Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Documentation
Documentation
Uploaded by
Eugene Paul Brian SebiloOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Documentation
Documentation
Uploaded by
Eugene Paul Brian SebiloCopyright:
Available Formats
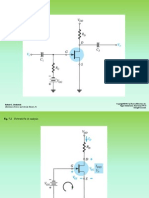
INTRODUCTION In this experiment, we observe how full wave rectifier works specifically, a bridge type full wave rectifier.
We should find out how efficient it is to be used than a half-wave rectifier to the extent that it is used for a large scale voltage regulator. We also observe how a capacitor affects the voltage output of the rectifier and compare the results to the half- wave.
OBJECTIVES 1. Ability to recognise a full wave rectified waveform, with and without a reservoir capacitor. 2. Understand the working of a diode bridge circuit as a full-wave rectifier and its advantage over half-wave rectification. 3. Awareness of the two- diode method of obtaining full- wave rectification.
EQUIPMENT REQUIRED Operating PC (Windows Seven OS) Circuit Simulation Software (Multisim 11.01)
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE Open Multisim Put all required components needed for the experiment Connect the components using wires Put Ground on the Circuit Assign both Voltmeter and Oscilloscope to their instructed position Simulate the circuits Display the results of Voltmeter and Oscilloscope Write the obtained data of the peak voltages on the Oscilloscope by adjusting the T1/T2 button to know the voltage and its corresponding time result Write the mean voltages results displayed by the Voltmeter
Save the results to clipboard using Snip Tool
QUESTIONS 1. Should Vpk be the same as it was for a half- wave rectifier? Does your observation confirm your answer? 2. How does the mean value compare with that found for half wave rectification?
EXPERIMENT IMAGES
OBTAINED DATA AC supply: Load: Vpk = 16.971 V @ 5 ms Vpk = 15.637 V @ 5 ms
ANSWER TO QUESTIONS 1. No, due to the fact that it is a full-wave rectifier, which means that it generated twice the voltage generated in a cycle of the half wave rectifier. It doesnt mean that the voltage peak of the full wave rectifier is higher than of the half- wave rectifier.
2. We can see the significant differences of their mean voltages. Half- wave mean voltage is 5.08 while the full- wave is 9.537, almost as twice as the other.
3. The Effect of a Reservoir Capacitor: Capacitor in 2.2F
Vpk = 15.634 V @ 5.075 ms
Capacitor in 47F
Vpk = 5.559 V @ 5.280 ms
CONCLUSION A full- wave rectifier gives a greater mean value and fewer ripples for a given load and reservoir capacitor than a half- wave rectifier. The effect of the capacitor connected to the full wave rectifier has the same results as the half wave, the higher the value of the capacitor, the lesser the ripples produced.
You might also like
- ISO Hazard Checklist (WW) IDM UpdateDocument6 pagesISO Hazard Checklist (WW) IDM UpdateKelly Lawson100% (1)
- SA 1 - Lab ReportDocument26 pagesSA 1 - Lab ReportLance SobreviñasNo ratings yet
- AHM650 Ground Incident Damage Report Sheet 01-02 PDFDocument4 pagesAHM650 Ground Incident Damage Report Sheet 01-02 PDFNarablues IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- Standard Rating of TransformerDocument12 pagesStandard Rating of TransformerCJP TV100% (1)
- Measurement and Instrumentation Lab 1Document10 pagesMeasurement and Instrumentation Lab 1Mompati Letsweletse100% (1)
- Gas Leakage Alarm With Power Failure SystemDocument64 pagesGas Leakage Alarm With Power Failure Systeminfo8103No ratings yet
- Fig. 7.1 Fixed-Bias Configuration.: Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 9eDocument103 pagesFig. 7.1 Fixed-Bias Configuration.: Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 9eNihala KhalidNo ratings yet
- CHPT 1 - Basic Measurement ConceptDocument73 pagesCHPT 1 - Basic Measurement ConceptSyah ReelNo ratings yet
- Pete CircuitsDocument41 pagesPete CircuitsRome Erwin Manalo FestinNo ratings yet
- Mapúa Institute of Technology: Analysis of Resistive Network: Series-Parallel CircuitsDocument10 pagesMapúa Institute of Technology: Analysis of Resistive Network: Series-Parallel CircuitsJohn FerreNo ratings yet
- Ifi-100-107 1Document58 pagesIfi-100-107 1diegosc2200No ratings yet
- Powering Disney's "Frozen" With A Carnot RefrigeratorDocument3 pagesPowering Disney's "Frozen" With A Carnot RefrigeratorInquit_No ratings yet
- Full Wave Rectification ExperimentDocument6 pagesFull Wave Rectification ExperimentDavid OkoyeNo ratings yet
- Activity 5 SimulinkDocument19 pagesActivity 5 Simulinkjanana marieNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument67 pagesTransformerlallyprabh100% (2)
- Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument53 pagesChapter 1 - Introductionjeff leonenNo ratings yet
- EE303 Exp-5 Group-4Document7 pagesEE303 Exp-5 Group-4Mohammad Mottahir AlamNo ratings yet
- EEA126 - Module 2 - SWsDocument12 pagesEEA126 - Module 2 - SWsGabriel Carl Alpuerto100% (1)
- Static Fluid Pressure and Fluid FlowDocument6 pagesStatic Fluid Pressure and Fluid FlowVivian TranNo ratings yet
- Clipper and Climper Circit PDFDocument6 pagesClipper and Climper Circit PDFOmar Said Abu RabieNo ratings yet
- Familiarization of Electronic Symbol: Experiment No.1Document12 pagesFamiliarization of Electronic Symbol: Experiment No.1ManuelitoBorjaNo ratings yet
- Expt No. 1 Design of Regulated Power SupplyDocument6 pagesExpt No. 1 Design of Regulated Power Supplyrani kumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment V Current Control of An SCR I. ObjectiveDocument4 pagesExperiment V Current Control of An SCR I. ObjectiveDenisse Torizo Olan100% (1)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Oscilloscope and CapacitorDocument2 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Oscilloscope and CapacitorAngelyn Taberna Natividad100% (1)
- Circuits 2 Lab Report No. 5Document4 pagesCircuits 2 Lab Report No. 5Carlo Caniedo80% (5)
- Introduction To Ac Circuits: Sinusoidal Voltages and CurrentsDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Ac Circuits: Sinusoidal Voltages and Currentsczds6594No ratings yet
- Experiment 10: Junction Field Effect Transistor: Operation and Its Characteristic CurveDocument6 pagesExperiment 10: Junction Field Effect Transistor: Operation and Its Characteristic CurveDan Joshua EspinaNo ratings yet
- Experiment#3 Power Factor Improvement ObjectivesDocument8 pagesExperiment#3 Power Factor Improvement ObjectivesAmeer HamzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - Mesh AnalysisDocument21 pagesChapter 03 - Mesh AnalysisHidayah KamaludinNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Series and Parallel Circuits by Praewa 1108 4Document13 pagesLab Report Series and Parallel Circuits by Praewa 1108 4api-439639600No ratings yet
- Activity 3: DC Power Measurements 3.1 Power in A Series Resistive Circuit 3.1.1 Program Outcomes (Pos) Addressed by The ActivityDocument24 pagesActivity 3: DC Power Measurements 3.1 Power in A Series Resistive Circuit 3.1.1 Program Outcomes (Pos) Addressed by The ActivityKrissy Ann Martinez SottoNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument16 pagesElectricityAnonymous 737JUauMzHNo ratings yet
- Case Study 7 Load CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesCase Study 7 Load CharacteristicsMark John ChavezNo ratings yet
- For Reference OnlyDocument2 pagesFor Reference OnlyBenmark Jabay100% (1)
- Assignment No 2 Name: Muhammad Ali Reg Id: 12249 Section: ES Semester: 1 Course: BSSE Subject: Applied Physics Teacher Name: Qazi Haseeb YousufDocument11 pagesAssignment No 2 Name: Muhammad Ali Reg Id: 12249 Section: ES Semester: 1 Course: BSSE Subject: Applied Physics Teacher Name: Qazi Haseeb YousufAli KhanNo ratings yet
- Applications of Dynamics in Automotive EngineeringDocument10 pagesApplications of Dynamics in Automotive EngineeringUmar Ayaz0% (1)
- Section 7: Thyristors and SwitchesDocument18 pagesSection 7: Thyristors and Switcheschrist9088No ratings yet
- CHEM 167 Houk Grantd SI Session 34-4-28-13 AnswersDocument2 pagesCHEM 167 Houk Grantd SI Session 34-4-28-13 AnswersEmman0% (1)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab - Full Wave Rectifier With and Without Filters - Notes - SboDocument6 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Lab - Full Wave Rectifier With and Without Filters - Notes - SboECEOCETNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 2 - Diode Characteristics - Don Bernard D. MijaresDocument14 pagesLaboratory 2 - Diode Characteristics - Don Bernard D. MijaresDon Bernard MijaresNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document6 pagesExperiment 1Jomel JomelNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions of Electric Current and OhmDocument11 pagesMultiple Choice Questions of Electric Current and OhmVanaVihari DasNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 DIRECT - CURRENT INSTRUMENT AND MEASUREMENTSDocument2 pagesExperiment 1 DIRECT - CURRENT INSTRUMENT AND MEASUREMENTSErroll100% (1)
- Source Transformations PDFDocument9 pagesSource Transformations PDFSailokesh NagaruruNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 1Document13 pagesLaboratory 1Rn NatNo ratings yet
- Activity On Semiconductor Diodes PDFDocument7 pagesActivity On Semiconductor Diodes PDFRaymund TanapNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Lake Cleaning Ro-BoatDocument18 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Lake Cleaning Ro-BoatRathan Kumar SMNo ratings yet
- Wave Guids PDFDocument32 pagesWave Guids PDFlakshman donepudiNo ratings yet
- Transmi FinalsDocument2 pagesTransmi FinalsHarold De Chavez0% (1)
- Electronics Module 2Document13 pagesElectronics Module 2tirsollantadaNo ratings yet
- CHAP 3 - Zener DiodeDocument65 pagesCHAP 3 - Zener DiodeAnees Ahmad100% (1)
- Chap 1 - Measurement ErrorDocument8 pagesChap 1 - Measurement ErrorHuan HuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2, TransformerDocument28 pagesChapter 2, Transformertemesgen adugnaNo ratings yet
- Resistors: Fig: 1.1 Colour Coding On ResistorDocument107 pagesResistors: Fig: 1.1 Colour Coding On ResistorRasool ReddyNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Resistive NetworksDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Resistive NetworksNoelJonathanBaclaoNo ratings yet
- EE 179.1 Activity 1Document10 pagesEE 179.1 Activity 1YUUYANo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument12 pagesZener DiodeallyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document31 pagesUnit 1araz_1985No ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics Laboratory Group Iii ECE 4-1Document11 pagesIndustrial Electronics Laboratory Group Iii ECE 4-1MaimaiFabilonaDumalaogNo ratings yet
- Pico Power: A Boon For Rural Electrification: Rajat KapoorDocument8 pagesPico Power: A Boon For Rural Electrification: Rajat KapoorBamNo ratings yet
- What Are The Two Types of BJT Transistor? Draw The Symbol For EachDocument11 pagesWhat Are The Two Types of BJT Transistor? Draw The Symbol For EachJace MacaspacNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectificationDocument6 pagesFull Wave RectificationDavid OkoyeNo ratings yet
- TH Mạch điện 2 - Lab 1 RectifierDocument4 pagesTH Mạch điện 2 - Lab 1 Rectifiertrankhanhhung316No ratings yet
- SG 248055Document566 pagesSG 248055Sofiane HamidNo ratings yet
- Course Outline - Allied and Professional Courses (ME)Document4 pagesCourse Outline - Allied and Professional Courses (ME)zakibrant23No ratings yet
- Activities Section 1 2011 AnswersDocument28 pagesActivities Section 1 2011 Answersgeooorgie b ♥No ratings yet
- 1 Home Base Work March 19-MRCH 31Document3 pages1 Home Base Work March 19-MRCH 31Celso AmotoNo ratings yet
- Map of The GD&T WorldDocument2 pagesMap of The GD&T WorldMariamVTNo ratings yet
- Richard Clem Over-Unity Engine - 1992Document11 pagesRichard Clem Over-Unity Engine - 19921357531100% (1)
- Shipment API en v2Document35 pagesShipment API en v2matejkahuNo ratings yet
- ITEM 700 Latest 2004Document64 pagesITEM 700 Latest 2004Michael John EnfestaNo ratings yet
- Patterns 2 CreationalDocument47 pagesPatterns 2 Creationalapi-26214845No ratings yet
- Acta Materialia: Dirk Herzog, Vanessa Seyda, Eric Wycisk, Claus EmmelmannDocument22 pagesActa Materialia: Dirk Herzog, Vanessa Seyda, Eric Wycisk, Claus EmmelmannKarteek RaghuNo ratings yet
- Dial Indicators and Digital Indicators: Mounting A Dial IndicatorDocument1 pageDial Indicators and Digital Indicators: Mounting A Dial IndicatorozanNo ratings yet
- Configuring A Zone-Based Policy Firewall (ZPF)Document13 pagesConfiguring A Zone-Based Policy Firewall (ZPF)JahazielCruzMonzon100% (1)
- Link Belt Rec Parts LastDocument15 pagesLink Belt Rec Parts LastBishoo ShenoudaNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Vertical Axis Wind TurbineDocument75 pagesImplementation of Vertical Axis Wind TurbineOsama Abd ElkawiNo ratings yet
- Electrical DrawingDocument292 pagesElectrical DrawinginterrogaNo ratings yet
- 15 NeyrpicDocument5 pages15 Neyrpictestem156845No ratings yet
- Buku G.S. Manku Chapter 8Document5 pagesBuku G.S. Manku Chapter 8Taro PurpleNo ratings yet
- Metals Removal From Acid Mine Drainage by Ion Exchange: MEND Report 3.21.1 (B)Document61 pagesMetals Removal From Acid Mine Drainage by Ion Exchange: MEND Report 3.21.1 (B)Gustavo TaquichiriNo ratings yet
- Peugeot Expert Tepee Range BrochureDocument20 pagesPeugeot Expert Tepee Range BrochurepeugeotUKNo ratings yet
- 1 EES Fatigue Testing Machine Is Used For Studying The Effects of Fatigue Using ADocument7 pages1 EES Fatigue Testing Machine Is Used For Studying The Effects of Fatigue Using AFrank.JNo ratings yet
- Info On Axis Energy Nusantara - 2020Document5 pagesInfo On Axis Energy Nusantara - 2020ErwinNo ratings yet
- Mvh-285bt Operating Manual Ing - Esp - PorDocument84 pagesMvh-285bt Operating Manual Ing - Esp - PorBrian Camacho OrtizNo ratings yet
- HRE Prelim FinalsDocument163 pagesHRE Prelim FinalsPatrick PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Section AC - Heater and Air Conditioner NoRestriction (YRV)Document34 pagesSection AC - Heater and Air Conditioner NoRestriction (YRV)rahim ghazaliNo ratings yet
- Edb CDDocument187 pagesEdb CDAnonymous W79EljRNo ratings yet
- Eee2210 Analogue Electronics IIDocument19 pagesEee2210 Analogue Electronics IIembugua426No ratings yet