Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Emergency Drug Doses - PBS Doctor's Bag Items - Australian Prescriber
Emergency Drug Doses - PBS Doctor's Bag Items - Australian Prescriber
Uploaded by
Chhabilal BastolaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Emergency Drug Doses - PBS Doctor's Bag Items - Australian Prescriber
Emergency Drug Doses - PBS Doctor's Bag Items - Australian Prescriber
Uploaded by
Chhabilal BastolaCopyright:
Available Formats
1/17/13 Emergency drug doses PBS doctors bag items - Australian Prescriber
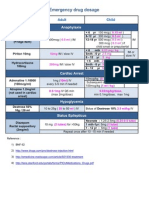
Emergency drug doses PBS* doctors bag items
Aust Prescr 2012;35:25-7
DRUG Adrenaline (1000 microgram in 1 mL injection equivalent to 1:1000) 1000 microgram = 1 mg
INDIC ATION Anaphylaxis1
DOSE 510 microgram/kg IM approximates to: Adults: <50 kg 0.250.5 mL >50 kg 0.5 mL C hildren: 10 kg (12 years) 0.1 mL 15 kg (23 years) 0.15 mL 20 kg (46 years) 0.2 mL 30 kg (710 years) 0.3 mL Repeat dose every 5 minutes if no response
C ardiac arrest
Adults: 0.51mg IV Flush with normal saline to aid entry into the circulation C hildren: 10 microgram/kg slow IV (Dilute 1 mL adrenaline injection 1:1000 with 9 mL sodium chloride (0.9%) and give 0.1 mL/kg)
Atropine (0.6 mg in 1mL injection)
Severe bradycardia, asystole
Adults: 1mg IV, repeat every 35 minutes until desired heart rate is reached or to a maximum of 3 mg C hildren: 20 microgram/kg IV (maximum dose 0.5 mg), repeat every 5 minutes until desired heart rate is reached or to a total maximum of 1mg
Benztropine (2 mg in 2 mL injection) Benzylpenicillin (600 mg or 3 g powder, dissolve in water for injections) C hlorpromazine (50 mg in 2 mL injection)
Acute dystonic reactions
Adults: 12mg IM or IV C hildren >3 years: 20microgram/kg IM or IV (maximum 1mg). Repeat after 15 minutes if needed.
Severe infections, including suspected meningococcal disease
Adults and children 10 years: 1.2 g IV or IM C hildren aged 19 years: 600 mg IV or IM C hildren <1 year: 300 mg IV or IM
Acute psychosis, severe behavioural disturbance
Avoid parenteral use injections cause pain and skin irritation. Use haloperidol instead. Adults: If there is no alternative, chlorpromazine 2550 mg (12.525 mg in the elderly) can be given by deep IM injection (buttock or deltoid)
Dexamethasone sodium phosphate (4 mg in 1 mL injection)
Acute severe asthma 2 Severe croup Bacterial meningitis
Adults: 412 mg IV slowly C hildren: 0.15 mg/kg IM if oral route is not possible Start before or at the same time as antibiotic Adults: 10 mg IV C hildren aged >3 months: 0.15mg/kg IV
www.australianprescriber.com/magazine/35/1/25/7
1/4
1/17/13 Emergency drug doses PBS doctors bag items - Australian Prescriber
Diazepam (10 mg in 2mL injection)
Severely disturbed patients
Adults: 510mg IV over 12 minutes (halve dose in elderly) in a large vein. Repeat if necessary every 510minutes (maximum 30mg). Adults: 10mg IV slowly in a large vein. Repeat once if necessary. 1020 mg rectally if IV access not possible. Repeat once if necessary. C hildren: 0.20.3mg/kg IV slowly in a large vein (maximum 10mg). Repeat once if necessary. 0.30.5mg/kg rectally (maximum 10mg). Repeat once if necessary.
Seizures
Dihydroergotamine (1 mg in 1 mL injection) Diphtheria and tetanus booster vaccine (0.5 mL pre-filled syringe) Frusemide (20 mg in 2 mL injection) Glucagon (injection kit containing 1 mg glucagon and 1 mL solvent in syringe) Glyceryl trinitrate (400 microgram per dose, 200 doses as sublingual spray) Haloperidol (5 mg in 1 mL injection) Hydrocortisone sodium succinate (100mg or 250mg with 2 mL solvent for injection)
Severe migraine
Adults: 0.51 mg SC or IM. Repeat every hour if needed (maximum 3 mg daily). Adults and children >8 years: 0.5 mL IM
Tetanus prophylaxis
Left ventricular failure, acute pulmonary oedema Severe hypoglycaemia
Adults: 2040 mg IV slowly or IM
Adults and children >5 years: 1 mg SC , IM or IV C hildren <5 years: 0.5 mg SC , IM or IV
Acute angina, acute left ventricular failure
Adults: 12 sprays under the tongue. Repeat after 5 minutes if needed (maximum 3 sprays).
Acute psychosis, severe behavioural disturbance Acute severe asthma Anaphylaxis Acute adrenal insufficiency
Adults: 210 mg IM (0.52 mg in the elderly)
Adults: 100mg IV C hildren: 4mg/kg IV Adults: 100 mg IV or IM C hildren: 24 mg/kg IV Adults: 100 mg IV or IM C hildren 112 years: 50 mg IV or IM C hildren 112 months: 25 mg IV or IM
Lignocaine (100mg in 5 mL injection)
Sustained ventricular tachycardia
Lignocaine has serious adverse effects including the potential to worsen arrhythmia and cardiac failure. Do not use outside of hospital. Adults and children: 1mg/kg IV over 12 minutes. Repeat after 5 minutes if needed.
Metoclopramide (10 mg in 2 mL injection)
Nausea and vomiting
Adults: IV or IM >60 kg 10 mg starting dose 3059 kg 5 mg starting dose (maximum 0.5 mg/kg daily) Not generally recommended in children as there is a risk of extrapyramidal adverse effects
Methoxyflurane (3 mL plus inhaler) Morphine sulfate (15 mg or 30 mg in 1 mL injection)
Pain after acute trauma Severe pain
Adults and children (who are able to use the device, usually 5 years): 68 breaths at a time (maximum 6 mL/day) Adults: SC or IM starting at lower dose <39 years 7.512.5 mg 4059 years 510 mg 6069 years 2.57.5 mg 7085 years 2.55 mg >85 years 23 mg
2/4
www.australianprescriber.com/magazine/35/1/25/7
1/17/13 Emergency drug doses PBS doctors bag items - Australian Prescriber
C an also be given as IV increments of 0.52 mg titrated to effect C hildren >1 year and <50 kg: 0.050.1 mg/kg SC or IM Naloxone (2 mg in 5 mL injection) Opioid overdose Adults and children: 0.40.8 mg IV, IM or SC repeated as necessary Neonates born with low APGAR scores to mothers taking opioids: 0.1 mg/kg IV, IM or SC . Repeat if needed. Severe infections (only suitable for infections where prolonged low concentrations are appropriate) Nausea and vomiting, vertigo Adults: 11.5 g by deep IM injection C hildren: 50 mg/kg by deep IM injection Adults: 12.5 mg IM or IV
Procaine penicillin (1.5 mg in 3.4 mL injection) Prochlorperazine (12.5 mg in 1 mL injection) Promethazine hydrochloride (50 mg in 2 mL injection) Salbutamol inhaler (100 microgram per dose, 200 doses) Salbutamol nebuliser solution (2.5 mg or 5 mg in 2.5 mL per dose, 30 doses)
Allergic reactions Nausea and vomiting Acute asthma, bronchospasm
Adults and children >12 years: 2550 mg IM C hildren >2 years: 0.125 mg/kg IM Adults and children >12 years: 12.525 mg IM Adults and children: 4 puffs (400 microgram) via spacer. Repeat after 4 minutes if needed. If still no improvement, continue giving 4 puffs every 4 minutes until ambulance arrives. Adults and children >2 years: 2.55mg by nebuliser as required C hildren <2 years: 0.1 mg/kg up to 2.5 mg by nebuliser as required For anaphylaxis give 5 mg by nebuliser to adults and children, repeat if required
Acute asthma, bronchospasm
Terbutaline (500 microgram in 1 mL injection) Tramadol (100 mg in 2 mL injection) Verapamil (5 mg in 2 mL injection)
Acute asthma
Adults: 250 microgram SC C hildren: 5 microgram/kg SC
Pain
Adults: 50100 mg IV over 23 minutes or IM
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia in patients who are not: - taking beta blockers - having an infarction - in second or third degree atrioventricular block
Do not use outside of hospital Adults: 5 mg IV slowly (over at least 3 minutes), repeat after 510 minutes if no response C hildren: 0.10.3 mg/kg IV, repeat after 30 minutes if no response (maximum 5 mg)
* Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme IM intramuscular IV intravenousSC subcutaneous A guide to paediatric weights10 kg at 12 years15 kg at 23 years20 kg at 46 years 30 kg at 710 years
PBS* doctor's bag items for palliative care patients
These drugs should only be used after consultation with a palliative care specialist DRUG C lonazepam (oral liquid containing 25 mg in 10 mL) Hyoscine butylbromide (20 mg in 1 mL injection) INDIC ATION Preventing seizures, hiccups DOSE Adults: 0.251 mg orally or sublingually
Noisy breathing and secretions
Adults: 1020 mg subcutaneously
www.australianprescriber.com/magazine/35/1/25/7
3/4
1/17/13 Emergency drug doses PBS doctors bag items - Australian Prescriber
PBS* Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme
REFERENC ES 1. Anaphylaxis: emergency management for health professionals [wall chart]. Aust Prescr 2011;34:124. 2. National Asthma C ouncil Australia. Asthma Management Handbook 2006. www.nationalasthma.org.au/handbook FURTHER READING Holmes JL. Time to restock the doctor's bag. Aust Prescr 2012;35:79. Baird A. Drugs for the doctor's bag. Aust Prescr 2007;30:143-6.
First published online: February - 2012
www.australianprescriber.com/magazine/35/1/25/7
You might also like
- New Vet Jumpstart Guide: Twenty common general practice cases simplifiedFrom EverandNew Vet Jumpstart Guide: Twenty common general practice cases simplifiedNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Drug Dosage - All in One PDFDocument15 pagesPediatric Drug Dosage - All in One PDFHuang Hasjim33% (9)
- RHU Blue Book 6 - 070852 1Document14 pagesRHU Blue Book 6 - 070852 1Jm Jm100% (1)
- Internship 1 4Document75 pagesInternship 1 4Mariah Sharmane Juego Santos100% (2)
- BupivacaineDocument6 pagesBupivacaineAngelica Dalit MendozaNo ratings yet
- Ped Med HandbookDocument27 pagesPed Med HandbookSoad Shedeed0% (1)
- ACLS Pocket GuideDocument5 pagesACLS Pocket Guidedragnu100% (1)
- Pediatric Guidelines For MedicationsDocument24 pagesPediatric Guidelines For MedicationsjonatasmartinezNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drug Doses - PBS Doctor's Bag ItemsDocument3 pagesEmergency Drug Doses - PBS Doctor's Bag ItemsPopa D. SilviuNo ratings yet
- DozeDocument3 pagesDozeCaterina PrepelitaNo ratings yet
- Obat AnestesiDocument9 pagesObat AnestesiNatanael SusantoNo ratings yet
- HTAR FormularyDocument204 pagesHTAR FormularyMay TanNo ratings yet
- What Is Allopurinol?Document10 pagesWhat Is Allopurinol?'Prasada WedatamaNo ratings yet
- AnalgesicsedationdrugsDocument4 pagesAnalgesicsedationdrugshevere6273No ratings yet
- Drug Doses12Document45 pagesDrug Doses12Asghar Shah100% (1)
- Table 1. Essential Emergency DrugsDocument3 pagesTable 1. Essential Emergency DrugsMariel Febreo MerlanNo ratings yet
- Adult: PO Acute Bronchospasm 2-4 MG 3-4 Times/day, Up To 8 MG 3-4 Times/day. AsDocument3 pagesAdult: PO Acute Bronchospasm 2-4 MG 3-4 Times/day, Up To 8 MG 3-4 Times/day. AswidiyaNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument8 pagesDiazepamramtaroNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Drug DosageDocument13 pagesAnesthesia Drug DosageLuqman HakimNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Drug Dosage - All in OneDocument15 pagesPediatric Drug Dosage - All in OneBJ Tiew100% (1)
- The Drug Doses in The Following Pages Are ReproducDocument168 pagesThe Drug Doses in The Following Pages Are ReproducAsghar ShahNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drug DosageDocument1 pageEmergency Drug DosagemarishuenNo ratings yet
- Drugs in Medicine by Medad Team FinalDocument5 pagesDrugs in Medicine by Medad Team Finalعبد الرحمن100% (2)
- Resuscitation MedicationDocument1 pageResuscitation MedicationDen SinyoNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis Wallchart 2022Document1 pageAnaphylaxis Wallchart 2022Aymane El KandoussiNo ratings yet
- Magnesium SulfateDocument5 pagesMagnesium SulfateRyan Inapan100% (1)
- IV Push MedicationsDocument67 pagesIV Push Medicationsbtalera100% (1)
- Medical Emergencies in Dental OfficeDocument112 pagesMedical Emergencies in Dental OfficeShohanNo ratings yet
- What Is The Dose?: Acetaminophen (Paracetamol)Document5 pagesWhat Is The Dose?: Acetaminophen (Paracetamol)Nadeem ChohanNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Daftar ObatDocument6 pagesKumpulan Daftar ObatZega AgustianNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Drug UsageDocument13 pagesPaediatric Drug UsageasmaNo ratings yet
- MPC Antidote ChartDocument1 pageMPC Antidote Chartogodothomas51No ratings yet
- 6.1 Quick Ref Guide MNGT Antivenom Reactions SGB2021 Ver. 2Document3 pages6.1 Quick Ref Guide MNGT Antivenom Reactions SGB2021 Ver. 2anju sulishaNo ratings yet
- Morphine SulfateDocument4 pagesMorphine SulfateWAQAS AHMADNo ratings yet
- Route/Dosage: Concentration: Not To Exceed 10 Mg/ml. Do NotDocument2 pagesRoute/Dosage: Concentration: Not To Exceed 10 Mg/ml. Do NotMaria MargaritaNo ratings yet
- 1-Amiodarone (Cordarone, Pacerone) : Duration: 30-45 MinutesDocument3 pages1-Amiodarone (Cordarone, Pacerone) : Duration: 30-45 MinutesMahmmoud FuqahaNo ratings yet
- Formulari Ubat KKM Bil.2 2013Document170 pagesFormulari Ubat KKM Bil.2 2013zilott90No ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs Drug StudyDocument15 pagesEmergency Drugs Drug StudyCathrine Sandile Tangwara100% (1)
- AirwaydrugsDocument5 pagesAirwaydrugshevere6273No ratings yet
- Drug Card Emergency DepartmentDocument2 pagesDrug Card Emergency Departmentdrmohdtanveer100% (3)
- Antidoturi Disponibile in Camera de GardaDocument4 pagesAntidoturi Disponibile in Camera de GardaTOXCROMNo ratings yet
- ASCIA Guidelines Acute Management Anaphylaxis 2017 Updated PDFDocument8 pagesASCIA Guidelines Acute Management Anaphylaxis 2017 Updated PDFAyu WahyuniNo ratings yet
- AzithromycinDocument4 pagesAzithromycinBrittany ClontzNo ratings yet
- Formulations of Representative Drugs From Antibiotics, Antipyretics, Steroids, Injectables and VitaminsDocument4 pagesFormulations of Representative Drugs From Antibiotics, Antipyretics, Steroids, Injectables and VitaminsChandraprakash JangidNo ratings yet
- Recommended Doses of Medications To Treat Children With An Acute Asthma ExacerbaDocument3 pagesRecommended Doses of Medications To Treat Children With An Acute Asthma Exacerbaمعاذ الشريفNo ratings yet
- IV Push List PedsDocument5 pagesIV Push List PedskrizzywhizzyNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin 125 MG 250 MG 5 ML Oral SuspensionDocument16 pagesAmoxicillin 125 MG 250 MG 5 ML Oral SuspensionAshrafNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyChristine PunsalanNo ratings yet
- Prescrption WritingDocument47 pagesPrescrption Writingashwarythakur712No ratings yet
- Diphenhydramine - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument7 pagesDiphenhydramine - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfKomang SubitaNo ratings yet
- Drug Doses & Frequency (Nicu) .12.mayDocument20 pagesDrug Doses & Frequency (Nicu) .12.mayTulasi100% (2)
- Homeo Drug CompenDocument6 pagesHomeo Drug CompenSittie Nadia MangondatoNo ratings yet
- 2022 Batch Prescription Writing 1st InternalDocument10 pages2022 Batch Prescription Writing 1st Internaldiwakar4123sawNo ratings yet
- AnaphylaxisdrugsDocument1 pageAnaphylaxisdrugshevere6273No ratings yet
- Pediatric Drug DosesDocument7 pagesPediatric Drug DosesSadr AkrmNo ratings yet
- Frank Shann - 040315153700Document63 pagesFrank Shann - 040315153700juwitapratiwiNo ratings yet
- Emergency Parenteral Drugs ListDocument4 pagesEmergency Parenteral Drugs ListRem Remoreras75% (4)
- AtropinDocument9 pagesAtropinarfitaaaaNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsFrom EverandDimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Opioids in AnaesthesiaDocument28 pagesOpioids in AnaesthesiaChhabilal BastolaNo ratings yet
- Oxygen TherapyDocument44 pagesOxygen TherapyChhabilal BastolaNo ratings yet
- CG en PDFDocument335 pagesCG en PDFJessicaPaolaGutiérrezAranaNo ratings yet
- Altered Sensorium and Care of Unconscious PatientsDocument17 pagesAltered Sensorium and Care of Unconscious PatientsChhabilal BastolaNo ratings yet
- Dental Anatomy For MBBSDocument33 pagesDental Anatomy For MBBSChhabilal BastolaNo ratings yet
- Resusgl 2010Document157 pagesResusgl 2010Salman IslamNo ratings yet
- Snake Bite ManagementDocument49 pagesSnake Bite ManagementChhabilal Bastola100% (1)
- Step 3: Content Description and General InformationDocument73 pagesStep 3: Content Description and General Informations1234321No ratings yet
- How - To - Read - Guitar TabDocument29 pagesHow - To - Read - Guitar TabChhabilal Bastola100% (4)
- UsmleDocument58 pagesUsmleFaisal Chukwudera Adam100% (1)
- 2010 Step 2 CKDocument76 pages2010 Step 2 CKandres ord100% (2)
- Pharmaceutics I Theory and Practical ForDocument21 pagesPharmaceutics I Theory and Practical ForNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hospital Pharmacy NotesDocument15 pagesHospital Pharmacy NotesChunnie JakosalemNo ratings yet
- Clinical Research BrochureDocument8 pagesClinical Research BrochureBen TennisonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of A SigDocument2 pagesAnatomy of A Sigkoki74No ratings yet
- AlbendazoleDocument7 pagesAlbendazoleSami SamiNo ratings yet
- Andrew Kim-HSHSPDocument1 pageAndrew Kim-HSHSPAndrew KimNo ratings yet
- Stok Obat 6 Sept 18 PDFDocument32 pagesStok Obat 6 Sept 18 PDFMargareta BokaNo ratings yet
- Acute Toxicity Study of Malli Chooranam A Siddha FormulationDocument2 pagesAcute Toxicity Study of Malli Chooranam A Siddha FormulationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Canamed 2011Document5,256 pagesCanamed 2011LucianNo ratings yet
- NIV MakassarDocument40 pagesNIV MakassarEmil LasulikaNo ratings yet
- Brief Notes On PharmacovigilanceDocument78 pagesBrief Notes On Pharmacovigilancejay100% (1)
- MarketLineIC - Pfizer Inc. - Profile - 120323Document74 pagesMarketLineIC - Pfizer Inc. - Profile - 120323JULIAN MAURICIO MARTINEZ ORTEGONNo ratings yet
- Nejmoa SEMAGLUTIDEDocument13 pagesNejmoa SEMAGLUTIDEraymundo lopez silvaNo ratings yet
- By Dr. AlabastroDocument9 pagesBy Dr. Alabastro2013SecBNo ratings yet
- Formularium Final 1Document196 pagesFormularium Final 1Klinik HARAPAN KITA BATAMNo ratings yet
- All Registered Products 30 - 06 - 17Document263 pagesAll Registered Products 30 - 06 - 17Filimone ThumboNo ratings yet
- APSARD PosterDocument1 pageAPSARD PosternaNo ratings yet
- Pregabalin: Information For Pain Clinic PatientsDocument6 pagesPregabalin: Information For Pain Clinic PatientsghyonasNo ratings yet
- What Is AmifostineDocument2 pagesWhat Is Amifostinecindy delafuenteNo ratings yet
- College DetailsDocument48 pagesCollege Detailsvivek chauhanNo ratings yet
- Oyol Componding FixDocument10 pagesOyol Componding FixYolandhaAiAnataNo ratings yet
- Moawya Abu-Rashed: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesMoawya Abu-Rashed: ObjectiveMoawya H. Abu RashedNo ratings yet
- NDDS (BP704) IDocument22 pagesNDDS (BP704) Ihasan.aliNo ratings yet
- 2021.12.10.Public-Alert Protonitazene NPS-Discovery 121021Document1 page2021.12.10.Public-Alert Protonitazene NPS-Discovery 121021Paris AfricaNo ratings yet
- Uses of Water As Therapeutic AgentDocument3 pagesUses of Water As Therapeutic AgentJake ArizapaNo ratings yet
- Rogerian EssayDocument4 pagesRogerian Essayapi-653591630No ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Intravenous Solutions, Equipment, and CalculationsDocument48 pagesChapter 14 Intravenous Solutions, Equipment, and CalculationsEn RasNo ratings yet
- Pca Epic Order SetsDocument4 pagesPca Epic Order Setsapi-244230664No ratings yet