Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cardio Assessment
Cardio Assessment
Uploaded by
MabesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cardio Assessment
Cardio Assessment
Uploaded by
MabesCopyright:
Available Formats
ASSESSMENT OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
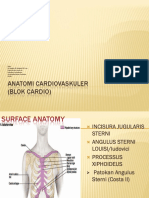
Inspection and Palpation of Pericardium Position: Supine Normal No pulsations, thrills (vibrations), lifts or heaves (similar to wheezing sound) Pulsations are visible to 50% of adults & Palpable at Point of Maximal Impulse or PMI (Apical Pulse in Mitral Area) located at 5th Left ICS medial to MCL Abnormal: Presence of Pulsations
Inspection of Jugular Distention Position: Supine with head of bed elevated at 30 45 degree angle (Semi Fowler) Measure in cm from the level of highest visible point of distention to the level of sternal angle. Normal: No visible veins (indicates normal functioning of right side of the heart) Abnormal: Veins visibly distended (indicates Congestive Heart Failure or CHF)
Auscultation of Heart Sounds Position Supine w/ head of bed elevated in 30 45 degree angle (Semi Fowler) Reassess in upright sitting position (certain sounds are more audible) Use both bell and diaphragm Normal Assessment 1. S1 (Lub) AV valve closes; low pitched, dull sound Best heard with diaphragm over Mitral Area heard 2. S2 (Dub) SV valve closes; high pitched sound shorter than S2 Best heard with diaphragm over Aortic area. 3. S3 (Sounds like Ken tuc ky) Position: Left Lateral / Sims / Semi Prone Extra heart sound after S2 Normal in Children & in Young Adults; Disappears while sitting Abnormal in Adults Best heard with bell over Mitral Area. Abnormal Heart Sound: 4. S4 (Sounds like Ten nes see)
Position: Supine Sign of Hypertension; Common in Older Adults Best heard with bell over Mitral Area.
Grading Heart Murmurs (blowing sound) Use bell w/c is effective for low frequency sounds like heart murmurs 1. Grade 1 barely audible 2. Grade 2 audible but soft and quiet 3. Grade 3 moderately loud, without thrills or thrust 4. Grade 4 loud with thrills 5. Grade 5 very loud with thrills or thrust 6. Grade 6 loud enough to be heard before the stethoscope comes in contact with the chest. Auscultation Tips: When you auscultate a patients heart 1. 2. 3. 4. Concentrate as you listen to each heart sound Dont auscultate through clothing or wound dressing b/c it can block the sound. Keep away the stethoscope tubing from the patients body and other surfaces. Until you became proficient on auscultation and can examine a patient quickly, explain to patient that even though you may listen to his chest for a long period, it doesnt mean something is wrong. 5. Ask the patient to breathe normally and hold his breath periodically to enhance the sound that is difficult to hear. Chronological: 5 Areas for Cardiac Auscultation or Heart Sound Sites 1. Aortic second right interspace close to sternum (second ICS right parasternal) 2. Pulmonic - second left interspace close to sternum (second ICS left parasternal) 3. Erbs Point third left interspace close to sternum; can hear murmurs of aortic and pulmonic area. 4. Tricuspid fourth to fifth left interspace close to sternum 5. Mitral or Apical fifth left interspace medial to midclavicular line (fifth ICS left midclavicular line)
You might also like
- Step2Ck Nbme 8 QuestionsDocument166 pagesStep2Ck Nbme 8 Questionstaha albarghathy100% (1)
- Nervous System Activity SheetDocument3 pagesNervous System Activity SheetTonyC.Reyes100% (3)
- Ekg Plain and Simple 4th Edition Ellis Test BankDocument11 pagesEkg Plain and Simple 4th Edition Ellis Test Bankbrandicarrilloretfdampgw100% (10)
- Medicine Long Cases - DR - PraveenDocument118 pagesMedicine Long Cases - DR - Praveendileepa madurangaNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Thorax and LungsDocument3 pagesAssessing The Thorax and LungsZJ GarcianoNo ratings yet
- Sample Nursing Exams-BudekDocument4 pagesSample Nursing Exams-BudekLj FerolinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 Assessing Children Infancy Through AdolescenceDocument3 pagesChapter 23 Assessing Children Infancy Through AdolescenceAmber Nicole Hubbard100% (1)
- The Endocrine SystemDocument14 pagesThe Endocrine SystemCrisanto Christopher Bidan Sanares100% (3)
- Where Hormone Is Produced Hormone Secreted Chemical Class Target Cell Location Hormone FunctionDocument3 pagesWhere Hormone Is Produced Hormone Secreted Chemical Class Target Cell Location Hormone FunctionRNStudent1100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology-Intestinal ObstructionDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology-Intestinal ObstructionRaisa Robelle Quicho75% (8)
- An Overview Of: Acute Kidney Injury (Aki: Hasan BasriDocument22 pagesAn Overview Of: Acute Kidney Injury (Aki: Hasan BasriDz PutraNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDiaphragm Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Cvsassessmentby 180123144727Document29 pagesCvsassessmentby 180123144727sas100% (1)
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument10 pagesCongenital Heart DiseaseMarisa PetersonNo ratings yet
- History Taking For C-1Document48 pagesHistory Taking For C-1Merahit AberaNo ratings yet
- Konsep Palliative Care Pada AnakDocument48 pagesKonsep Palliative Care Pada AnakDayu Dani100% (1)
- Trauma and OrthopedicsDocument134 pagesTrauma and OrthopedicsAdebisiNo ratings yet
- Mock OSPEDocument34 pagesMock OSPEsahirbuleNo ratings yet
- The Main Applications of The ECG Nursing Lecture NotesDocument19 pagesThe Main Applications of The ECG Nursing Lecture NotesMaria Rowena O. SalvoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examination of The AbdomenDocument13 pagesClinical Examination of The AbdomenNur Miladiyah100% (1)
- GCNM - Lecture 1Document45 pagesGCNM - Lecture 1itsukoNo ratings yet
- Adult Physical AssessmentDocument185 pagesAdult Physical AssessmentD. Melba S.S ChinnaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument45 pagesCongenital Heart DiseaseBrandedlovers OnlineshopNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis - Questions For Step1Document11 pagesCystic Fibrosis - Questions For Step1InnaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Question Acn FinalDocument11 pagesMultiple Choice Question Acn FinalIqra rizwanNo ratings yet
- WEB Intro To Health Assessment - Techniques-General SurveyDocument31 pagesWEB Intro To Health Assessment - Techniques-General SurveyKomal RamzaanNo ratings yet
- CorrectsDocument46 pagesCorrectsnursing_hallNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine Sample Osce Examination Component Questions eDocument2 pagesInternal Medicine Sample Osce Examination Component Questions eGhada ElhassanNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The BloodDocument35 pagesDisorders of The BloodNoor IbrahimNo ratings yet
- BluePrint 5th QuestionsDocument25 pagesBluePrint 5th QuestionsAbuFreihNo ratings yet
- Chapter 39: Nursing Assessment: Gastrointestinal System Test BankDocument6 pagesChapter 39: Nursing Assessment: Gastrointestinal System Test BankNurse UtopiaNo ratings yet
- Case Study #1 ScenarioDocument12 pagesCase Study #1 ScenarioHMG TVNo ratings yet
- MG Test1Document7 pagesMG Test1CherryNo ratings yet
- Post Operative HemorrhageDocument16 pagesPost Operative Hemorrhagenishimura89No ratings yet
- 780 Adult Cardio Resp Assess DSTDocument10 pages780 Adult Cardio Resp Assess DSTGursangeet Kaur100% (1)
- Mock Exam 1 - 25 MCQsDocument4 pagesMock Exam 1 - 25 MCQsIAMSANWAR019170No ratings yet
- Cad PamphletDocument2 pagesCad Pamphletapi-546509005No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Gemst Assessment PabilloreDocument7 pagesLesson 2 Gemst Assessment PabilloreInward Demons CommunityNo ratings yet
- Pedia MCQ 2020Document11 pagesPedia MCQ 2020ANUM NOORINo ratings yet
- ASA ClassificationDocument20 pagesASA ClassificationDeepak SolankiNo ratings yet
- MCQ Mood DisorderDocument26 pagesMCQ Mood DisorderD. W. S Jayarathna100% (1)
- College Final Paper 2-1-2Document6 pagesCollege Final Paper 2-1-2Rita PrinceNo ratings yet
- Bladder DiverticulaDocument23 pagesBladder DiverticulaJeanette CallejasNo ratings yet
- Febrile Convulsions & Epilepsy (L)Document25 pagesFebrile Convulsions & Epilepsy (L)Touseef Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Balance in Clinical PracticeDocument8 pagesFluid Balance in Clinical Practicefernando_vaz2010100% (1)
- Presentation EpilepsyDocument38 pagesPresentation EpilepsypertinenteNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases 1.Kmtc-1Document546 pagesCommunicable Diseases 1.Kmtc-1Mutai KiprotichNo ratings yet
- Final Exam NCM 100Document8 pagesFinal Exam NCM 100Jacq CalaycayNo ratings yet
- Community Diagnosis: Prepared and Comfiled By: Juanaly Almonte-Badiola, RN, ManDocument87 pagesCommunity Diagnosis: Prepared and Comfiled By: Juanaly Almonte-Badiola, RN, Manjuanamay30gmailcomNo ratings yet
- History Taking: DR Anwar H. SiddiquiDocument26 pagesHistory Taking: DR Anwar H. SiddiquiAssad mustafNo ratings yet
- Which of The Following Statements by The Nurse WouldDocument7 pagesWhich of The Following Statements by The Nurse WouldFreeNursingNotesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Practice Questions With Answers: A. B. C. D. EDocument93 pagesPathophysiology Practice Questions With Answers: A. B. C. D. EVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Rationale - Habon, CristineDocument21 pagesRationale - Habon, Cristinecha liNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment: Nursing ProcessDocument7 pagesHealth Assessment: Nursing ProcessAngelrica TumbadoNo ratings yet
- FR Dur I Ski'ta - S: SK Ti 25-f $kifiDocument6 pagesFR Dur I Ski'ta - S: SK Ti 25-f $kifijerayne50% (2)
- Nurses Therapeutic CommunicationDocument11 pagesNurses Therapeutic Communicationsabu0099No ratings yet
- Caring For Children Receiving Chemotherapy, Antimicrobial Therapy and Long-Term Insulin TherapyDocument34 pagesCaring For Children Receiving Chemotherapy, Antimicrobial Therapy and Long-Term Insulin TherapyRubinaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Assessment Quiz QuestionsDocument2 pagesRespiratory System Assessment Quiz QuestionsخالدالقحطانيNo ratings yet
- PBL NCM 112 2nd ROTATIONDocument3 pagesPBL NCM 112 2nd ROTATIONLeanne Princess Gamboa50% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EarDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EarrizzarNo ratings yet
- Section 3. Eye ProblemsDocument5 pagesSection 3. Eye ProblemsAliNo ratings yet
- Section16 - Questions and AnswersDocument62 pagesSection16 - Questions and Answersdivine venturoNo ratings yet
- Assignment On: Transcultural NursingDocument16 pagesAssignment On: Transcultural NursingSuman SambharwalNo ratings yet
- MCQ On NeurologyDocument2 pagesMCQ On NeurologynamsoNo ratings yet
- Care of Terminally IllDocument34 pagesCare of Terminally Illbemina jaNo ratings yet
- Ancc Gerontology Sample QuestionsDocument5 pagesAncc Gerontology Sample QuestionsCARL JOHN MANALONo ratings yet
- Pediatrics Block 2Document207 pagesPediatrics Block 2Ghada ElhassanNo ratings yet
- Asepsis and InfectionDocument6 pagesAsepsis and InfectionMabes100% (1)
- Prof Ad BON and NursesDocument7 pagesProf Ad BON and NursesMabesNo ratings yet
- Enema Administration: Size of Rectal TubeDocument3 pagesEnema Administration: Size of Rectal TubeMabesNo ratings yet
- Commonly Asked Emergency DrugsDocument17 pagesCommonly Asked Emergency DrugsrianneNo ratings yet
- Bowel Diversion: Parameter Colostomy IleostomyDocument1 pageBowel Diversion: Parameter Colostomy IleostomyMabesNo ratings yet
- CHN GapuzDocument23 pagesCHN GapuzMabes100% (1)
- PainDocument3 pagesPainMabesNo ratings yet
- Basic or InstrumentsDocument21 pagesBasic or InstrumentsMabes100% (1)
- Decubitus Ulcer / Pressure SoresDocument1 pageDecubitus Ulcer / Pressure SoresMabesNo ratings yet
- Triage PrinciplesDocument2 pagesTriage PrinciplesMabesNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Purpose: 9. Check Blood For Presence of BubblesDocument2 pagesBlood Transfusion Purpose: 9. Check Blood For Presence of BubblesMabes100% (1)
- Therapeutic Diet NutritionistDocument3 pagesTherapeutic Diet NutritionistMabesNo ratings yet
- Parenteral Therapy:: Intravenous Therapy (IVT) or VenipunctureDocument3 pagesParenteral Therapy:: Intravenous Therapy (IVT) or VenipunctureMabes100% (1)
- PositioningDocument3 pagesPositioningMabesNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesNervous SystemMabesNo ratings yet
- Taste and SmellDocument1 pageTaste and SmellMabesNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Recommendation For Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument5 pagesNutritional Recommendation For Cardiovascular DiseaseMabesNo ratings yet
- All Nursing TheoriesDocument26 pagesAll Nursing TheoriesMabesNo ratings yet
- Mabes Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesDocument15 pagesMabes Fluid and Electrolyte ImbalancesMabesNo ratings yet
- Suture and NeedlesDocument5 pagesSuture and NeedlesMabesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nursing TheoriesDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Nursing TheoriesMabes100% (2)
- Roses Are Red, Violets Are Blue, Without Your Lungs Your Blood Would Be, Too.Document249 pagesRoses Are Red, Violets Are Blue, Without Your Lungs Your Blood Would Be, Too.MabesNo ratings yet
- Fat Soluble VitaminsDocument5 pagesFat Soluble VitaminsMabesNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy Summary of BookDocument17 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy Summary of BookMabes100% (2)
- Water Soluble VitaminsDocument6 pagesWater Soluble VitaminsMabesNo ratings yet
- Basic Therapeutic DietsDocument3 pagesBasic Therapeutic DietsMabes100% (1)
- Factors That Affect Eating and NurtritureDocument3 pagesFactors That Affect Eating and NurtritureMabesNo ratings yet
- The Concepts of Man and His Basic NeedsDocument5 pagesThe Concepts of Man and His Basic NeedsMabes94% (17)
- Anatomi Kardio PDFDocument49 pagesAnatomi Kardio PDFDestrini Anjani LandaNo ratings yet
- Digistive Detailed Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesDigistive Detailed Lesson PlanMark Anthony Telan Pitogo100% (2)
- Kel 8 Biology AvesDocument47 pagesKel 8 Biology AvesAbdu RohmanNo ratings yet
- Liver Stagnation Self Assessment and TrainingDocument3 pagesLiver Stagnation Self Assessment and TrainingEliosNo ratings yet
- IABP Learning PackageDocument35 pagesIABP Learning Packagekingjoon 78100% (1)
- Kidney Problems and DialysisDocument3 pagesKidney Problems and DialysismarymakinNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument11 pagesAcute Kidney InjuryKaren b.No ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument3 pagesHuman AnatomyManjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Departemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraDocument23 pagesDepartemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraLoshseniNo ratings yet
- Acute Cardiac EKG Interpretation - Basics Part 1 - ScriptDocument2 pagesAcute Cardiac EKG Interpretation - Basics Part 1 - ScriptDarby GravinoNo ratings yet
- Histology of Synapse and Neuroglia by Dr. RoomiDocument18 pagesHistology of Synapse and Neuroglia by Dr. RoomiMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- MCN Introduction :physiologic Changes in Pregnancy..Document14 pagesMCN Introduction :physiologic Changes in Pregnancy..janet_alexisNo ratings yet
- Fibrocystic Breast Disease: Fatima Jaina H. Sala Cmz-Ward ADocument24 pagesFibrocystic Breast Disease: Fatima Jaina H. Sala Cmz-Ward AJai SalaNo ratings yet
- FULL Download Ebook PDF Human Anatomy 6th Edition by Kenneth Saladin PDF EbookDocument41 pagesFULL Download Ebook PDF Human Anatomy 6th Edition by Kenneth Saladin PDF Ebookdaniel.welton458100% (45)
- Ncert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 10Document10 pagesNcert Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 10JollyNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Kelainan PayudaraDocument44 pagesKuliah Kelainan PayudaradewiswahyuNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument18 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseAde Cahyo IslamiNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Muscle PhysiologyDocument4 pagesCardiac Muscle PhysiologyRenatoCosmeGalvanJuniorNo ratings yet
- The Pathology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument4 pagesThe Pathology of Congestive Heart FailureMar Ble50% (2)
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Bobby Laksana D Putri Priela Pembimbing: Dr. Nursamsu, SPPDDocument30 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: Bobby Laksana D Putri Priela Pembimbing: Dr. Nursamsu, SPPDfrostedsurgeonNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Lab Report General IntroductoryDocument5 pagesIntegumentary System Lab Report General Introductoryapi-296590891No ratings yet
- Systems 1 Test 4Document59 pagesSystems 1 Test 4bjpalmer100% (2)
- Acute Renal FailureDocument59 pagesAcute Renal Failurepaul_v_44440% (1)