Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NECAP InquirySchema
NECAP InquirySchema
Uploaded by
foglemanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NECAP InquirySchema
NECAP InquirySchema
Uploaded by
foglemanCopyright:
Available Formats
NECAP Assessment of Inquiry
The third session of the NECAP Science Assessment is an Inquiry Task that measures each student’s
ability to engage in the science process as defined by the thirteen constructs of the Four Broad Areas of
Inquiry. The Inquiry Tasks at Grades 4, 8, and 11 have items from each of the Four Broad Areas, but
not every construct will be represented in each task each year.
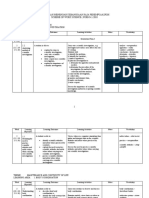
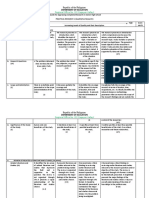
NECAP Schema for Assessing Scientific Inquiry (with DOK levels for constructs)
Broad Areas of Formulating Planning and Developing and
Conducting
Inquiry to be Questions & Critiquing of Evaluating
Investigations
Assessed Hypothesizing Investigations Explanations
Constructs for each 1. Analyze 4. Identify 7. Follow procedures 11. Analyze data,
Broad Area of information from information/evidence for collecting and including
Inquiry observations, that needs to be recording qualitative determining if data
(including intended research, or collected in order to or quantitative data, are relevant, artifact,
DOK Ceiling Levels, experimental data for answer the question, using equipment or irrelevant, or
based on Webb the purpose of hypothesis, measurement devices anomalous
Depth of Knowledge formulating a prediction accurately (DOK 2 – specify
Levels for Science – question, hypothesis, (DOK 2 – routine; (DOK 1 – use tools; relationships
see also Section II) or prediction: DOK 3 non- routine procedure; between facts;
Inquiry Constructs (DOK 3) routine/ more than DOK 2 – follow ordering, classifying
answer the question: 1a. Appropriate for one dependant multi-step data)
What is it about the answering with variable) procedures; make
broad area of scientific observations) 12. Use evidence to
Inquiry that we investigation 5. Develop an support and justify
want students to 1b. For answering organized and logical interpretations and
know and be able to 8. Use accepted
using scientific approach to methods for conclusions or
do? knowledge investigating the explain how the
organizing,
question, including representing, and evidence refutes the
controlling variables manipulating data hypothesis
2. Construct
coherent argument in (DOK 2 – routine; (DOK 2 – compare (DOK 3)
support of a DOK 3 non-routine) data; display data)
question, hypothesis, 13. Communicate
prediction 6. Provide reasoning how scientific
9. Collect sufficient
(DOK 2 or 3 for appropriateness data to study knowledge applies to
depending on of materials, tools, question, hypothesis, explain results,
complexity of procedures, and scale or relationships propose further
argument) used in the investigations, or
investigation (DOK 2 – part of construct and analyze
3. Make and describe following
observations in order (DOK 2) alternative
procedures) explanations
to ask questions,
hypothesize, make (DOK 3)
predictions related to 10. Summarize
topic results based on data
(DOK 2) (DOK 2)
You might also like
- Verbal (Non Verbal) Therapeutic Communication Technique Used Rationale and Feelings of Nurse EvaluationDocument13 pagesVerbal (Non Verbal) Therapeutic Communication Technique Used Rationale and Feelings of Nurse EvaluationLei Ortega80% (10)
- Integrated Science Curriculum MapDocument5 pagesIntegrated Science Curriculum Mapapi-417027192No ratings yet
- Scientific Method: Research ProblemDocument4 pagesScientific Method: Research ProblemKhaye Reyes HerreraNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Science Stage 5 NSW Syllabus - 1 - Working ScientificallyDocument30 pagesCambridge Science Stage 5 NSW Syllabus - 1 - Working ScientificallyDK01No ratings yet
- K To 12 Senior High School - Inquiries, Investigations and ImmersionDocument2 pagesK To 12 Senior High School - Inquiries, Investigations and ImmersionMariel CarabuenaNo ratings yet
- EAPP QUARTER 4 Written Work2Document2 pagesEAPP QUARTER 4 Written Work2Bastasa Allen JamesNo ratings yet
- SeptDocument2 pagesSeptapi-522668425No ratings yet
- AO2 & AO3 Space MissionsDocument6 pagesAO2 & AO3 Space MissionsMasterNo ratings yet
- 2 NgssDocument4 pages2 Ngssapi-235408695No ratings yet
- Research Methodologies: Intellectual Property RightsDocument12 pagesResearch Methodologies: Intellectual Property RightsGagan RaiNo ratings yet
- I II III IV: SCIENCE: PhysicsDocument6 pagesI II III IV: SCIENCE: PhysicsvirtualgardnerNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Raja Perempuan, Ipoh Scheme of Work Science (Form 4) 2010Document33 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Raja Perempuan, Ipoh Scheme of Work Science (Form 4) 2010magisperanNo ratings yet
- Curriculum 2a Assessment-1Document5 pagesCurriculum 2a Assessment-1api-522285700No ratings yet
- S2 Standards AlignmentDocument1 pageS2 Standards AlignmentybrikzerepNo ratings yet
- Q4 Prac1 Lecture Lesson4Document3 pagesQ4 Prac1 Lecture Lesson4MarielNo ratings yet
- Guide For Appraising Completed Research in Senior High School QUALIDocument6 pagesGuide For Appraising Completed Research in Senior High School QUALIAlyzza Mae Becera MarquezNo ratings yet
- SLE Final Unit Grade 4Document60 pagesSLE Final Unit Grade 4Verma GunjanNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1 CompilationDocument68 pagesPractical Research 1 Compilationrence121701100% (1)
- 3BGU Course Outlines 2021-2022Document1 page3BGU Course Outlines 2021-2022johnosborneNo ratings yet
- S&T Learning NeedsDocument6 pagesS&T Learning NeedsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- 2014 Yr 7 Science Parachute ExperimenDocument5 pages2014 Yr 7 Science Parachute Experimenthe.efroNo ratings yet
- RPT SC Year 5 (DLP) 2022-2023Document24 pagesRPT SC Year 5 (DLP) 2022-2023norainippgsceNo ratings yet
- Teaching LearningDocument333 pagesTeaching LearningManish Verma100% (1)
- Science s5 Sampleu1-WordDocument15 pagesScience s5 Sampleu1-WordReanne Mae BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum 2bDocument33 pagesCurriculum 2bapi-408430724100% (1)
- Research Methodology For Circuit Branches: 4.2 Designing A Conceptual Structure For Carrying Out ResearchDocument4 pagesResearch Methodology For Circuit Branches: 4.2 Designing A Conceptual Structure For Carrying Out Researchpaul macasaetNo ratings yet
- 10.siniflar Fizik 1.konu Dominoes ProjectDocument5 pages10.siniflar Fizik 1.konu Dominoes ProjectCemNo ratings yet
- Module For The Fourth Quarter Period: A I C SDocument34 pagesModule For The Fourth Quarter Period: A I C SCarmelo Justin Bagunu AllauiganNo ratings yet
- Compendium OF Research Methods Topic 10 The Research Process: Elements of Research Design Experimental DesignsDocument16 pagesCompendium OF Research Methods Topic 10 The Research Process: Elements of Research Design Experimental DesignsTarusengaNo ratings yet
- ASF Grade 8 Science StandardsDocument4 pagesASF Grade 8 Science StandardsJolanta NitoslawskaNo ratings yet
- Unit-I BRMDocument16 pagesUnit-I BRMTamil piratesNo ratings yet
- S6 - Week 6Document16 pagesS6 - Week 6BOLIVAR EMANUEL LÓPEZ ARCOSNo ratings yet
- WLP SCI7 Q1Week 2Document3 pagesWLP SCI7 Q1Week 2JonathanEncomiendaNo ratings yet
- The Research ProcessDocument26 pagesThe Research ProcessShefferd BernalesNo ratings yet
- Inquiries, Investigation, ImmersionDocument17 pagesInquiries, Investigation, ImmersionCharry Cervantes75% (4)
- 2.2 - Research Characteristics and Skills Needed To Conduct ResearchDocument2 pages2.2 - Research Characteristics and Skills Needed To Conduct ResearchcarlNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 PDFDocument57 pagesLec 2 PDFKhuram Iqbal AwanNo ratings yet
- RSME Week1 2023 24 2Document9 pagesRSME Week1 2023 24 2do trainingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document23 pagesChapter 2Bùi Ngọc ÁnhNo ratings yet
- Miguel Huerta q4 Presentation Teacher RubricDocument2 pagesMiguel Huerta q4 Presentation Teacher Rubricapi-538965270No ratings yet
- Research Designs: Dr. Vidya Naik Session 7 1Document17 pagesResearch Designs: Dr. Vidya Naik Session 7 1hrishikeshNo ratings yet
- Common CoreDocument5 pagesCommon Coreapi-302262307No ratings yet
- Science Investigatory Project PDFDocument2 pagesScience Investigatory Project PDFNick john CaminadeNo ratings yet
- Educ642 Scientific Method UbdDocument6 pagesEduc642 Scientific Method Ubdapi-261868573No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document13 pagesUnit 2DanielOvieObuwomaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Writing APA FormatDocument59 pagesThesis Writing APA FormatMarinelle MejiaNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work Form 1 Term 1Document6 pagesScheme of Work Form 1 Term 1api-513861322No ratings yet
- Grammar - Pho's Move and StepDocument4 pagesGrammar - Pho's Move and StepMarchella NANo ratings yet
- Melcs in Inquiries Investigation and ImmersionDocument2 pagesMelcs in Inquiries Investigation and Immersionchristopher rabaraNo ratings yet
- Curriculum 2b Assessment 1Document12 pagesCurriculum 2b Assessment 1api-408493824No ratings yet
- Practical Research 1Document112 pagesPractical Research 1Nikka Marie Francisco100% (2)
- Intro Notes MMDocument19 pagesIntro Notes MMNeels van HeerdenNo ratings yet
- UNIT III Collecting Data July 1Document13 pagesUNIT III Collecting Data July 1michael sto domingoNo ratings yet
- Research Methods ECSU NewDocument4 pagesResearch Methods ECSU NewabebeMBANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Research Process and Design: By: Group:191-200Document18 pagesIntroduction To Research Process and Design: By: Group:191-200surbhiNo ratings yet
- Empirical - From Experience or Experiment Peculiar - Unusual Phenomena - Peculiar Incidents That Can HappenDocument4 pagesEmpirical - From Experience or Experiment Peculiar - Unusual Phenomena - Peculiar Incidents That Can HappenJiselleNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work Practical Research 2Document2 pagesBudget of Work Practical Research 2LmNo ratings yet
- First Grade NgssDocument5 pagesFirst Grade Ngssapi-386821964No ratings yet
- 9th Physical Science Map StandardsDocument10 pages9th Physical Science Map Standardsgriffinkid121168No ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument1 pageResearch ReviewerJOSEPH DANIEL DOMINGONo ratings yet
- Rites PD Study Intro - 2014-09-10Document9 pagesRites PD Study Intro - 2014-09-10foglemanNo ratings yet
- RI Science Professional Development and Student Opportunity Bulletin 2-21-14Document26 pagesRI Science Professional Development and Student Opportunity Bulletin 2-21-14foglemanNo ratings yet
- RI Science Professional Development and Student Opportunity Bulletin 10-4-13Document10 pagesRI Science Professional Development and Student Opportunity Bulletin 10-4-13foglemanNo ratings yet
- RI Science Professional Development and Student Opportunity Bulletin 8-16-13Document5 pagesRI Science Professional Development and Student Opportunity Bulletin 8-16-13foglemanNo ratings yet
- RI Science Professional Development and Student Opportunity Bulletin 8-30-13aDocument7 pagesRI Science Professional Development and Student Opportunity Bulletin 8-30-13afoglemanNo ratings yet
- RI Science Professional Development and Student Opportunity Bulletin 6-28-13Document6 pagesRI Science Professional Development and Student Opportunity Bulletin 6-28-13foglemanNo ratings yet
- RI Science Professional Development and Student Opportunity Bulletin 5-31-13aDocument6 pagesRI Science Professional Development and Student Opportunity Bulletin 5-31-13afoglemanNo ratings yet
- RI Science Professional Development and Student Opportunity Bulletin 6-14-13Document5 pagesRI Science Professional Development and Student Opportunity Bulletin 6-14-13foglemanNo ratings yet
- RI Science Professional Development and Student Opportunity Bulletin 5-3-13Document8 pagesRI Science Professional Development and Student Opportunity Bulletin 5-3-13foglemanNo ratings yet
- RI Science Professional Development and Student Opportunity Bulletin 3-22-13aDocument13 pagesRI Science Professional Development and Student Opportunity Bulletin 3-22-13afoglemanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Biogeography of The EarthDocument44 pagesChapter 12 - Biogeography of The EarthAsmawi Bin AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Kasal MCDocument6 pagesKasal MCIris Rozeth Javier100% (2)
- Activity2 BAGSAC MMEP611Document7 pagesActivity2 BAGSAC MMEP611ivy bagsacNo ratings yet
- Describing People The Composition Should Be Divided in Three PartsDocument3 pagesDescribing People The Composition Should Be Divided in Three Partsrrrosaco100% (1)
- 2012 Oregon Sport Fish RegsDocument112 pages2012 Oregon Sport Fish RegsRoeHuntingResourcesNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle (Vehicle DTC Information) Document ID# 910473Document20 pagesDiagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List - Vehicle (Vehicle DTC Information) Document ID# 910473Carlos Alberto CruzNo ratings yet
- Ecn - Spin A PositionDocument4 pagesEcn - Spin A Positionkawa.yoga2No ratings yet
- Sol. Man. Chapter 9 Income Taxes 2021Document18 pagesSol. Man. Chapter 9 Income Taxes 2021Kim HanbinNo ratings yet
- History of HockeyDocument11 pagesHistory of HockeyLes LeynesNo ratings yet
- Curriculo E. Civil Final 15-01-2015Document164 pagesCurriculo E. Civil Final 15-01-2015Ângelo Soares67% (3)
- Gems 2019Document179 pagesGems 2019Wahyuni BerliantiNo ratings yet
- Natres Pe Benito MidtermsDocument27 pagesNatres Pe Benito MidtermsJay TabuzoNo ratings yet
- Test 3 MаrlinsDocument2 pagesTest 3 MаrlinsStaicy ErmakovitchNo ratings yet
- Oral Health ProgramDocument11 pagesOral Health Programapi-233877887No ratings yet
- Oracle20110102 DLDocument76 pagesOracle20110102 DLzakiyur5567No ratings yet
- Group 9 FOREX Rate Determination and InterventionDocument37 pagesGroup 9 FOREX Rate Determination and InterventionShean BucayNo ratings yet
- White Paper Introduction of SAP GTS - The Customs Solution: SapstroomDocument7 pagesWhite Paper Introduction of SAP GTS - The Customs Solution: SapstroomRafael RibNo ratings yet
- Quantum Hall EffectsDocument131 pagesQuantum Hall EffectsArmando IdarragaNo ratings yet
- PushkalavatiDocument5 pagesPushkalavatiSana KhanNo ratings yet
- Study of CRM at IBM An IT GiantDocument4 pagesStudy of CRM at IBM An IT GiantDarrick AroraNo ratings yet
- Romanesque Architecture in ItalyDocument35 pagesRomanesque Architecture in ItalySheree Labe100% (1)
- Isik Doll Body and OutfitDocument34 pagesIsik Doll Body and Outfitdeniselopdi100% (1)
- Research Paper On Yin and YangDocument4 pagesResearch Paper On Yin and Yangnikuvivakuv3100% (1)
- 60 Free TB ActivitiesDocument11 pages60 Free TB ActivitiesochioreanuNo ratings yet
- TIA Openness GettingStartedAndDemo V14SP1 enDocument35 pagesTIA Openness GettingStartedAndDemo V14SP1 enjoneschnNo ratings yet
- Ada Blackjack Answers (11-09-2021)Document4 pagesAda Blackjack Answers (11-09-2021)Blob BlobbyNo ratings yet
- I Believe That Books ...... DisappearDocument6 pagesI Believe That Books ...... DisappearDhanush PNo ratings yet
- Activity Plagiarism...Document2 pagesActivity Plagiarism...Max GCNo ratings yet
- Production (Lfpis+Lfgis) Iaas of Gcis Treasury: Int. System (Bi Server) A BDocument4 pagesProduction (Lfpis+Lfgis) Iaas of Gcis Treasury: Int. System (Bi Server) A BLinus HarriNo ratings yet