Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inventor 3
Inventor 3
Uploaded by
Mai Van DongCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Engineering Graphics Essentials by Kirstie PlantenbergDocument627 pagesEngineering Graphics Essentials by Kirstie PlantenbergDo Thi My LeNo ratings yet
- HB 3-1996 Electrical and Electronic Drawing Practice For StudentsDocument8 pagesHB 3-1996 Electrical and Electronic Drawing Practice For StudentsSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Designing A StaplerDocument41 pagesDesigning A StaplerEmmanuel Morales ChilacaNo ratings yet
- ME6261-Computer Aided Drafting and Modeling Lab PDFDocument64 pagesME6261-Computer Aided Drafting and Modeling Lab PDFRamesh Jangala100% (1)
- Id Desing With SolidworksDocument27 pagesId Desing With SolidworksLeonard ReinaNo ratings yet
- CATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part II: Part ModelingFrom EverandCATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part II: Part ModelingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Essay of Engineering Design and Graphics With Solidworks 2016Document4 pagesEssay of Engineering Design and Graphics With Solidworks 2016Manuel SanchezNo ratings yet
- Modul SW EnglishDocument15 pagesModul SW EnglishrezaardNo ratings yet
- Highway Design With Civil 3DDocument36 pagesHighway Design With Civil 3DJeewana Meegahage100% (1)
- Acad and Solid WorksDocument18 pagesAcad and Solid Worksapi-3748063100% (3)
- Beginner'S Guide To Solidworks 2007: Alejandro Reyes, MsmeDocument46 pagesBeginner'S Guide To Solidworks 2007: Alejandro Reyes, MsmenaimakrukNo ratings yet
- Autodesk Inventor® Part Modeling: The First Step (Part 1)Document8 pagesAutodesk Inventor® Part Modeling: The First Step (Part 1)avgpaulNo ratings yet
- Ucf - Solidworks IIIDocument60 pagesUcf - Solidworks IIIameg15100% (1)
- Mouldexercises Parting Slider CATIADocument5 pagesMouldexercises Parting Slider CATIASri Navin100% (1)
- Solidworks Teacher Guide Lesson6: School'S Name Teacher'S Name DateDocument56 pagesSolidworks Teacher Guide Lesson6: School'S Name Teacher'S Name DateRafael Diaz RomeroNo ratings yet
- Detailed Intro To 3D Designing On SolidworksDocument24 pagesDetailed Intro To 3D Designing On SolidworksAbdullah Basit24No ratings yet
- Solidworks Drawing TutorialDocument4 pagesSolidworks Drawing TutorialMarco Alonzo Rodriguez MallquiNo ratings yet
- 7 Shades of ArtDocument40 pages7 Shades of ArtsamiNo ratings yet
- Cad Cam Practical Record BookDocument125 pagesCad Cam Practical Record BookAKASHNo ratings yet
- Solidworks 2011 Tutorial PDFDocument63 pagesSolidworks 2011 Tutorial PDFSatya Behera100% (1)
- Introduction To The Freestyle Surface Modeling ProcessDocument30 pagesIntroduction To The Freestyle Surface Modeling ProcessEmmanuel Morales Chilaca100% (1)
- Drafting FundamentalsDocument828 pagesDrafting FundamentalsArun KumarNo ratings yet
- 5 5 A B CadmodelfeaturesDocument12 pages5 5 A B Cadmodelfeaturesapi-312626334No ratings yet
- InventorDocument103 pagesInventorbashone60% (5)
- Drafting Projects: Estimated Time To Complete This Course: 1 - 2 HoursDocument33 pagesDrafting Projects: Estimated Time To Complete This Course: 1 - 2 HoursseventhhemanthNo ratings yet
- By: Dr. S. SumathiDocument36 pagesBy: Dr. S. SumathiTko Kai OnnNo ratings yet
- Fusion 360 FundamentalsDocument10 pagesFusion 360 FundamentalsHossein NajafzadehNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing - BasicsDocument38 pagesTechnical Drawing - Basicsbasarica100% (2)
- Design Academy Razor ProjectDocument9 pagesDesign Academy Razor ProjectRodolfo GarciaNo ratings yet
- AutoCad Tutorial LayoutsDocument6 pagesAutoCad Tutorial LayoutsLarry9302No ratings yet
- 978 1 58503 656 1 3Document65 pages978 1 58503 656 1 3Milorad1583% (6)
- ProE Surfacing - Module 1Document52 pagesProE Surfacing - Module 1inthemoney8100% (1)
- Commands Guide Tutorial For Solidworks 2012: A Comprehensive Reference Guide With Over 240 TutorialsDocument64 pagesCommands Guide Tutorial For Solidworks 2012: A Comprehensive Reference Guide With Over 240 TutorialsKamel FedaouiNo ratings yet
- Ornamental Pro BasicsDocument18 pagesOrnamental Pro BasicsSpitfire51No ratings yet
- Feature Based ModelingDocument10 pagesFeature Based ModelingamirNo ratings yet
- AUTOCAD 2012: Productivity ToolDocument20 pagesAUTOCAD 2012: Productivity ToolBala SaiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document38 pagesLesson 2Ankit NehraNo ratings yet
- Drawing Tutorial 1 PDFDocument15 pagesDrawing Tutorial 1 PDFJustin MillerNo ratings yet
- Googles Sketchup 8Document26 pagesGoogles Sketchup 8Varun Siddha100% (2)
- Solidworks TutorialDocument52 pagesSolidworks TutorialAMar Ridhwan100% (1)
- Solidworks Teacher Guide Lesson 10: School'S Name Teacher'S Name DateDocument27 pagesSolidworks Teacher Guide Lesson 10: School'S Name Teacher'S Name DateRafael Diaz RomeroNo ratings yet
- Study Unit 2Document8 pagesStudy Unit 2Juandre Van EedenNo ratings yet
- TolerancijeDocument46 pagesTolerancijeNenad FemicNo ratings yet
- Abe 201Document2 pagesAbe 201RechelleNo ratings yet
- Proe TutorialDocument15 pagesProe TutorialRajumhaveri HaveriNo ratings yet
- Licao LoftsDocument16 pagesLicao Loftsrcaleta100% (1)
- Solidworks Lesson 6 - Assembly & Part Drawings: UCF EngineeringDocument31 pagesSolidworks Lesson 6 - Assembly & Part Drawings: UCF EngineeringAriantoNo ratings yet
- Autocad Interview EvaluationDocument23 pagesAutocad Interview EvaluationmarklesterNo ratings yet
- Lab 10Document5 pagesLab 10darakhshan.mujtaba06No ratings yet
- CAD Module-4Document30 pagesCAD Module-4Mark JosephNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Drawing Editing ToolsDocument18 pagesLecture 5: Drawing Editing ToolsroseNo ratings yet
- Layout: Model Space and Paper SpaceDocument4 pagesLayout: Model Space and Paper SpaceybouriniNo ratings yet
- Commands Guide Tutorial For Solidworks 2013: A Comprehensive Reference Guide With Over 240 TutorialsDocument69 pagesCommands Guide Tutorial For Solidworks 2013: A Comprehensive Reference Guide With Over 240 Tutorialskishor mNo ratings yet
- NX 9 for Beginners - Part 2 (Extrude and Revolve Features, Placed Features, and Patterned Geometry)From EverandNX 9 for Beginners - Part 2 (Extrude and Revolve Features, Placed Features, and Patterned Geometry)No ratings yet
- Autodesk Inventor 2019 For Beginners - Part 1 (Part Modeling)From EverandAutodesk Inventor 2019 For Beginners - Part 1 (Part Modeling)No ratings yet
- CBLM - Isometric DrawingDocument15 pagesCBLM - Isometric DrawingGlenn F. Salandanan100% (6)
- TD Third Term Ss2 Lesson NotesDocument23 pagesTD Third Term Ss2 Lesson NotesColeman GodsealNo ratings yet
- Medha Institute of Science&TechnologyDocument10 pagesMedha Institute of Science&TechnologyRama PrasadNo ratings yet
- Engineering DrawingDocument7 pagesEngineering DrawingNagulan VegneswaranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Isometric DrawingDocument14 pagesChapter 4 - Isometric DrawingMirul AkiaNo ratings yet
- ISOMETRICDocument39 pagesISOMETRICKaustubh MallikNo ratings yet
- Isometric ProjectionsDocument22 pagesIsometric ProjectionsSakshiNo ratings yet
- How To Take Care of Drafting ToolsDocument25 pagesHow To Take Care of Drafting Toolsmaureen mae mana-ayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Isometric and ObliqueDocument28 pagesChapter 4: Isometric and Obliquehisham_eyesNo ratings yet
- Front: 1. Front View 2. Top View 3. Right Side View 4. Dimensions 5. Isometric SketchDocument4 pagesFront: 1. Front View 2. Top View 3. Right Side View 4. Dimensions 5. Isometric SketchAhmed Sheick SaladNo ratings yet
- Gcse Exam Questions On Plans and ElevationsDocument6 pagesGcse Exam Questions On Plans and ElevationsMarzila MohamedNo ratings yet
- RTU Solution 5CS4-04 Computer Graphics & MultimediaDocument43 pagesRTU Solution 5CS4-04 Computer Graphics & MultimediaShrinath TailorNo ratings yet
- drwing-IIT Que-1 PDFDocument14 pagesdrwing-IIT Que-1 PDFNur Alam100% (1)
- Introduction To Isometric DrawingsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Isometric Drawingsjacqueline trejoNo ratings yet
- Activity 3.2 H Unit Conversion Homework AnswersDocument6 pagesActivity 3.2 H Unit Conversion Homework Answersafeueffmk100% (1)
- ND Mech Eng TechDocument183 pagesND Mech Eng TechShamsudeen Abubakar SodangiNo ratings yet
- Caed QB1Document11 pagesCaed QB1nandukushi100% (1)
- Piping Coordination Systems - Piping Isometrics, Isometric Views and Orthographic ViewsDocument6 pagesPiping Coordination Systems - Piping Isometrics, Isometric Views and Orthographic Viewsjpeg144No ratings yet
- Caed 14Document5 pagesCaed 14SameerAhsanNo ratings yet
- TD Third Term SS 1 Lesson NotesDocument15 pagesTD Third Term SS 1 Lesson NotesTriple Jay COCNo ratings yet
- Visualization and Design: Engineering Graphics Stephen W. Crown PH.DDocument17 pagesVisualization and Design: Engineering Graphics Stephen W. Crown PH.DAdhi ThyanNo ratings yet
- 6 2.1.A.AK IsometricSketchingAnswerKeyDocument6 pages6 2.1.A.AK IsometricSketchingAnswerKeyhagathaNo ratings yet
- 3D ProjectionDocument35 pages3D ProjectionjayNo ratings yet
- Unit V-Isometric Projection and Perspective ViewDocument15 pagesUnit V-Isometric Projection and Perspective ViewVenkatesh Mohan100% (1)
- Draughtsman Mechanical 1st Year (Volume I of II) TPDocument246 pagesDraughtsman Mechanical 1st Year (Volume I of II) TPAkshay Kumar KNo ratings yet
- CDT: Design and CommunicationDocument7 pagesCDT: Design and CommunicationLavanya GoleNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD Plant 3D - 07 IsomDocument20 pagesAutoCAD Plant 3D - 07 IsomAlberto CarrizoNo ratings yet
- IsometricDocument3 pagesIsometrickumar0% (1)
Inventor 3
Inventor 3
Uploaded by
Mai Van DongOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Inventor 3
Inventor 3
Uploaded by
Mai Van DongCopyright:
Available Formats
1
PLTW Introduction to Engineering Design Notes
Brad Hill Instructor Severna Park Senior High 60 Robinson Rd, Severna Park, MD 21146 STI University of Colorado at Colorado Springs 2005 Institutors - Dr. Peter Gorder - UCCS Deborah Elliott - Scripps Ranch High School
Editor and Contributors Herman Singh Brad Jewell Diego Solano Andrew Bork
March 16, 2006
Project Lead the Way
Curriculum CD v6.0, 2005
(Uses some power points)
Table of Contents
1. Cover Sheet and Credits 2. Table of Contents 3. Notes on the Design Process 4. Notes on the Design Process Continued 5. Notes on AutoDesk Inventor 6. Types of Sketches 7. Puzzle Outline 8. Inventor Vocabulary/Notes 9. Puzzle Instructions and Views 10. Unconsumed Sketches Assembly and Constraints 11. Custom Templates 12. Title Block, Tools and Grid 13. Assembly Animation Notes 14. Orthographic Projection 15. Balloons 16. Drilled Holes 17. Editing Text and Assembly 18. Assembly Animation Instructions 19. Notes on Curved Lines 20. Coils, Lines, and Holes Instructions 21. Hole Callout Assignment 22. Twists and Blending Shapes Instructions 23. Physical Properties of a Part
1. Intro To Design
Brainstorming Generate Ideas No Bad Ideas Set up questions and parameters before you start brainstorming Have a monitor to keep the group on task Can do it individually on paper Brainstorm 1. Focus on problem 2. Moderation 3. Communicate -Written -Pictures -Spoken Word Design Process- 5 Simple Steps Design is solving of a specific problem Not a random process Incorporates a logical sequence of steps 1. Identify The Problem- Who does it affect Self Others 2. Plan Project- Determine the Layout Resources Schedule Direction 3. Problem Specifications Verify the exact problem Dont add unneeded items Is money something that is of importance (Does the design require extra cost due to complexity?) DO NOT PREDETERMINE THE SOLUTION 4. Conceptual Design Concept Generation- Brainstorm and research possible solutions Concept Evaluation- Look at all the possibilities and take components of those possible Use design selection matrix to compare 2-4 designs Use one as a datum and compare the rest to it Give + or for each area then take the best and use as your datum and repeat again and again until only one is left 5. Final Design
4 Engineering Analysis- stress analysis /analytical software (Use analytical tools before you build) Prototype Testing- need to build to test functionality of design in an Engineering Analysis Design Refinement Final Testing Documentation- What gets developed for the consumer -Drawings Presentation that includes data, testing results, and maintenance manuals -Justify that your solution is the best
AutoDesk 3D Inventor Notes
Cartesian Coordinates X Y Z Orthogonal- Perpendicular to each other
Polar Coordinates
r2=x2+y2 tangent ? = y/x
Cylindrical Coordinates Polar coordinates with the distance of the z axis (depth). Absolute Coordinates Coordinates that start from an established origin (0,0).
Relative Coordinates Coordinates that start from a designated point Spherical Coordinates Coordinates that contain two angles and one distant
Sketching
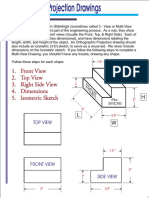
Orthographic Orthogonal Projections
Orthographic Principal Views
Note how the views are oriented. Each view is adjacent to the other as if they were unfolded from a 3D shape.
Front, Top and Right views are used most often. You can see how other views resemble these three except they are not as clear due to hidden lines.
Click to go back to ISO view.
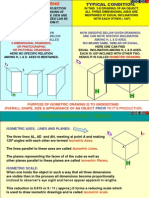
ISO
Oblique
Isometric
Oblique
Proposed Notebook Sample
Width lines are parallel with the horizon. In Cabinet Oblique depth is half size. This allows the view to look more realistic.
Shows design details Size requirements.
Title
Front view is true size and shape.
Initialed and dated.
Perspectives
Two Point Perspective
In two point perspective the depth lines converge on one vanishing point (VP2) and the width lines converge on the other vanishing point (VP1).
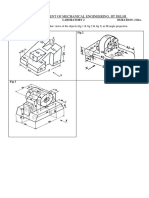
Puzzle
6 Puzzle Pieces 2 Solutions
Isos and CAD Both
Orthos and CAD Both
Exploded ISO Assembly 1 Puzzle Dimension Orthos 1 Puzzle Assembled ISO 1 Puzzle
Inventor
Browse Bar- Tracks everything youve done
Panel Bar-
Most Parts standard
.ipt (Inventor Pact File) For Parts .iam (Assembly) .ipm (Presentation) For Animation .idw (Drawing Orthographic)
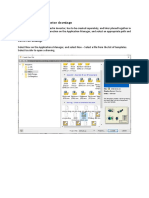
New Project with multiple parts- Start a new project Every new project needs a folder!!!!!!!!!!!!! Open
9 Click New Puzzle Project Name Puzzle Cube Designate File Location- Add name at the end of the file Puzzle Cube Finish Naming and click Done Hold Wheel and pull (0,0) to bottom left on pan tool Minor Grid- 1/8 Major Grid- 1 Right Click Isometric (Do NOT Click 3D Editor) Look At Button (Opening Book) Rotate Tool Space Bar allows you to toggle to common view or Right Click
To reset the isometric view, right click while in the common view rotate tool, and click redefine isometric.
10
Unconsumed Sketches Any sketch that is in purple is not a consumed sketch, meaning it has not been used up by an extrusion, hole, etc. These sketches must be deleted. To delete, go into the browser bar, select the sketch and delete it. Assembly Standard iam 1. Place Component 2. Click and use 3. Use rotate to get orientation close then space for common view to click nose on arrow to provide the isometric view 4. Place the component and all other pieces 5. Rotate component close to its desired position Constraints Contain starting points 1st part surface 2nd part surface Use mate and finish to assemble parts *You can edit parts using the browser bar (Model)
11
Custom Templates
Standard idw To add automatic name- Left Box- Type Properties Browser Sheet 1 Right Click Editor Sheet- Select ANSI A- then ok Delete ANSI Large and delete default boarder To get to default border- right click and insert new border. Right click title block and define as new Draw title block- then right click and save as Browser- select new title block File save C- Program files Autodesk Inventor 10 Completers- Give it a name and save To change open browser and select edit definition After the SPHS template is opened- bring in all of your views. When prompted for text- make a text box Type- PROMPT ENTRY To Edit Title Block -Browser Sheet 1 or Appropriate Sheet Expand Title Block Field Text Edit Field Text
Bring in projected view and arrange right top isometric- right click create Panel Bar change drawing view panel to drawing animation
12 Part 2 NEW SPHS Title Block Enter Info Preview and select direction Projected View Top Right Isometric Right Click Create Drawing View Panel To Drawing Animation Select Isometric- Right click Then edit view Style- Shade
Parts Sketch
Tools- Document Settings
Sketch -change grid minor line 8 for 1/8 4 for
Tools
Application Options Colors recommended depending on presentation or presenter Display- take off edge display to eliminate lines on round objects Then swap to Grid Right click done Right click snap to grid
13
Assembly Animation
Standard .ipn- Create View (from Assembly) Open and tweak components Move components to finish and hit close to move to next piece Animation Intervals of 15 are good Play to see if it is good Edit if needed Record- save- ok- ok- record button- play When finished take off record and import into power point Plane of Origin Default is XY Strategize How You Are Going To Draw You are going to be adding and subtracting material Think about how to orient your drawing
Lofting
Sketch 1st face to be lofted; Finish Sketch Add a new work plane and move it back to sketch 2nd face; Finish Sketch (Make sure that each face is closed, otherwise the loft will not work properly) Select Loft from part features Click Sketch 1 from model Click Sketch 2 and click Ok Should pick up intro Select remove then ok
14
Orthographic
Center lines- Drawing animation Center Mark Center Bisector Center Platter Shade isometric in orthographic by selecting view (red marching ants) Right Click Edit View Shade Icon (Yellow Barrel)
Work Axis Part Feature Work Axis Select Sketch- Model Expand Origin and Select YZ Right Click Slice Graphic Sketch Panel and Project Geometry to show edges
15 Balloons (Puzzle Project) New SPHS .IDW
Fill in information- Base View Open Puzzle Open IPN Select View- Red Marching Ants -Right Click -Edit View If to big select view again Edit View and Scale To Size Then Drawing Animation Select Balloon -Select part and right click on an edge (Dont hide arrow on surface) Dialogue Box is OK- Left Click- Right Click- Continue Parts List -Drawing Annotation -Parts list- OK Double Click on List to EDIT Move color to description
16
Drilled Holes
1. Make a center point in sketch mode 2. Select hole in Part Feature Keyways 1. Complete Hole 2. Draw Rectangle Any Size 3. Dim To Correct Size 4. Right Click- Done 5. Right Click- Constraints 6. Select Coincident 7. Click Circle- Click Corner Of Rectangle 8. Click Circle- Click Other Corner
Share Sketch- Allows you to do more than 1 extrusion 1. To eliminate Dimension in isometric right click on sketch in model and click off visibility 2. In model select the extrude and expand 3. Select sketch- Right Click and shape Sections Drawing View Panel Section View 1. Click on view and get solid red box 2. Click to section points at solid red line 3. Right click continue 4. Place Section View
Note: You can select centers and midpoints by moving the cursor in the general area
17 Editing Text Symbols Such As Depth Select the text, dimension estimate to edit Right click symbols are right side Assembly iam Open- Part Orient the isometric how you want to make true isometric in common view. Right click redefine isometric Rotate component is needed To do centers click an edge of one hole and move other part to use its hole with vertical line. You can also move components without changing constraints by selecting move component Inserting pins in holes- Select constraints and insert icon Inserting Pins 1. Applying insert constraint you need to have face of head pin highlighted as wide as the face 2. Flip icon in constraint allows you to reverse direction of component 3. May constrain work axis and work planes
18 To Animate an Object - Drive Constraints Complete ipts for Air Compressor Complete iam assembly -Select Flywheel -Place Work Plane -XZ or YZ -Bring it close to center -Select constraints- Angles -Select work plane- Select base and apply -Right Click in model (browser) -Find the work plane and right click and turn off visibility -Model Browser- Select angle and right click -Drive constraint and fill in end degrees (change increments) Applying Drive Constraints Used for such things such as gears Activate the assembly panel Go to the angle in the Model -Right Click drive constraint To see if tools activate contact solver -Hover over gear (make real) -Right Click and make sure the contrast is set
19 Curved Lines In A Sketch Spline- In line fly out -Right click done- click on mode and you can move Polygon Tool- Just like in turbo CAD but you can pick the corner or the middle of the line. -You can also constrain with constrain fly out just below locate. Shell- Tool hollows out extruded object Work Plane- Under Parts feature -You can select an existing plane Ribs- Inside hallow object -Draw a line at the angle designated for a rib Sweep- Draw something circular and will finish sketch -Draw a path (starting from the center point of circle) perpendicular to circle and trim the excess -Under parts feature- Sweep
20 Coil Select new IPT -Vertical line is Radius
Axis Line
-Finish sketch Coil -Select axis -Select direction -Coil eye tab -Pitch -Revolutions -OK- Finish
Changing Hidden Lines And Center Lines -Can stretch by click and pull -Can change scale by selecting and right clicking Rectangular Pattern Select geometry (hole, cube) Direction- Click on edge of object and turn geometry on. Hole Threads -On drawing annotation panel Scale -Right Click on drawing surface -Edit drawing and change scale Precision Inputs Utilizes the X, Y, and Z-axes. -View- Toolbar- Precise Input
21 Hole Callout Assignment 1.Draw 2.Holes on separate sketch 3.Section
4.Hole Table a. Drawing Annotation b. Down to hole table- hole table view c. Click at the corner of the first hole d. Place Table
5.Make Threads in HOLE TOOL NOT USING THE THREAD TOOL!!!
22
Blending 2 Shapes
-Draw Shape and Extrude -Insert Work Plane -Offset Work Plane -Draw Another Shape And Extrude -Select Loft -Select At Face- Done
Twists
Open .ipt Draw a shape Finish Sketch Go into Origin, apply visibility to XY Plane Go to Isometric view Use New Work Plane feature to offset the XY plane (makes Work Plane 1) 7. On new work plane, draw same shape, only angled 45 8. Finish Sketch 9. Offset Work Plane 1 to make Work Plane 2 (continue in same direction as before) 10. Draw same shape, again angled 45 from the previous sketch 11. Finish Sketch 12. Go to Isometric View 13. Begin new 3D Sketch 14. Use the Spline tool (flyout of Line) to connect corresponding points starting from the farthest sketch (Origin Work Plane) to the middle (Work Plane 1) and finally Work Plane 3. 15. Use Loft feature to select first the sketch of Origin Work Plane, then Work Plane 1, finally Work Plane 2 (MUST be done in order). Then select the rails that were created in the 3D Sketch. 16. Finish Loft. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
23
How to Use the Coil Feature
By: Ryan Janes & Shawn Laser
24 How to Use the Coil Feature
The coil feature is a very easy feature to use once you understand the process but it can also create some of the most impressive designs. For example, this piece only took about 2 minutes. How to Make This 1. First begin by making a simple cylinder with the extrusion or revolution feature. The size does not matter as long as you begin with a cylinder.
25 2. In the Model Tool Bar, select the pending axis. The correct axis will demonstrate a vertical slice your cylinder. -Revolution: XY Axis -Extrusion: YZ Axis Right click and select New Sketch and you will see your plane cutting the cylinder.
3. Now that you plane has divided your cylinder, the Sketch (#) is highlighted. Right click the Sketch (#) and select Slice Graphics (F7).
After selecting the Slice Graphic Feature, Your sketch plane will be working on the divided section of your cylinder drawing.
26
4. Next create a square shape in the upper left corner as shown here. This is the only part that involves creativity as it will generate the shape of the thread. 5. For now, were using this shape because it is a simple. Later when you better understand the process, you may wish to complicate the thread. I used a different sketch to imitate an auger bit.
27 This is my sketch.
6. Exit sketch mode and select the Coil feature. Next select the axis that generates the centerline of your cylinder. 7. Using the various attributes available to you, you can create different pitches and sizes that can make your coil more appealing.
28 Stress Analysis on Autodesk Inventor 11 By Andrew Bork 1. To start, make a simple 1 square cube
2. Then Click on the Part Features toolbar and click on the dropdown menu to change it to Stress Analysis
3. A popup menu will appear. Chose your specified material. The rest of this tutorial will use ABS Plastic. 4. Click on the force button in the new panel. 5. Now click on the cube where you would like the force applied. 6. The amount of force applied is represented by the number in the white box. You can change it to however much you want. 7. Without constraints all the force would do is push the block in the specified direction. Click on the fixed constraint button and click on any face or edge except the one you applied the force to. You can constraint multiple faces or edges to see different results. 8. now click on the stress analysis update button
29 9. you should see something like this
10. The gray outline represents the former position and the colored section represents the deformation based on the force applied and the constraints. I applied a 100lb force to the top and constrained the opposite face so that the block was compressed. 11. If you change the amount of force and it looks like the same picture, click on the Deformation Style button on the toolbar and make sure the scale is set to Actual
30
Physical Properties Of a Part
Use for Sports Bottle - volume File- Properties- Physical Properties Cones/ Bottles Etc. -Make a bottle using a shell -Draw half of the cone and add center line -Revolve the cone Screws Content Counter- Categories
You might also like
- Engineering Graphics Essentials by Kirstie PlantenbergDocument627 pagesEngineering Graphics Essentials by Kirstie PlantenbergDo Thi My LeNo ratings yet
- HB 3-1996 Electrical and Electronic Drawing Practice For StudentsDocument8 pagesHB 3-1996 Electrical and Electronic Drawing Practice For StudentsSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Designing A StaplerDocument41 pagesDesigning A StaplerEmmanuel Morales ChilacaNo ratings yet
- ME6261-Computer Aided Drafting and Modeling Lab PDFDocument64 pagesME6261-Computer Aided Drafting and Modeling Lab PDFRamesh Jangala100% (1)
- Id Desing With SolidworksDocument27 pagesId Desing With SolidworksLeonard ReinaNo ratings yet
- CATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part II: Part ModelingFrom EverandCATIA V5-6R2015 Basics - Part II: Part ModelingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Essay of Engineering Design and Graphics With Solidworks 2016Document4 pagesEssay of Engineering Design and Graphics With Solidworks 2016Manuel SanchezNo ratings yet
- Modul SW EnglishDocument15 pagesModul SW EnglishrezaardNo ratings yet
- Highway Design With Civil 3DDocument36 pagesHighway Design With Civil 3DJeewana Meegahage100% (1)
- Acad and Solid WorksDocument18 pagesAcad and Solid Worksapi-3748063100% (3)
- Beginner'S Guide To Solidworks 2007: Alejandro Reyes, MsmeDocument46 pagesBeginner'S Guide To Solidworks 2007: Alejandro Reyes, MsmenaimakrukNo ratings yet
- Autodesk Inventor® Part Modeling: The First Step (Part 1)Document8 pagesAutodesk Inventor® Part Modeling: The First Step (Part 1)avgpaulNo ratings yet
- Ucf - Solidworks IIIDocument60 pagesUcf - Solidworks IIIameg15100% (1)
- Mouldexercises Parting Slider CATIADocument5 pagesMouldexercises Parting Slider CATIASri Navin100% (1)
- Solidworks Teacher Guide Lesson6: School'S Name Teacher'S Name DateDocument56 pagesSolidworks Teacher Guide Lesson6: School'S Name Teacher'S Name DateRafael Diaz RomeroNo ratings yet
- Detailed Intro To 3D Designing On SolidworksDocument24 pagesDetailed Intro To 3D Designing On SolidworksAbdullah Basit24No ratings yet
- Solidworks Drawing TutorialDocument4 pagesSolidworks Drawing TutorialMarco Alonzo Rodriguez MallquiNo ratings yet
- 7 Shades of ArtDocument40 pages7 Shades of ArtsamiNo ratings yet
- Cad Cam Practical Record BookDocument125 pagesCad Cam Practical Record BookAKASHNo ratings yet
- Solidworks 2011 Tutorial PDFDocument63 pagesSolidworks 2011 Tutorial PDFSatya Behera100% (1)
- Introduction To The Freestyle Surface Modeling ProcessDocument30 pagesIntroduction To The Freestyle Surface Modeling ProcessEmmanuel Morales Chilaca100% (1)
- Drafting FundamentalsDocument828 pagesDrafting FundamentalsArun KumarNo ratings yet
- 5 5 A B CadmodelfeaturesDocument12 pages5 5 A B Cadmodelfeaturesapi-312626334No ratings yet
- InventorDocument103 pagesInventorbashone60% (5)
- Drafting Projects: Estimated Time To Complete This Course: 1 - 2 HoursDocument33 pagesDrafting Projects: Estimated Time To Complete This Course: 1 - 2 HoursseventhhemanthNo ratings yet
- By: Dr. S. SumathiDocument36 pagesBy: Dr. S. SumathiTko Kai OnnNo ratings yet
- Fusion 360 FundamentalsDocument10 pagesFusion 360 FundamentalsHossein NajafzadehNo ratings yet
- Technical Drawing - BasicsDocument38 pagesTechnical Drawing - Basicsbasarica100% (2)
- Design Academy Razor ProjectDocument9 pagesDesign Academy Razor ProjectRodolfo GarciaNo ratings yet
- AutoCad Tutorial LayoutsDocument6 pagesAutoCad Tutorial LayoutsLarry9302No ratings yet
- 978 1 58503 656 1 3Document65 pages978 1 58503 656 1 3Milorad1583% (6)
- ProE Surfacing - Module 1Document52 pagesProE Surfacing - Module 1inthemoney8100% (1)
- Commands Guide Tutorial For Solidworks 2012: A Comprehensive Reference Guide With Over 240 TutorialsDocument64 pagesCommands Guide Tutorial For Solidworks 2012: A Comprehensive Reference Guide With Over 240 TutorialsKamel FedaouiNo ratings yet
- Ornamental Pro BasicsDocument18 pagesOrnamental Pro BasicsSpitfire51No ratings yet
- Feature Based ModelingDocument10 pagesFeature Based ModelingamirNo ratings yet
- AUTOCAD 2012: Productivity ToolDocument20 pagesAUTOCAD 2012: Productivity ToolBala SaiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document38 pagesLesson 2Ankit NehraNo ratings yet
- Drawing Tutorial 1 PDFDocument15 pagesDrawing Tutorial 1 PDFJustin MillerNo ratings yet
- Googles Sketchup 8Document26 pagesGoogles Sketchup 8Varun Siddha100% (2)
- Solidworks TutorialDocument52 pagesSolidworks TutorialAMar Ridhwan100% (1)
- Solidworks Teacher Guide Lesson 10: School'S Name Teacher'S Name DateDocument27 pagesSolidworks Teacher Guide Lesson 10: School'S Name Teacher'S Name DateRafael Diaz RomeroNo ratings yet
- Study Unit 2Document8 pagesStudy Unit 2Juandre Van EedenNo ratings yet
- TolerancijeDocument46 pagesTolerancijeNenad FemicNo ratings yet
- Abe 201Document2 pagesAbe 201RechelleNo ratings yet
- Proe TutorialDocument15 pagesProe TutorialRajumhaveri HaveriNo ratings yet
- Licao LoftsDocument16 pagesLicao Loftsrcaleta100% (1)
- Solidworks Lesson 6 - Assembly & Part Drawings: UCF EngineeringDocument31 pagesSolidworks Lesson 6 - Assembly & Part Drawings: UCF EngineeringAriantoNo ratings yet
- Autocad Interview EvaluationDocument23 pagesAutocad Interview EvaluationmarklesterNo ratings yet
- Lab 10Document5 pagesLab 10darakhshan.mujtaba06No ratings yet
- CAD Module-4Document30 pagesCAD Module-4Mark JosephNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Drawing Editing ToolsDocument18 pagesLecture 5: Drawing Editing ToolsroseNo ratings yet
- Layout: Model Space and Paper SpaceDocument4 pagesLayout: Model Space and Paper SpaceybouriniNo ratings yet
- Commands Guide Tutorial For Solidworks 2013: A Comprehensive Reference Guide With Over 240 TutorialsDocument69 pagesCommands Guide Tutorial For Solidworks 2013: A Comprehensive Reference Guide With Over 240 Tutorialskishor mNo ratings yet
- NX 9 for Beginners - Part 2 (Extrude and Revolve Features, Placed Features, and Patterned Geometry)From EverandNX 9 for Beginners - Part 2 (Extrude and Revolve Features, Placed Features, and Patterned Geometry)No ratings yet
- Autodesk Inventor 2019 For Beginners - Part 1 (Part Modeling)From EverandAutodesk Inventor 2019 For Beginners - Part 1 (Part Modeling)No ratings yet
- CBLM - Isometric DrawingDocument15 pagesCBLM - Isometric DrawingGlenn F. Salandanan100% (6)
- TD Third Term Ss2 Lesson NotesDocument23 pagesTD Third Term Ss2 Lesson NotesColeman GodsealNo ratings yet
- Medha Institute of Science&TechnologyDocument10 pagesMedha Institute of Science&TechnologyRama PrasadNo ratings yet
- Engineering DrawingDocument7 pagesEngineering DrawingNagulan VegneswaranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Isometric DrawingDocument14 pagesChapter 4 - Isometric DrawingMirul AkiaNo ratings yet
- ISOMETRICDocument39 pagesISOMETRICKaustubh MallikNo ratings yet
- Isometric ProjectionsDocument22 pagesIsometric ProjectionsSakshiNo ratings yet
- How To Take Care of Drafting ToolsDocument25 pagesHow To Take Care of Drafting Toolsmaureen mae mana-ayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Isometric and ObliqueDocument28 pagesChapter 4: Isometric and Obliquehisham_eyesNo ratings yet
- Front: 1. Front View 2. Top View 3. Right Side View 4. Dimensions 5. Isometric SketchDocument4 pagesFront: 1. Front View 2. Top View 3. Right Side View 4. Dimensions 5. Isometric SketchAhmed Sheick SaladNo ratings yet
- Gcse Exam Questions On Plans and ElevationsDocument6 pagesGcse Exam Questions On Plans and ElevationsMarzila MohamedNo ratings yet
- RTU Solution 5CS4-04 Computer Graphics & MultimediaDocument43 pagesRTU Solution 5CS4-04 Computer Graphics & MultimediaShrinath TailorNo ratings yet
- drwing-IIT Que-1 PDFDocument14 pagesdrwing-IIT Que-1 PDFNur Alam100% (1)
- Introduction To Isometric DrawingsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Isometric Drawingsjacqueline trejoNo ratings yet
- Activity 3.2 H Unit Conversion Homework AnswersDocument6 pagesActivity 3.2 H Unit Conversion Homework Answersafeueffmk100% (1)
- ND Mech Eng TechDocument183 pagesND Mech Eng TechShamsudeen Abubakar SodangiNo ratings yet
- Caed QB1Document11 pagesCaed QB1nandukushi100% (1)
- Piping Coordination Systems - Piping Isometrics, Isometric Views and Orthographic ViewsDocument6 pagesPiping Coordination Systems - Piping Isometrics, Isometric Views and Orthographic Viewsjpeg144No ratings yet
- Caed 14Document5 pagesCaed 14SameerAhsanNo ratings yet
- TD Third Term SS 1 Lesson NotesDocument15 pagesTD Third Term SS 1 Lesson NotesTriple Jay COCNo ratings yet
- Visualization and Design: Engineering Graphics Stephen W. Crown PH.DDocument17 pagesVisualization and Design: Engineering Graphics Stephen W. Crown PH.DAdhi ThyanNo ratings yet
- 6 2.1.A.AK IsometricSketchingAnswerKeyDocument6 pages6 2.1.A.AK IsometricSketchingAnswerKeyhagathaNo ratings yet
- 3D ProjectionDocument35 pages3D ProjectionjayNo ratings yet
- Unit V-Isometric Projection and Perspective ViewDocument15 pagesUnit V-Isometric Projection and Perspective ViewVenkatesh Mohan100% (1)
- Draughtsman Mechanical 1st Year (Volume I of II) TPDocument246 pagesDraughtsman Mechanical 1st Year (Volume I of II) TPAkshay Kumar KNo ratings yet
- CDT: Design and CommunicationDocument7 pagesCDT: Design and CommunicationLavanya GoleNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD Plant 3D - 07 IsomDocument20 pagesAutoCAD Plant 3D - 07 IsomAlberto CarrizoNo ratings yet
- IsometricDocument3 pagesIsometrickumar0% (1)