Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Explanation Text
Explanation Text
Uploaded by
Ulil AbsorOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Explanation Text
Explanation Text
Uploaded by
Ulil AbsorCopyright:
Available Formats
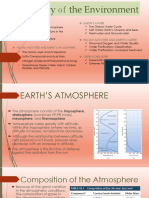
Explanation Text : Greenhouse Effect | The Greenhouse effect is raised temperature at the planet's surface as result of heat energy
being trapped by gases in the atmosphere. Certain gases cause the atmosphere to act like the glass in a greenhouse. As a result, thetemperature of a planet's surface may be higher than it otherwise would beon Earth about 33 C (59F) higher. The main gases that produce the greenhouse effect on Earth are water vapour and carbon dioxide. Scientists suspect that an increased discharge of carbon dioxide from human activity (notably motor transport and industry) is contributing to global warming. Greenhouse gases are fairly transparent to the shortwavelength, visible and ultraviolet lightthat brings most of the Sun's energy, though about 25% is reflected by the atmosphere, and 25% is absorbed by it. About 5% is reflected from the Earth, which absorbs the rest. Some of this absorbed energy rises again in thermals or in the heat of evaporated moisture. The rest is reradiated as long wavelength infrared rays. The infrared radiation emitted by the Earth is partially transmitted straight back into space. A much greater amount is absorbed by the greenhouse gases, which are very efficient absorbers of the long infrared wavelengths. Some of the absorbed heat is reradiated into space, but a lot is radiated downwards to fuel global warming. Half the world's population lives on lowlying coastal areas, such as the Bay of Bengal which is particularly vulnerable to flooding. Global warming could cause the sea level to rise. A 2m (6ft) rise in sea level would inundate close to 20% of Bangladesh and require tens of millions to be evacuated. A larger rise of 5m (16ft) would drown close to half the country.
Explanation Text About How The Water Cycle Works / Hydrological Cycle Solar energy evaporates exposed water from seas, lakes, rivers, and wet soil; the majority of this evaporation takes place over the seas. Water is also released into the atmosphere by the plants through photosynthesis. During this process, known as evapotranspiration, water vapour rises into the atmosphere. Clouds form when air becomes saturated with water vapour. The two major types of cloud formation are stratified or layered grey clouds called stratus and billowing white or dark grey cloud called cumulus clouds. Precipitation as rain, or hail ensures that water returns to Earths surface in a fresh form. Some of this rain, however, falls into the seas and is not accessible to humans. When rain falls, it either washes down hill slopes or seeps underground; when snow and hail melts, this water may also sink into the ground. Rain fall also replenishes river water supplies, as does underground water. Snow fall may consolidate into glaciers and ice sheets which, when they melt, release their water into the ground, into stream or into the seas.
Explanation Text: Acid Rain Acid rain is rain that is highly acidic because of sulphur oxides, nitrogen oxides, and other air pollutants dissolved in it. Normal rain is slightly acidic, with a pH of 6. Acid rain may have a pH value as low as 2.8. Acid rain can severely damage both plant and animal life. Certain lakes, for example, have lost all fish and plant life because of acid rain. Acid rain comes from sulphur in coal and oil. When they burn, they make sulphur dioxide (SO2). Most sulphur leaves factory chimneys as the gaseous sulphur dioxide (SO2) and most nitrogen is also emitted as one of the nitrogen oxides (NO or NO2), both of which are gases. The gases may be dry depositedabsorbed directly by the land, by lakes or by the surface vegetation. If they are in the atmosphere for any time, the gases will oxidise (gain an oxygen atom) and go into solution as acids. Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) and the nitrogen oxides will become nitric acid (HNO3). The acids usually dissolve in cloud droplets and may travel great distances before being precipitated as acid rain. Catalysts such as hydrogen peroxide, ozone and ammonium help promote the formation of acids in clouds. More ammonium (NH4) can be formed when some of the acids are partially neutralised by airborne ammonia (NH3). Acidification increases with the number of active hydrogen (H+) ions dissolved in acid. Hydrocarbons emitted by for example, car exhausts will react in sunlight with nitrogen oxides to produce ozone. Although it is invaluable in the atmosphere, low level ozone causes respiratory problems and also hastens the formation of acid rain. When acid rain falls on the ground it dissolves and liberates heavy metals and aluminium (Al). When it is washed into lakes, aluminium irritates the outer surfaces of many fish. As acid rain falls or drains into the lake the pH of the lake falls. Forests suffer the effect of acid rain through damage to leaves, through the loss of vital nutrients, and through the increased amounts of toxic metals liberated by acid, which damage roots and soil micro organisms. The Water Cycle There will never be any more freshwater on Earth than there is now. No new water is being made and water cant escape from the Earth. The water we use is recycled over and over again. The water cycle is the simplest natural cycle on Earth. Solar energy evaporates water from the ocean, lakes and rivers. Millions of litres of water rise into the atmosphere as an invisible gas - water vapour. This process is called evaporation. As the water vapour is pushed over the land by winds and rises over mountains, the water vapour cools and turns back into tiny water droplets, forming clouds. The droplets joining together is termed condensation. These droplets fall to earth as rain (precipitation). The rain runs into streams and rivers, which eventually flow into lakes or the sea and the cycle begins all over again.
You might also like
- Final Test IeltsDocument12 pagesFinal Test IeltsAbbas Ali20% (5)
- Liu Gong CLG835-Op. y MantenimientoDocument105 pagesLiu Gong CLG835-Op. y MantenimientoIvan Alex Escobar100% (6)
- Effects of Air Polllution On The AtmosphereDocument19 pagesEffects of Air Polllution On The Atmospherechristian ringorNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic Cycle: AtmosphereDocument4 pagesHydrologic Cycle: AtmosphereJennifer SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Environmental Cycles and ProcessesDocument6 pagesChapter 5: Environmental Cycles and ProcessesAko lang ToNo ratings yet
- Cycling of Nutrients: REG NO:15BEE0305 Name:Madhankumar.S Slot:G1 Sub Code:Chy1002Document9 pagesCycling of Nutrients: REG NO:15BEE0305 Name:Madhankumar.S Slot:G1 Sub Code:Chy1002Thennarasu RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Meteorolgy: Air Is Tasteless, Odorless, and Invisible, Sun's EnergyDocument4 pagesEssentials of Meteorolgy: Air Is Tasteless, Odorless, and Invisible, Sun's EnergyAlexandrea ModillasNo ratings yet
- PollutionDocument49 pagesPollutionkailash chandNo ratings yet
- En Unit 2 Hydrosphere AtmosphereDocument45 pagesEn Unit 2 Hydrosphere Atmospheremaytte.ahaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry IGCSE NotesDocument38 pagesChemistry IGCSE NotesRaneem94% (16)
- Biogeochemical CycleDocument7 pagesBiogeochemical CycleArnel AdinoNo ratings yet
- Group 1 ReportDocument19 pagesGroup 1 ReportKimmy Jane FloresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Preservation and Conservation of The EnvironmentDocument4 pagesChapter 3: Preservation and Conservation of The EnvironmentPhooi Kiet LamNo ratings yet
- Water CycleDocument11 pagesWater Cycleanika tahsinNo ratings yet
- Aecc 13Document52 pagesAecc 13Sachin PatelNo ratings yet
- SH2173 - Environmental Science In-Semester Exam-2 (ISE-2) : Roll Number Name Department Class DivisionDocument11 pagesSH2173 - Environmental Science In-Semester Exam-2 (ISE-2) : Roll Number Name Department Class DivisionSourabh KoshtiNo ratings yet
- Ozone Depletion Describes Two Distinct But Related Phenomena Observed Since The Late 1970s: A SteadyDocument7 pagesOzone Depletion Describes Two Distinct But Related Phenomena Observed Since The Late 1970s: A Steadydyep31No ratings yet
- The Greenhouse EffectDocument2 pagesThe Greenhouse EffectHannah E. SheppardNo ratings yet
- BiogeoDocument24 pagesBiogeoGetteMacaalayNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CycleDocument6 pagesBiogeochemical CycleJanen Vea Padua DavidNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: Guru Nanak Dev UniversityDocument20 pagesAcid Rain: Guru Nanak Dev UniversityManwinder Singh GillNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution - Biology Presentation Chapter 5 HandoutsDocument2 pagesAir Pollution - Biology Presentation Chapter 5 HandoutsthesmolweirdopotatoNo ratings yet
- Pollution Is The Introduction of Harmful Materials Into The EnvironmentDocument9 pagesPollution Is The Introduction of Harmful Materials Into The EnvironmentLETCHUMY A/P MARIPAN MoeNo ratings yet
- EnvironmentDocument17 pagesEnvironmentuzmakhan9309364No ratings yet
- Assignment7 THE HUMAN IMPACT ON CLIMATE AND THE ATMOSPHEREDocument2 pagesAssignment7 THE HUMAN IMPACT ON CLIMATE AND THE ATMOSPHEREHavier EsparagueraNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument9 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesJoe SellerNo ratings yet
- Global Warming: Air Is The Name Given To Atmosphere Used inDocument15 pagesGlobal Warming: Air Is The Name Given To Atmosphere Used insamoooonNo ratings yet
- Global Warming and Green House EffectDocument3 pagesGlobal Warming and Green House EffectPrajval J ShettyNo ratings yet
- Sci NotDocument13 pagesSci NotShekinah BandiezNo ratings yet
- What Is Acid RainDocument6 pagesWhat Is Acid RainPrerna VoraNo ratings yet
- What Is Acid RainDocument6 pagesWhat Is Acid RainPrerna VoraNo ratings yet
- Environmental Cycles or Biogeochemical CycleDocument14 pagesEnvironmental Cycles or Biogeochemical Cyclemohidul islamNo ratings yet
- University of Technology Faculty of Science and SportDocument13 pagesUniversity of Technology Faculty of Science and SportCördïî X CördïîNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Natural ResourcesDocument17 pagesChapter 6 Natural ResourcesThikshika . NNo ratings yet
- Optical Properties: Scattering:When Light Passes Through Our Atmosphere, Photons InteractDocument7 pagesOptical Properties: Scattering:When Light Passes Through Our Atmosphere, Photons InteractmilabelmilabelNo ratings yet
- Acid RainDocument17 pagesAcid RainGurinder kaurNo ratings yet
- Pollution Is A Global ProblemDocument10 pagesPollution Is A Global Problemalifah adanyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument38 pagesChemistry NotesTedNo ratings yet
- HydroDocument5 pagesHydrojoanne_mendoza_1No ratings yet
- U 1b Energy and EnvironmentDocument4 pagesU 1b Energy and EnvironmentAJ PrinceNo ratings yet
- Midterm Envio SummerDocument8 pagesMidterm Envio SummerIlhan KlisuraNo ratings yet
- Contoh Explanation Text Global WarmingDocument3 pagesContoh Explanation Text Global WarmingjiyesthaNo ratings yet
- The EarthDocument3 pagesThe EarthloheesNo ratings yet
- AKB M.SC - 3rd Sem Topic Acid Rain and Ozone Layer DepletionDocument20 pagesAKB M.SC - 3rd Sem Topic Acid Rain and Ozone Layer DepletionworkwithsnehhNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Composition PresentationDocument23 pagesAtmospheric Composition PresentationInjeel AwanNo ratings yet
- The Biosphere-What Makes It UpDocument4 pagesThe Biosphere-What Makes It UpSarahNo ratings yet
- Natural Resources: Presented by ClassDocument10 pagesNatural Resources: Presented by ClassmithiNo ratings yet
- Composition and Structure of The AtmosphereDocument47 pagesComposition and Structure of The AtmosphereJulia FlorencioNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain: Acid Rain Is A Rain or Any Other Form of Precipitation That Is Unusually AcidicDocument5 pagesAcid Rain: Acid Rain Is A Rain or Any Other Form of Precipitation That Is Unusually AcidicLucille BallaresNo ratings yet
- Concept Map NotesDocument2 pagesConcept Map NotesChrisNo ratings yet
- Finish Line & Beyond: WWW .E X Ce LLDocument9 pagesFinish Line & Beyond: WWW .E X Ce LLrakeshkyNo ratings yet
- Finish Line & BeyondDocument8 pagesFinish Line & BeyondAjay AnandNo ratings yet
- MCB 311 Lecture 2Document12 pagesMCB 311 Lecture 2ejohn8340No ratings yet
- Running Head: ACID RAIN 1Document9 pagesRunning Head: ACID RAIN 1William DelphNo ratings yet
- Climate SystemDocument25 pagesClimate SystemtoufiqNo ratings yet
- CH 18 ChemDocument29 pagesCH 18 ChemJustin GrantosNo ratings yet
- Hydrologic CycleDocument3 pagesHydrologic CycleDjoanna Joyce LeanoNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument5 pagesGlobal WarmingjefriNo ratings yet
- Acid Rain by Zerkash SheikhDocument12 pagesAcid Rain by Zerkash Sheikhشیخ زرکاش امرتسریہNo ratings yet
- Environmental StudiesDocument11 pagesEnvironmental StudiesAbdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Global Climate Change: Carmela Ariane D. Aliazas BS Chemistry 311Document21 pagesGlobal Climate Change: Carmela Ariane D. Aliazas BS Chemistry 311arialiazasNo ratings yet
- Evaporation, Transpiration and Precipitation | Water Cycle for Kids | Children's Water BooksFrom EverandEvaporation, Transpiration and Precipitation | Water Cycle for Kids | Children's Water BooksNo ratings yet
- Gurps 4e - Unofficial GURPS Magic Errata by Steven EhrbarDocument5 pagesGurps 4e - Unofficial GURPS Magic Errata by Steven EhrbarhamulynNo ratings yet
- Coring&Core AnalysisDocument156 pagesCoring&Core AnalysisVi Dang100% (1)
- Strategies For Mitigation Ethanol and Methanol Stress Corrosion CrackingDocument76 pagesStrategies For Mitigation Ethanol and Methanol Stress Corrosion CrackingCarlos Bermejo AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Canal LiningDocument10 pagesCanal LiningShahid RøckzzNo ratings yet
- Living in The Environment 19th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesLiving in The Environment 19th Edition Miller Solutions ManualMorganLoganposxg100% (55)
- Water Supply 5Document11 pagesWater Supply 5ahmed almhjaniNo ratings yet
- What Is The Clean Water ActDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Clean Water ActMary Shaynah JungwirthNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Thesis TopicsDocument4 pagesIrrigation Thesis Topicsafjwdprlzaxewj100% (1)
- Saturation Index WaterChem3Document13 pagesSaturation Index WaterChem3Mai TranNo ratings yet
- 06 Plenary2 HansstielstraDocument37 pages06 Plenary2 HansstielstraImran KhanNo ratings yet
- Soil PollutionDocument32 pagesSoil PollutionNikhil GautamNo ratings yet
- FeSO4 7H2O WatertreatmentDocument10 pagesFeSO4 7H2O Watertreatmentlhphong021191No ratings yet
- Carbon Footprint: A Science ProjectDocument33 pagesCarbon Footprint: A Science Projectफरहान खानNo ratings yet
- Hydrology For Civil EngineeringDocument9 pagesHydrology For Civil EngineeringLeo SerasingheNo ratings yet
- Dams in PakistanDocument2 pagesDams in PakistanIrfan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Water UsageDocument1 pageWater UsageKhay PholrobNo ratings yet
- SBM Plastic Waste BookDocument90 pagesSBM Plastic Waste BookChetana ThoratNo ratings yet
- Examination Control Division: Subject: - Irrigation and Drainage EngineeringDocument2 pagesExamination Control Division: Subject: - Irrigation and Drainage Engineeringrahul100% (2)
- Environmental Diploma Examiners Report December 20162332017421159Document17 pagesEnvironmental Diploma Examiners Report December 20162332017421159francis100% (2)
- Most Open Valve Concept WWTP EE AnalysisDocument29 pagesMost Open Valve Concept WWTP EE AnalysisRahmi ArslanNo ratings yet
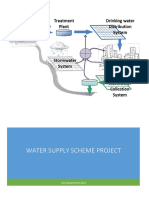
- Water Supply Scheme Project D-17Document81 pagesWater Supply Scheme Project D-17Malik TalhaNo ratings yet
- Evidence of Rock Art From Paniam Quartzitic Formation at KunukuntlaDocument12 pagesEvidence of Rock Art From Paniam Quartzitic Formation at KunukuntlaAjAy Kumar RammoorthyNo ratings yet
- The Biodiversity Friendly Enterprise (BDFE) Was Implemented For The Socio-EconomicDocument13 pagesThe Biodiversity Friendly Enterprise (BDFE) Was Implemented For The Socio-EconomicQuennie Lyn Catudio ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Biology Project HemaDocument9 pagesBiology Project Hemashankar100% (1)
- Chou, Lim, Leng. 1992. The Coastal Resources o F Brunei Darussalam Status, Utilization and ManagementDocument226 pagesChou, Lim, Leng. 1992. The Coastal Resources o F Brunei Darussalam Status, Utilization and ManagementAzb 711No ratings yet
- 11-Ecology Notes PDFDocument41 pages11-Ecology Notes PDFManish AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Green BuildingDocument6 pagesGreen BuildingAbood Buriahi100% (1)
- Pelleting Presses For Small and Medium ProductionsDocument2 pagesPelleting Presses For Small and Medium ProductionsELANo ratings yet