Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circl
Circl
Uploaded by
SantoshOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circl
Circl
Uploaded by
SantoshCopyright:
Available Formats
CIRCLE
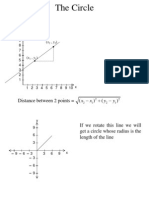
Definition :- The locus of a point in a plane at a constant distance from the fixed point is called as the circle. The fixed point is called as the centre and the constant distance is called as the radius of the circle. Equation of the cirle in various forms :1) Standard form :The circle whose centre is at origin is called as the standard circle. The equation of circle with centre at origin and radius a is x2 + y2 = a2.
Tangent in Parametric form : The equation of tangent to the circle x2 + y2 = a2 at the point P() is xcos + y sin = a Condition for Tangency and Equation of Tangent in terms of Slope :The line y = mx + c is a tangent to the circle x2 + y2 = a2, if c2 = a2 (m2 + 1) and the equation of tangent in terms of slope is y = mx + a 1 + m2. and the point of contact of this tangent is (+
2) Centre - Radius form :The equation of circle with centre at (h, k) and radius r is (x - h)2 + (y - k)2 = r2.
3) Diameter form :The equation of circle whose end points of the diameter are (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is (x - x1)(x - x2) + (y - y1)(y - y2) = 0 4) General form :The equation x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 represents the general equation of circle with centre at (-g, -f) and radius g2 + f2 - c .
5) Parametric Equations of the circle :(i) The parametric equations of the circle x2 + y2 = a2 are x = acos and y = asin. where is called as the param eter of any point on the circle.Thus any point on the circle is P() (acos, asin). (ii) The parametric equations of the circle : (x - h)2 + (y - k)2 = a2 are x = h + acos and y = k + asin. where is called as the parameter of any point on the circle. Thus any point on the circle is P() (h + acos, k + asin).
Condition for the general second degree equation to represent the circle :The general second degree equation ax2 + 2hxy + by2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 represents the circle, if (i) a = b and (ii) h = 0. Two Circles Touching Each Other :If C1 and C2 are the centres and r1, r2 are the radii of two circles, then (i) The circles touch each other externally, if C1C2 = r1 + r2, and the point of contact divides the segment joining C1 and C2 internally in the ratio r1 : r2. ii) The circles touch each other internally, if C1C2 = | r1 - r2 | and the point of contact divides the segment joining C1 and C2 externally in the ratio r1 : r2. iii) The circles intersect at two points, if | r1 - r2 | < C1C2 < r1 + r2 . iv) The circles neither intersect nor touch each other, if C1C2> r1+ r2 or C1C2 < | r1 - r2|. Position Of a Point w.r.t. a Circle :The point P(x1, y1) lies outside, on or inside a circle S x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 according as S1 x12 + y12 + 2gx1 + 2fy1 + c > = or < 0
Po pad es Re lian ce
Tangents to a Circle :Tangent at a given point of the circle :1) The equation of tangent to the circle x2 + y2 = a2 at the point (x1, y1) of it is x x1 + y y1 = a2. 2) The equation of tangent to the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 at the point (x1, y1) of it is x x1 + y y1 + g (x + x1) + f (y + y1) + c = 0.
Ma ths Ac ade my Par bha ni
g f c
ma a ) ,+ 2 1 + m 1 + m2
Orthogonal Circles :Two circles are said to be orthogonal, if the tangents at their point of intersection are at right angles, i.e. r12 + r22 = d2 , where r1, r2 are the radii and d is the distance between two centres of the circles. The two circles x2 + y2 + 2g1x + 2f1y + c1 = 0 and x2 + y2 + 2g2x + 2f2y + c2 = 0 cut each other orthogonally, if 2g1g2 + 2f1f2 = c1 + c2.
Director Circle :The locus of a point, the tangents from which to the circle are perpendicular to each other is called as the director circle. The equation of the director circle of the circle x2 + y2 = a2 is x2 + y2 = 2a2.
Concentric Circle :The circles having the same centre are called as the concentric circles. The equation of the circle concentric with the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 is x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + k = 0, where k is any real number. Length of the tangent segment : 1. The length of the tangent segment drawn to the circle x2 + y2 = a2 from the point (x1, y1) is S = x12 + y12 - a2 2. The length of the tangent segment drawn to the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 from the point (x1, y1) is S = x12 + y12 + 2gx1 + 2fy1 + c Points to Remember : 1. The lengths of the intercepts on the coordinate axes made by the general circle are 2 g2 - c and 2 f2 -c
2. If OA and OB are the tangents from the origin to the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 and C is the centre of the circle, then the area of the quadrilateral OACB is c(g2 + f2 - c) 3. The angle between the tangents from (x1, y1) to the circle x2 + y2 = a2 is a 2 tan-1( ) x12 + y12 - a2 4. If two tangents drawn from the origin to the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 are perpendicular to each other, then g2 + f2 = 2c 5. The length of the tangent drawn from any point on the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c1 = 0 to the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 is c - c1. 6. If the radius of the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 be r and it touches both the axes, then g = f = c = r 7. If the circles x2 + y2 + 2gx + c2 = 0 and x2 + y2+2fy + c2 = 0 touch each other, then 1 1 1 + 2 = 2 2 S.M.Popade
Believe on your strength
CIRCLE Multiple Choice Questions
1. The area of circle centred at (1, 2) and passing through (4, 6) a) 5 . b) 10 c) 25 d) None of these. 2. If ( -3, 2) lies on the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 which is concentric with the circle x2 + y2 + 6x + 8y - 5 = 0. then c is a) 11 b) -11 c) 24 d) None of these. 3. Equation of a circle through (- 1. - 2) and concentric with the circle x2 + y2 - 3x + 4y - c = 0 is a) x2 + y2- 3x + 4y - 1 = 0 b) x2 + y2 - 3x + 4y = 0 c) x2 + y2 - 3x + 4y + 2 = 0 d) None of these. 4 The equation of a circle passing through the point (4, 5) having the centre at (2. 2) is a) x2 + y2 + 4x + 4y - 5 = 0 b) x2 + y2 - 4x - 4y - 5 = 0 c) x2 + y2 - 4x = 13 d) x2 + y2 - 4x - 4y + 5 = 0. 5. If the line y = x + 3 meets the cilcle x2 + y2 = a2 at A and B, then equation of the circle on AB as diameter is a) x2 + y2 + 3x - 3y - a2 + 9 = 0 b) x2 + y2 - 3x + 3y - a2 + 9 = 0 c) x2 + y2 + 3x + 3y - a2 + 9 = 0 d) None of these. 6. If the coordinates at one end of a diameter of the circle x2 + y2 - 8x - 4y + c = 0 are (- 3, 2), then the coordinates at the other end are a) (5, 3) b) (6. 2) c) (l. - 8) d) (11,2). 7. Equation of the circle through origin which cuts intercepts of length a and b on axes is a) x2 + y2 + ax + by = 0 b) x2 + y2 - ax - by = 0 c) x2 + y2 + bx + ay = 0 d) None of these. 8. Equation of the diameter of the circle x2 + y2 - 2x + 4y = 0 which passes through the origin is a) x + 2y = 0 b) x - 2y = 0 c) 2x + y = 0 d) 2x - y = 0. 9. The line x + 3y = 0 is the diameter of the circle a) x2 + y2 + 6x + 2y = 0. b) x2 + y2- 6x + 2y = 0 c) x2 + y2 - 6x - 2y = 0 d) x2 + y2 + 8x - 2y = 0. 10. The equation ax2 + by2 + 2hxy + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 represents a circle, the condition will be a) a = b and.c = 0 b) f = g and h = 0 c) a = b and h = 0 d) f = g and c = 0. 11. Length of the chord on the line 4x - 3y - 10 = 0 cut off by the circle x2 + y2 - 2x + 4y - 20 = 0 is a) 10 b) 6 c) 12 d) None of these. 12. From origin, chords are drawn to the circle x2 + y2 -2y = 0 The locus of the middle points of these chords is a) x2 + y2 - y = 0 b) x2 + y2 - x = 0 c) x2 + y2 - 2x = 0 d) x2 + y2 - x - y = 0 13. A square is inscribed in the circle x2 + y2 - 2x + 4y + 3 = 0 Its sides are parallel to the coordinate axes. Then one vertex of the square is a) (1 +2, - 2 ) b) (1 - 2, - 2 ) c) (1, -2 +2 ) c) (2, -3)
Popades Reliance Maths Academy, Parbhani 9822772673
Po pad es Re lian ce
Ma ths Ac ade my Par bha ni
14.The equation of the circumcircle of the triangle formed by the lines y + 3x = 6, y - 3x = 6 and y = 0 is a) x2 + y2 - 4y = 0 . b) x2 + y2 + 4x = 0 c) x2 + y2 - 4y = 12 d) x2 + y2 + 4x = 12. 15. Locus of a point such that the ratio of its distances from two fixed points is constant is a) a circle b) a straight line c) an ellipse d) None of these. 2 2 16. The circles x + y - 10x + 16 = 0 and x2 + y2 = r2 intersect each other in two distinct points if a) r < 2 b) r > 8 c) 2 < r < 8 d) 2 < r < 8. 17. The length of the intercept cut by the circle x2 + y2 - 7x + 5y + 12 = 0 on x-axis is equal to a) 3 b) 1 c) 4 d) 2. 18. A circle is given by x2 + y2 - 6x + 8y - 11 = 0 and there are two points (0, 0) and (1, 8). These points lie a) one outside and one inside the circle b) both inside the circle d) both outside the circle d) one on and the other inside the circle 19. If a circle passes through the points of intersection of the
coordinate axes with the lines lx - y + 1 = 0 and x -2y + 3 = 0.then the velue of l is
a) 2 b) 1/3 c) 6 d) 3 20. The number of integral values of k for which x2 + y2 + kx + (1 - k) y + 5 = 0 represents a circle whose radius cannot exceed 5, is : a) 14 b) 16 c) 18 d) 20. 21. Given the circles x2+ y2 - 4x- 5 = 0 and x2+ y2 + 6x - 2y + 6 = 0. Let P be a point (,) such that the tangents from P on both the circles are equal in length. Then a) 2 + 10 + 11 = 0 b)2 - 10 + 11 = 0 c) l0-2+ 11 = 0 d) l0+2+ 11 = 0. 22.Range of values of m for which the straight line y = mx + 2 cuts the circle x2 + y2 = 1 in distinct or coincident points is : a) [-3, 3 ] b) [3, ) c) (-, -3 ] [3, ) d) None of these 23. The equation of the tangents drawn from the origin to the circle x2 + y2 - 2rx - 2hy + h2 = 0 are a) x = 0, b) y = 0 2 2 c) (h - r )x - 2hry = 0 d) (h2 - r2)x + 2hry = 0 24. The two circles x2 + y2 - 10x + 4y - 20 = 0 and x2 + y2 + 14x - 6y + 22 = 0 are related by a) touch externally b) intersect in real points c) donot intersect d) one is contained in other 2 25. The tangent to the circle x + y2 = 5 at the point (1, -2) also touches the circle x2 + y2 - 8x + 6y + 20 = 0 at a) (-2, 1) b) (-3, 0) c) (-1, -1) d) (3, -1) 2 2 26. Image of the circle x + y + 14x + 6y + 42 = 0 in the line 2x + 3y = 16 is a) x2 + y 2 + 2x - 12y + 21 = 0 b) x2 + y 2 - 2x - 12y + 21 = 0 c) x2 + y 2 - 2x + 12y + 21 = 0 d) x2 + y 2 + 2x - 12y - 21 = 0
27. The equation of the circle which touches the y-axis at a
distance 4 from the origin and intercepts a length 6 on xaxis is a) x2 + y2 + 10x - 8y + 10 = 0 b) x2 + y2 + 10x - 8y - 16 = 0 c) x2 + y2 + 10x + 8y + 16 = 0 d) None of these
42. The locus of the point of intersection of two perpendicular tangents to the circle is (a) Auxilliary Circle (b) Director Circle (c) Straight line (d) None of these 43. The radius of the circle through (2, 3) , (-1, 6) and having centre on 2x + 5y + 1 = 0 is (a) 13 (b) 23 (c) 29 (d) 31 44. The equation x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 represents a circle , if (a) g2 + f 2 - c < 0 (b) g2 + f 2 - c > 0 2 2 (c) g + f - c = 0 (b) g = f
Po pad es Re lian ce
2 2 a) ( -a , -a m ) c c a2 , a2m ) c) ( c c 2 a2 b) ( -a m , ) c c 2 -a2 d) ( -a m , ) c c
28. The length of the tangent from (5, 1) to the circle x2 + y2 + 6x - 4y - 3 = 0, is a) 81 b) 29 c) 7 d) 21 29. The equation of the circle passing through (4, 5) and having the centre at (2, 2) is a) x2 + y2 + 4x + 4y - 5 = 0 b) x2 + y2 - 4x - 4y - 5 = 0 c) x2 + y2 - 4x = 13 d) x2 + y2 - 4x - 4y + 5 = 0 30. The equation of the tangents drawn from the origin to the circle x2 + y2 - 2rx - 2hy + h2 = 0 are a) x = 0, b) y = 0 c) (h2 - r2)x - 2hry = 0 d) (h2 - r2)x + 2hry = 0 31. The two circles x2 + y2 - 10x + 4y - 20 = 0 and x2 + y2 + 14x - 6y + 22 = 0 are related by a) touch externally b) intersect in real points c) donot intersect d) one is contained in other 32. The tangent to the circle x2 + y2 = 5 at the point (1, -2) also touches the circle x2 + y2 - 8x + 6y + 20 = 0 at a) (-2, 1) b) (-3, 0) c) (-1, -1) d) (3, -1) 33. The lengths of the intercept made by the circle x2 + y2 - 5x 13y - 14 = 0 on X and Y axes are a) 9, 13 b) 5, 13 c) 9, 15 d) None of these 34. The equation of the circle which touches the y-axis at a distance 4 from the origin and intercepts a length 6 on xaxis is a) x2 + y2 + 10x - 8y + 10 = 0 b) x2 + y2 + 10x - 8y - 16 = 0 d) x2 + y2 + 10x + 8y + 16 = 0 d) None of these 35. Centre of a circle is (2, 3). If the line x + y = 1 touches it, its equation is a) x2 + y2 - 4x - 6y + 4 = 0 b) x2 + y2 - 4x - 6y + 5 = 0 d) x2 + y2 - 4x - 6y - 5 = 0 d) None of these 36. The tangent to the circle x2 + y2 = 169 at (5, 12) & (12, -5) are a) parallel b) Perpendicular c) Coincide d) None of these 37. The locus of the point of intersection of the perpendicular tangents of x2 + y2 = 4 is a) x2 + y2 = 8 b) x2 + y2 = 12 2 2 c) x + y = 16 d) x2 + y2 = 43 38. The equation of the circle passing through (2, 1) and touching the coordinate axes is a) x2 + y2 - 2x - 2y + 1 = 0 b) x2 + y2 + 2x + 2y + 1 = 0 d) x2 + y2 - 2x - 2y - 1 = 0 d) x2 + y2 + 2x + 2y - 1 = 0 39. Circle which passes through (1, -2) and (4, -3) and whose centre lies on 3x + 4y = 7 is a) x2 + y2 + 3x + 12y + 2 = 0 b) x2 + y2 + 12x + 3y + 2 = 0 c) x2 + y2 - 3x - 12y + 2 = 0 d) x2 + y2 - 12x - 3y + 2 = 0 40. The length of the tangent from the point (1, 2) to the circle 2x2 + 2y2 + 6x - 8y + 3 = 0 is a) 3/2 b) 3 / 2 c) (3/2) d) None of these 41.The line y = mx + c touches the circle x2 + y2 = a2 at
45. The slope of the tangent at the point (h, h) to the circle x2 + y2 = a2 is a) 0 (b) 1 c) -1 d) Depends on h. 46. The equations of the tangents to the circle x2 + y2 = 4 which are inclined at 600 with x-axis a) 3 x - y + 3 = 0 b) 3 y - x + 3 = 0 c) 3 x - y + 4 = 0 d) None of these 47. The line 3x + 4y = k touches the circle x2 + y2 = 10x, then k is a) -40 b) 10 c) 40 b) -10 48. The radius of the circle 4x2 + 4y2 - 10x + 5y + 5 = 0 is a) 35/8 b) 35/7 c) 35 d) 5 49. The point of contact of the two circles x2 + y2 + 2x + 8y - 23 = 0 and x2 + y2 - 4x - 10y + 19 = 0 divides the segment C1C2 in the ratio a) 3 : 1 b) 1 : 2 c) 2 : 1 d) 1 : 3 50. The equation of the circle whose centre is (-4, 2) and its tangent is x - y = 3 is a) x2 + y2 + 8x - 4y - 41 = 0 b) 2x2 + 2y2 + 16x - 4y + 20 = 0 c) 2x2 + 2y2 + 16x - 8y - 41 = 0 d) x2 + y2 + 16x - 4y - 24 = 0 51. The equations of the tangents drawn from the point (0, 1) to the circle x2 + y2 - 2x + 4y = 0 a) 2x - y - 1 = 0, x - 2y + 2 = 0 b) 2x - y + 1 = 0, x + 2y - 2 = 0 c) x - y + 1 = 0, x + y + 2 = 0 d) None of these. 52. The equation of the circle with centre at (a, a) and radiusa a) x2 + y2 + 2ax + 2ay + a2 = 0 b) x2 + y2 = a2 c) x2 + y2 - 2ax - 2ay + a2 = 0 d) None of these. 53. The centre and radius of the circle x2 + y2 = 2 is a) (0, 0); 2 b) (2, 2); 2 c) (0, 0); 4 d) (0, 0); 2 54. The centre and radius of circle 2x2 + 2y2 - 6x + 4y - 3 = 0 is a) (3/2, -1); 19/2 b) (3/2, -1) 19/2 c) (-3/2, 1); 19/2 d) (-3/2, 1) 19/2 55. The equations of circles with radius r and touching the x- axis at (h, 0) a) x2 + y2 - 2hx - 2ry + h2 = 0, x2 + y2 - 2hx + 2ry + h2 = 0 b) x2 + y2 + 2hx + 2ry + h2 = 0, x2 + y2 - 2hx - 2ry + h2 = 0 c) x2 + y2 + 2hx + 2ry + h2 - r2 = 0, x2 + y2 - 2hx - 2ry = 0 d) None of these 56. The centre and radius of the circle (x - 5)(x - 3) + (y - 2)(y - 4) = 0 is a) (3, 4); 2 b) (4, 3) ; 2 c) (4, 3); 2 d) (5, 3) ; 4 57. The equation of the circle with centre at (3, -2) and touching the x-axis is a) x2 + y2 - 6x + 4y + 13 = 0 b) x2 + y2 - 3x + 2y + 9 = 0 c) x2 + y2 + 6x - 4y + 9 = 0 d) x2 + y2 - 6x + 4y + 9 = 0 58. The equation of the circle through the points (4, 1), (-3, -6) and (-2, 1) is a) x2 + y2 - 2x + 6y - 15 = 0 b) x2 + y2 - 4x - 5y + 9 = 0 c) x2 + y2 + 4x + 4y + 7 = 0 d) x2 + y2 + 2x - 6y - 15 = 0 59. The values of a and h for which the equation, ax2 + hxy + 2y2 + 16x - 8y + 5 = 0 represents a circle a) a = 0, h = 0 b) a = 2, h = 2 c) a = 5, h = 2 d) None of these 60. If (-3, 2) lies on the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 which is concentrc with x2 + y2 + 6x + 8y - 5 = 0, then c is a) 11 b) -11 c) 24 d) None of these
Ma ths Ac ade my Par bha ni
RMA PBN
61. The length of the intercept cut off by the circle x2 + y2 _ 6x - 4y - 12 = 0 on the line 4x - 3y + 5 = 0 is a) (2126)/5 b) (4126)/5 c) (126)/5 d) None of these. 62. The locus of the mid-points of the chords of the circle x2 + y2 = 4 which subtends a right angle at the origin is a) x + y = 2 b) x2 + y2 = 1 2 2 c) x + y = 2 d) x + y = 1 63. The equation of the circle having its centre on the line x + 2y - 3 = 0, and passing through the points of intersection of the circles x2 + y2 - 2x - 4y + 1 = 0 and x2 + y2 - 4x - 2y + 4 = 0 is a) x2 + y2 - 6x + 7 = 0 b) x2 + y2 - 3x + 4 =0 2 2 c) x + y - 2x - 2y + 1 =0 d) x2 + y2 +2x - 4y + 4 = 0. 64. Given two circles x2 + y2 - 4x - 5 = 0, x2 + y2 6y + 8 = 0 Let P (h, k) be a point such that the tangents from P to both circles are equal in length, then a) 4h - 6k + 13 = 0 b) 4h - 6k - 13 = 0 c) 4x + 6y - 3 = 0 d) None of these. 65. The circles x2 + y2- 4x + 6y + 8 = 0 and x2 + y2 - l0x - 6y + 14 = 0, a) touch externally b) touch internally c) intersect d) Do not touch. 66. Two circles x2 + y2 = 6 and x2 + y2 - 6x + 8 = 0 are given. Then the equation of the circle through their points of intersection and the point (1, 1) is a) x2 + y2 - 6x + 4 = 0 b) x2 + y2 - 3x + 1 = 0 2 2 c) x + y - 4y + 2 = 0 d) None of these. 67. If the two circles x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy = 0 and x2 + y2 + 2g| x + 2f | y = 0 touch each other, then a) fg = f | g| b)f | g = f g| | | c) f f = g g d) None of these. 68. The condition for the two circles x2 + y2 + 2k1x + k2 = 0 and x2 + y2 + 2k2x + k2 = 0 to touch each other externally is a) k12 + k22 = k2 b) k12 - k22 = k2 2 2 2 2 2 c) k ( k1 - k2 ) = k1 .k2 d) k2 ( k12 + k22 ) = k12.k22 2 2 69. The circles (x - 1) + (y - 2) = 16 and (x + 4)2 + (y + 3)2 = 1 a) touch b) are concentric c) intersect d) None of these. 70. The lines 3x - 4y + 4 = 0 and 3x - 4y - 5 = 0 are tangents to the same circle. The radius of this circle is a) 9/5 b) 9/10 c) 1/5 d) 1/10. 71. If the lines 2x - 4y = 9 and 6x - 12y + 7 = 0 touch a circle, then the radius of the circle is a) 3/5 b) 17/65 c) 25/3 d) 17/35 72.The equation of the line passing through the points of intersection of the circles x2 + y2 - 2x - 4y - 4 = 0 and x2 + y2 - 8x - 12y + 51 = 0 is a) 6x + 8y - 55 = 0 b) 6x + 8y + 55 = 0 c) No such line d) None of these. 73. If 3x + y = 0 is a tangent to the circle which has its centre at the point (2. - 1), then the equation of the other tangent to the circle from the origin is a) x - 3y = 0 b) x + 3y = 0 c) 3x- Y = 0 d) x + 2y = 0. 74.Equation of circle drawn on the chord 2x + 3y = 13 of the circle x2 + y2 = 13 as diameter is a) x2 + y2 - 4x - 6y + 13 = 0 b) x2 + y2 + 4x + 6y + 13 = 0 c) x2 + y2 - 4x + 6y + 13 = 0 d) None of these. 75.Values of p and q for which the equation (x + y - 41)2 - (x + 7y - 7) (px + qy + 1) = 0 represents a circle, are given by a) p = 7/25, q = 1/25 b) p = 1/25, q = 7/25 c) p = - 7/25, q = -1/25 d) None of these. 76. The number of common tangents to two circles x2 + y2 = 4 and x2 + y2 - 8x + 12 = 0 is a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4.
Po pad es Re lian ce
77. If OA and OB are the tangents from origin to the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 (c < 0) and C is the centre of the circle. the area of the quadrilateral OACB is a) 1/2 [(c (g2 +f 2 - c)] b) [(c (g2 +f 2 - c)] 2 2 c) c g +f - c d) None of these. 78. The abscissae of two points A and B are the roots of the equation x2 + 2ax - b2 = 0 and their ordinates are the roots of the equation x2 + 2px - a2 = 0. The radius of the circle with AB as diameter is a) (a2 + p2) b) (b2 + q2) 2 2 2 2 c) (a + b + p + q ) d) None of these. 79. The area of the triangle formed by joining the origin to the points of intersection of the line x.5 + 2y = 3.5 and circle x2 + y2 = 10, is a) 3 b) 4 c) 5 d) 6. 80. The number of common tangents to the circles x2 + y2 = 4 and x2 + y2 - 6x - 8y = 24 is a) 0 b) 1 c) 3 d) 4 81. The equation of the circle which has tangent 2x - y - 1 = 0 at (3, 5) on it and with the centre on x + y = 5. is a) x2 + y2 + 6x - 16y + 28 = 0 b) x2 + y2 - 6x + 16y - 28 = 0 c) x2 + y2 + 6x + 6y - 28 = 0 d) x2 + y2 - 6x - 6y - 28 = 0. 82. The circles x2 + y2 + 4x + 6y - 8 = 0 and x2 + y2 + 6x - 8y + c = 0, cut orthogonally, if c = a) -4 b) 4 c) 2 d) -2 83. If the circles of same radius a and centres at (2, 3) and (5, 6) cut orthogonally, then a = a) 3 b) -3 c) 4 d) 2 84. The equation 2x2 + 2y2 - 6x + 8y + k = 0 represents a point circle, if k is a) 2/25 b) 25 c) 25/2 d) 2 85. Equation of the circle having diametres 2x - 3y = 5 and 3x - 4y = 7 and radius 8, is a) (x - 1)2 + (y - 1)2 = 82 b) (x - 1)2 + (y + 1)2 = 82 2 2 2 c) (x + 1) + (y - 1) = 8 d) (x + 1)2 + (y + 1)2 = 82 86. The vertices of a right angled triangles are A(2, -2), B(-2, 1) and C(5, 2). The equation of circumcircle is, a) (x + 5)(x - 5) + (y - 1)(y - 2) = 0 b) (x + 5)(x + 5) + (y - 1)(y - 2) = 0 c) (x + 5)(x - 5) + (y - 1)(y + 2) = 0 d) None of these. 87. Centre of the circle (x - a)(x - b) + (y - p)(y - q) = 0, is a) (a/2, b/2) c) (p/2, q/2) b) ( a - b , p - q ) 2 2 a+b p+q d) ( , ) 2 2
Ma ths Ac ade my Par bha ni
88. The angle between the tangents drawn from the point (13, 0) to the circle x2 + y2 = 25 are a) tan-1(5/12) b) 2tan-1(5/12) c) tan-1(12/5) d) None of these 89. The equations of the tangents drawn from the point (0, 1) to the circle x2 + y2 - 2x + 4y = 0 are a) 2x - y - 1 = 0, x - 2y + 2 = 0 b) 2x - y + 1 = 0, x + 2y - 2 = 0 c) x - y + 1 = 0, x + y + 2 = 0 d) None of these. 90. A circle with radius 12 lies in the first quadrant and touches both the axes, another circle has its centre at (8, 9) and radius 7. Which of the following is true a) circles touch each other internally b) circles touch each other externally c) circles intersect each other at two points d) None of these
RMA PBN
Po pad es Re lian ce
95. The radius of the circle inscribed in the triangle formed by the lines x = 0, y = 0 and 4x + 3y - 24 = 0 is : a) 12 b) 2 c) 2/3 d) 6. 96. The equation of the chord of the circle x2 + y2 - 4x = 0, whose mid-point is (1, 0) is : a) y = 2 b) y = 1 c) x = 2 d) x = 1. 97. A variable circle passes through the fixed point A (p, q) and touches x-axis. The locus of the other end of the diameter through A is : a) (x - p)2 = 4qy b) (x - q)2 = 4py 2 c) (y - p) = 4qx d) (y - q)2 = 4px. 98. The equation of the circle whose radius is 5 and which touches the circle x2 + y2 - 2x - 4y - 20 = 0 at the point (5, 5) a) x2 + y2 + 18x + 16y + 120 = 0 b) x2 + y2 - 18x - 16y + 120 = 0 c) x2 + y2 - 18x + 16y + 120 = 0 d) x2 + y2 + 18x - 16y + 120 = 0. 99.The tangent to the circle x2 + y2 = 9, which is parallel to y-axis and does not lie in the third quadrant, touches the circle at the point: . a) (3,0) b) (- 3, 0) c) (0, 3) d) (0, - 3). 100. A circle passes through the points of intersection of the line x = 0 and the circle x2 + y2 + 2x = 3. If this circle passes through (13, 0), then its centre is : a) (0, 0) b) (0, 1) c) (1, 0) d) (1, 1). 101.If x = 7 touches the circle x2 + y2 - 4x - 6y - 12 = 0, then the coordinates of the point of contact are : a) (7, 3) b) (7, 4) c) (7, 8) d) (7, 2). 102. The centre of a circle passing through the points (0, 0), (1, 0) and touching the circle x2 + y2 = 9 is: a) (3/2, 1/2) b) (1/2, 3/2) c) (1/2, 1/2) d) (1/2, + 2) 2 (y + 2)2 (x + 1) 103. If the equation k + = 1 represents a 4 3 circle, then the value of k is a) 3/2 b) 1 c) 3/4 d) None of these 104. If the line 2x - y + k = 0 is a diameter of the circle x2 + y2 + 6x - 6y + 5 = 0, then k is : a) 6 b) 9 c) 12 d) None of these. 105. The condition that the line (x + g) cos + (y + f) sin = k is a tangent to x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 : a) g2 + f 2 = c2 + k b) g2 + f 2 = c + k 2 2 c) g + f = c + k d) None of these. 106. If the straight line 3x + 4y = k touches the circle x2 + y2 l0x = 0, then the value of k is: a) 2 or 20 b) - 2 or 20 c) - 1 or 20 d) - 10 or 40. 107. The triangle PQR is inscribed in the circle x2 + y2 = 25. If Q and R have coordinates (3, 4) and (- 4, 3) respec-tively, then QPR is equal to : a) /2 b) /3 c) /4 d) /6. 108. If 2x2 + kxy + 2y2 + (k - 4)x + 6y - 5 = 0 represents a circle, then its radius is a) 22 b) 32 c) 23 d) None of these 109.The equation of the diameter of the circle x2 + y2 = 2ay that is perpendicular to the line x + 2y = 4 is : a) 2x - y + a = 0 b) x + 2y - a = 0 c) 2x - 2y + a = 0 d) None of these 110.The circles x2 + y2-25 = 0 & 3(x2 + y2)- 30x + 40y + 175 = 0 touch each other at a) (3, 4) b) (1, 2) c) (4, 5) d) None of these
111. The tangents drawn to the circle x2 + y2 = 10 from the point (2, -4) include an angle of measure a) 600 b) 450 0 c) 30 d) 900 112. The value of k, if the line 2x - 3y + k = 0 is a tangent to the circle x2 + y2 + 2x - 4y - 8 = 0 a) -21, 5 b) 21, -5 d) + 13 c) + 13 113.Tangents drawn from the point P(3, 4) to the circle x2 + y2 = 16 touch it at Q and R. O is the centre of the circle, then the area of the quadrilateral OQPR is a) 6 units b) 24 units c) 12 units d) 48 units 114. The equation of the circle concentic with x2 + y2 - 6x + 12y + 15 = 0 and having double radius is a) (x - 3)2 + (y + 6)2 = 120 b) x2 + y2 - 6x + 12y + 45 = 0 c) (x - 3)2 + (y + 6)2 = 45 d) None of these 115. The length of the y-intercept of the circle x2 + y2 + 4x - 7y + 12 = 0 is a) 1 b) 3 c) 4 d) 7 116. If two circles x2 + y2 - 3x + ky - 5 = 0 and 4x2 + 4y2 - 12x - y - 9 = 0 are concentric, then k = a) 1/4 b) -1/4 c) 4 d) -4 117. The radius of the circle touching the lines 3x - 4y + 5 = 0 and 6x - 8y - 9 = 0 is a) 19/10 b) 9/10 c) 1/2 d) None of these. 118. The equation of the diameter of the circle x2 + y2 + 2x - 4y + 1 = 0 parallel to x-axis is a) y = 2 b) y = 4 c) 3x + 2y + 4 = 0 d) y = -2 119. Coordinates of the point from which the lengths of tangents to the following three circles x2 + y2 = 4, x2 + y2 - 2x - 4y + 1 = 0, x2 + y2 - 4x - 2y + 1 = 0 are equal, are a) (5/6, 5/6) b) (5/6, 6/5) c) (5/6, - 5/6) d) (-5/6, 5/6). 120. Equation of the circle which passes through the origin and cuts orthogonally each of the circles x2 + y2- 8y+ 12= 0 is x2 + y2 - 4x - 6y - 3 = 0 a) x2 + y2 + 6x + 3y = 0 b) x2 + y2 + 3x- 6y = 0 2 2 c) x + y + 6x - 3y = 0 d) x2 + y2 - 3x + 6y = 0 121. The equation of the common chord of the circles x2 + y2 - 6x = 0 and x2 + y2 - 4y = 0 is a) 3x + 2y + 1 = 0 b) 3x - 2y = 0 c) 3x + 2y = 0 d) 3x - 2y - 1 = 0. 122. Equation of common chord of the circles x2 + y2 - 2x - 4y + 1 = 0 and x2 + y2 - l0x + 8y + 25 = 0 is a) 2x - 3y - 6 = 0 b) 2x + 3y + 6 = 0 c) x - 2y - 3 = 0 d) None of these.
Ma ths Ac ade my Par bha ni
RMA PBN
123. The number of tangents, which can be drawn from the point (1, 2) to the circle x2 + y2 = 5, is : a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 0. 124. Points (2, 0), (0, 1), (4, 5) and (0, a) are concyclic for a = a) 14/3 or 1 b) 14 or 1/3 c) -14/3 d) None of these 125. The equation of the circle which has two normals (x - 1)(y - 2) = 0 and a tangent 3x + 4y = 6 is a) x2 + y2 - 2x - 4y + 4 = 0 b) x2 + y2 + 3x - 4y + 5 = 0 c) x2 + y2 = 5 d) (x - 3)2 + (y - 4)2 = 5 126. The line joining (5, 0) to (10cos, 10sin) is divided internally in the ratio 2 : 3 at P. If varies, then the locus of P is a) a pair of straight line b) a circle c) a straight line d) None of these
The most important key to achieving great success is to decide upon your goal and launch, get started, take action, move.
Po pad es Re lian ce
127. The equation of the circle of radius 5 in the first quadrant which touches x-axis and the line 4y = 3x is a) x2 + y2 - 2x - 4y - 20 = 0 b) x2 + y2 + 10x - 30y + 25 = 0 c) x2 + y2 + 30x - 10y - 225 = 0 d) x2 + y2-30x - 10y + 225 = 0 128. The area of the triangle formed by the tangents from the point (4, 3) to the circle x2 + y2 = 9 and the line joining their points of contact is a) 192 b) 192/24 c) 192/25 d) None of these 129. The equation of the circle which touches the axes of the coordinate axes and the line (x/3) + (y/4) = 1 and whose centre lies in the first quadrant is x2 + y2 - 2cx - 2cy + c2 = 0 then c is a) 1, 6 b) 2, 3 c) 3, 4 d) 4, 5 130. The locus of the centre of a circle which cuts orthogonally the circle x2 + y2 - 20x + 4 = 0 and which touches x = 2 is a) y2 = 16x b) x2 = 16y 2 c) y = 16x + 4 d) x2 = 16y + 4 131.The coordinates of radical centre of the circles x2 + y2 = 9, x2 + y2 - 2x - 2y = 5 and x2 + y2 + 4x + 6y = 19 is a) (0, 0) b) (1, 1) c) (-1, 1) d) (1, -1) 132. The common tangents to the ciercles x2 + y2 + 2x = 0 and x2 + y2 - 6x = 0 form a triangle which is a) isosceles b) equilateral c) right angled d) None of these 133. The circle passing through the intersection of the circle S = 0 and the line P = 0 is a) S + kP b) S - k P c) kS + P d) All the above 134. The area of the circle whose centre is (h, k) and radius is a is a) b) 22 c) a2 d) None of these 135. The equation of the tangents which make equal intercepts on the positive coordinate axes is given by a) x + y + 22 = 0 b) x + y = 22 c) x + y = 23 d) None of these 136. The point at which the line x = 0 touches the circle x2 + y2 - 2x - 6y + 9 = 0 is a) (0, 2) b) (0, 8) c) (0, 3) d) (0, 4) 137. For the circle x2 + y2 + 3x + 3y = 0, which of the follow ing relation is true a) centre lies on the x -axis b) centre lies on the y-axis c) centre at origin d) circle pass through origin 138. For the given circles x2 + y2 - 6x - 2y + 1 = 0 and x2 + y2 + 2x - 8y + 13 = 0, which of the following is true a) one circle lies inside the other b) one circle lies completely outside the other c) two circles intersect in two points d) They touch each other 139. The points of intersection of the circles x2 + y2 = 25 and x2 + y2 - 8x + 7 = 0 are a) (4, 3) and (4, -3) b) (2, -3) and (-3, -2) c) (-6, 3) and (4, 3) d) (2, 3) and (3, 4) 140. If the radius of the circle x2 + y2 - 18x + 12y + k = 0 is 11, then k = a) -3 b) 4 c) -4 d) 3 141. The straight line (x - 2) + (y + 3) = 0 cuts the circle (x - 1)2 + (y - 3)2 = 11 at a) No point b) one point c) Two points d) Three points
142.The equation of the circle which touches both the axes and whose centre is (x1, y1) is a) x2 + y2 + 3x1(x + y) + x12 = 0 b) x2 + y2 - 2x1(x + y) + x12 = 0 c) x2 + y2 + 3xx1 + 2yy1 = 0 d) x2 + y2 = x12 + y12 143. A circle with radius 12 lies in the first quadrant and touches both the axes, another circle has its centre at (8, 9) and radius 7. Which of the following is true a) circles touch each other internally b) circles touch each other externally c) circles intersect each other at two points d) None of these 144. The locus of the point whose shortest distance from the circle x2 + y2 - 2x + 6y - 6 = 0 is equal to its distance from the line x - 3 = 0 a) x2 + 6y - 4x - 9 = 0 b) y2 - 6y + 4x + 9 = 0 2 c) x - 6y - 4x - 9 = 0 d) y2 + 6y - 4x + 9 = 0 2 2 145. If the circle x + y + px + qy + c = 0 touches the x-axis, then a) p2 = c b) p2 = 4c 2 c) q = 4c d) None of these 146. The circumference of the circle 9x2 + 9y2 - 12x - 24y 124 = 0 is a) 4 b) 8 c) 16 d) 20 147.The locus of the centre of the circle which touches the xaxis and cuts off an intercept of constant length k from the y-axis is a) x2 + y2 = k2/4 b) x2 - y2 = k2/4 2 2 2 c) y - x = k /4 d) x2 - y2 = k2 148. A(4, 1) is a point on the circle x2 + y2 - 2x + 6y - 15 = 0, then the equation of the tangent to the circle, which is parallel to the tangent at A is a) 3x + y = 0 b) 3x + 4y - 16 = 0 c) 3x - 10y = 34 d) 3x + 4y + 34 = 0 149. The area of the largest rectangle which can inscribed in the circle x2 + y2 - 4x - 6y - 12 = 0 is a) 50 b) 100 c) 25 d) 10 150. The points A(3, 1), B(7, -1) and C(5, 0) are collinear. Then the length of the tangent drawn from A to any circle through B and C is a) 10 b) 10 c) 210 d) None of these 151. The perimeter of the square, such that the circle (x - h)2 + (y - k)2 = r2 is inscribed in the square is a) 4r b) 8r c) 4r d) 8r 152. The circles (x + a)2 + (y + b)2 = a2 and (x + )2 + (y + )2 = b2 intersect orthogonally, iff a) a + b = 2 + 2 b) a + b = a2 + b2 2 2 c) 2(a + b) = + d) a + b = b2 - a2 153. If the distance between the centres of two circle of radii 2sec2500 and 2tan2500 is 2, then they a) touch externally b) touch internally c) do not touch d) do not intersect 154. Which of the following lines is perpendicular to the line of centres of the circles x2 + y2 + 2x + y + l = 0 and x2 + y2 - x + 2y + 3 = 0 ? a) 3x - y = 0 b) 3x - y - 2 = 0 c) x + y = 0 d) none of these 155. The value of p for which the equation 7x2 + py2 - 5x + 7y - 3 = 0 represents a circle is a) 7 b) 6 c) 5 d) none of these 156.The circumference of the circle 4x2 + 4y2 - 4x - 4y = 7 is a) 2 b) c) 9/4 d) 3
Ma ths Ac ade my Par bha ni
RMA PBN
c) x2 + y2 + 2x + 2y - 23 = 0 d) x2 + y2 + 2x - 2y - 23 = 0
159. If the circles x2 + y2 + 2ax + cy + a = 0 and x2 + y2 - 3ax + dy - 1 = 0 intersect in two distinct points P and Q, then the line 5x + by - a = 0 passes through P and Q for: a) exactly two values of a b) infinitely many values of a c) no value of a d) exactly one value of a 160. A circle touches the x-axis and also touches the circle with centre at (0, 3) and radius 2. The locus of the centre of the circle is : a) a parabola b) a hyperbola c) a circle d) an ellipse 161. Let AB be a chord of the circle x2 + y2 = r2 subtending a right angle at the centre. Then the locus of the centroid of the PAB as P moves on the circle is : a) a parabola b) a circle c) an ellipseC d) a pair of straight line 162. If a > 2b > 0, then the positive value of m for which the line y = mx - b l + m2 is a common tangent to x2 + y2 = b2 and (x - a)2 + y2 = b2, is : 2b a - 4b2 2b c) a - 2b a)
2
b)
a2 - 4b2
2b b d) a - 2b
Po pad es Re lian ce
163. If the tangent at the point P on the x2 + y2 + 6x + 6y = 2 meets the straight 5x - 2y + 6 = 0 at a point Q on the yaxis, then the length of PQ is a) 4 b) 25 c) 5 d) 35 164. The centre of circle inscribed in square formed by the lines x2 - 8x + 12 = 0 and y2 -14y + 45 = 0, is a) (4, 7) b) (7, 4) c) (9, 4) d) (4, 9) 165. If one of the diameter of the x2 + y2 - 2x - 6y + 6 = 0 is a chord to the circle with centre (2, 1), then the radius of circle is : a) 3 b) 2 c) 3 d) 2 . 166. The tangent at (1, 7) to the curve x2 = y - 6 touches the circle x2 + y2 + 16x + 12y + c = 0 at : a) (6, 7) b) (-6, 7) c) (6, -7) d) (-6, -7) 167. A line through (0, 0) cuts the circle x2 + y2 - 2ax = 0 at A and B, then locus of the centre of the circle drawn AB as diameter is :, a) x2 + y2 - 2ay = 0 b) x2 + y2 + ay = 0 c) x2 + y2 + ax = 0 d) x2 + y2 - ax = 0 168. Equation of radical axis of circles x2 + y2 - 3x - 4y + 5 = 0 and 2x2 + 2y2 - l0x - 12y + 12 = 0 is: a) 2x + 2y -1 = 0 b) 2x + 2y + 1 = 0 c) x + y + 7 = 0 d) x + y - 7 = 0
Ma ths Ac ade my Par bha ni
x2 + y2 - 4x + 6y - 12 = 0 is
157. If a circle passes through the point (a, b) and cuts the circle x2 + y2 = 4 orthogonally, then the locus of its centre is : a) 2ax + 2by + {a2 + b2 + 4) = 0 b) 2ax + 2by - (a2 + b2 + 4) = 0 c) 2ax - 2by + (a2 + b2 + 4) = 0 d) 2ax - 2by - (a2 + b2 + 4) = 0 158. If the lines 2x + 3y + 1 = a and 3x - y - 4 = a lies along diameter of a circle of circumference 10, then the equation of the circle is : a) x2 + y2 - 2x + 2y - 23 = 0 b) x2 + y2 - 2x - 2y - 23 = 0
169. The equation of the circle which passes through the intersection of x2 + y2 + 13x - 3y = 0 and 2x2 + 2y2 + 4x -7y - 25 = 0 and whose centre lies on 13x + 30y = 0, is : a) x2 + y2 + 30x -13y - 25 = 0 b) 4x2 + 4y2 + 30x -13y - 25 = 0 c) 2x2 + 2y2 + 30x -13y - 25 = 0 d) x2 + y2 + 30x -13y + 25 = 0 170. The number of common tangents that can be drawn to two circles x2 + y2 = 6x and x2 + y2 + 6x + 2y + 1 = 0 is : a) 4 b) 5 c) 2 . d) 1 171. The equation of the circle of radius 5 and touching the co-ordinate axes in third quadrant is : a) (x - 5)2 + (y + 5)2 = 25 b) (x + 4)2 + (y + 4)2 = 25 2 2 c) (x + 6) + (y + 6) = 25 d) (x + 5)2 + (y + 5)2 = 25 172. If P is a point such that the ratio of the squares of the lengths of the tangents from P to the circles x2 + y2 + 2x - 4y - 20 = 0 and x2 + y2 - 4x + 2y - 44 = 0 is 2 : 3, then the locus of P is a circle with centre: a) (7, - 8) b) (-7, 8) c) (7, 8) d) ( -7, - 8) 173. The circle x2 + y2 - 6x - 8y + 9 = 0 touches externally a circle with centre at origin. Then the radius of the second circle is a) 1 b) 16 c) 21 d) none of these 174. The locus of the centre of the circle which cuts the circles x2 + y2 + 2g1x + 2f1y + c = 0 and x2 + y2 + 2g2x + 2f2y + c2 = 0 orthogonally is a) The radical axis of the given circles b) a conic c) another circle d) none of these 175. One diameter of a circle is the join of A(-3, 7) and B(2, -5). The tangent at A to the circle is a) 5x - 12y + 99 = 0 b) 5x - 12y - 70 = 0 c) 5x - 12y + 44 = 0 d) none of these 176. The circle x2 + y2 = 9 meets the coordinate axes at A, B, C and D. Then the area of the square ABCD is a) 9 b) 36 c) 18 d) none of these . 177. From a point on the line x - y = 4, the lengths of the tangents to the two circles x2 + y2 - 9 = 0 and x2 + y2 - 2x + 8y - 7 = 0 are equal. Then the point is a) (5, -2) b) (-5, 1) c) (5, 1) d) (1, 5) 178. The line x - 3y = c meets the circle x2 + y2 = 2a2 at exactly one point if c2 = a) 40a2 b) 10a2 2 c) 20a d) none of these 179. The equation of the unit circle concentric with the circle a) x2 + yZ - 4x + 6y - 12 = 0 b) x2 + y2 - 4x + 6y - 15 = 0 c) x2 + y2 - 4x + 6y + 25 = 0 d) x2 + y2 - 4x + 6y + 12 = 0 180. The equations of the circles which touch x = 0, y = 0 and x = c are a) x2 + y2 - cx + cy + (1/4)c2 = 0 b) x2 + y2 + cx - cy + (1/4)c2 = 0 c) x2 + y2 - cx - cy + (1/4)c2 = 0 d) None of these 181.The number of tangents to the circle x2 + y2 - 8x - 6y + 9 = 0, which pass through (3, -2) is a) 1 b) 2 c) 0 d) None of these 182.The centre of the circle 16x2 + 16y2 + 160x - 256y -377 = 0 is a) (-5, 8) b) (5, -8) c) (-10, 16) d) none of these
RMA PBN
a) PQ.RS c) 2PQ.RS PQ + RS
PQ + RS 2 PQ2 + RS2 d) 2 b)
Po pad es Re lian ce
Ma ths Ac ade my Par bha ni
128. The area of the triangle formed by the tangents from the point (4, 3) to the circle x2 + y2 = 9 and the line joining their points of contact is a) 192 b) 192/24 c) 192/25 d) None of these 135. The length of the chord joining the points (4cos, 4sin) and (4cos( + 600), 4sin( + 600)) of the circle x2 + y2 = 16 a) 16 b) 2 c) 8 d) 4 136. Let PQ and RS be the tangents at the extrimities of the diameter PR of a circle of radius r. If PS and QR intersect at a point X on the circumference of the circle, then 2r equals
183. The locus of the point whose shortest distance from the circle x2 + y2 - 2x + 6y - 6 = 0 is equal to its distance from the line x - 3 = 0 a) x2 + 6y - 4x - 9 = 0 b) y2 - 6y + 4x + 9 = 0 2 c) x - 6y - 4x - 9 = 0 d) y2 + 6y - 4x + 9 = 0 184. The equation of normal to the circle x2 + y2 = a2 at the point (x1, y1) of it is a) xx1 + yy1 = a2 b) xy1 - yx1 = 0 c) xy1 + yx1 = 0 d) xy1 - yx1 = a2
185. The equation of normal to the circle x2 + y2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 at the point (x1, y1) of it is a) xx1 + yy1 + g(x + x1) + f(y + y1) + c = 0 b) xx1 - yy1 + g(x - x1) + f(y - y1) + c = 0 c) (y1 + f)x - (x1 + g)y + (gy1 - x1f) = 0 d) (x1 + f)x - (y1 + g)y + (gx1 - y1f) = 0 186. The equation of tangent to the circle x2 + y2 = 64 at the point A(2/3) of it is a) x + 5y + 17 = 0 b) x -
3 y + 16 = 0
c) 5x + y - 17 = 0 d) 5x + y + 17 = 0 #187. The equation of common tangent to the two circles x2 + y2 - 4x + 10y + 20 = 0 and x2 + y2 + 8x - 6y - 24 = 0 is a) 3x - 4y - 11 = 0 b) 3x + 4y + 11 = 0 c) 4x - y - 13 = 0 d) x - 2y - 11 = 0 188. The equation of normal to the circle x2 + y2 = 25 at (-4, -3) is a) 3x - 4y = 0 b) 3x + 4y = 0 c) 4x + 3y + 25 = 0 d) 3x - 4y - 25 = 0 189. The equation of normal to the circle 2x2 + 2y2 - 2x + 4y 6 = 0 at the point (2, -5) is a) 3x - 8y - 18 = 0 b) 3x - 8y = 0 c) 8x + 3y - 1 = 0 d) 8x + 3y - 25 = 0 190. If and are the inclinations of the tangents drawn to the circle x2 + y2 = a2 from the point P, then the locus of point P such that cot.cot = 4 is a) x2 + 4y2 - 3a2 = 0 b) 3x2 - 2xy - 3a2 = 0 2 2 2 c) 4x - 3y + a = 0 d) x2 - 4y2 + 3a2 = 0
Po pad es Re lian ce
205. Four distinct points (2k, 3k), (1, 0), (0, 1) and (0, 0) lie on a circle for a) For integral values of k b) 0 < k < 1 c) k < 0 d) k = 5/13 206. The length of the chord joining the points (4cos, 4sin) 191. The equation of director circle of the circle (x - 2)2 + and (4cos( + 600), 4sin( + 600)) of the circle x2 + y2 = 16 (y - 3)2 = 36 is a) 16 b) 2 a) (x - 2)2 + (y - 3)2 = 72 b) (x + 2)2 + (y + 3)2 = 72 c) 8 d) 4 2 2 2 2 c) (x - 3) + (y - 2) = 72 d) (x + 3) + (y + 2) = 72 207. Let PQ and RS be the tangents at the extrimities of the 192. The circle coaxial with the circles x2 + y2 - 6x + 4y - 8 = 0 diameter PR of a circle of radius r. If PS and QR intersect at and x2 + y2 + 2x + y + 4 = 0 and passing through the origin is a point X on the circumference of the circle, then 2r equals a) x2 + y2 - 2x + 6y = 0 b) 3x2 + 3y2 - x + y = 0 PQ + RS c) 3x2 + 3y2 - 2x + 6y = 0 d) none of these a) PQ.RS b) 2 193. The equation of the circle which is concentric with the circle 2 2 2PQ.RS c) d) PQ + RS x2 + y2 - 4x + 6y - 3 = 0 and having double its area is PQ + RS 2 a) x2 + y2 - 4x + 6y + 3 = 0 b) x2 + y2 - 4x + 6y - 51 = 0 208. The area of the triangle formed by the tangents from the c) x2 + y2 - 4x + 6y - 34 = 0 d) x2 + y2 - 4x + 6y - 19 = 0 point (4, 3) to the circle x2 + y2 = 9 and the line joining their points of contact is 194. The line 2x - y + 1 = 0 is a tangent to the circle at (2, 5) and a) 192 b) 192/24 the centre lies on the line x + y = 9, then the equation of c) 192/25 d) None of these circle is 2 2 2 2 209. The coordinates of point P(/4) on the circle x2 + y2 = 25 a) x + y - 4x - 14y + 3 = 0 b) x + y - 12x - 6y - 20 = 0 a) (1/2, 7/2 ) b) (2, 3) c) x2 + y2 - 4x - 14y + 25 = 0 d) x2 + y2 - 12x - 6y + 25 = 0 c) (5/2, 5/2 ) d) None of these 195. The equation of the director circle of the circle x2 + y2 - 6x 210. The coordinates of a point on the circle x2 + y2 = 9 whose + 4y + 12 = 0 is parameter is /6 a) x2 + y2 - 6x + 4y + 11 = 0 b) x2 + y2 - 4x - 6y - 13 = 0 a) (33/2, 3/2) b) (33, 3/2) c) x2 + y2 - 6x + 4y + 15 = 0 d) x2 + y2 - 2x - 6y + 11 = 0 c) (3/2, 3/2) d) (3/2, 3/2) 196. The tangents from the point P(3, 2) to the circle x2 + y2 - 6x 211. (a, b) and (5, -1) are the end points of the diameter of the - 8y + 23 = 0 meet the circle at the points A and B. If C is circle x2 + y2 + 4x - 4y - 2 = 0, then the values of a, b resp. the centre of the circle, then PACB is a a) 1, 3 b) 3, 1 a) parallelogram b) rectangle c) -1, -3 d) None of these c) rhombus d) Square # Equation of common tangent can be obtained by substracting one equation of circle from another equation.
Ma ths Ac ade my Par bha ni
197. The locus of the point of intersection of the lines xcos + ysin = a and xsin - ycos = b is a circle given by a) x2 + y2 = a2 b) x2 + y2 = a2 - b2 2 2 2 2 c) x + y = a + b d) x2 + y2 = b2 198. The radii of the three circles x2 + y2 - 2x + 2y + 1 = 0, x2 + y2 + 4x - 6y - 3 = 0 and x2 + y2 - 8x - 10y - 8 = 0 are a) in G.P b) in A.P. c) in H.P. d) equal 199. The centres of the three circles x2 + y2 + 4x + 12y + 2 = 0, x2 + y2 - 2x - 6y - 9 = 0 and x2 + y2 = 16 form a) an equilateral triangle b) an isosceles triangle c) a right angled triangle d) are collinear 200. A and B are fixed points in a plane and a point P moves in the plane such that PA = 2 PB, then the locus of P is a) a circle b) a parabola c) an ellipse d) a hyperbola 201. The equation of the diameter of the circle (x - 6)(x - 4) + (y - 8)(y - 2) = 0, parallel to X-axis is a) y = 5 b) y = 7 c) y + 5 = 0 d) y = 3 202. The equation of the circle circumscribing the triangle formed by the lines y = x, y = 3x + 2 and y = 2x is a) x2 + y2 - 3x + 4y = 0 b) x2 + y2 + 6x - 8y = 0 2 2 c) x + y + 6x + 8y = 0 d) x2 + y2 - 6x + 8y = 0 203. The equation of normal the circle x = acos, y = asin at the point P() of it is a) xcos + ysin = a b) xcos - ysin = 0 c) xsin - ycos = 0 d) xsin - ycos = a 204. One of the lines given by the equation 6x2 - xy - y2 = 0 touches the circle x2 + y2 + 2x - 6y + 5 = 0, then the equation of that line is a) 3x + y = 0 b) 2x - y = 0 c) 3x - y = 0 d) x - 2y = 0
A persons probability of success is directly proportional to the belief and execution of their abilities. RMA PBN
You might also like
- Circle: Einstein ClassesDocument20 pagesCircle: Einstein ClassesAnuj AroraNo ratings yet
- Analytical GeometryDocument78 pagesAnalytical GeometryChinnaGurappaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Maths Notes - Circles PDFDocument14 pagesCBSE Class 11 Maths Notes - Circles PDFBhawani Singh Balot100% (1)
- Circle Prob Maths MCQ A DasguptaDocument4 pagesCircle Prob Maths MCQ A DasguptaArjun Here100% (1)
- Percentile: ClassesDocument10 pagesPercentile: ClassesVIBHANSHU SINGHNo ratings yet
- Circle (Part 1)Document20 pagesCircle (Part 1)Sachin Kumar100% (1)
- Notes CircleDocument32 pagesNotes CircleKapil Gupta67% (3)
- Circles & System of Circles QnsDocument8 pagesCircles & System of Circles QnsLokesh Kumar100% (1)
- CircleDocument11 pagesCirclePrajuwalThakurNo ratings yet
- Circle Theory EDocument18 pagesCircle Theory EthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Circle TheoryDocument8 pagesCircle Theoryapi-278074538100% (3)
- Circle-01 - TheoryDocument20 pagesCircle-01 - TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 9 CIRCLE(@MRBEASTJEE)Document22 pages9 CIRCLE(@MRBEASTJEE)vivektendstotan90No ratings yet
- Circle (EXERCISE-1) : Conceptual Question: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15Document7 pagesCircle (EXERCISE-1) : Conceptual Question: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15gaurav nigamNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument70 pagesCircleArun KumarNo ratings yet
- E5 QuestionsDocument3 pagesE5 QuestionsRamchandra MurthyNo ratings yet
- Best Approach: CircleDocument47 pagesBest Approach: CircleARNAV KAPOOR100% (1)
- Maths Notes and Definitions Class 11 Chapter 11 Conic Section Part 1 Circles PDFDocument13 pagesMaths Notes and Definitions Class 11 Chapter 11 Conic Section Part 1 Circles PDFMohsin Manzoor BhatNo ratings yet
- Co OrdinateDocument37 pagesCo OrdinateVincent VetterNo ratings yet
- Circles CPP#04,05 PDFDocument3 pagesCircles CPP#04,05 PDFMaanvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Circle Complete Exercise 1676134670830Document86 pagesCircle Complete Exercise 1676134670830Vikrant OjhaNo ratings yet
- Circles Eamcet Questions - 1Document40 pagesCircles Eamcet Questions - 1umaketham18No ratings yet
- 03 CircleDocument13 pages03 CircleJoseNo ratings yet
- Ref. MCGCL - TT1 233s Circle 04.12.22 FINALDocument2 pagesRef. MCGCL - TT1 233s Circle 04.12.22 FINALUtsav AnalNo ratings yet
- 01 01 Circles 1Document19 pages01 01 Circles 1rohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Circle - Key Concept PDFDocument24 pagesCircle - Key Concept PDFjay soni100% (1)
- Circle TheoryexercisesheetDocument38 pagesCircle TheoryexercisesheetKritikaNo ratings yet
- Circles Part I PDFDocument21 pagesCircles Part I PDFHimanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- 08 Circle SheetDocument63 pages08 Circle Sheetsayan Manna100% (1)
- IIB-1.Circles 1-10Document5 pagesIIB-1.Circles 1-10eamcetmaterials100% (6)
- Circle FinalDocument16 pagesCircle Finaldsfref fewefw100% (1)
- Jee 2014 Booklet2 HWT CirclesDocument10 pagesJee 2014 Booklet2 HWT CirclesvarunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Bansal Classes: Mathematics IDocument12 pagesBansal Classes: Mathematics ISatyanneshi ERNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument121 pagesCircleAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Circle - QuestionsDocument6 pagesCircle - QuestionsNameet JainNo ratings yet
- CIRCLE TheoryDocument3 pagesCIRCLE TheoryARJUN AGGARWALNo ratings yet
- Circles-Aloke SirDocument7 pagesCircles-Aloke Sircsankha95No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 The CircleDocument21 pagesChapter 12 The CircleGaziisrarNo ratings yet
- Mathematics CircleDocument7 pagesMathematics Circleabc159753No ratings yet
- Conic SectionDocument22 pagesConic SectionMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Circles TheoryDocument21 pagesCircles Theorykishangopi123No ratings yet
- Circle PC US935zNDocument31 pagesCircle PC US935zNabhinashNo ratings yet
- Circles PDFDocument8 pagesCircles PDFmathew1965No ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry of Circles - TestDocument5 pagesCoordinate Geometry of Circles - TestajithrailwayNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument30 pagesCirclesSiddhanth VengaliNo ratings yet
- Cicle CPPDocument3 pagesCicle CPPtryambakabanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Family of Circles PDFDocument21 pagesFamily of Circles PDFJohnNo ratings yet
- Circle: Section - I: Straight Objective TypeDocument8 pagesCircle: Section - I: Straight Objective TyperashidNo ratings yet
- Circle (Practice Question)Document14 pagesCircle (Practice Question)Asish Mahapatra50% (2)
- Circle (TN For Faculty)Document19 pagesCircle (TN For Faculty)Raju Singh100% (1)
- Assign - Circle - Set 4 - 2 YearDocument12 pagesAssign - Circle - Set 4 - 2 YearKAPIL SHARMANo ratings yet
- Circle FinalDocument16 pagesCircle Finalileesha mittalNo ratings yet
- Equation of A Circle in Various FormsDocument59 pagesEquation of A Circle in Various FormsPrasann KatiyarNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument5 pagesCircleRon HartNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument201 pagesCirclesRocky Raj100% (1)
- Brahmastra - CircleDocument14 pagesBrahmastra - CircleVikas Mittal100% (1)
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Capr I En1101Document22 pagesCapr I En1101SantoshNo ratings yet
- Ode MCQDocument19 pagesOde MCQSantoshNo ratings yet
- Quality of Life OntarioDocument25 pagesQuality of Life OntarioSantoshNo ratings yet
- Board Pattern PapersDocument8 pagesBoard Pattern PapersSantoshNo ratings yet
- Tahsil Profile: Census of India 2011Document6 pagesTahsil Profile: Census of India 2011SantoshNo ratings yet
- Tahsil Profile: Census of India 2011Document6 pagesTahsil Profile: Census of India 2011SantoshNo ratings yet
- %Q.2 (B) To Compute An Approximate Value of The Integration by The Trapeziodal Method Int (Sinx) From 0 To Pi X 0:pi/100:pi y Sin (X) Z Trap (X, Y)Document1 page%Q.2 (B) To Compute An Approximate Value of The Integration by The Trapeziodal Method Int (Sinx) From 0 To Pi X 0:pi/100:pi y Sin (X) Z Trap (X, Y)SantoshNo ratings yet
- Attendance Management System Software Manual (Ams)Document94 pagesAttendance Management System Software Manual (Ams)Santosh100% (1)
- Scolarship For Higher EducationDocument1 pageScolarship For Higher EducationSantoshNo ratings yet
- Complex NumbersDocument18 pagesComplex NumbersSantoshNo ratings yet
- Gamma FunctionDocument9 pagesGamma FunctionSantoshNo ratings yet
- Credit Indices PrimerDocument13 pagesCredit Indices PrimerSanket PatelNo ratings yet
- 3.5 - Differential CalculusDocument6 pages3.5 - Differential CalculusJustine DublinNo ratings yet
- 4 6021360109643367463 PDFDocument265 pages4 6021360109643367463 PDFEndayenewMollaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document63 pagesChapter 4deathfrombelowpykeNo ratings yet
- Assign4 PDFDocument1 pageAssign4 PDFAkhlaq HusainNo ratings yet
- Linear Response Theory: 3.1 Measurements and Correlation FunctionsDocument32 pagesLinear Response Theory: 3.1 Measurements and Correlation FunctionsJahan ClaesNo ratings yet
- Lectures Matrix FieldDocument358 pagesLectures Matrix FieldLuisgarciaBerlanga100% (1)
- Math Grade 8Document15 pagesMath Grade 8gcimorelli0% (1)
- Activity Sheet in Mathematics 7 Quarter 2-Week 7&8Document9 pagesActivity Sheet in Mathematics 7 Quarter 2-Week 7&8Xyla Joy PerezNo ratings yet
- c1 - Intro and Error AnalysisDocument35 pagesc1 - Intro and Error AnalysisMuhammad FirdawsNo ratings yet
- Tabel PoissonDocument3 pagesTabel PoissonHilmiNo ratings yet
- Chap15 - 240-253Document14 pagesChap15 - 240-253jfarrell_ie5767No ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of AlgorithmsDocument21 pagesDesign and Analysis of AlgorithmsUmer FarooqNo ratings yet
- Module 1.4 Relationship Between Fibonacci Sequence and Golden RatioDocument2 pagesModule 1.4 Relationship Between Fibonacci Sequence and Golden RatioEmmanuel AguadoNo ratings yet
- Discrete-MathematicsDocument557 pagesDiscrete-MathematicsRicardo Elias Roche100% (2)
- The Simple Pendulum: Deriving The Equation of MotionDocument4 pagesThe Simple Pendulum: Deriving The Equation of MotionPriyaranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- Gowda Pharmaceutical Mathematics-ContentsDocument12 pagesGowda Pharmaceutical Mathematics-ContentsSanjeev SinghNo ratings yet
- Maths Formulas For Class 12 - Download PDF For All Concepts and ChaptersDocument6 pagesMaths Formulas For Class 12 - Download PDF For All Concepts and ChaptersHoward0% (1)
- Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos: Bruce E KendallDocument8 pagesNonlinear Dynamics and Chaos: Bruce E KendallHeintz ZaccagniniNo ratings yet
- QuComp - Practical Introduction To Tensor Networks PDFDocument111 pagesQuComp - Practical Introduction To Tensor Networks PDFmaburekNo ratings yet
- Probability DistributionDocument7 pagesProbability DistributionJeff balesNo ratings yet
- Define Loads in Etabs-Part3Document34 pagesDefine Loads in Etabs-Part3Abdul HafeezNo ratings yet
- Rotating Reference Frames and Relative Motion: MEAM 211Document13 pagesRotating Reference Frames and Relative Motion: MEAM 211manoNo ratings yet
- Nptel: Computational Fluid Dynamics For Turbomachinery - Web CourseDocument3 pagesNptel: Computational Fluid Dynamics For Turbomachinery - Web CourseAissa AMOURNo ratings yet
- Chris McMullen - Intermediate Algebra Skills Practice Workbook With Answers - Functions, Radicals, Polynomials, Conics, Systems, Inequalities, and (2021, Zishka Publishing) - Libgen - LiDocument502 pagesChris McMullen - Intermediate Algebra Skills Practice Workbook With Answers - Functions, Radicals, Polynomials, Conics, Systems, Inequalities, and (2021, Zishka Publishing) - Libgen - Liadrian Hernandez100% (2)
- Summer 578 Assignment 2 SolutionsDocument13 pagesSummer 578 Assignment 2 SolutionsGradu8tedOne100% (1)
- MATHS (Social) Model ExamDocument7 pagesMATHS (Social) Model Examhebaallah magdy elshimyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SU (2) LQGDocument67 pagesIntroduction To SU (2) LQGpablomorosNo ratings yet
- OperationDocument7 pagesOperationEmmanuel NicholasNo ratings yet