Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Magnesium Sulfate
Magnesium Sulfate
Uploaded by
Silinna May Lee SanicoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Drug Study: Davao Doctors College General Malvar ST., Davao City Nursing ProgramDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Davao Doctors College General Malvar ST., Davao City Nursing ProgramJear RomeroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-Med WardDocument2 pagesDrug Study-Med WardErnest Brian FernandezNo ratings yet
- Med Template - Ipratropium Bromide AtroventDocument2 pagesMed Template - Ipratropium Bromide AtroventAshlee KeeferNo ratings yet
- Pharma CardsDocument5 pagesPharma CardsazancheNo ratings yet
- All Kinds of DrugsDocument11 pagesAll Kinds of DrugsRene John Francisco100% (1)
- Adults and Children 15 Y Pediatric 6 - 14 YDocument2 pagesAdults and Children 15 Y Pediatric 6 - 14 YFildehl Janice Bomediano Catipay100% (1)
- Drugs Study ER LEAD Drug (Yntig)Document5 pagesDrugs Study ER LEAD Drug (Yntig)Herbert Almendras HuyoNo ratings yet
- Cesarean SectionDocument3 pagesCesarean SectionJohnmark DubdubanNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide (Reglan)Document1 pageMetoclopramide (Reglan)ENo ratings yet
- Warfarin - Drug InformationDocument23 pagesWarfarin - Drug InformationTestesteNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShane Arroyo100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyChickz HunterNo ratings yet
- BisacodylDocument1 pageBisacodylJewel GutierrezNo ratings yet
- PhenytoinDocument5 pagesPhenytoinRhawnie B. GibbsNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyJM AcNo ratings yet
- Beclomethasone DipropionateDocument3 pagesBeclomethasone Dipropionateapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Omeprazole, Potassium Chloride, Citicoline, GlimepirideDocument5 pagesOmeprazole, Potassium Chloride, Citicoline, GlimepirideJenivic Empig PuedanNo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug Study Forms FINALDocument9 pagesNCP and Drug Study Forms FINALVince Troy AquinoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - IbuprofenDocument3 pagesDrug Study - IbuprofenThalia UyNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan: University of Cebu - BaniladDocument2 pagesDischarge Plan: University of Cebu - BaniladCHINGCHONG SLAYERNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug Studykennethbote0% (1)
- Omeprazole: (Oh Me' Pray Zol)Document3 pagesOmeprazole: (Oh Me' Pray Zol)Athea MelosantosNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyNedemar OcampoNo ratings yet
- Levalbuterol XopenexDocument2 pagesLevalbuterol XopenexCassie100% (1)
- Drug Name Dosa Ge Mechanis Mof Action Indicatio N Contraindic Ation Adverse/Side Effects Nursing InterventionsDocument14 pagesDrug Name Dosa Ge Mechanis Mof Action Indicatio N Contraindic Ation Adverse/Side Effects Nursing InterventionsVin LandichoNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 5M Case Analysis PDFDocument9 pagesNCM 107 5M Case Analysis PDFKisha BethelNo ratings yet
- GentamicinDocument2 pagesGentamicinDeprama Sutikti100% (1)
- Javier, Jomar A. BSN121 Group 83 Nursing Care Plan (Pediatric Patient)Document7 pagesJavier, Jomar A. BSN121 Group 83 Nursing Care Plan (Pediatric Patient)Julie AnnNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CHN 2Document6 pagesDrug Study CHN 2Raymond Christopher LimNo ratings yet
- KetoconazoleDocument2 pagesKetoconazolenatinlalaNo ratings yet
- Hyoscine ButylbromideDocument2 pagesHyoscine ButylbromideKenneth ColeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process in Drug TherapyDocument32 pagesNursing Process in Drug TherapyChaseNo ratings yet
- LantusDocument1 pageLantusSandrine BarredoNo ratings yet
- Halamang Gamot TableDocument3 pagesHalamang Gamot TableReyo VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- GCP Cs DrugsDocument13 pagesGCP Cs DrugsBel CortezNo ratings yet
- Activity-11 - Nursing Care Plan - ICPDocument6 pagesActivity-11 - Nursing Care Plan - ICPCloe CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Triamcinolone (Topical) - Drug InformationDocument5 pagesTriamcinolone (Topical) - Drug InformationMauricio Sv0% (1)
- TrazodoneDocument20 pagesTrazodoneAjay MehtaNo ratings yet
- Family PlanningDocument16 pagesFamily PlanningAnas Abdul SalamNo ratings yet
- Random Drug StudyDocument94 pagesRandom Drug Studykonzen456No ratings yet
- FlagylDocument3 pagesFlagylAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosage, Frequency, Route Indication Action Drug Interaction Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Generic Name: Brand NameDocument3 pagesDrug Dosage, Frequency, Route Indication Action Drug Interaction Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Generic Name: Brand NameRobert Martin Rivera PuertaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyGian Era100% (1)
- Q-MED ADRENALINE INJECTION 1 MG - 1 ML PDFDocument2 pagesQ-MED ADRENALINE INJECTION 1 MG - 1 ML PDFchannalingeshaNo ratings yet
- OB Drug StudyDocument12 pagesOB Drug StudyCj AttoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Metronidazole (Flagyl)Document1 pageDrug Study - Metronidazole (Flagyl)Jule SantoyaNo ratings yet
- Voglibose PiDocument2 pagesVoglibose PiAmit KhuntNo ratings yet
- Drug Study.Document9 pagesDrug Study.Chelsea Therese GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Tranexamic AcidDocument18 pagesTranexamic AcidFatima Love Ariate-ArcasetasNo ratings yet
- PonstanDocument2 pagesPonstanianecunar100% (2)
- ParacetamolDocument1 pageParacetamolChelsy MurielNo ratings yet
- HNBBDocument3 pagesHNBBManelle SingzonNo ratings yet
- NCP FveDocument2 pagesNCP FveFortuna Grace AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Flagyl)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Flagyl)ELyssa Anne Maristelle DizonNo ratings yet
- Ketessee FCT Dexketoprofen Jul 2012Document8 pagesKetessee FCT Dexketoprofen Jul 2012Dhurai OnelyNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Complete Drugs StudyDocument13 pagesComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- Labs Drug Study 1Document17 pagesLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Drug 25Document17 pagesDrug 25carol_gigliotti24100% (1)
- Drug Study Drug Name Classifications Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindication Nursing Responsibility CnsDocument4 pagesDrug Study Drug Name Classifications Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindication Nursing Responsibility CnsMarielle SorianoNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument21 pagesControllingSilinna May Lee SanicoNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument21 pagesControllingSilinna May Lee SanicoNo ratings yet
- DR JournalDocument2 pagesDR JournalSilinna May Lee SanicoNo ratings yet
- RN Heals JournalDocument2 pagesRN Heals JournalSilinna May Lee SanicoNo ratings yet
- NCP (Actual)Document2 pagesNCP (Actual)Silinna May Lee SanicoNo ratings yet
- NCP (Ideal) Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesNCP (Ideal) Nursing DiagnosisSilinna May Lee SanicoNo ratings yet
- Minor Surgical Procedures...Document10 pagesMinor Surgical Procedures...Silinna May Lee SanicoNo ratings yet
Magnesium Sulfate
Magnesium Sulfate
Uploaded by
Silinna May Lee SanicoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Magnesium Sulfate
Magnesium Sulfate
Uploaded by
Silinna May Lee SanicoCopyright:
Available Formats
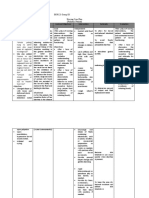
NAME OF DRUG Magnesium Sulfate
DOSAGE, ROUTE & FREQUENCY 5 gm; deep IM
CLASSIFICATIO N Anticonvulsant
MECHANISM OF ACTION May decrease acetylcholine released by nerve impulses but anticonvulsant mechanism is unknown
INDICATION
CONTRAINDICATION
SIDE EFFECTS
NURSING RESPOSIBILITIES Before: asssess patients condition before therapy assess prior drug history; there are many drug interaction during: monitor for signs of magnesium toxicity: disappearance of knee-jerk and patellar reflexes and signs of early magnesium toxicity monitor respiration: RR 16 per minute. watch respiratory depression and signs of heart block. After: Stress importance of immediate reporting of any adverse reaction.
Used as an anticonvulsant. Lowers intracranial pressure. For hypomagnesem ia in patients receiving total parenteral nutrition. Prevention and control of seizures in toxemia, avute nephritis in children and other conditions like epilepsy. Electrolyte additive. Inhibits uterine contraction in tocolysis. Also used for the treatment of life threatening arrhythmias such as atypical ventricular tachycardia. Counteracts intense muscle stimulating effects of barium poisoning
Patients with heart block of myocardial damage
Flushing, sweating, hypotension, muscular weakness, sedation, confusion. Nueromuscular agents, an excess of Mg ions in the body fluids causes direct depressant effect on skeletal muscles, decrease release of acetylcholine by motor nerve impulses and reduced sensitivity of the motor in place of acetylcholine
You might also like
- Drug Study: Davao Doctors College General Malvar ST., Davao City Nursing ProgramDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Davao Doctors College General Malvar ST., Davao City Nursing ProgramJear RomeroNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-Med WardDocument2 pagesDrug Study-Med WardErnest Brian FernandezNo ratings yet
- Med Template - Ipratropium Bromide AtroventDocument2 pagesMed Template - Ipratropium Bromide AtroventAshlee KeeferNo ratings yet
- Pharma CardsDocument5 pagesPharma CardsazancheNo ratings yet
- All Kinds of DrugsDocument11 pagesAll Kinds of DrugsRene John Francisco100% (1)
- Adults and Children 15 Y Pediatric 6 - 14 YDocument2 pagesAdults and Children 15 Y Pediatric 6 - 14 YFildehl Janice Bomediano Catipay100% (1)
- Drugs Study ER LEAD Drug (Yntig)Document5 pagesDrugs Study ER LEAD Drug (Yntig)Herbert Almendras HuyoNo ratings yet
- Cesarean SectionDocument3 pagesCesarean SectionJohnmark DubdubanNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide (Reglan)Document1 pageMetoclopramide (Reglan)ENo ratings yet
- Warfarin - Drug InformationDocument23 pagesWarfarin - Drug InformationTestesteNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyShane Arroyo100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyChickz HunterNo ratings yet
- BisacodylDocument1 pageBisacodylJewel GutierrezNo ratings yet
- PhenytoinDocument5 pagesPhenytoinRhawnie B. GibbsNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyJM AcNo ratings yet
- Beclomethasone DipropionateDocument3 pagesBeclomethasone Dipropionateapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Omeprazole, Potassium Chloride, Citicoline, GlimepirideDocument5 pagesOmeprazole, Potassium Chloride, Citicoline, GlimepirideJenivic Empig PuedanNo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug Study Forms FINALDocument9 pagesNCP and Drug Study Forms FINALVince Troy AquinoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - IbuprofenDocument3 pagesDrug Study - IbuprofenThalia UyNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan: University of Cebu - BaniladDocument2 pagesDischarge Plan: University of Cebu - BaniladCHINGCHONG SLAYERNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug Studykennethbote0% (1)
- Omeprazole: (Oh Me' Pray Zol)Document3 pagesOmeprazole: (Oh Me' Pray Zol)Athea MelosantosNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyNedemar OcampoNo ratings yet
- Levalbuterol XopenexDocument2 pagesLevalbuterol XopenexCassie100% (1)
- Drug Name Dosa Ge Mechanis Mof Action Indicatio N Contraindic Ation Adverse/Side Effects Nursing InterventionsDocument14 pagesDrug Name Dosa Ge Mechanis Mof Action Indicatio N Contraindic Ation Adverse/Side Effects Nursing InterventionsVin LandichoNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 5M Case Analysis PDFDocument9 pagesNCM 107 5M Case Analysis PDFKisha BethelNo ratings yet
- GentamicinDocument2 pagesGentamicinDeprama Sutikti100% (1)
- Javier, Jomar A. BSN121 Group 83 Nursing Care Plan (Pediatric Patient)Document7 pagesJavier, Jomar A. BSN121 Group 83 Nursing Care Plan (Pediatric Patient)Julie AnnNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CHN 2Document6 pagesDrug Study CHN 2Raymond Christopher LimNo ratings yet
- KetoconazoleDocument2 pagesKetoconazolenatinlalaNo ratings yet
- Hyoscine ButylbromideDocument2 pagesHyoscine ButylbromideKenneth ColeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process in Drug TherapyDocument32 pagesNursing Process in Drug TherapyChaseNo ratings yet
- LantusDocument1 pageLantusSandrine BarredoNo ratings yet
- Halamang Gamot TableDocument3 pagesHalamang Gamot TableReyo VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- GCP Cs DrugsDocument13 pagesGCP Cs DrugsBel CortezNo ratings yet
- Activity-11 - Nursing Care Plan - ICPDocument6 pagesActivity-11 - Nursing Care Plan - ICPCloe CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Triamcinolone (Topical) - Drug InformationDocument5 pagesTriamcinolone (Topical) - Drug InformationMauricio Sv0% (1)
- TrazodoneDocument20 pagesTrazodoneAjay MehtaNo ratings yet
- Family PlanningDocument16 pagesFamily PlanningAnas Abdul SalamNo ratings yet
- Random Drug StudyDocument94 pagesRandom Drug Studykonzen456No ratings yet
- FlagylDocument3 pagesFlagylAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosage, Frequency, Route Indication Action Drug Interaction Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Generic Name: Brand NameDocument3 pagesDrug Dosage, Frequency, Route Indication Action Drug Interaction Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Generic Name: Brand NameRobert Martin Rivera PuertaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyGian Era100% (1)
- Q-MED ADRENALINE INJECTION 1 MG - 1 ML PDFDocument2 pagesQ-MED ADRENALINE INJECTION 1 MG - 1 ML PDFchannalingeshaNo ratings yet
- OB Drug StudyDocument12 pagesOB Drug StudyCj AttoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Metronidazole (Flagyl)Document1 pageDrug Study - Metronidazole (Flagyl)Jule SantoyaNo ratings yet
- Voglibose PiDocument2 pagesVoglibose PiAmit KhuntNo ratings yet
- Drug Study.Document9 pagesDrug Study.Chelsea Therese GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Tranexamic AcidDocument18 pagesTranexamic AcidFatima Love Ariate-ArcasetasNo ratings yet
- PonstanDocument2 pagesPonstanianecunar100% (2)
- ParacetamolDocument1 pageParacetamolChelsy MurielNo ratings yet
- HNBBDocument3 pagesHNBBManelle SingzonNo ratings yet
- NCP FveDocument2 pagesNCP FveFortuna Grace AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Flagyl)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Flagyl)ELyssa Anne Maristelle DizonNo ratings yet
- Ketessee FCT Dexketoprofen Jul 2012Document8 pagesKetessee FCT Dexketoprofen Jul 2012Dhurai OnelyNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Complete Drugs StudyDocument13 pagesComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoNo ratings yet
- Labs Drug Study 1Document17 pagesLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Drug 25Document17 pagesDrug 25carol_gigliotti24100% (1)
- Drug Study Drug Name Classifications Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindication Nursing Responsibility CnsDocument4 pagesDrug Study Drug Name Classifications Action Indication Adverse Effects Contraindication Nursing Responsibility CnsMarielle SorianoNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument21 pagesControllingSilinna May Lee SanicoNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument21 pagesControllingSilinna May Lee SanicoNo ratings yet
- DR JournalDocument2 pagesDR JournalSilinna May Lee SanicoNo ratings yet
- RN Heals JournalDocument2 pagesRN Heals JournalSilinna May Lee SanicoNo ratings yet
- NCP (Actual)Document2 pagesNCP (Actual)Silinna May Lee SanicoNo ratings yet
- NCP (Ideal) Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesNCP (Ideal) Nursing DiagnosisSilinna May Lee SanicoNo ratings yet
- Minor Surgical Procedures...Document10 pagesMinor Surgical Procedures...Silinna May Lee SanicoNo ratings yet