNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardDocument7 pagesPharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardyannahmaeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyRye IbarraNo ratings yet
- EMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyDocument33 pagesEMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyNicole GarciaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 408Document13 pagesDrug Study 408Jheryck SabadaoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studysarah1217No ratings yet
- ClonazepamDocument3 pagesClonazepamapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument6 pagesGeneric NameDibb Fabiania Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug StudyMc Joewell HudencialNo ratings yet
- Pharmaco 1Document10 pagesPharmaco 1Joyce Blancaflor LoganNo ratings yet
- Metoclopromide Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMetoclopromide Drug Studymarklesterdeguzman087No ratings yet
- AlprazolamDocument3 pagesAlprazolamapi-3797941100% (1)
- Pharmacology 1Document54 pagesPharmacology 1Sung Joong RaNo ratings yet
- High Risk DrugsDocument12 pagesHigh Risk Drugsarshiya.manasekiNo ratings yet
- EMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyDocument39 pagesEMERGENCY DRUGS: A Drug StudyJenny Rose GriñoNo ratings yet
- MetronidazoleDocument2 pagesMetronidazolehauteanicoleNo ratings yet
- Phenytoin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPhenytoin Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Amiodarone Hydro ChlorideDocument4 pagesAmiodarone Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Pharma Cards.Document19 pagesPharma Cards.Brent NicholsNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyAldrin Ian Oraza AlpeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NRMFDocument11 pagesDrug Study NRMFKristine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyRoselle SorianoNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman Book ReadingDocument7 pagesRangkuman Book ReadingBlackswannnNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing ManagementDocument3 pagesName of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing Managementjhappo31No ratings yet
- Med Cards Starting With EDocument4 pagesMed Cards Starting With Ebright dayNo ratings yet
- Drugs 3aDocument2 pagesDrugs 3aRowena Rivera CariñoNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- Concise Guide to Clinical Dentistry: Common Prescriptions In Clinical DentistryFrom EverandConcise Guide to Clinical Dentistry: Common Prescriptions In Clinical DentistryNo ratings yet
- Brand NameDocument8 pagesBrand NameChristine Joy CamachoNo ratings yet
- Coarctation of The AortaDocument4 pagesCoarctation of The AortaChristine Joy CamachoNo ratings yet
- KARDEXDocument2 pagesKARDEXChristine Joy Camacho100% (1)
- KARDEXDocument2 pagesKARDEXChristine Joy Camacho100% (1)
- Ahu 01 (STD)Document5 pagesAhu 01 (STD)onspsnonsNo ratings yet
- Mongodb DocsDocument313 pagesMongodb DocsDevendra VermaNo ratings yet
- Task 1 - PCK8Document8 pagesTask 1 - PCK8Andrea SantosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Naming and Drawing of Carboxylic Acids and EsterDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Naming and Drawing of Carboxylic Acids and Esterkartika.pranotoNo ratings yet
- List - Parts of Bahay Na Bato - Filipiniana 101Document7 pagesList - Parts of Bahay Na Bato - Filipiniana 101Eriellynn Liza100% (1)
- NIT Application For Examination and Membership FormDocument1 pageNIT Application For Examination and Membership FormRhea Mae CarantoNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument6 pagesSyllabusMadhu ChauhanNo ratings yet
- TR - 2D Game Art Development NC IIIDocument66 pagesTR - 2D Game Art Development NC IIIfor pokeNo ratings yet
- TechDS DV1800AP-DV28500WPDocument4 pagesTechDS DV1800AP-DV28500WPHendri KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Singles NumericDocument27 pagesSingles Numericestevaocanan85No ratings yet
- CC Pinwheel BWDocument1 pageCC Pinwheel BWTariq ZuhlufNo ratings yet
- BPO - Bank Payment ObligationDocument2 pagesBPO - Bank Payment ObligationshreyaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 9 - ClimateChangeDocument1 pageWorksheet 9 - ClimateChangeVanessa MondejarNo ratings yet
- EMTECH DLP Week3Document5 pagesEMTECH DLP Week3Joanne GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Ib 150 Al2Document16 pagesIb 150 Al2QasimNo ratings yet
- EDUC 3 Module 1-Lesson 1Document12 pagesEDUC 3 Module 1-Lesson 1Ma. Kristel OrbocNo ratings yet
- Generator Manual 1Document392 pagesGenerator Manual 1Gopal Radhakrishnan100% (5)
- CR 48JACPAdrenalmediastinalcystDocument4 pagesCR 48JACPAdrenalmediastinalcystKartik DuttaNo ratings yet
- Hammond TexturesDocument37 pagesHammond TexturesMartin Zegarra100% (3)
- 33 05 13 Manholes and Structures 10Document4 pages33 05 13 Manholes and Structures 10salamNo ratings yet
- SfdfdsDocument4 pagesSfdfdsDominikCampanellaNo ratings yet
- Almario, Rich L. - InvestmentDocument6 pagesAlmario, Rich L. - InvestmentRich Lopez AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Water Flow and Heat Transport Including Icewater Phase Change in Porous Media Numerical Simulation and ApplicationDocument11 pagesWater Flow and Heat Transport Including Icewater Phase Change in Porous Media Numerical Simulation and ApplicationNorick CahyaNo ratings yet
- Oblicon Reviewer Q and ADocument13 pagesOblicon Reviewer Q and ARussel SirotNo ratings yet
- India To Open Up Cowin For The World: PM: Bourses, Top Executives To Pay For Technical GlitchesDocument20 pagesIndia To Open Up Cowin For The World: PM: Bourses, Top Executives To Pay For Technical GlitchesSatish WadawadagiNo ratings yet
- Manual Del Gemcom Surpac - Underground Ring DesignDocument43 pagesManual Del Gemcom Surpac - Underground Ring DesignDavid GarciaNo ratings yet
- SPM Linear LawDocument5 pagesSPM Linear LawNg YieviaNo ratings yet
- Web - DOW Industrial Reaction Engineering Course Flyer PDFDocument1 pageWeb - DOW Industrial Reaction Engineering Course Flyer PDFChintan Milan ShahNo ratings yet
- ECOi SPW-CR485GXH56BDocument10 pagesECOi SPW-CR485GXH56BJesus Raul Murillo EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Inmarsat C System Definition Manula - Google SearchDocument2 pagesInmarsat C System Definition Manula - Google SearchasdfaNo ratings yet