Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Primary Aldosteronism
Primary Aldosteronism
Uploaded by
Vernadeth DumagatOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Primary Aldosteronism
Primary Aldosteronism
Uploaded by
Vernadeth DumagatCopyright:
Available Formats
VISION A premier university in historic Cavite recognized for excellence in the development of morally upright and globally competitive
individuals.
Republic of the Philippines CAVITE STATE UNIVERSITY Don Severino Delas Alas Campus Indang, Cavite
College of Nursing
Dumagat, Vernadeth B. PRIMARY ALDOSTERONISM Identification
MISSION Cavite State University shall provide excellent, equitable and relevant educational opportunities in the arts, science and technology through quality instruction and relevant research and development activities. It shall produce professional, skilled and morally upright individuals for global competitiveness.
BSN 3-1
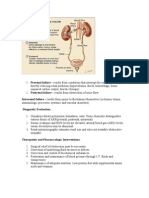
1. A steroid hormone located at adrenal cortex which regulates salt and water balance in the body. 2. Overproduction of minerolocorticoid hormone which regulates sodium in the kidney. 3. Part of the adrenal gland where the hormone aldosterone located. 4. Surgical removal of the adrenal tumor. 5. Inability of the part of the kidney to acidify or concentrate the urine wherein the urine volume is excessive. 6. An adrenal cortex steroid drug used to maintain blood pressure in clients with primary aldosteronism. 7. A benign tumor of the adrenal gland. 8. Most prominent and universal sign of patient with primary aldosteronism. 9. Decline in serum levels of potassium. 10. A decrease in ionized serum calcium level. 11. Part of nephrons leads away from the glumerolus. 12. Small but richly artery located at the neck. 13. A type of adrenalectomy which replacement of corticosteroid may be lifelong. 14. A condition wherein serum is concentrated or increased or an increased in thirst. 15. An abnormality that indirectly results in pathology through a predictable physiologic pathway, a renin producing tumor leads to increased aldosterone, as the body's aldosterone production is normally regulated by renin levels.
Multiple Choice 16. Muscle weakness, cramping and fatigue are signs and symptoms of what particular clinical manifestations in client with primary aldosteronism? a. Hyperkalemia c. Hypokalemia b. Hypothyrodism d. Hyponatremia 17. In client with primary aldosteronism, it is used to assess neuromuscular irritability before tetany and paresthesia occur. a. Serum Free T4 Test c. Sensory Reflex Test b. Trousseaus and Chvosteks d. Neurologic Vital Signs Test 18. In client taking spironolactone, which of the following nursing responsibility should be in need of supervision? a. Taking the drug early because of frequent urination. b. Weighing on monthly basis and record it. c. Avoid foods rich in potassium. d. None of the above. 19. What was the primary action of spironolactone? a. Blocks the effects of aldosterone in the renal tubule. b. Stimulates the adrenal cortex to synthesize and secrete adrenocortical hormones. c. Responsible for anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive (glucocorticoid), and salt-retaining (mineralocorticoid) actions. d. None of the above. 20. Post-operative nursing management of client undergone adrenalectomy are shown below except. a. Provide comfort measures. b. Watch out for Tachycardia and Hypotension. c. Provide rest periods. d. Take V/S to detect early signs and symptoms of adrenal insufficiency and hemorrhage. 21. What are the indications of Alkalosis in client with primary aldosteronism? a. Decrease in cardiac output and increase in systemic vascular resistance. b. Increase in pH and decrease in partial carbon dioxide. c. Increase in pH and increase in serum bicarbonate concentration. d. All of the above. 22. What is the useful diagnostic test for primary aldosteronism? a. Fasting Blood Sugar c. Deoxycorticosterone Acetate b. Bilateral Adrenal-Venous (DOCA) test Sampling d. Renin-Aldosterone Test
23. Clinical manifestation of primary aldosteronism in relation to insulin production. a. Glucose Intolerance c. Polydypsia b. Hyperglycemia d. Glycosuria 24. What type of adrenalectomy involves suppression of normal adrenal by high levels of adrenal hormones? a. Bilateral Adrenalectomy c. Open Adrenalectomy d. Laparoscopic b. One Adrenal Right Adrenalectomy 25. What was the primary action of Renin? a. Decrease the secretion of enzyme by the juxtaglumelurar cells of the kidney. b. Hydrolyzes angiotensinogen to angiotensin I. c. Both a and b. d. Neither a and b. 26. One side effect of spironolactone is increase thirst, what is an immediate nursing intervention given below? a. Give plenty of water. c. Instruct to eat citrus fruits. b. Suck on sugarless food. d. None of the above. 27. Clinical Manifestations of client with primary aldosteronism are high or normal serum sodium level and a low serum potassium level. What were its diagnostic studies indicates? a. Low serum aldosterone and high serum renin levels. b. Low serum aldosterone and low serum renin levels. c. High serum aldosterone and low serum renin levels. d. High serum aldosterone and high serum renin levels. 28. Coricosteroid are used extensively for adrenal insufficiency. Their antiinflammatory and anti-allergy actions make corticosteroids effective in treating rheumatic or connective tissue diseases such as: a. Multiple Sclerosis and Osteoporosis b. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis c. Gouty Arthritis and Osteoarthritis d. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Osteomyelitis 29. What causes primary aldosteronism to categorize its universal sign to be arterial hypertension? a. It occurs during visits to the doctor but may have normal blood pressure at home. b. It affects the part of the circulatory system that connects the heart and lungs interfering with the lungs ability to transfer oxygen and the heart ability to pump blood. c. The condition affects blood flow to organs such as the kidneys, placenta, brain, and liver.
d. It affects the nerve receptors, carotid sinus which greatly contributes to regulate heart rate and blood pressure. 30. In what type of adrenal hormone does aldosterone belong? a. Glucocorticoid Hormones c. Adrenal Sex Hormones b. Mineralocorticoid Hormones d. None of the above
ANSWERS: Identification Part: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Aldosterone Primary Aldosteronism Adrenal Cortex Adrenalectomy Polyuria Corticosteroid Adrenal Adenoma Hypertension 9. Hypokalemia 10. Hypocalcemia 11. Renal Tubule 12. Carotid Sinus 13. Bilateral Adrenalectomy 14. Polydipsia 15. Secondary Aldosteronism
Multiple Choice Part with Rationale: 16. C. Hypokalemia. Skeletal muscle weakness, thread rapid pulse, faint heart sound, decrease BP, lethargy and decrease or absent of reflexes are more profound signs and symptoms of hypokalemia. 17. B. Trousseaus and Chvosteks Test. It is used to assess for hypocalcemia which is a clinical manifestation of client with primary aldosteronism. 18. B. Weighing on monthly basis and record it. One nursing responsibility for client who is taking spironolactone is to instruct the client to weigh on regular basis, same time, same clothing and record the weight on a calendar daily. 19. A. Blocks the effects of aldosterone in the renal tubule. It causes the loss of sodium and water therefore retention of potassium in the kidney. 20. B. Watch out for Tachycardia and Hypotension. This post-op nursing management is mostly seen in patient having metabolic alkalosis. 21. C. Increase in pH and increase in serum bicarbonate concentration. Metabolic Alkalosis can be seen in patient with primary aldosteronism as manifested by increased hydrogen ions secreted in the renal tubule. 22. D. Renin-Aldosterone Test. This is the measurement of aldosterone excretion rate after salt loading. 23. A. Glucose Intolerance. Hypokalemia which is a clinical manifestation in client with primary aldosteronism interferes with insulin secretion from the pancreas.
24. B. One Adrenal. It is temporary because of suppression of normal adrenal by high levels of adrenal hormones. One adrenal gland must be removed in this operation. 25. C. Both a and b. Renin had a big part on diagnostics of primary aldosteronism. 26. B. Suck on sugarless food. It is done together with frequent mouth care to lubricate dry oral mucosa of the patient. 27. C. High serum aldosterone and low serum renin levels. In high serum aldosterone, there is an increase in sodium retention while in low serum renin levels; there is a decrease in secretion of the enzyme by the juxtaglumelurar cells of the kidney. 28. B. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis. The symptoms from these diseases are caused by the immune system mistakenly attacking the body's own tissues, causing an inflammatory reaction (inflammation). 29. D. It affects the nerve receptors, carotid sinus which greatly contributes to regulate heart rate and blood pressure. Carotid Sinus is an artery located at the neck which mainly affects arterial blood pressure. 30. B. Mineralocorticoid Hormones. Types of steroid hormones which regulates salt and water balance in the body. References: Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing 12th Edition Volume 1, Brunner and Suddarth, pp. 1284-1285 2011s Lippincotts Nursing Drug Guide, Amy Karch, pp. 1101-1102 Merriam Websters Medical Dictionary, 2006.
You might also like
- Pharmacology Test 3 ReviewDocument6 pagesPharmacology Test 3 ReviewNatalia BortellNo ratings yet
- INTERNAL MEDICINE - Nephrology SystemDocument8 pagesINTERNAL MEDICINE - Nephrology SystemAiswarya100% (1)
- Case Report FarterDocument7 pagesCase Report Fartersarikusumaa100% (2)
- Addisons DiseaseDocument12 pagesAddisons DiseaseChinju CyrilNo ratings yet
- 2019 Explanation k2Document261 pages2019 Explanation k2berdaderagaNo ratings yet
- 6 Krok GitDocument14 pages6 Krok GitRodriguez Vivanco Kevin DanielNo ratings yet
- Addison DiseaseDocument23 pagesAddison DiseaseKompari EvansNo ratings yet
- True: Normal Range Is 3.5-5.0 Meq/L (So This Is Hypokalemia)Document8 pagesTrue: Normal Range Is 3.5-5.0 Meq/L (So This Is Hypokalemia)Megan BarreraNo ratings yet
- Pathology Exam Review MCQsDocument6 pagesPathology Exam Review MCQsyonem11615No ratings yet
- Revision MCQsDocument6 pagesRevision MCQswiamNo ratings yet
- NCM103 12th Endoc IIDocument9 pagesNCM103 12th Endoc IIKamx MohammedNo ratings yet
- WatermelonDocument27 pagesWatermelonSunny Mae T PuigNo ratings yet
- SurgDocument8 pagesSurgJudi Townsend100% (1)
- ACP Board Review Nephrology 20052ndDocument35 pagesACP Board Review Nephrology 20052nddoctormido2010100% (1)
- Internal medicine שחזוריםDocument66 pagesInternal medicine שחזוריםLaith Bajis NassarNo ratings yet
- GroupA RenalDisordersDocument13 pagesGroupA RenalDisordersPaulNo ratings yet
- Siadh and Di QuestionsDocument18 pagesSiadh and Di QuestionsRegiever Salvante100% (1)
- Renal ReviewDocument10 pagesRenal ReviewZen Lenin CaroNo ratings yet
- Medicine/Medicine 4th Year 2016Document25 pagesMedicine/Medicine 4th Year 2016abmad t45No ratings yet
- Prelim Ans KeyDocument13 pagesPrelim Ans KeyBernz KyNo ratings yet
- Case Study 10 Renal FailureDocument19 pagesCase Study 10 Renal FailureAriadne Cordelette100% (2)
- Musawi 25Document22 pagesMusawi 25Full MarksNo ratings yet
- First Part Exam - October 2020Document16 pagesFirst Part Exam - October 2020hassan mohamedNo ratings yet
- 20 Board QuestionsDocument6 pages20 Board QuestionsAnne de VeraNo ratings yet
- Acute Glomerulonephritis (Agn)Document42 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis (Agn)Rowshon AraNo ratings yet
- CONNDocument1 pageCONNPhilip Gene II MalacasNo ratings yet
- Acute Biological CrisisDocument107 pagesAcute Biological CrisisJenes CernaNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis of Liver, Liver Cancer, HepatitisDocument72 pagesCirrhosis of Liver, Liver Cancer, HepatitisBabita DhruwNo ratings yet
- 28.03.23 Nephrology SeminarDocument5 pages28.03.23 Nephrology SeminarJerin XavierNo ratings yet
- RENALDocument9 pagesRENALChelsea GulfanNo ratings yet
- KGMC BLOCK L 2023. Revisedd (Follow Yellow)Document29 pagesKGMC BLOCK L 2023. Revisedd (Follow Yellow)noorNo ratings yet
- Homeostatis F & EDocument11 pagesHomeostatis F & EYa Mei LiNo ratings yet
- Ug NotesDocument538 pagesUg NotesSteven IStudy SmithNo ratings yet
- F&E ExamDocument3 pagesF&E ExamDino PringNo ratings yet
- First Part Exam - March 2021Document28 pagesFirst Part Exam - March 2021hassan mohamedNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Solve Past PaperDocument26 pagesEndocrine Solve Past Paperplex servery100% (1)
- Compre F&EDocument6 pagesCompre F&EArcon AlvarNo ratings yet
- CT Week9Document4 pagesCT Week9Princess Laira CañeteNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument15 pagesAcute Renal FailureFilip DadićNo ratings yet
- Intrarenal Failure - Results From Injury To The Kidneys Themselves (Ischemia, ToxinsDocument2 pagesIntrarenal Failure - Results From Injury To The Kidneys Themselves (Ischemia, ToxinsReizen MangilaNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms Vital SignsDocument3 pagesSigns and Symptoms Vital SignsCris CandoNo ratings yet
- Observation Report - Hemodialysis - Kit P. RoaquinDocument15 pagesObservation Report - Hemodialysis - Kit P. Roaquineljhayar_18No ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest Due To Lymphocytic ColitisDocument4 pagesCardiac Arrest Due To Lymphocytic Colitisjhuzt4_facebook_343onlyNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes 4Document8 pagesFluids and Electrolytes 4Potchiee PfizerNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes2Document8 pagesFluids and Electrolytes2Potchiee PfizerNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes2Document8 pagesFluids and Electrolytes2Potchiee PfizerNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tests GosayeDocument188 pagesDiagnostic Tests GosayeAbdii TolasaNo ratings yet
- Surgery Quiz Topics 1 5Document48 pagesSurgery Quiz Topics 1 5Hello AngelNo ratings yet
- Managing A Patient With Es RD 23Document3 pagesManaging A Patient With Es RD 23Undefined RegisterNo ratings yet
- Glomerulonephritis 1Document2 pagesGlomerulonephritis 1Riny KhurshidNo ratings yet
- Disorders of AcidDocument36 pagesDisorders of AcidMariela Manrique ChavezNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Fluid and Electrolytes FVD FVEDocument7 pagesMedical Surgical Fluid and Electrolytes FVD FVEMichaelaKatrinaTrinidadNo ratings yet
- Integrated Therapeutics IiDocument165 pagesIntegrated Therapeutics IiSalahadinNo ratings yet
- Questions About KidneysDocument30 pagesQuestions About KidneysKristine Mae AbrasaldoNo ratings yet
- NCLEX HomeostasisDocument10 pagesNCLEX HomeostasisAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Renal Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Renal Tissue PerfusionHendra Tanjung100% (4)
- ABC Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesABC Lecture NotesLady Shayne YapNo ratings yet
- CirrhosisDocument10 pagesCirrhosisJames FlanneryNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandLiver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis-Pedrosa, Joan ADocument27 pagesDiagnosis-Pedrosa, Joan AJoan Alde PedrosaNo ratings yet
- Ex10 - Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesEx10 - Cardiovascular System葡萄蘿蔔No ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Prep U.odtDocument9 pagesChapter 20 Prep U.odtShade ElugbajuNo ratings yet
- The Antipsychiatry Movement: Dead, Diminishing, or Developing?Document3 pagesThe Antipsychiatry Movement: Dead, Diminishing, or Developing?José Alberto Pacheco OsornioNo ratings yet
- PsychiatryDocument23 pagesPsychiatryNaveenKumarNo ratings yet
- Reticulocytes Count: Prepared by Hadeel Al SadounDocument10 pagesReticulocytes Count: Prepared by Hadeel Al SadounAhmed GaberNo ratings yet
- Usmle ExamDocument13 pagesUsmle ExamAmal Alameen67% (3)
- Adrogué-Madias Acido-Base (NEJM, 1998)Document5 pagesAdrogué-Madias Acido-Base (NEJM, 1998)amazeyragNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus NCPDocument5 pagesDiabetes Mellitus NCPCazze SunioNo ratings yet
- Glucagon For Injection Glucagon For Injection: Information For The PhysicianDocument2 pagesGlucagon For Injection Glucagon For Injection: Information For The PhysicianBryan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Joycie 4-7Document2 pagesJoycie 4-7Jay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Facet Syndrome - BogdukDocument8 pagesLumbar Facet Syndrome - BogdukSamSchroetkeNo ratings yet
- Harrisons Endocrinology 4Th Edition J Larry Jameson Full ChapterDocument57 pagesHarrisons Endocrinology 4Th Edition J Larry Jameson Full Chaptersally.kimberlin556100% (3)
- Guia Aha Asa Stroke PDFDocument77 pagesGuia Aha Asa Stroke PDFAndrea Cayufilo CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Microbiota Therapy Acts via a Regulatory T Cell MyD88:RORγt Pathway to Suppress Food AllergyDocument29 pagesMicrobiota Therapy Acts via a Regulatory T Cell MyD88:RORγt Pathway to Suppress Food AllergyFelipe Gálvez JirónNo ratings yet
- Eszopiclone LunestaDocument25 pagesEszopiclone LunestaNadia BashirNo ratings yet
- Case Control StudyDocument23 pagesCase Control StudySwapna JaswanthNo ratings yet
- Perilite Exposure JuecoDocument3 pagesPerilite Exposure JuecoTrishaNo ratings yet
- Price List All Disc SM - DSM 170622Document1 pagePrice List All Disc SM - DSM 170622Rhesa GuttamaNo ratings yet
- Acupoint Stimulation For Fibromyalgia 2013Document15 pagesAcupoint Stimulation For Fibromyalgia 2013silkofosNo ratings yet
- Case Study PP - AdhdDocument21 pagesCase Study PP - Adhdapi-482726932100% (1)
- Periampullary Carcinoma - Surgical Treatment - NCBI Bookshelf PDFDocument4 pagesPeriampullary Carcinoma - Surgical Treatment - NCBI Bookshelf PDFAsif.N.IqbalNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sumait Hospital: Final Investigation ReportDocument10 pagesDr. Sumait Hospital: Final Investigation ReportShafici CqadirNo ratings yet
- CircumcisionDocument3 pagesCircumcisionHasan MohammedNo ratings yet
- Ic-01-049 Infection Control in Clinical EngineeringDocument4 pagesIc-01-049 Infection Control in Clinical EngineeringDerick RanaNo ratings yet
- FEMM Charting Brochure (Bi-Fold)Document2 pagesFEMM Charting Brochure (Bi-Fold)teachingtashoilsNo ratings yet
- Takushige Retreat J LSTRDocument5 pagesTakushige Retreat J LSTRPascalis Adhi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Red Eye - Conjunctivitis I Dr. Nuke Erlina Mayasari, SPMDocument23 pagesRed Eye - Conjunctivitis I Dr. Nuke Erlina Mayasari, SPMismkipendprowil2No ratings yet
- The Art of Kindness - Mayo Clinic Health SystemDocument1 pageThe Art of Kindness - Mayo Clinic Health SystemAlesandra Lei De LeonNo ratings yet
- Amniotic Fluid EmbolismDocument13 pagesAmniotic Fluid Embolismelfa riniNo ratings yet