Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Jan 02
Jan 02
Uploaded by
Romel BhaiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- ISO-8295-1995 Friction CoeficientDocument9 pagesISO-8295-1995 Friction CoeficientDaniela CamachoNo ratings yet
- Iec 61340-4-1-2015Document54 pagesIec 61340-4-1-2015srdjan.djordjevic0603No ratings yet
- Exp 10: Synthesis of (Co (NH3) 5Cl) Cl2Document8 pagesExp 10: Synthesis of (Co (NH3) 5Cl) Cl2Marla Basa95% (20)
- 601 Notes AllDocument546 pages601 Notes AllJack CavaluzziNo ratings yet
- Compounding and Dispensing 519 Lab Manual FinalDocument39 pagesCompounding and Dispensing 519 Lab Manual FinalAnonymous gSOBy38Y7100% (3)
- SATELLITE COMMUNICATION Question and AnswersDocument7 pagesSATELLITE COMMUNICATION Question and AnswersRubini RavichandranNo ratings yet
- NumericalDocument31 pagesNumericalrafiNo ratings yet
- QBDocument8 pagesQBSoundararajan RajagopalanNo ratings yet
- RapportSTING CLémentNguyen PDFDocument41 pagesRapportSTING CLémentNguyen PDFAnonymous 1fguovnNo ratings yet
- Technical Part 3Document22 pagesTechnical Part 3PriyaNo ratings yet
- Extended Essay Rough CompDocument19 pagesExtended Essay Rough CompBenjamin KnezNo ratings yet
- Govt. Engineering College, Ajmer: Electrical Measurement LabDocument5 pagesGovt. Engineering College, Ajmer: Electrical Measurement LabAnkitNo ratings yet
- Ec1015 Satellite CommunicationDocument13 pagesEc1015 Satellite Communicationainugiri100% (1)
- WWW - Studyguide.pk: AS Physics - Revision Notes Unit 3 - Medical PhysicsDocument3 pagesWWW - Studyguide.pk: AS Physics - Revision Notes Unit 3 - Medical Physicsnazran68No ratings yet
- Greg Hodowanec Mini MRADocument18 pagesGreg Hodowanec Mini MRAdetroit_me2553No ratings yet
- Reading 4Document5 pagesReading 4Dai NgoNo ratings yet
- Phy Proj Edit 2Document26 pagesPhy Proj Edit 2jujuNo ratings yet
- Electrical PowerDocument20 pagesElectrical PowerNaser A SosiyNo ratings yet
- Load Test of Single Phase TransformerDocument6 pagesLoad Test of Single Phase TransformerKevin DanyNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9-Electronics (Teacher's Guide)Document36 pagesChapter 9-Electronics (Teacher's Guide)Zulkarnain AgosNo ratings yet
- CyclotronDocument5 pagesCyclotronstewclel7No ratings yet
- 2005 June: Section 6 Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument43 pages2005 June: Section 6 Magnetism and ElectromagnetismMecid AliyevNo ratings yet
- CBSE 2011 Model Test Paper For Physics 12thDocument6 pagesCBSE 2011 Model Test Paper For Physics 12thp_k_soni_iit_physicsNo ratings yet
- (Total 1 Mark) (Total 1 Mark) (Total 1 Mark)Document8 pages(Total 1 Mark) (Total 1 Mark) (Total 1 Mark)Allan GunawanNo ratings yet
- DOE Fundamentals: Electrical Science DC CircuitsDocument23 pagesDOE Fundamentals: Electrical Science DC Circuitsnidhiaithal11_770999No ratings yet
- Two Mark QuestionsDocument18 pagesTwo Mark Questionsgayathiridevi RNo ratings yet
- BOOKLET - 3b Circular MotionDocument24 pagesBOOKLET - 3b Circular MotionSteven ChapmanNo ratings yet
- Objective: Apparatus Required:: Reflex Klystron CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesObjective: Apparatus Required:: Reflex Klystron Characteristicsratan lal mouryaNo ratings yet
- 3.12.1.3 Specific Charge of The ElectronDocument38 pages3.12.1.3 Specific Charge of The ElectronPhan Minh ViệtNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8. (B) : Date: AimDocument8 pagesExperiment 8. (B) : Date: Aimsanthu141986No ratings yet
- End Sem QuestionsDocument9 pagesEnd Sem QuestionsAakansha SuchittaNo ratings yet
- Power Transfer Through Strongly Coupled Resonances: Andr6 KursDocument0 pagesPower Transfer Through Strongly Coupled Resonances: Andr6 KursDuc DucNo ratings yet
- Important Questions - Electromagnetic WavesDocument4 pagesImportant Questions - Electromagnetic WavesswadhinNo ratings yet
- 1: Uses of The Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (C.R.O) 9.1.1: Thermionic EmissionDocument21 pages1: Uses of The Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (C.R.O) 9.1.1: Thermionic EmissionKalai SelviNo ratings yet
- Lab AssignmentDocument12 pagesLab Assignmentvachna ramNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document25 pagesChapter 6dedy krisnayanaNo ratings yet
- (Semiconductors and Semimetals) Lightwave Communications Technology - Photodetectors Volume 22 - Chapter 1 Physics of Avalanche PhotodiodesDocument172 pages(Semiconductors and Semimetals) Lightwave Communications Technology - Photodetectors Volume 22 - Chapter 1 Physics of Avalanche PhotodiodesSpeedraw FremyNo ratings yet
- IB Physics Review-WavesDocument21 pagesIB Physics Review-WavesTheEinsteinofTomorrow100% (1)
- Antenna Basic R&SDocument32 pagesAntenna Basic R&SKelvin AranaNo ratings yet
- Anh CNDocument12 pagesAnh CNHung Phi VuNo ratings yet
- General Instructions:: Time Allotted: 3hrs. Max. Marks: 70Document5 pagesGeneral Instructions:: Time Allotted: 3hrs. Max. Marks: 70varrshuNo ratings yet
- Amplitude Modulation - Lab1Document12 pagesAmplitude Modulation - Lab1Muhammad AfzaalNo ratings yet
- Electric Fields and Magnetism - Practice TestDocument5 pagesElectric Fields and Magnetism - Practice Testharkeerat singhNo ratings yet
- Capacitor When SwitchingDocument4 pagesCapacitor When SwitchingAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- Electric Field and CapacitorsDocument18 pagesElectric Field and CapacitorsTharushiNethmiNo ratings yet
- 2008 TJC Prelims h2 Physics p2Document15 pages2008 TJC Prelims h2 Physics p2Avinash BoodhooNo ratings yet
- Electro Erf EffectsDocument246 pagesElectro Erf Effectsaeroseb1No ratings yet
- To Accelerate The Alpha Particle or Other ParticleDocument11 pagesTo Accelerate The Alpha Particle or Other ParticleRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- 12 2005 Physics 2Document5 pages12 2005 Physics 2Dr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Isipathana College Physics: Answer Four Questions OnlyDocument11 pagesIsipathana College Physics: Answer Four Questions Onlyfazeelm24No ratings yet
- UlangkajiDocument7 pagesUlangkajiNor ShuhadaNo ratings yet
- Change in Energy and Energy Transformations AnsDocument33 pagesChange in Energy and Energy Transformations Anslokapavani_senthilNo ratings yet
- LightDocument35 pagesLightMelva GuerraNo ratings yet
- W 4 BookDocument55 pagesW 4 BookAdri De Udok100% (1)
- D. Bauer - Theory of Intense Laser-Matter InteractionDocument106 pagesD. Bauer - Theory of Intense Laser-Matter InteractionYsam2No ratings yet
- Introduction: Basic Concepts. Passive Elements.: University of Geneva TPA-ElectroniqueDocument25 pagesIntroduction: Basic Concepts. Passive Elements.: University of Geneva TPA-ElectroniqueDante FilhoNo ratings yet
- Report of PhysicsDocument21 pagesReport of PhysicsNafih ZebariNo ratings yet
- LRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronFrom EverandLRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronNo ratings yet
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 3: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #3From EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 3: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #3No ratings yet
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingFrom EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingNo ratings yet
- Rezaei 2009Document10 pagesRezaei 2009Química InvestChimNo ratings yet
- Alpha Decay 2Document6 pagesAlpha Decay 2parasnitinNo ratings yet
- 152 809 2 PBDocument12 pages152 809 2 PBsujal jhaNo ratings yet
- Aits Full Test - 3 Jee Advance (PCM - 1) On 14-1-18Document16 pagesAits Full Test - 3 Jee Advance (PCM - 1) On 14-1-18Mukund Varma T me18b157No ratings yet
- Table of Specifications Quarter 2 Grade 10 - ScienceDocument5 pagesTable of Specifications Quarter 2 Grade 10 - ScienceJhonalyn Toren-Tizon Longos100% (1)
- How Cells Harvest Energy: Life Is Driven by EnergyDocument24 pagesHow Cells Harvest Energy: Life Is Driven by EnergyNasreen MinNo ratings yet
- NEET Sample EbookDocument117 pagesNEET Sample EbookmisostudyNo ratings yet
- Revision For Test 1 (SET 2) Answer All Question Within 1 Hour. Total Marks Is 40 MarksDocument4 pagesRevision For Test 1 (SET 2) Answer All Question Within 1 Hour. Total Marks Is 40 MarkshadassahhadidNo ratings yet
- 9702 s14 QP 11Document24 pages9702 s14 QP 11Jing WangNo ratings yet
- Neet Booster Test Series (NBTS) For Neet-2021 Test - 2: PhysicsDocument15 pagesNeet Booster Test Series (NBTS) For Neet-2021 Test - 2: PhysicsupsahuNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document29 pagesModule 1Jeslyn MonteNo ratings yet
- Sizing and Wall ThicknessDocument37 pagesSizing and Wall ThicknessMuhammad NursalamNo ratings yet
- ME2151-1 Cooling Rate EffectDocument17 pagesME2151-1 Cooling Rate EffectAngelique PorterNo ratings yet
- Lab Report of PhysicsDocument12 pagesLab Report of PhysicsMuhammad AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Coating 1Document9 pagesCoating 1Chirlly UlaiNo ratings yet
- Magnetic CircuitsDocument25 pagesMagnetic Circuitstk techboy100% (1)
- JUNE 2018: Gauteng Department of Education Provincial ExaminationDocument18 pagesJUNE 2018: Gauteng Department of Education Provincial Examinationtabethtabeth15No ratings yet
- Formation of PolymersDocument3 pagesFormation of PolymersDavid KegayaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On The Synthesis of Ferrocene Appended Organotin CompoundDocument35 pagesLiterature Review On The Synthesis of Ferrocene Appended Organotin CompoundSouravNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument39 pagesElectrostaticsshreyas bulbule100% (1)
- The Influence of Temperature On The Operation of Batteries and Other Electrochemical Energy Storage SystemsDocument11 pagesThe Influence of Temperature On The Operation of Batteries and Other Electrochemical Energy Storage Systemssiraj udinNo ratings yet
- Ch04 Watervapor v102bDocument32 pagesCh04 Watervapor v102bAhmed Al QawasNo ratings yet
- Acceleration and MOIDocument30 pagesAcceleration and MOIIcy45No ratings yet
- National Standard Examination in Physics 2015 (22!11!2015)Document35 pagesNational Standard Examination in Physics 2015 (22!11!2015)anirudhNo ratings yet
Jan 02
Jan 02
Uploaded by
Romel BhaiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Jan 02
Jan 02
Uploaded by
Romel BhaiCopyright:
Available Formats
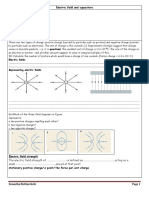
1.
In February 2000 scientists at CERN announced that they had made some "quark-gluon plasma" (QGP) - the extremely dense energetic matter that was present throughout the universe about 1 s after the Big Bang. They did this by colliding lead ions in the accelerator. A particular isotope of lead (symbol Pb) has 82 protons and 124 neutrons in its nucleus. Complete the symbol for this particular nucleus . ...........
Pb
(1)
What other particles are present in a neutral atom of this lead isotope`? (1) When QGP existed in the early universe, all the particles listed in the table below were present. Quarks Name up down charm strange top bottom Symbol u d c s t b Charge + 2/3 - 1/3 + 2/3 - 1/3 + 2/3 - 1/3 Name electron electron-neutrino muon muon-neutrino tau tau-neutrino Leptons Symbol e
-
Charge -1 0 -1 0 -1 0
ve v v
Protons and neutrons are made entirely of up and down quarks. Show how an appropriate number of quarks can combine to give the correct charge for a proton.
(2)
Explain briefly what circumstances are required for the remaining quarks in the table to be created.
(2) The early universe also contained positrons. Describe how the positron relates to one of the particles in the table.
(2) (Total 8 marks)
2.
Advances in digital technology mean that it is now possible to send telecommunications in digital form. This means that cable TV suppliers must convert analogue TV camera signals to digital before transmission and the receiver must convert them back to analogue for use in a TV set. State one advantage and one limitation of using a digital system instead of an analogue system to transmit the signal. Advantage ........................................................................................................................
Limitation ......................................................................................................................... (2) Describe how the cable TV suppliers use pulse code modulation to convert the analogue signal into a digital signal.
(3) Explain briefly why the sampling rate must be at least twice the maximum frequency of the signal being sampled.
(1)
One way in which a signal can be degraded is by dispersion; this is caused by the light in a single pulse taking a variety of paths down the optical fibre. Figure I represents a single pulse as it enters the optical fibre. Add to Figure 2 the likely shape of this pulse after transmission.
(2) A very high bit rate is required for the digital TV transmission. Explain how dispersion imposes an upper limit on the transmission bit rate.
(2) State and explain one way in which the effect of dispersion can be reduced.
(2) (Total 12 marks)
3.
The diagram shows a solar sail, a possible method of propelling spacecraft.
The solar sail uses "radiation pressure" caused by the momentum of photons of sunlight as they strike the sail. A sail with an area of 1.5 x 106 m2 could be used to propel a spacecraft of mass 1.2 x 103 kg. The energy E and momentum p of a photon are related by the expression E = p c, where c is the speed of light. Calculate the total momentum of the photons striking 1 m2 of sail in one second. Assume the solar radiation flux (intensity) is 1400 W m-2.
Momentum = ............................................................ (2)
Hence find the force exerted on the whole sail if it is completely non-reflective so that all of the incident light is absorbed.
Force = ...................................................................... (2) Explain why this force is doubled if a totally reflective material is used.
(2) An advantage of this form of propulsion is that it can be used for long periods of time allowing high speeds to be attained. Calculate the maximum increase in speed during one week, using a non-reflective sail. Assume the solar radiation flux remains constant during this time. 1 week = 604 800 s.
Maximum speed increase = .............................................................. (3) (Total 9 marks)
4.
The following is an extract from an article about ultrasound. "High frequency sounds do not travel far because they are exponentially attenuated by air, and for ultrasounds these losses become very severe. At 100 kHz half the ultrasound energy is lost for every metre travelled; for comparison, half the energy of a middle - C note (256 Hz) is still present as sound energy at 3 km." Explain the meaning of the phrase exponentially attenuated.
(2) Show that for ultrasound of frequency 100 kHz, the fraction of energy remaining after travelling 3 to is one eighth of the original energy.
(2) Show, using values given above, that the attenuation constant , for sound of 256 Hz travelling through air is about 2 x 10-4 m-1.
(3)
The corresponding values for three frequencies are as follows: f / Hz 256 100 000 212 000 / m-1 0.0002 0.693 1.90
It is suggested that may be proportional to f. Carry out a numerical check to decide whether this is a reasonable suggestion.
(3) (Total 10 marks)
5.
The timer on an electric toaster uses a resistor-capacitor circuit. When the bread is lowered, switch S1 is closed and the capacitor C starts to charge up. When the voltage across it reaches 4.0 V, another circuit is activated which makes the toast pop up, and at the same time switch S1 is opened and switch S2 is closed for a few seconds (to discharge the capacitor). The resistor R can be varied. The capacitance C = 100 F.
Calculate the energy stored in the capacitor when the voltage across it reaches 4.0 V.
Energy stored = ........................................................ (2) Which parts of this circuit will transfer this energy to the surroundings at the end of the toasting cycle?
(1) Discuss whether this energy transfer process may damage the toaster.
(1) The toaster is set so that switch S1 opens after 200 s. Complete the graph below to show how the voltage across the capacitor will vary with time from the moment (at t = 0 s) when S1 is closed.
(3)
By estimating the time constant for the circuit, calculate an approximate value for R when C = 100 F.
R = ............................................................................ (2) Discuss the effect of increasing the resistance, R.
(2) (Total 11 marks)
6.
There have been several space missions experimenting with tethered satellites. In a 1992 mission, the tethered satellite was connected to the shuttle Atlantis by a long conducting cable, the satellite being in the higher orbit. As the shuttle orbited through the Earth's magnetic field, an e.m.f. was induced in the conducting cable. The shuttle, cable and satellite were all moving through the ionosphere, which contains many charged particles. The charged particles were able to complete a circuit, allowing a current to flow through the cable. One result of this current was that the orbit height of the shuttle, cable and satellite gradually became less. Explain (a) (b) the origin of the induced e.m.f., the reduction in the orbit height due to the flow of current.
(Total 5 marks)
7.
A model of a fairground ride consists of a track with a circular loop in it of radius 0.50 m. A model vehicle is rolling freely on a track which has negligible resistance to motion. The vehicle is raised to a certain height above the level of the top of the loop and then released.
The vehicle will not fall off the track at the top of the loop if its centripetal acceleration at that point is greater than g. Calculate the minimum height x above the top of the loop (marked x on the diagram) from which the vehicle can be released and still complete the loop while staying in contact with the track.
x = ............................................................................. (Total 5 marks)
You might also like
- ISO-8295-1995 Friction CoeficientDocument9 pagesISO-8295-1995 Friction CoeficientDaniela CamachoNo ratings yet
- Iec 61340-4-1-2015Document54 pagesIec 61340-4-1-2015srdjan.djordjevic0603No ratings yet
- Exp 10: Synthesis of (Co (NH3) 5Cl) Cl2Document8 pagesExp 10: Synthesis of (Co (NH3) 5Cl) Cl2Marla Basa95% (20)
- 601 Notes AllDocument546 pages601 Notes AllJack CavaluzziNo ratings yet
- Compounding and Dispensing 519 Lab Manual FinalDocument39 pagesCompounding and Dispensing 519 Lab Manual FinalAnonymous gSOBy38Y7100% (3)
- SATELLITE COMMUNICATION Question and AnswersDocument7 pagesSATELLITE COMMUNICATION Question and AnswersRubini RavichandranNo ratings yet
- NumericalDocument31 pagesNumericalrafiNo ratings yet
- QBDocument8 pagesQBSoundararajan RajagopalanNo ratings yet
- RapportSTING CLémentNguyen PDFDocument41 pagesRapportSTING CLémentNguyen PDFAnonymous 1fguovnNo ratings yet
- Technical Part 3Document22 pagesTechnical Part 3PriyaNo ratings yet
- Extended Essay Rough CompDocument19 pagesExtended Essay Rough CompBenjamin KnezNo ratings yet
- Govt. Engineering College, Ajmer: Electrical Measurement LabDocument5 pagesGovt. Engineering College, Ajmer: Electrical Measurement LabAnkitNo ratings yet
- Ec1015 Satellite CommunicationDocument13 pagesEc1015 Satellite Communicationainugiri100% (1)
- WWW - Studyguide.pk: AS Physics - Revision Notes Unit 3 - Medical PhysicsDocument3 pagesWWW - Studyguide.pk: AS Physics - Revision Notes Unit 3 - Medical Physicsnazran68No ratings yet
- Greg Hodowanec Mini MRADocument18 pagesGreg Hodowanec Mini MRAdetroit_me2553No ratings yet
- Reading 4Document5 pagesReading 4Dai NgoNo ratings yet
- Phy Proj Edit 2Document26 pagesPhy Proj Edit 2jujuNo ratings yet
- Electrical PowerDocument20 pagesElectrical PowerNaser A SosiyNo ratings yet
- Load Test of Single Phase TransformerDocument6 pagesLoad Test of Single Phase TransformerKevin DanyNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9-Electronics (Teacher's Guide)Document36 pagesChapter 9-Electronics (Teacher's Guide)Zulkarnain AgosNo ratings yet
- CyclotronDocument5 pagesCyclotronstewclel7No ratings yet
- 2005 June: Section 6 Magnetism and ElectromagnetismDocument43 pages2005 June: Section 6 Magnetism and ElectromagnetismMecid AliyevNo ratings yet
- CBSE 2011 Model Test Paper For Physics 12thDocument6 pagesCBSE 2011 Model Test Paper For Physics 12thp_k_soni_iit_physicsNo ratings yet
- (Total 1 Mark) (Total 1 Mark) (Total 1 Mark)Document8 pages(Total 1 Mark) (Total 1 Mark) (Total 1 Mark)Allan GunawanNo ratings yet
- DOE Fundamentals: Electrical Science DC CircuitsDocument23 pagesDOE Fundamentals: Electrical Science DC Circuitsnidhiaithal11_770999No ratings yet
- Two Mark QuestionsDocument18 pagesTwo Mark Questionsgayathiridevi RNo ratings yet
- BOOKLET - 3b Circular MotionDocument24 pagesBOOKLET - 3b Circular MotionSteven ChapmanNo ratings yet
- Objective: Apparatus Required:: Reflex Klystron CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesObjective: Apparatus Required:: Reflex Klystron Characteristicsratan lal mouryaNo ratings yet
- 3.12.1.3 Specific Charge of The ElectronDocument38 pages3.12.1.3 Specific Charge of The ElectronPhan Minh ViệtNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8. (B) : Date: AimDocument8 pagesExperiment 8. (B) : Date: Aimsanthu141986No ratings yet
- End Sem QuestionsDocument9 pagesEnd Sem QuestionsAakansha SuchittaNo ratings yet
- Power Transfer Through Strongly Coupled Resonances: Andr6 KursDocument0 pagesPower Transfer Through Strongly Coupled Resonances: Andr6 KursDuc DucNo ratings yet
- Important Questions - Electromagnetic WavesDocument4 pagesImportant Questions - Electromagnetic WavesswadhinNo ratings yet
- 1: Uses of The Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (C.R.O) 9.1.1: Thermionic EmissionDocument21 pages1: Uses of The Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (C.R.O) 9.1.1: Thermionic EmissionKalai SelviNo ratings yet
- Lab AssignmentDocument12 pagesLab Assignmentvachna ramNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document25 pagesChapter 6dedy krisnayanaNo ratings yet
- (Semiconductors and Semimetals) Lightwave Communications Technology - Photodetectors Volume 22 - Chapter 1 Physics of Avalanche PhotodiodesDocument172 pages(Semiconductors and Semimetals) Lightwave Communications Technology - Photodetectors Volume 22 - Chapter 1 Physics of Avalanche PhotodiodesSpeedraw FremyNo ratings yet
- IB Physics Review-WavesDocument21 pagesIB Physics Review-WavesTheEinsteinofTomorrow100% (1)
- Antenna Basic R&SDocument32 pagesAntenna Basic R&SKelvin AranaNo ratings yet
- Anh CNDocument12 pagesAnh CNHung Phi VuNo ratings yet
- General Instructions:: Time Allotted: 3hrs. Max. Marks: 70Document5 pagesGeneral Instructions:: Time Allotted: 3hrs. Max. Marks: 70varrshuNo ratings yet
- Amplitude Modulation - Lab1Document12 pagesAmplitude Modulation - Lab1Muhammad AfzaalNo ratings yet
- Electric Fields and Magnetism - Practice TestDocument5 pagesElectric Fields and Magnetism - Practice Testharkeerat singhNo ratings yet
- Capacitor When SwitchingDocument4 pagesCapacitor When SwitchingAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- Electric Field and CapacitorsDocument18 pagesElectric Field and CapacitorsTharushiNethmiNo ratings yet
- 2008 TJC Prelims h2 Physics p2Document15 pages2008 TJC Prelims h2 Physics p2Avinash BoodhooNo ratings yet
- Electro Erf EffectsDocument246 pagesElectro Erf Effectsaeroseb1No ratings yet
- To Accelerate The Alpha Particle or Other ParticleDocument11 pagesTo Accelerate The Alpha Particle or Other ParticleRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- 12 2005 Physics 2Document5 pages12 2005 Physics 2Dr. Pradeep Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Isipathana College Physics: Answer Four Questions OnlyDocument11 pagesIsipathana College Physics: Answer Four Questions Onlyfazeelm24No ratings yet
- UlangkajiDocument7 pagesUlangkajiNor ShuhadaNo ratings yet
- Change in Energy and Energy Transformations AnsDocument33 pagesChange in Energy and Energy Transformations Anslokapavani_senthilNo ratings yet
- LightDocument35 pagesLightMelva GuerraNo ratings yet
- W 4 BookDocument55 pagesW 4 BookAdri De Udok100% (1)
- D. Bauer - Theory of Intense Laser-Matter InteractionDocument106 pagesD. Bauer - Theory of Intense Laser-Matter InteractionYsam2No ratings yet
- Introduction: Basic Concepts. Passive Elements.: University of Geneva TPA-ElectroniqueDocument25 pagesIntroduction: Basic Concepts. Passive Elements.: University of Geneva TPA-ElectroniqueDante FilhoNo ratings yet
- Report of PhysicsDocument21 pagesReport of PhysicsNafih ZebariNo ratings yet
- LRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronFrom EverandLRL Accelerators, The 184-Inch SynchrocyclotronNo ratings yet
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 3: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #3From EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 3: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #3No ratings yet
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingFrom EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingNo ratings yet
- Rezaei 2009Document10 pagesRezaei 2009Química InvestChimNo ratings yet
- Alpha Decay 2Document6 pagesAlpha Decay 2parasnitinNo ratings yet
- 152 809 2 PBDocument12 pages152 809 2 PBsujal jhaNo ratings yet
- Aits Full Test - 3 Jee Advance (PCM - 1) On 14-1-18Document16 pagesAits Full Test - 3 Jee Advance (PCM - 1) On 14-1-18Mukund Varma T me18b157No ratings yet
- Table of Specifications Quarter 2 Grade 10 - ScienceDocument5 pagesTable of Specifications Quarter 2 Grade 10 - ScienceJhonalyn Toren-Tizon Longos100% (1)
- How Cells Harvest Energy: Life Is Driven by EnergyDocument24 pagesHow Cells Harvest Energy: Life Is Driven by EnergyNasreen MinNo ratings yet
- NEET Sample EbookDocument117 pagesNEET Sample EbookmisostudyNo ratings yet
- Revision For Test 1 (SET 2) Answer All Question Within 1 Hour. Total Marks Is 40 MarksDocument4 pagesRevision For Test 1 (SET 2) Answer All Question Within 1 Hour. Total Marks Is 40 MarkshadassahhadidNo ratings yet
- 9702 s14 QP 11Document24 pages9702 s14 QP 11Jing WangNo ratings yet
- Neet Booster Test Series (NBTS) For Neet-2021 Test - 2: PhysicsDocument15 pagesNeet Booster Test Series (NBTS) For Neet-2021 Test - 2: PhysicsupsahuNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document29 pagesModule 1Jeslyn MonteNo ratings yet
- Sizing and Wall ThicknessDocument37 pagesSizing and Wall ThicknessMuhammad NursalamNo ratings yet
- ME2151-1 Cooling Rate EffectDocument17 pagesME2151-1 Cooling Rate EffectAngelique PorterNo ratings yet
- Lab Report of PhysicsDocument12 pagesLab Report of PhysicsMuhammad AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Coating 1Document9 pagesCoating 1Chirlly UlaiNo ratings yet
- Magnetic CircuitsDocument25 pagesMagnetic Circuitstk techboy100% (1)
- JUNE 2018: Gauteng Department of Education Provincial ExaminationDocument18 pagesJUNE 2018: Gauteng Department of Education Provincial Examinationtabethtabeth15No ratings yet
- Formation of PolymersDocument3 pagesFormation of PolymersDavid KegayaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On The Synthesis of Ferrocene Appended Organotin CompoundDocument35 pagesLiterature Review On The Synthesis of Ferrocene Appended Organotin CompoundSouravNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument39 pagesElectrostaticsshreyas bulbule100% (1)
- The Influence of Temperature On The Operation of Batteries and Other Electrochemical Energy Storage SystemsDocument11 pagesThe Influence of Temperature On The Operation of Batteries and Other Electrochemical Energy Storage Systemssiraj udinNo ratings yet
- Ch04 Watervapor v102bDocument32 pagesCh04 Watervapor v102bAhmed Al QawasNo ratings yet
- Acceleration and MOIDocument30 pagesAcceleration and MOIIcy45No ratings yet
- National Standard Examination in Physics 2015 (22!11!2015)Document35 pagesNational Standard Examination in Physics 2015 (22!11!2015)anirudhNo ratings yet