Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acct 402
Acct 402
Uploaded by
zhentang89Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- PMAN635 Course OverviewDocument10 pagesPMAN635 Course OverviewDerrick Antonio GardnerNo ratings yet
- Unit Assessment Pack (UAP) - Cover Sheet: Student and Trainer/Assessor DetailsDocument44 pagesUnit Assessment Pack (UAP) - Cover Sheet: Student and Trainer/Assessor DetailsKomal Sharma0% (1)
- 2021 QTI MGT489 Course OutlineDocument5 pages2021 QTI MGT489 Course OutlineNahida akter jannat 1712024630No ratings yet
- MGMT3101 International Business Strategy S22014Document24 pagesMGMT3101 International Business Strategy S22014BonnieBaoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Understanding Culture, Society & PoliticsDocument7 pagesSyllabus Understanding Culture, Society & PoliticsVIRGILIO JR FABINo ratings yet
- CGT 163 Fall 2019 Syllabus 08-16-2019Document7 pagesCGT 163 Fall 2019 Syllabus 08-16-2019api-477909819No ratings yet
- MANA 5361 Spring Sec 703Document7 pagesMANA 5361 Spring Sec 703paratroop66620000% (1)
- International Business SyllabusDocument5 pagesInternational Business SyllabusTeguh SulistiyonoNo ratings yet
- FINS3641 Course Outline (Part A B Combined) S12014 CurrentDocument18 pagesFINS3641 Course Outline (Part A B Combined) S12014 CurrentDeagle_zeroNo ratings yet
- ACCT102 MA Course Outline 2021-2022 S2 FinalDocument9 pagesACCT102 MA Course Outline 2021-2022 S2 FinalCherlin LeongNo ratings yet
- Course Outline ManagementDocument10 pagesCourse Outline ManagementnaseembalochNo ratings yet
- Badm 106 2019 04 02Document6 pagesBadm 106 2019 04 02Vishal GuptaNo ratings yet
- SMK K48isb Jan-April 2024Document9 pagesSMK K48isb Jan-April 2024Anh Nguyen Tran NhatNo ratings yet
- Level 5 Project Management FinalDocument8 pagesLevel 5 Project Management FinalDr Kerry GoughNo ratings yet
- FINC765NY Portfolio MASTER SYLLABUS Fall 2020 PDFDocument10 pagesFINC765NY Portfolio MASTER SYLLABUS Fall 2020 PDFRahil VermaNo ratings yet
- FINS5513 S2 2013 Course OutlineDocument12 pagesFINS5513 S2 2013 Course OutlineTanya HoNo ratings yet
- FINN 100-Salman Khan Spring 2019Document8 pagesFINN 100-Salman Khan Spring 2019Qudsia AbbasNo ratings yet
- AC2104 Semester 1, 2017 18: S/No Components % Individual GroupDocument10 pagesAC2104 Semester 1, 2017 18: S/No Components % Individual GroupcccqNo ratings yet
- All About Learning Outcomes - DR Vijay Kumar Chattu MD, MPHDocument5 pagesAll About Learning Outcomes - DR Vijay Kumar Chattu MD, MPHDr Vijay Kumar Chattu MD, MPHNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument9 pagesSyllabusapi-308313181No ratings yet
- MKTG 742Document9 pagesMKTG 742venkat raNo ratings yet
- BSC Investment and Financial Risk ManagementDocument13 pagesBSC Investment and Financial Risk ManagementchimaegbukoleNo ratings yet
- MGMT1001 Managing Organisations and People S12015Document16 pagesMGMT1001 Managing Organisations and People S12015Sarthak GargNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument10 pagesSyllabus임민수No ratings yet
- Flip CourseOutline - STM - Fall 16-05sep16Document7 pagesFlip CourseOutline - STM - Fall 16-05sep16Saad SohailNo ratings yet
- PGP Handbook 2011 13Document59 pagesPGP Handbook 2011 13rajiimk07No ratings yet
- Course Outline BComm Fall 2021Document7 pagesCourse Outline BComm Fall 2021simrah zafarNo ratings yet
- FINS3616 - Course OutlineDocument15 pagesFINS3616 - Course OutlineJulie ZhuNo ratings yet
- CB4303 Strategy & Policy: Department of ManagementDocument6 pagesCB4303 Strategy & Policy: Department of ManagementhaileyNo ratings yet
- Neu - Aep: International Business PolicyDocument5 pagesNeu - Aep: International Business PolicyHuong VuNo ratings yet
- Ion IndividualsDocument6 pagesIon IndividualsVladimir IvanovNo ratings yet
- MAN7064 - International Operations and Project Management Assessment 2020-06Document6 pagesMAN7064 - International Operations and Project Management Assessment 2020-06Shah Taj Aftab Shaikh0% (1)
- Published: January 2018 ISBN (Digital) : 978-1-4533-8682-8Document6 pagesPublished: January 2018 ISBN (Digital) : 978-1-4533-8682-8Ajay Kumar BinaniNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management - MGT532: Course DescriptionDocument9 pagesStrategic Management - MGT532: Course DescriptionMohamed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior. A Course - Outline - S 2022Document6 pagesConsumer Behavior. A Course - Outline - S 2022Mehrab AliNo ratings yet
- Ebus635 Business Simulation and Analysis Module Handbook 2023-24Document13 pagesEbus635 Business Simulation and Analysis Module Handbook 2023-24Sagar SubedarNo ratings yet
- Om 636 - Syllabus RevisedDocument5 pagesOm 636 - Syllabus RevisedNda-jiya SuberuNo ratings yet
- Unit of Study Outline FINC2012bDocument8 pagesUnit of Study Outline FINC2012bMichaelTimothy0% (1)
- Subject Overview ACC3044 (March 2014)Document6 pagesSubject Overview ACC3044 (March 2014)Gurrajvin SinghNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship & SMEs MGT641-CDFDocument8 pagesEntrepreneurship & SMEs MGT641-CDFMai El RihanyNo ratings yet
- Applied Corporate FinanceDocument8 pagesApplied Corporate FinanceSafi Ullah KhanNo ratings yet
- TIM 305 Financial Management of Travel Industry SPRING 2022 W F 09:00 - 10:15 A.M. Jan 10 - May 13 Kwanglim SeoDocument6 pagesTIM 305 Financial Management of Travel Industry SPRING 2022 W F 09:00 - 10:15 A.M. Jan 10 - May 13 Kwanglim SeoS JNo ratings yet
- FINS3616 International Business Finance S12013Document17 pagesFINS3616 International Business Finance S12013Dev LioNo ratings yet
- Module 3.1 Program Outcomes and Student Learning OutcomesDocument12 pagesModule 3.1 Program Outcomes and Student Learning OutcomesKaren FrancoNo ratings yet
- UEL-SG-7001 - Module SpecificationDocument4 pagesUEL-SG-7001 - Module SpecificationNea MillsNo ratings yet
- Course Outline FINS3616Document12 pagesCourse Outline FINS3616Erica DaviesNo ratings yet
- FINN 100 Course OutlineDocument9 pagesFINN 100 Course Outlinerizwanf026No ratings yet
- Acct408 - Cheng Nam SangDocument5 pagesAcct408 - Cheng Nam SangHohoho134No ratings yet
- BBA Syllabus 2021-22Document56 pagesBBA Syllabus 2021-22Muskan hamdevNo ratings yet
- Course Guide Sem. 1 2011Document6 pagesCourse Guide Sem. 1 2011sir bookkeeperNo ratings yet
- Outline OS-617 MSSC Spring 2021Document14 pagesOutline OS-617 MSSC Spring 2021Heena ZubairNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For TECH6102Document9 pagesSyllabus For TECH6102api-342200066No ratings yet
- Summer Internship GuidelinesDocument9 pagesSummer Internship GuidelinesTamseel NajmiNo ratings yet
- Finn 400 Outline Spring 2020 PDFDocument8 pagesFinn 400 Outline Spring 2020 PDFadam jamesNo ratings yet
- ACCTFIN 7017 - Financial Statement Analysis (M) - Course OutlinesDocument7 pagesACCTFIN 7017 - Financial Statement Analysis (M) - Course OutlinesRanjeetaTiwariNo ratings yet
- Setara 2009 - CriteriaDocument2 pagesSetara 2009 - CriteriajosuyaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BUS 520 Summer 2009Document25 pagesSyllabus BUS 520 Summer 2009CSCaseNo ratings yet
- Course Outline 240 02Document7 pagesCourse Outline 240 02Vinayak DixitNo ratings yet
- Global Business Strategies SummerDocument5 pagesGlobal Business Strategies SummerCalidad LafNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Course OutlineDocument9 pagesHuman Resource Management Course OutlineEphrem BelayNo ratings yet
- Co Operative Education Revised June 2011Document50 pagesCo Operative Education Revised June 2011ibrahimshareef1No ratings yet
- Assessment and Feedback in Higher Education: A Guide for TeachersFrom EverandAssessment and Feedback in Higher Education: A Guide for TeachersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Leadership U.: Preparing Students for College, Career, and Beyond: Grades 11–12: Thriving in College and BeyondFrom EverandLeadership U.: Preparing Students for College, Career, and Beyond: Grades 11–12: Thriving in College and BeyondNo ratings yet
- 2013-14 Academic CalendarDocument1 page2013-14 Academic Calendarzhentang89No ratings yet
- December 2012: Monday Tuesday Wednesday ThursdayDocument5 pagesDecember 2012: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursdayzhentang89No ratings yet
- Set C Set D: 2位 (pax) $118++ 2位 (pax) $138++ 8位 (pax) $458++ 8位 (pax) $558++Document2 pagesSet C Set D: 2位 (pax) $118++ 2位 (pax) $138++ 8位 (pax) $458++ 8位 (pax) $558++zhentang89No ratings yet
- Prepaid SIM Card 98 Card Top Up 200 Taxi Fare From MRT 16 Dinner 30 Wellcome Market 447.9Document2 pagesPrepaid SIM Card 98 Card Top Up 200 Taxi Fare From MRT 16 Dinner 30 Wellcome Market 447.9zhentang89No ratings yet
- Chap 001Document33 pagesChap 001zhentang89No ratings yet
- ACCT5955 Management Accounting Control Systems S12005Document17 pagesACCT5955 Management Accounting Control Systems S12005Sucipto Antoni100% (1)
- CS101 Lab 01Document90 pagesCS101 Lab 01chaosofdoomxNo ratings yet
- Arch1102 - 2010 OutlineDocument8 pagesArch1102 - 2010 OutlineZoha A. FardNo ratings yet
- Advanced Research Methods in ArchitectureDocument9 pagesAdvanced Research Methods in Architectureksnbh007100% (1)
- Topics in Product Development in Mechanical EngineeringDocument12 pagesTopics in Product Development in Mechanical EngineeringYASH BHAVSARNo ratings yet
- ENGG2600 - Lecture 1 IntroductionDocument41 pagesENGG2600 - Lecture 1 IntroductionValar MorghulisNo ratings yet
- MKT 113-12120 Fa '15Document14 pagesMKT 113-12120 Fa '15Matthew CropleyNo ratings yet
- ACC 2203 Syllabus Sp-2018Document12 pagesACC 2203 Syllabus Sp-2018Jay REyNo ratings yet
- MAT172 SP23 PaulDocument11 pagesMAT172 SP23 PaulGiselle KyandaNo ratings yet
- Course Manual - CPC-2022Document13 pagesCourse Manual - CPC-2022keerthana RaaviNo ratings yet
- Isom2500 2018Document3 pagesIsom2500 2018Yanis ChanNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Econ252 (AY2023-24 Term 1) 2Document4 pagesCourse Outline Econ252 (AY2023-24 Term 1) 2ANG ZHENG NANNo ratings yet
- Iso Obe Syllabus Opportunity SeekingDocument12 pagesIso Obe Syllabus Opportunity SeekingPatrick ManatadNo ratings yet
- FRL 2013.03 SPRING 2021 SyllabusDocument9 pagesFRL 2013.03 SPRING 2021 SyllabusBigAsianPapiNo ratings yet
- 2022 2023 FTD Cve 4 Ce PC405Document5 pages2022 2023 FTD Cve 4 Ce PC405DeepakNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Course OutlineDocument11 pagesStrategic Management Course OutlineRajat SinghNo ratings yet
- OPD Discipline Handbook 2020 - 12.4.20Document72 pagesOPD Discipline Handbook 2020 - 12.4.20Erolle Linus MirandaNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Entp6v99.001.11s Taught by Daniel Bochsler (dcb091000)Document13 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Entp6v99.001.11s Taught by Daniel Bochsler (dcb091000)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Community Mediation: Theory and PracticeDocument105 pagesCommunity Mediation: Theory and Practiceeliasox123100% (2)
- Media and Global Communication MCC-UE 1300Document7 pagesMedia and Global Communication MCC-UE 1300Hoang CaoNo ratings yet
- BUSN 6530 Syllabus Su19Document4 pagesBUSN 6530 Syllabus Su19lookingforfunonlyNo ratings yet
- POG 100 Course Outline F2007Document8 pagesPOG 100 Course Outline F2007Samuel100% (1)
- Unit 16 Marketing Essentials For Travel and Tourism June 2020Document10 pagesUnit 16 Marketing Essentials For Travel and Tourism June 2020Dyya EllenaNo ratings yet
- Geog 301 SyllabusDocument4 pagesGeog 301 SyllabusbradleysgardenerNo ratings yet
- FIN 5411 - Financial Management - Spring 2021 - Akashi HongoDocument5 pagesFIN 5411 - Financial Management - Spring 2021 - Akashi HongoLimSiEianNo ratings yet
- American Culture SyllabusDocument5 pagesAmerican Culture Syllabuspaleoman8No ratings yet
Acct 402
Acct 402
Uploaded by
zhentang89Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acct 402
Acct 402
Uploaded by
zhentang89Copyright:
Available Formats
This course outline (AY2012 Term 1) is provided to you as a sample course outline.
There may be minor changes in the course outline for the coming term.
Instructor: Joanne TAY FOO See Liang Date: 16/10/2012
ACCT402 Governance & Risk Management
Course Outline 2012/2013 Term 1
A. Instructor and Contact Information Dr Joanne Tay Associate Professor of Accounting (Education) School of Accountancy(SOA) Singapore Management University Singapore 178900 Tel: (65) 6808-5175 Fax: (65) 6828-0600 Email: joannetay@smu.edu.sg
Consultation: Phone and email queries are welcome at any time. Please make an appointment for office consultation.
B. Course Description Recurring scandals have highlighted the need for improved standards of governance; continuing volatility has demonstrated the need for more effective risk management systems to deliver sustainable performance and satisfactory conformance. The market continues to demand assurance from organisations in both these areas. Governance & Risk Management (GRM)
explores the drive for greater corporate transparency, accountability and oversight to create, sustain, protect and assure corporate value from multifarious external and internal risks. It examines the concepts, frameworks, principles and practices that must be recognized and implemented to ensure the resilience of organizations. (Note course prerequisites: ACCT203/221 Accounting Information Systems)
C. Learning Goals, Course Objectives and Skill Developments GRM has two related objectives: to equip students with a sound foundation of GRM concepts, frameworks, principles and practices; and to develop their technical skills and professional attitudes. The course explores the governance objectives and framework that organizations pursue and implement; the strategic, operational, compliance and reporting risks that threaten attainment of objectives; different methods and approaches that are used to identify, understand and manage these risks; and ways of providing internal and external assurance that contribute to an organization culture of doing the right thing, at the right time, in the right way. On completing this course, students are expected to be able to: Recognise, explain and interpret the concepts, framework and principles that underlie GRM guidelines and practices; Identify and analyse the external and internal governance environments of real-world organizations; Examine and critique real-world risk management scenarios; Develop practicable solutions to real-world problems that integrate governance, risk management and assurance.
The GRM course pedagogy and assessments are designed to enable students to be actively engaged in all aspects of their learning. Assessments, projects and class learning activities will develop their individual competencies as follows: Communication Skills: Students will develop their communication skills by actively participating in class discussions and group discussions, and writing group summaries, mid-term group project reports and final exam answers. Analytical Skills: Analytical skills will be developed through field observations, regular case discussions, the mid-term group project and the final exam. Team work: The mid-term group project, weekly group discussions and group summaries are important elements of the course that require students to work in teams as partners who share the work load. Discussion groups will be formed by Week 3, and the mid-term project group members will be randomly assigned. The BAcc qualification leads students to a professional career, and the CIRCLE values form an essential component of SMU education. The GRM professional conduct assessment is designed to motivate and reward students who behave with Commitment, Integrity, Responsibility, Collegiality, Leadership and Excellence in all aspects of this course, and conduct themselves professionally throughout. Students are expected to: prepare and be punctual for class, submit their own work promptly as required, be polite and cooperative with the instructor and one another, and persevere with a positive attitude.
D. Assessment The assessment components are described below:
c d
Class learning activities: Class participation (class & group discussion/exercise, news articles, student reflection) Professional conduct Progress assessments: Group summary Mid-term test Mid-term team project Final Examination Total
20%
15%
15% 50% 100%
(a) Class learning activities Class participation class & group discussion, news articles, student reflection (CP): 10% The seminars in weeks 2-6 and 9-12 will comprise sessions of class discussion, usually followed by group discussion and exercises. During Weeks 1 and 2, students will form groups of between 6-7 members. These groups will form the basis for the group discussion and exercise. Students are expected to contribute consistently to both types of discussion by: describing what they have learnt from readings assigned, asking questions to clarify areas of doubt, sharing current examples of issues being discussed which they have read about or observed, recommending practicable solutions and developing new ideas for practice. During the group exercises in particular, students are required to summarise their group discussion and conclusions clearly and succinctly by identifying the main points of their analysis and justifying their evaluation. In weeks 10 &11, each student is required to contribute one current news item to illustrate the topic for the week. This will enable students to appreciate different aspects of the topic studied, and internalize their learning. At the end of the seminars in weeks 3, 7 and 11, students are given the opportunity to reflect on what they have learnt. These reflections will enable them to integrate their learning from different parts of the course and identify any areas requiring clarification. Professional conduct (PC): 10% Throughout the course (weeks 2 to 15), students are expected to conduct themselves in accordance with the SMU CIRCLE values, in particular by being prepared and punctual for seminars (commitment and responsibility), prompt in work submission (integrity), cooperative and polite to instructor and fellow students (collegiality), and persevering and positive (leadership).
(b) Progress assessments Group summary (GS): 5% In weeks 4-7 and 9-11, discussion groups will be randomly assigned to prepare and submit a summary of the weeks seminar material and discussion. The summary is expected to capture the concepts, framework, principles and practices discussed in class; and the main points raised by the group discussions. Mid-term test (MT): 10% In week 7, students will take a mid-term test lasting not more than 1 hour. They will be expected to identify, explain, interpret and analyse material relating to the topics covered in weeks 1-6.
(c) Mid-term team project (MTP): 15% In week 7, students will be randomly assigned to teams of 6-7 members and issued instructions on information to collect and prepare. During the seminar time in week 9, each team will analyse
and critique the information collected to submit a short written report of its findings, evaluation and conclusion. (d) Final examination: 50% The final examination will be a case-based paper lasting 2 hours. Students will be allowed to bring in 2 A4 sides of notes and/or diagrams for reference. They are expected to recognize and explain material covered during the whole course, and apply their knowledge to distinguish and assess circumstances and formulate practicable solutions. Students are expected to clarify their understanding on the requirements and details of each of the assessment components in Seminar 1.
Policy of Academic Integrity All acts of academic dishonesty (including, but not limited to, plagiarism, cheating, fabrication, facilitation of acts of academic dishonesty by others, unauthorized possession of exam questions, or tampering with the academic work of other students) are serious offences. All work (whether oral or written) submitted for purposes of assessment must be the students own work. Penalties for violation of the policy range from zero marks for the component assessment to expulsion, depending on the nature of the offence. When in doubt, students should consult the instructor of the course. Details on the SMU Code of Academic Integrity may be accessed at http://www.smuscd.org/resources.html.
E. Textbook and References There is currently no comprehensive textbook for the GRM course. The main references are: Code of Corporate Governance (including proposed revisions), Corporate Governance Council, 2005 & 2011. Available from http://www.mas.gov.sg under News / Press releases/ 14 June 2011 Evaluating and Improving Governance in Organisations, International Good Practice Guidance, IFAC 2009 Available from http://web.ifac.org/publications/professional-accountants-in-businesscommittee/international-good-practice#evaluating-and-improving-governance-in-organizations Risk Management Principles and Guidelines, ISO/FDIS 31000 Available in the SMU Library Reserves (HD61.I58.2009). Framework for Assurance Engagements, Singapore Standard on Auditing, SSA Framework, ICPAS 2005 Available from http://www.icpas.org.sg under Technical Resources / Members Handbook / Vol 2 A significant amount of material on models for business, risk analysis and the control environment will be referenced from the following text: Auditing: Assurance & Risk, WR Knechel, SE Salterio and B Ballou, 3rd ed, Thomson/SouthWestern, 2007.
This text is used on ACCT331: Audit & Assurance Services, so students who will be doing that course may choose to purchase it now. It is also available in the SMU Library. Additional readings will be assigned as term progresses, and details of these will be included in the weekly seminar materials posted on eLearn.
Research Guide A research guide created for this course brings together various useful library and web-based resources for company and industry analysis. The guide is available at http://researchguides.smu.edu.sg/acct402 or through the Library homepage, under Research Guides.
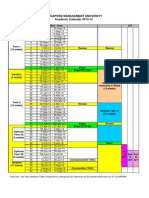
F. LESSON PLAN The summarised lesson plan is shown on the next page. Detailed seminar schedules, including readings and questions for the group discussion/exercise, will be provided on eLearn. Note that the Lesson Plan may be subject to some amendment as the term progresses.
GRM LESSON PLAN Week 1 Topic GRM Overview: Components & Framework Governance Framework: Objectives, Concepts & Principles, Process Governance Practices Activities Course briefing Field observation Class discussion Group discussion Class discussion Group exercise Student reflection 1 Class discussion Group exercise Class discussion Group exercise Class discussion Group exercise Mid-term test Class discussion CP / PC Assessment components
CP / PC
Risk Management Process: Context, Risk Identification & Communication Risk Management Process: Risk Analysis, Evaluation & Communication Risk Management Process: Risk Treatment, Monitoring & Communication Risk Management Framework
CP / PC / GS
CP / PC / GS
CP / PC / GS
MT / CP / PC / GS
Student reflection 2 8 9 MID-TERM BREAK Integrating Governance & Risk Management Risk Management for Performance Sustainability & Business Continuity Management Risk Management for Conformance IT Governance & Fraud Team discussion & report Class discussion Group exercise News articles Class discussion Group exercise News articles Class discussion Group exercise Class discussion Exam briefing Student reflection 3 PC / MTP
10
CP / PC / GS
11
CP / PC / GS
12
Assurance Concepts, Process & Techniques GRM Review
CP / PC / GS
13
CP / PC
14 15
Revision Final exam
Prepared by: Joanne Tay, July 20, 2012
Approved by: Themin Suwardy, August 1, 2012
You might also like
- PMAN635 Course OverviewDocument10 pagesPMAN635 Course OverviewDerrick Antonio GardnerNo ratings yet
- Unit Assessment Pack (UAP) - Cover Sheet: Student and Trainer/Assessor DetailsDocument44 pagesUnit Assessment Pack (UAP) - Cover Sheet: Student and Trainer/Assessor DetailsKomal Sharma0% (1)
- 2021 QTI MGT489 Course OutlineDocument5 pages2021 QTI MGT489 Course OutlineNahida akter jannat 1712024630No ratings yet
- MGMT3101 International Business Strategy S22014Document24 pagesMGMT3101 International Business Strategy S22014BonnieBaoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Understanding Culture, Society & PoliticsDocument7 pagesSyllabus Understanding Culture, Society & PoliticsVIRGILIO JR FABINo ratings yet
- CGT 163 Fall 2019 Syllabus 08-16-2019Document7 pagesCGT 163 Fall 2019 Syllabus 08-16-2019api-477909819No ratings yet
- MANA 5361 Spring Sec 703Document7 pagesMANA 5361 Spring Sec 703paratroop66620000% (1)
- International Business SyllabusDocument5 pagesInternational Business SyllabusTeguh SulistiyonoNo ratings yet
- FINS3641 Course Outline (Part A B Combined) S12014 CurrentDocument18 pagesFINS3641 Course Outline (Part A B Combined) S12014 CurrentDeagle_zeroNo ratings yet
- ACCT102 MA Course Outline 2021-2022 S2 FinalDocument9 pagesACCT102 MA Course Outline 2021-2022 S2 FinalCherlin LeongNo ratings yet
- Course Outline ManagementDocument10 pagesCourse Outline ManagementnaseembalochNo ratings yet
- Badm 106 2019 04 02Document6 pagesBadm 106 2019 04 02Vishal GuptaNo ratings yet
- SMK K48isb Jan-April 2024Document9 pagesSMK K48isb Jan-April 2024Anh Nguyen Tran NhatNo ratings yet
- Level 5 Project Management FinalDocument8 pagesLevel 5 Project Management FinalDr Kerry GoughNo ratings yet
- FINC765NY Portfolio MASTER SYLLABUS Fall 2020 PDFDocument10 pagesFINC765NY Portfolio MASTER SYLLABUS Fall 2020 PDFRahil VermaNo ratings yet
- FINS5513 S2 2013 Course OutlineDocument12 pagesFINS5513 S2 2013 Course OutlineTanya HoNo ratings yet
- FINN 100-Salman Khan Spring 2019Document8 pagesFINN 100-Salman Khan Spring 2019Qudsia AbbasNo ratings yet
- AC2104 Semester 1, 2017 18: S/No Components % Individual GroupDocument10 pagesAC2104 Semester 1, 2017 18: S/No Components % Individual GroupcccqNo ratings yet
- All About Learning Outcomes - DR Vijay Kumar Chattu MD, MPHDocument5 pagesAll About Learning Outcomes - DR Vijay Kumar Chattu MD, MPHDr Vijay Kumar Chattu MD, MPHNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument9 pagesSyllabusapi-308313181No ratings yet
- MKTG 742Document9 pagesMKTG 742venkat raNo ratings yet
- BSC Investment and Financial Risk ManagementDocument13 pagesBSC Investment and Financial Risk ManagementchimaegbukoleNo ratings yet
- MGMT1001 Managing Organisations and People S12015Document16 pagesMGMT1001 Managing Organisations and People S12015Sarthak GargNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument10 pagesSyllabus임민수No ratings yet
- Flip CourseOutline - STM - Fall 16-05sep16Document7 pagesFlip CourseOutline - STM - Fall 16-05sep16Saad SohailNo ratings yet
- PGP Handbook 2011 13Document59 pagesPGP Handbook 2011 13rajiimk07No ratings yet
- Course Outline BComm Fall 2021Document7 pagesCourse Outline BComm Fall 2021simrah zafarNo ratings yet
- FINS3616 - Course OutlineDocument15 pagesFINS3616 - Course OutlineJulie ZhuNo ratings yet
- CB4303 Strategy & Policy: Department of ManagementDocument6 pagesCB4303 Strategy & Policy: Department of ManagementhaileyNo ratings yet
- Neu - Aep: International Business PolicyDocument5 pagesNeu - Aep: International Business PolicyHuong VuNo ratings yet
- Ion IndividualsDocument6 pagesIon IndividualsVladimir IvanovNo ratings yet
- MAN7064 - International Operations and Project Management Assessment 2020-06Document6 pagesMAN7064 - International Operations and Project Management Assessment 2020-06Shah Taj Aftab Shaikh0% (1)
- Published: January 2018 ISBN (Digital) : 978-1-4533-8682-8Document6 pagesPublished: January 2018 ISBN (Digital) : 978-1-4533-8682-8Ajay Kumar BinaniNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management - MGT532: Course DescriptionDocument9 pagesStrategic Management - MGT532: Course DescriptionMohamed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior. A Course - Outline - S 2022Document6 pagesConsumer Behavior. A Course - Outline - S 2022Mehrab AliNo ratings yet
- Ebus635 Business Simulation and Analysis Module Handbook 2023-24Document13 pagesEbus635 Business Simulation and Analysis Module Handbook 2023-24Sagar SubedarNo ratings yet
- Om 636 - Syllabus RevisedDocument5 pagesOm 636 - Syllabus RevisedNda-jiya SuberuNo ratings yet
- Unit of Study Outline FINC2012bDocument8 pagesUnit of Study Outline FINC2012bMichaelTimothy0% (1)
- Subject Overview ACC3044 (March 2014)Document6 pagesSubject Overview ACC3044 (March 2014)Gurrajvin SinghNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship & SMEs MGT641-CDFDocument8 pagesEntrepreneurship & SMEs MGT641-CDFMai El RihanyNo ratings yet
- Applied Corporate FinanceDocument8 pagesApplied Corporate FinanceSafi Ullah KhanNo ratings yet
- TIM 305 Financial Management of Travel Industry SPRING 2022 W F 09:00 - 10:15 A.M. Jan 10 - May 13 Kwanglim SeoDocument6 pagesTIM 305 Financial Management of Travel Industry SPRING 2022 W F 09:00 - 10:15 A.M. Jan 10 - May 13 Kwanglim SeoS JNo ratings yet
- FINS3616 International Business Finance S12013Document17 pagesFINS3616 International Business Finance S12013Dev LioNo ratings yet
- Module 3.1 Program Outcomes and Student Learning OutcomesDocument12 pagesModule 3.1 Program Outcomes and Student Learning OutcomesKaren FrancoNo ratings yet
- UEL-SG-7001 - Module SpecificationDocument4 pagesUEL-SG-7001 - Module SpecificationNea MillsNo ratings yet
- Course Outline FINS3616Document12 pagesCourse Outline FINS3616Erica DaviesNo ratings yet
- FINN 100 Course OutlineDocument9 pagesFINN 100 Course Outlinerizwanf026No ratings yet
- Acct408 - Cheng Nam SangDocument5 pagesAcct408 - Cheng Nam SangHohoho134No ratings yet
- BBA Syllabus 2021-22Document56 pagesBBA Syllabus 2021-22Muskan hamdevNo ratings yet
- Course Guide Sem. 1 2011Document6 pagesCourse Guide Sem. 1 2011sir bookkeeperNo ratings yet
- Outline OS-617 MSSC Spring 2021Document14 pagesOutline OS-617 MSSC Spring 2021Heena ZubairNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For TECH6102Document9 pagesSyllabus For TECH6102api-342200066No ratings yet
- Summer Internship GuidelinesDocument9 pagesSummer Internship GuidelinesTamseel NajmiNo ratings yet
- Finn 400 Outline Spring 2020 PDFDocument8 pagesFinn 400 Outline Spring 2020 PDFadam jamesNo ratings yet
- ACCTFIN 7017 - Financial Statement Analysis (M) - Course OutlinesDocument7 pagesACCTFIN 7017 - Financial Statement Analysis (M) - Course OutlinesRanjeetaTiwariNo ratings yet
- Setara 2009 - CriteriaDocument2 pagesSetara 2009 - CriteriajosuyaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BUS 520 Summer 2009Document25 pagesSyllabus BUS 520 Summer 2009CSCaseNo ratings yet
- Course Outline 240 02Document7 pagesCourse Outline 240 02Vinayak DixitNo ratings yet
- Global Business Strategies SummerDocument5 pagesGlobal Business Strategies SummerCalidad LafNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Course OutlineDocument9 pagesHuman Resource Management Course OutlineEphrem BelayNo ratings yet
- Co Operative Education Revised June 2011Document50 pagesCo Operative Education Revised June 2011ibrahimshareef1No ratings yet
- Assessment and Feedback in Higher Education: A Guide for TeachersFrom EverandAssessment and Feedback in Higher Education: A Guide for TeachersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Leadership U.: Preparing Students for College, Career, and Beyond: Grades 11–12: Thriving in College and BeyondFrom EverandLeadership U.: Preparing Students for College, Career, and Beyond: Grades 11–12: Thriving in College and BeyondNo ratings yet
- 2013-14 Academic CalendarDocument1 page2013-14 Academic Calendarzhentang89No ratings yet
- December 2012: Monday Tuesday Wednesday ThursdayDocument5 pagesDecember 2012: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursdayzhentang89No ratings yet
- Set C Set D: 2位 (pax) $118++ 2位 (pax) $138++ 8位 (pax) $458++ 8位 (pax) $558++Document2 pagesSet C Set D: 2位 (pax) $118++ 2位 (pax) $138++ 8位 (pax) $458++ 8位 (pax) $558++zhentang89No ratings yet
- Prepaid SIM Card 98 Card Top Up 200 Taxi Fare From MRT 16 Dinner 30 Wellcome Market 447.9Document2 pagesPrepaid SIM Card 98 Card Top Up 200 Taxi Fare From MRT 16 Dinner 30 Wellcome Market 447.9zhentang89No ratings yet
- Chap 001Document33 pagesChap 001zhentang89No ratings yet
- ACCT5955 Management Accounting Control Systems S12005Document17 pagesACCT5955 Management Accounting Control Systems S12005Sucipto Antoni100% (1)
- CS101 Lab 01Document90 pagesCS101 Lab 01chaosofdoomxNo ratings yet
- Arch1102 - 2010 OutlineDocument8 pagesArch1102 - 2010 OutlineZoha A. FardNo ratings yet
- Advanced Research Methods in ArchitectureDocument9 pagesAdvanced Research Methods in Architectureksnbh007100% (1)
- Topics in Product Development in Mechanical EngineeringDocument12 pagesTopics in Product Development in Mechanical EngineeringYASH BHAVSARNo ratings yet
- ENGG2600 - Lecture 1 IntroductionDocument41 pagesENGG2600 - Lecture 1 IntroductionValar MorghulisNo ratings yet
- MKT 113-12120 Fa '15Document14 pagesMKT 113-12120 Fa '15Matthew CropleyNo ratings yet
- ACC 2203 Syllabus Sp-2018Document12 pagesACC 2203 Syllabus Sp-2018Jay REyNo ratings yet
- MAT172 SP23 PaulDocument11 pagesMAT172 SP23 PaulGiselle KyandaNo ratings yet
- Course Manual - CPC-2022Document13 pagesCourse Manual - CPC-2022keerthana RaaviNo ratings yet
- Isom2500 2018Document3 pagesIsom2500 2018Yanis ChanNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Econ252 (AY2023-24 Term 1) 2Document4 pagesCourse Outline Econ252 (AY2023-24 Term 1) 2ANG ZHENG NANNo ratings yet
- Iso Obe Syllabus Opportunity SeekingDocument12 pagesIso Obe Syllabus Opportunity SeekingPatrick ManatadNo ratings yet
- FRL 2013.03 SPRING 2021 SyllabusDocument9 pagesFRL 2013.03 SPRING 2021 SyllabusBigAsianPapiNo ratings yet
- 2022 2023 FTD Cve 4 Ce PC405Document5 pages2022 2023 FTD Cve 4 Ce PC405DeepakNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Course OutlineDocument11 pagesStrategic Management Course OutlineRajat SinghNo ratings yet
- OPD Discipline Handbook 2020 - 12.4.20Document72 pagesOPD Discipline Handbook 2020 - 12.4.20Erolle Linus MirandaNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Entp6v99.001.11s Taught by Daniel Bochsler (dcb091000)Document13 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Entp6v99.001.11s Taught by Daniel Bochsler (dcb091000)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Community Mediation: Theory and PracticeDocument105 pagesCommunity Mediation: Theory and Practiceeliasox123100% (2)
- Media and Global Communication MCC-UE 1300Document7 pagesMedia and Global Communication MCC-UE 1300Hoang CaoNo ratings yet
- BUSN 6530 Syllabus Su19Document4 pagesBUSN 6530 Syllabus Su19lookingforfunonlyNo ratings yet
- POG 100 Course Outline F2007Document8 pagesPOG 100 Course Outline F2007Samuel100% (1)
- Unit 16 Marketing Essentials For Travel and Tourism June 2020Document10 pagesUnit 16 Marketing Essentials For Travel and Tourism June 2020Dyya EllenaNo ratings yet
- Geog 301 SyllabusDocument4 pagesGeog 301 SyllabusbradleysgardenerNo ratings yet
- FIN 5411 - Financial Management - Spring 2021 - Akashi HongoDocument5 pagesFIN 5411 - Financial Management - Spring 2021 - Akashi HongoLimSiEianNo ratings yet
- American Culture SyllabusDocument5 pagesAmerican Culture Syllabuspaleoman8No ratings yet