Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Manila Central University
Manila Central University
Uploaded by
hezekeahOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Manila Central University
Manila Central University
Uploaded by
hezekeahCopyright:
Available Formats
MANILA CENTRAL UNIVERSITY
COLLEGE OF NURSING A CASE STUDY DIABETES MELLITUS TYPE II
Presented By: GROUP 3 Dayuno, Amalia T. Mercado, Kim Shermaine M. Velasco, Eveth DS. Presented To: Mr. Cyrill Consuelo
I.
Health History
A Demographic Profile
Name: Patient X Gender: Female Age: 66 years old Birthdate: August 12,1945 Marital Status: Widowed Nationality: Filipino Religion: Catholic Address: Black 37A lot 27 Phase III F Kayak aley Educational background: High School
B. Source and Reability of information The patient x is the Primary source of information. She is conscious and coherent, able to speak tagalog fluently,Her grandchild is also considered as a source of information regarding patient status and condition. C. Reason for seaking care or chief complaint.
Walking impaired Risk for infection Skin integrity
INTRODUCTION:
Diabetes mellitus is a condition in which the pancreas no longer produces enough insulin or cells stop responding to the insulin that is produced, so that glucose in the blood cannot be absorbed into the cells of the body. Symptoms include frequent urination, lethargy, excessive thirst, and hunger. The treatment includes changes in diet, oral medications, and in some cases, daily injections of insulin. The most common form of diabetes is Type II, It is sometimes called age-onset or adult-onset diabetes, and this form of diabetes occurs most often in people who are overweight and who do not exercise. Type II is considered a milder form of diabetes because of its slow onset (sometimes developing over the course of several years) and because it usually can be controlled with diet and oral medication. The consequences of uncontrolled and untreated Type II diabetes, however, are the just as serious as those for Type I. This form is also called noninsulin-dependent diabetes, a term that is somewhat misleading. Many people with Type II diabetes can control the condition with diet and oral medications, however, insulin injections
are sometimes necessary if treatment with diet and oral medication is not working. The causes of diabetes mellitus are unclear, however, there seem to be both hereditary (genetic factors passed on in families) and environmental factors involved. Research has shown that some people who develop diabetes have common genetic markers. In Type I diabetes, the immune system, the bodys defense system against infection, is believed to be triggered by a virus or another microorganism that destroys cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. In Type II diabetes, age, obesity, and family history of diabetes play a role. resistant to the insulin produced and it may not work as effectively. Symptoms of Type II diabetes can begin so gradually that a person may not know that he or she has it. Early signs are lethargy, extreme thirst, and frequent urination. Other symptoms may include sudden weight loss, slow wound healing, urinary tract infections, gum disease, or blurred vision. It is not unusual for Type II diabetes to be detected while a patient is seeing a doctor about another health concern that is actually being caused by the yet undiagnosed diabetes. Individuals who are at high risk of developing Type II diabetes mellitus include people who: Are obese (more than 20% above their ideal body weight) Have a relative with diabetes mellitus Belong to a high-risk ethnic population (African-American, Native American, Hispanic, or Native Hawaiian) Have been diagnosed with gestational diabetes or have delivered a baby weighing more than 9 lbs (4 kg) Have high blood pressure (140/90 mmHg or above) Have a high density lipoprotein cholesterol level less than or equal to 35 mg/dL and/or a triglyceride level greater than or equal to 250 mg/dL Have had impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose on previous testing Diabetes mellitus is a common chronic disease requiring lifelong behavioral and lifestyle changes. It is best managed with a team approach to empower the client to successfully manage the disease. As part of the team the, the nurse plans, organizes, and coordinates care among the various health disciplines involved; provides care and education and promotes the clients health and well being. Diabetes is a major public health worldwide. Its complications cause many devastating health problems.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Everybody's Different A Positive Approach To Teaching About Health, Puberty, Body Image, Nutrition, Self-Esteem and Obesity... (O'Dea, Jenny)Document338 pagesEverybody's Different A Positive Approach To Teaching About Health, Puberty, Body Image, Nutrition, Self-Esteem and Obesity... (O'Dea, Jenny)SalsaNo ratings yet
- Sabrina Strings - Fearing The Black Body - The Racial Origins of Fat Phobia-New York Univ PR (2019)Document306 pagesSabrina Strings - Fearing The Black Body - The Racial Origins of Fat Phobia-New York Univ PR (2019)mlaure445No ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Argument EssayDocument5 pagesArgument Essayapi-511589630No ratings yet
- Denotation and ConnotationDocument7 pagesDenotation and ConnotationERIKA LORENA GALVIS CRUZ100% (1)
- Nutrilite W.O.W: Bodykey Personalised Holistic Weight Management ProgramDocument19 pagesNutrilite W.O.W: Bodykey Personalised Holistic Weight Management Programrahul gajbhiye100% (2)
- Solution Manual For Williams Essentials of Nutrition and Diet Therapy 12th by SchlenkerDocument7 pagesSolution Manual For Williams Essentials of Nutrition and Diet Therapy 12th by Schlenkerzanewilliamhzkbr100% (15)
- Growth Charts (Kurva Pertumbuhan Anak CDC-NCHS)Document10 pagesGrowth Charts (Kurva Pertumbuhan Anak CDC-NCHS)Gita ListawatiNo ratings yet
- Pre-Activity: What I Know 1. D 2. C 3. A 4. B 5. D: Prince Girk S. Adlawan-Grade 12 Css2Document4 pagesPre-Activity: What I Know 1. D 2. C 3. A 4. B 5. D: Prince Girk S. Adlawan-Grade 12 Css2PegeeeyNo ratings yet
- Lifestyle & Weight ManagementDocument18 pagesLifestyle & Weight ManagementKathrina LingadNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Education Funding ResourcesDocument4 pagesNutrition Education Funding ResourcesGloria Dell Holland-YsaguirreNo ratings yet
- EENS 2019 (Adults)Document60 pagesEENS 2019 (Adults)Anna Charish Castillano ImaysayNo ratings yet
- Imagen Corporal CulturaDocument4 pagesImagen Corporal CulturaLady SanchezNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive DietDocument6 pagesHypertensive DietCarlos NiñoNo ratings yet
- Critical Reading W2 Worksheet-1Document3 pagesCritical Reading W2 Worksheet-1HiếuNo ratings yet
- Suzu Yokoyama Global-Essay R06Document9 pagesSuzu Yokoyama Global-Essay R06madhuNo ratings yet
- LDV 1 ScriptDocument7 pagesLDV 1 ScriptRama devi MuruganNo ratings yet
- Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Call To ActionDocument12 pagesManagement of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Call To ActionNur ArafahNo ratings yet
- Name: SEX:Male Age: Part 1: Health-Related Fitness Test (Week 4) A.BODY COMPOSITION: Body Mass Index (BMI)Document2 pagesName: SEX:Male Age: Part 1: Health-Related Fitness Test (Week 4) A.BODY COMPOSITION: Body Mass Index (BMI)JohncelNo ratings yet
- Stats QuestionsDocument3 pagesStats QuestionsMangesh Thore0% (1)
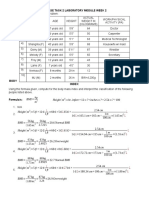
- Lab Module Week 2 (Diet Computation)Document2 pagesLab Module Week 2 (Diet Computation)Tala StarsNo ratings yet
- Japan Metabo LawDocument16 pagesJapan Metabo LawReginNo ratings yet
- Erich E. Racal ABM - 11E ACTIVITY 1: Video Critique and Lifestyle CheckDocument2 pagesErich E. Racal ABM - 11E ACTIVITY 1: Video Critique and Lifestyle CheckErich RacalNo ratings yet
- Effects of Tecar Therapy On Adipose Tissue Clinical TrialDocument12 pagesEffects of Tecar Therapy On Adipose Tissue Clinical Trialsilvia roca mejiaNo ratings yet
- Nurs FPX 4900 Assessment 5 Intervention Presentation and Capstone Video ReflectionDocument5 pagesNurs FPX 4900 Assessment 5 Intervention Presentation and Capstone Video Reflectionfarwaamjad771No ratings yet
- Physical Fitness Checklist: Name: - Course & SectionDocument3 pagesPhysical Fitness Checklist: Name: - Course & SectionCharlesNo ratings yet
- The Chris Hemsworth Thor Workout: Bonus PDF Workout GuideDocument5 pagesThe Chris Hemsworth Thor Workout: Bonus PDF Workout GuideJay Kewat100% (1)
- A-Quantitative-Study-on-Okra-Water-as-Treatment in Lowering The Blood Sugar of Strep-Induced White MiceDocument12 pagesA-Quantitative-Study-on-Okra-Water-as-Treatment in Lowering The Blood Sugar of Strep-Induced White MiceLeelee the GreatNo ratings yet
- L A 066Document7 pagesL A 066Cao Minh PhạmNo ratings yet
- RESEARCH ASSIGNMENT ManjeetDocument6 pagesRESEARCH ASSIGNMENT Manjeetnavya sharmaNo ratings yet
- Cuadernillo de Regularizacion de Ingles 1°, 2°, 3°Document33 pagesCuadernillo de Regularizacion de Ingles 1°, 2°, 3°Yuliana Belem Dix ZapataNo ratings yet