Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What You Require To Know About NOx Reduction.20130104.123704
What You Require To Know About NOx Reduction.20130104.123704
Uploaded by
anon_931869105Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Waste Management ProjectDocument42 pagesWaste Management ProjectNeha Sharma100% (1)
- The Institute of Energy's Second International Conference on COMBUSTION & EMISSIONS CONTROL: Proceedings of The Institute of Energy Conference Held in London, UK, on 4-5 December 1995From EverandThe Institute of Energy's Second International Conference on COMBUSTION & EMISSIONS CONTROL: Proceedings of The Institute of Energy Conference Held in London, UK, on 4-5 December 1995Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Formulas and Processes in Fluid DynamicsDocument8 pagesFormulas and Processes in Fluid DynamicsFenrir RozenNo ratings yet
- Cof g23 Noe Study MaterialsDocument58 pagesCof g23 Noe Study MaterialsMarco Alejandro100% (1)
- Boiler Combustion & EmissionDocument15 pagesBoiler Combustion & EmissionMustafa HusainNo ratings yet
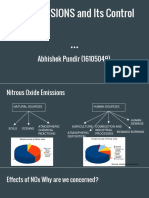
- Nox Emissions and Its Control: Abhishek Pundir (16105049)Document27 pagesNox Emissions and Its Control: Abhishek Pundir (16105049)SavitarNo ratings yet
- NOx Reductionhandout FINALDocument2 pagesNOx Reductionhandout FINALKunal ChandNo ratings yet
- NOx Control in Power Plants R1Document10 pagesNOx Control in Power Plants R1Vishal JaishankarNo ratings yet
- Handbook Nitrogen Oxides Pollution Prevention and ControlDocument5 pagesHandbook Nitrogen Oxides Pollution Prevention and ControlrupigapigaNo ratings yet
- Oxygen - Environmental RegulationsDocument2 pagesOxygen - Environmental RegulationsAnis.MNo ratings yet
- Profiles: Nox Control For Pulverised Coal Fired Power StationsDocument2 pagesProfiles: Nox Control For Pulverised Coal Fired Power StationsColin RobertsNo ratings yet
- Recent Development in Marine EnginesDocument81 pagesRecent Development in Marine EnginesShashidhar ChandraiahNo ratings yet
- Selective Catalytic ReductionDocument15 pagesSelective Catalytic ReductionJuan Esteban EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Nox Emissions Approaching Zero - Is It Worth The Price?Document12 pagesGas Turbine Nox Emissions Approaching Zero - Is It Worth The Price?hermans57No ratings yet
- CHAP9Document11 pagesCHAP9KARTHIKEYANNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 22 Boiler Pollution Control 1.: DLP/BOE-II/ 1-01092001Document16 pagesChapter - 22 Boiler Pollution Control 1.: DLP/BOE-II/ 1-01092001sunitbhaumikNo ratings yet
- Practical 12: To Study The Effect of Residual Gasses On EnvironmentDocument6 pagesPractical 12: To Study The Effect of Residual Gasses On EnvironmentMuhammad Arslan AfzalNo ratings yet
- NOx Reduction TechniquesDocument37 pagesNOx Reduction Techniquesengr kazamNo ratings yet
- Nox Reduction Using RDF (Refuse Derived Fuel) in Cement IndustryDocument2 pagesNox Reduction Using RDF (Refuse Derived Fuel) in Cement IndustryIzaz Ulhaq YousafziNo ratings yet
- Nitrogeoin Rejection Technology For Abu DhabiDocument10 pagesNitrogeoin Rejection Technology For Abu DhabiBeshuoNo ratings yet
- Nox ReductionDocument3 pagesNox Reductionsam1hi5No ratings yet
- Pollution Control Techniques: Submitted byDocument3 pagesPollution Control Techniques: Submitted byAayan ShahNo ratings yet
- NOx Control in Gas TurbineDocument10 pagesNOx Control in Gas TurbineDuyen Tran VanNo ratings yet
- Burner TechnologyDocument9 pagesBurner TechnologyTint TigerNo ratings yet
- Study On Exhaust Emissions and Its Reduction Techniques in Automotive EnginesDocument5 pagesStudy On Exhaust Emissions and Its Reduction Techniques in Automotive EnginesShreyash BalpandeNo ratings yet
- NOx Reduction TA Study v1 - December2005Document70 pagesNOx Reduction TA Study v1 - December2005Dilnesa Ejigu100% (1)
- Control of NOXDocument38 pagesControl of NOXsandp4uNo ratings yet
- STOC03 (Emissions)Document20 pagesSTOC03 (Emissions)tungluongNo ratings yet
- "Effect of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (Egr) On Nox Emission From C.I. Engine" - A Review StudyDocument5 pages"Effect of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (Egr) On Nox Emission From C.I. Engine" - A Review StudyShreyash BalpandeNo ratings yet
- NOx ComplianceDocument2 pagesNOx ComplianceUdhayakumar VenkataramanNo ratings yet
- Ref7 PDFDocument7 pagesRef7 PDFJulian BermudezNo ratings yet
- Precalciner Systems Cement IndustryDocument22 pagesPrecalciner Systems Cement IndustryfaheemqcNo ratings yet
- NOx Reduction TA Study Feb2010Document70 pagesNOx Reduction TA Study Feb2010naikNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 22 Boiler Pollution Control 1.: DLP/BOE-II/ 1-01092001Document16 pagesChapter - 22 Boiler Pollution Control 1.: DLP/BOE-II/ 1-01092001Jagdeep ArryNo ratings yet
- Nox Reduction Using RDF (Refuse Derived Fuel) in Cement IndustryDocument8 pagesNox Reduction Using RDF (Refuse Derived Fuel) in Cement IndustryIzaz Ulhaq YousafziNo ratings yet
- Post CombustionDocument15 pagesPost CombustionThe UltimateNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesSeminar Reportapi-3706848100% (1)
- EnvironmentDocument3 pagesEnvironmentPriyanka Bakshi YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Microturbine Fuels and EmissionsDocument4 pagesChapter 5 - Microturbine Fuels and EmissionsGarip GerçeklerNo ratings yet
- BurnersDocument4 pagesBurnersDhanny Miharja100% (1)
- 6 Tips For Improving Efficiency and Reducing NOX - 2018-09-13 - Process HeatingDocument15 pages6 Tips For Improving Efficiency and Reducing NOX - 2018-09-13 - Process Heatingwest kestNo ratings yet
- Nox Impacts On Environment and Human HealthDocument5 pagesNox Impacts On Environment and Human HealthnaikNo ratings yet
- AZEP - Development of An Integrated Air Separation Membrane - Gas TurbineDocument6 pagesAZEP - Development of An Integrated Air Separation Membrane - Gas TurbineeddyNo ratings yet
- Glass ManufacturingDocument4 pagesGlass ManufacturingMahfuzur Rahman SiddikyNo ratings yet
- "Effect of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (Egr) On Nox Emission From C.I. Engine" - A Review StudyDocument5 pages"Effect of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (Egr) On Nox Emission From C.I. Engine" - A Review Studyslv_prasaadNo ratings yet
- Ultralow NOx BurnersDocument3 pagesUltralow NOx Burnersdatalogger123456100% (2)
- Publications 012Document6 pagesPublications 012hassnain iqbalNo ratings yet
- Reduction of No Emission in Biodiesel Engines by Exhaust Gas Aftertreatment MethodDocument12 pagesReduction of No Emission in Biodiesel Engines by Exhaust Gas Aftertreatment MethodVijay Kumar DanapalNo ratings yet
- Nitric Acid 2000Document10 pagesNitric Acid 2000harikeshrl5477No ratings yet
- Report AJUDocument20 pagesReport AJUTHE DARK KNIGHTNo ratings yet
- Iesel Exhaust GAS AftertreatmentDocument16 pagesIesel Exhaust GAS AftertreatmentHarsh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- TopsoeDocument5 pagesTopsoelaiping_lumNo ratings yet
- 2011.12 PG International - Las Vegas - Advanced SNCR TechnologyDocument36 pages2011.12 PG International - Las Vegas - Advanced SNCR TechnologylightsonsNo ratings yet
- Nox Reduction TechsDocument4 pagesNox Reduction TechsMehulkumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Denox DesoxDocument20 pagesDenox DesoxArzu AkarNo ratings yet
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation System: October 2015Document7 pagesExhaust Gas Recirculation System: October 2015Luyen NguyenNo ratings yet
- How To Reduce NOX and SOXDocument3 pagesHow To Reduce NOX and SOXnoraiz fozanNo ratings yet
- NOx SOxDocument9 pagesNOx SOxYohannes DennisNo ratings yet
- (Document Title) : For Engine To Reduce Oxides of Nitrogen Is Chosen For Present WorkDocument22 pages(Document Title) : For Engine To Reduce Oxides of Nitrogen Is Chosen For Present WorkrassNo ratings yet
- ENV315 - Online Air Pollution Control Lecture 11Document23 pagesENV315 - Online Air Pollution Control Lecture 11Samim JubayerNo ratings yet
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation SystemDocument7 pagesExhaust Gas Recirculation Systemmalik visheshNo ratings yet
- Diesel Exhaust Gas AftertreatmentDocument16 pagesDiesel Exhaust Gas AftertreatmentlukhmanNo ratings yet
- Clean Ironmaking and Steelmaking Processes: Efficient Technologies for Greenhouse Emissions AbatementFrom EverandClean Ironmaking and Steelmaking Processes: Efficient Technologies for Greenhouse Emissions AbatementNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Operation & Maintenance CourseDocument100 pagesGas Turbine Operation & Maintenance Coursewaheed2286100% (4)
- MSDS - SGT - 2Document7 pagesMSDS - SGT - 2SajidNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 PPT Reservoir Engineering-1Document38 pagesUNIT 4 PPT Reservoir Engineering-1PE9001 AarthiNo ratings yet
- JT15D Series Head IndexDocument4 pagesJT15D Series Head IndexEgor85No ratings yet
- PAC Insider February 2013 FinalDocument8 pagesPAC Insider February 2013 FinalAsep TheaNo ratings yet
- Combustion StoichiometryDocument18 pagesCombustion StoichiometryARYAN PIRTANo ratings yet
- Plant Design CHEN 451Document42 pagesPlant Design CHEN 451lalitNo ratings yet
- Ms Ds NaphthaDocument12 pagesMs Ds NaphthaCatharina Natasa BellaFortunaNo ratings yet
- Rubia Tir 7400 15W-40 - MSDSDocument14 pagesRubia Tir 7400 15W-40 - MSDSabdulNo ratings yet
- Fire Extinguisher TrainingDocument32 pagesFire Extinguisher Trainingaulianur564830No ratings yet
- TNavigator Modules Available 2019 ENGDocument26 pagesTNavigator Modules Available 2019 ENGVitor Azevedo Jr100% (1)
- Sanet ST 3030439321Document108 pagesSanet ST 3030439321Guido van HoyweghenNo ratings yet
- SSP 424 Exhaust Gas Aftertreatment System Selective Catalytic ReductionDocument56 pagesSSP 424 Exhaust Gas Aftertreatment System Selective Catalytic Reductionjohangustafsson200No ratings yet
- Les Modeling of Combustion Applications Using Openfoam: M. Chapuis, C. Fureby, E. Fedina, N. Alin & J. TegnérDocument20 pagesLes Modeling of Combustion Applications Using Openfoam: M. Chapuis, C. Fureby, E. Fedina, N. Alin & J. TegnérErnesto SalzanoNo ratings yet
- Combustion Course - Ch2Document35 pagesCombustion Course - Ch2hassan ghNo ratings yet
- 1386 - C11 Burner Design PDFDocument32 pages1386 - C11 Burner Design PDFMartin Martin MartinNo ratings yet
- 1-1 Unit (2016-2017)Document113 pages1-1 Unit (2016-2017)goutham100% (1)
- Quenching of Flame Anaylsis by ManasDocument17 pagesQuenching of Flame Anaylsis by ManasManas Srivastav100% (1)
- AP&CDocument35 pagesAP&CChethan K. ReddyNo ratings yet
- ME304UB Model Answer Set-1Document13 pagesME304UB Model Answer Set-1Harshraj WaniNo ratings yet
- 10 Technologies - Methods For Controlling NOx & SOx Emissions From Ships PDFDocument6 pages10 Technologies - Methods For Controlling NOx & SOx Emissions From Ships PDFMihir MishraNo ratings yet
- Fuel Oil Analysis: Know The Condition of The Fuel Oils You Use!Document6 pagesFuel Oil Analysis: Know The Condition of The Fuel Oils You Use!lolo100% (1)
- Basic Knowledge and Skills of Fire Safety Requirements For Electrical Engineering (0531)Document90 pagesBasic Knowledge and Skills of Fire Safety Requirements For Electrical Engineering (0531)Susi SusilowatiNo ratings yet
- Eurofirefighter 2 PDFDocument480 pagesEurofirefighter 2 PDFlifyadortaNo ratings yet
- Batch Reactor HazardsDocument12 pagesBatch Reactor HazardsSteve Forster100% (1)
- 5070 w10 QP 42Document16 pages5070 w10 QP 42Shahnawaz MemonNo ratings yet
What You Require To Know About NOx Reduction.20130104.123704
What You Require To Know About NOx Reduction.20130104.123704
Uploaded by
anon_931869105Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What You Require To Know About NOx Reduction.20130104.123704
What You Require To Know About NOx Reduction.20130104.123704
Uploaded by
anon_931869105Copyright:
Available Formats
What You Want to Know About NOx Reduction
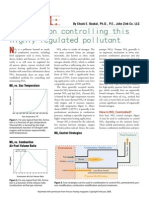
In normal temperatures, nitrogen and oxygen do not undergo chemical reaction to form oxides of nitrogen. But under high temperature conditions, for example in the furnace, nitrogen responds to oxygen forming NOx. NOx is not just a toxic contaminant into its are is capable of doing combining with substances in existence of sunlight. Nitrogen oxides react with water to make acid rain that is extremely corrosive and dangerous. It can break the structure from a building that is certainly repeatedly encountered with acid rain. All major manufacturers and industries produce NOx as a product of combustion of fuel. With the rise in industrialization, the emissions of NOx have raised manifold. NOx was classified as greenhouse gas in Kyoto protocol (1997). After that, much effort has become put into NOx reduction worldwide. Any industry or manufacturer must abide by the regulations set with the EPA and reduce their emission of nitrogen oxides. NOx reduction is now the best feature manufacturers who produce internal combustion engine. NOx reduction is possible in numerous methods. Low NOx Burners or LNBs - LNB uses techniques to modify combustion by precise mixing of air and fuel and recirculation from the combustion gas. NOx reburning - it can be applied to boilers of all kind. Around 50 - 70% of NOx could be reduced using these two methods. However, modern industries use some more methods for NOx reduction that happen to be considerably more efficient and are able to achieve around 90% decrease in NOx emission. The subsequent two methods are used in present day industries, though each of them include their particular advantages and limitations. Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR)- In the process of SCR, the flue gas or exhaust gas is mixed with a reductant like aqueous or anhydrous ammonia. The cooled gas mixture is then adsorbed on catalysts like oxides of vanadium, palladium, molybdenum, tungsten etc. However, SCR poses problems like high investment, operating cost and efficient disposal from the catalysts used. A nicely designed, efficient SCR process is able to reduce 90% from the emitted NOx. Selective Non - Catalytic Reduction (SNCR)-The NOx content from the exhaust gas is reduced chemically with this process. The chemical reactions are performed in the homogenous gas phase. To make sure maximum efficiency, the temperature of the gas have to be uniform. Unfortunately, it's not at all possible to take care of the temperature during the entire gas mixture therefore the efficiency of NOx reduction drops to 50%. Since catalysts aren't employed in this procedure, the problem of a good disposal won't arise in any respect.
Reciprocating Internal Combustion Engines (RICE) - These kinds of engines have suprisingly low emission which is incorporated in the range of 2.3 pounds /mmBtu to a few.2 pounds /mmBtu. The emission of NOx can be further reduced by tuning up the engine and utilizing catalysts for oxidation. Air pollution by NOx emission also its abatement is a burning issue now. All manufacturing and production companies stick to the regulations set by EPA and then for any non compliance to the telltale environmental regulations can lead to invalidation of license. Using the previously listed methods, industries can minimize their NOx emission in a cost effective as well as efficient way.
You might also like
- Waste Management ProjectDocument42 pagesWaste Management ProjectNeha Sharma100% (1)
- The Institute of Energy's Second International Conference on COMBUSTION & EMISSIONS CONTROL: Proceedings of The Institute of Energy Conference Held in London, UK, on 4-5 December 1995From EverandThe Institute of Energy's Second International Conference on COMBUSTION & EMISSIONS CONTROL: Proceedings of The Institute of Energy Conference Held in London, UK, on 4-5 December 1995Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Formulas and Processes in Fluid DynamicsDocument8 pagesFormulas and Processes in Fluid DynamicsFenrir RozenNo ratings yet
- Cof g23 Noe Study MaterialsDocument58 pagesCof g23 Noe Study MaterialsMarco Alejandro100% (1)
- Boiler Combustion & EmissionDocument15 pagesBoiler Combustion & EmissionMustafa HusainNo ratings yet
- Nox Emissions and Its Control: Abhishek Pundir (16105049)Document27 pagesNox Emissions and Its Control: Abhishek Pundir (16105049)SavitarNo ratings yet
- NOx Reductionhandout FINALDocument2 pagesNOx Reductionhandout FINALKunal ChandNo ratings yet
- NOx Control in Power Plants R1Document10 pagesNOx Control in Power Plants R1Vishal JaishankarNo ratings yet
- Handbook Nitrogen Oxides Pollution Prevention and ControlDocument5 pagesHandbook Nitrogen Oxides Pollution Prevention and ControlrupigapigaNo ratings yet
- Oxygen - Environmental RegulationsDocument2 pagesOxygen - Environmental RegulationsAnis.MNo ratings yet
- Profiles: Nox Control For Pulverised Coal Fired Power StationsDocument2 pagesProfiles: Nox Control For Pulverised Coal Fired Power StationsColin RobertsNo ratings yet
- Recent Development in Marine EnginesDocument81 pagesRecent Development in Marine EnginesShashidhar ChandraiahNo ratings yet
- Selective Catalytic ReductionDocument15 pagesSelective Catalytic ReductionJuan Esteban EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Nox Emissions Approaching Zero - Is It Worth The Price?Document12 pagesGas Turbine Nox Emissions Approaching Zero - Is It Worth The Price?hermans57No ratings yet
- CHAP9Document11 pagesCHAP9KARTHIKEYANNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 22 Boiler Pollution Control 1.: DLP/BOE-II/ 1-01092001Document16 pagesChapter - 22 Boiler Pollution Control 1.: DLP/BOE-II/ 1-01092001sunitbhaumikNo ratings yet
- Practical 12: To Study The Effect of Residual Gasses On EnvironmentDocument6 pagesPractical 12: To Study The Effect of Residual Gasses On EnvironmentMuhammad Arslan AfzalNo ratings yet
- NOx Reduction TechniquesDocument37 pagesNOx Reduction Techniquesengr kazamNo ratings yet
- Nox Reduction Using RDF (Refuse Derived Fuel) in Cement IndustryDocument2 pagesNox Reduction Using RDF (Refuse Derived Fuel) in Cement IndustryIzaz Ulhaq YousafziNo ratings yet
- Nitrogeoin Rejection Technology For Abu DhabiDocument10 pagesNitrogeoin Rejection Technology For Abu DhabiBeshuoNo ratings yet
- Nox ReductionDocument3 pagesNox Reductionsam1hi5No ratings yet
- Pollution Control Techniques: Submitted byDocument3 pagesPollution Control Techniques: Submitted byAayan ShahNo ratings yet
- NOx Control in Gas TurbineDocument10 pagesNOx Control in Gas TurbineDuyen Tran VanNo ratings yet
- Burner TechnologyDocument9 pagesBurner TechnologyTint TigerNo ratings yet
- Study On Exhaust Emissions and Its Reduction Techniques in Automotive EnginesDocument5 pagesStudy On Exhaust Emissions and Its Reduction Techniques in Automotive EnginesShreyash BalpandeNo ratings yet
- NOx Reduction TA Study v1 - December2005Document70 pagesNOx Reduction TA Study v1 - December2005Dilnesa Ejigu100% (1)
- Control of NOXDocument38 pagesControl of NOXsandp4uNo ratings yet
- STOC03 (Emissions)Document20 pagesSTOC03 (Emissions)tungluongNo ratings yet
- "Effect of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (Egr) On Nox Emission From C.I. Engine" - A Review StudyDocument5 pages"Effect of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (Egr) On Nox Emission From C.I. Engine" - A Review StudyShreyash BalpandeNo ratings yet
- NOx ComplianceDocument2 pagesNOx ComplianceUdhayakumar VenkataramanNo ratings yet
- Ref7 PDFDocument7 pagesRef7 PDFJulian BermudezNo ratings yet
- Precalciner Systems Cement IndustryDocument22 pagesPrecalciner Systems Cement IndustryfaheemqcNo ratings yet
- NOx Reduction TA Study Feb2010Document70 pagesNOx Reduction TA Study Feb2010naikNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 22 Boiler Pollution Control 1.: DLP/BOE-II/ 1-01092001Document16 pagesChapter - 22 Boiler Pollution Control 1.: DLP/BOE-II/ 1-01092001Jagdeep ArryNo ratings yet
- Nox Reduction Using RDF (Refuse Derived Fuel) in Cement IndustryDocument8 pagesNox Reduction Using RDF (Refuse Derived Fuel) in Cement IndustryIzaz Ulhaq YousafziNo ratings yet
- Post CombustionDocument15 pagesPost CombustionThe UltimateNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesSeminar Reportapi-3706848100% (1)
- EnvironmentDocument3 pagesEnvironmentPriyanka Bakshi YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Microturbine Fuels and EmissionsDocument4 pagesChapter 5 - Microturbine Fuels and EmissionsGarip GerçeklerNo ratings yet
- BurnersDocument4 pagesBurnersDhanny Miharja100% (1)
- 6 Tips For Improving Efficiency and Reducing NOX - 2018-09-13 - Process HeatingDocument15 pages6 Tips For Improving Efficiency and Reducing NOX - 2018-09-13 - Process Heatingwest kestNo ratings yet
- Nox Impacts On Environment and Human HealthDocument5 pagesNox Impacts On Environment and Human HealthnaikNo ratings yet
- AZEP - Development of An Integrated Air Separation Membrane - Gas TurbineDocument6 pagesAZEP - Development of An Integrated Air Separation Membrane - Gas TurbineeddyNo ratings yet
- Glass ManufacturingDocument4 pagesGlass ManufacturingMahfuzur Rahman SiddikyNo ratings yet
- "Effect of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (Egr) On Nox Emission From C.I. Engine" - A Review StudyDocument5 pages"Effect of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (Egr) On Nox Emission From C.I. Engine" - A Review Studyslv_prasaadNo ratings yet
- Ultralow NOx BurnersDocument3 pagesUltralow NOx Burnersdatalogger123456100% (2)
- Publications 012Document6 pagesPublications 012hassnain iqbalNo ratings yet
- Reduction of No Emission in Biodiesel Engines by Exhaust Gas Aftertreatment MethodDocument12 pagesReduction of No Emission in Biodiesel Engines by Exhaust Gas Aftertreatment MethodVijay Kumar DanapalNo ratings yet
- Nitric Acid 2000Document10 pagesNitric Acid 2000harikeshrl5477No ratings yet
- Report AJUDocument20 pagesReport AJUTHE DARK KNIGHTNo ratings yet
- Iesel Exhaust GAS AftertreatmentDocument16 pagesIesel Exhaust GAS AftertreatmentHarsh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- TopsoeDocument5 pagesTopsoelaiping_lumNo ratings yet
- 2011.12 PG International - Las Vegas - Advanced SNCR TechnologyDocument36 pages2011.12 PG International - Las Vegas - Advanced SNCR TechnologylightsonsNo ratings yet
- Nox Reduction TechsDocument4 pagesNox Reduction TechsMehulkumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Denox DesoxDocument20 pagesDenox DesoxArzu AkarNo ratings yet
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation System: October 2015Document7 pagesExhaust Gas Recirculation System: October 2015Luyen NguyenNo ratings yet
- How To Reduce NOX and SOXDocument3 pagesHow To Reduce NOX and SOXnoraiz fozanNo ratings yet
- NOx SOxDocument9 pagesNOx SOxYohannes DennisNo ratings yet
- (Document Title) : For Engine To Reduce Oxides of Nitrogen Is Chosen For Present WorkDocument22 pages(Document Title) : For Engine To Reduce Oxides of Nitrogen Is Chosen For Present WorkrassNo ratings yet
- ENV315 - Online Air Pollution Control Lecture 11Document23 pagesENV315 - Online Air Pollution Control Lecture 11Samim JubayerNo ratings yet
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation SystemDocument7 pagesExhaust Gas Recirculation Systemmalik visheshNo ratings yet
- Diesel Exhaust Gas AftertreatmentDocument16 pagesDiesel Exhaust Gas AftertreatmentlukhmanNo ratings yet
- Clean Ironmaking and Steelmaking Processes: Efficient Technologies for Greenhouse Emissions AbatementFrom EverandClean Ironmaking and Steelmaking Processes: Efficient Technologies for Greenhouse Emissions AbatementNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Operation & Maintenance CourseDocument100 pagesGas Turbine Operation & Maintenance Coursewaheed2286100% (4)
- MSDS - SGT - 2Document7 pagesMSDS - SGT - 2SajidNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 PPT Reservoir Engineering-1Document38 pagesUNIT 4 PPT Reservoir Engineering-1PE9001 AarthiNo ratings yet
- JT15D Series Head IndexDocument4 pagesJT15D Series Head IndexEgor85No ratings yet
- PAC Insider February 2013 FinalDocument8 pagesPAC Insider February 2013 FinalAsep TheaNo ratings yet
- Combustion StoichiometryDocument18 pagesCombustion StoichiometryARYAN PIRTANo ratings yet
- Plant Design CHEN 451Document42 pagesPlant Design CHEN 451lalitNo ratings yet
- Ms Ds NaphthaDocument12 pagesMs Ds NaphthaCatharina Natasa BellaFortunaNo ratings yet
- Rubia Tir 7400 15W-40 - MSDSDocument14 pagesRubia Tir 7400 15W-40 - MSDSabdulNo ratings yet
- Fire Extinguisher TrainingDocument32 pagesFire Extinguisher Trainingaulianur564830No ratings yet
- TNavigator Modules Available 2019 ENGDocument26 pagesTNavigator Modules Available 2019 ENGVitor Azevedo Jr100% (1)
- Sanet ST 3030439321Document108 pagesSanet ST 3030439321Guido van HoyweghenNo ratings yet
- SSP 424 Exhaust Gas Aftertreatment System Selective Catalytic ReductionDocument56 pagesSSP 424 Exhaust Gas Aftertreatment System Selective Catalytic Reductionjohangustafsson200No ratings yet
- Les Modeling of Combustion Applications Using Openfoam: M. Chapuis, C. Fureby, E. Fedina, N. Alin & J. TegnérDocument20 pagesLes Modeling of Combustion Applications Using Openfoam: M. Chapuis, C. Fureby, E. Fedina, N. Alin & J. TegnérErnesto SalzanoNo ratings yet
- Combustion Course - Ch2Document35 pagesCombustion Course - Ch2hassan ghNo ratings yet
- 1386 - C11 Burner Design PDFDocument32 pages1386 - C11 Burner Design PDFMartin Martin MartinNo ratings yet
- 1-1 Unit (2016-2017)Document113 pages1-1 Unit (2016-2017)goutham100% (1)
- Quenching of Flame Anaylsis by ManasDocument17 pagesQuenching of Flame Anaylsis by ManasManas Srivastav100% (1)
- AP&CDocument35 pagesAP&CChethan K. ReddyNo ratings yet
- ME304UB Model Answer Set-1Document13 pagesME304UB Model Answer Set-1Harshraj WaniNo ratings yet
- 10 Technologies - Methods For Controlling NOx & SOx Emissions From Ships PDFDocument6 pages10 Technologies - Methods For Controlling NOx & SOx Emissions From Ships PDFMihir MishraNo ratings yet
- Fuel Oil Analysis: Know The Condition of The Fuel Oils You Use!Document6 pagesFuel Oil Analysis: Know The Condition of The Fuel Oils You Use!lolo100% (1)
- Basic Knowledge and Skills of Fire Safety Requirements For Electrical Engineering (0531)Document90 pagesBasic Knowledge and Skills of Fire Safety Requirements For Electrical Engineering (0531)Susi SusilowatiNo ratings yet
- Eurofirefighter 2 PDFDocument480 pagesEurofirefighter 2 PDFlifyadortaNo ratings yet
- Batch Reactor HazardsDocument12 pagesBatch Reactor HazardsSteve Forster100% (1)
- 5070 w10 QP 42Document16 pages5070 w10 QP 42Shahnawaz MemonNo ratings yet