Professional Documents
Culture Documents
White Paper: An Introduction To IPTV
White Paper: An Introduction To IPTV
Uploaded by
Cindy MaldonadoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
White Paper: An Introduction To IPTV
White Paper: An Introduction To IPTV
Uploaded by
Cindy MaldonadoCopyright:
Available Formats
WHITE PAPER: text]Introduction to IPTV [Type An
WHITE PAPER: An Introduction to IPTV
January 2009
IN THIS WHITE PAPER...
What is IPTV? How does IPTV compare to traditional audio/visual (AV) solutions? And what are the benefits? Why organisations are adopting IPTV Markets where IPTV is already being used How it works
Version 6.1
WHITE PAPER: text]Introduction to IPTV [Type An
WHAT IS IPTV?
Internet Protocol Television, or IPTV, refers to television that is distributed over an IP network the same kind of network we use to surf the internet and exchange emails. In reality, much more than television can be sent over a network. Using IPTV technology, an organisation can easily distribute terrestrial and satellite television and radio, videos/DVDs, digital videos on-demand (VoDs), digital signage, information boards, and web content throughout their facility. All of this multimedia content can be viewed on standard and high definition TVs as well as PCs on every desktop. Types of IPTV Whether or not they are aware of it, many people encounter IPTV in their daily lives. There are four basics forms of IPTV. Internet IPTV is delivered over the internet to and from anywhere in the world. An example of this would be home videos on YouTube.com or TV programmes on Zattoo. As this type of IPTV travels over the public internet, there is no effort to optimise bandwidth or content delivery. Videos are easily displayed in a web browser but usually at low quality and with delays in transmission. Telco IPTV is delivered by your phone/internet/cable provider, also referred to as a Telecommunications provider. Often the television programs you watch at home have travelled across an IP network in the same fashion as your internet (and now
2
Version 6.1
WHITE PAPER: text]Introduction to IPTV [Type An
quality of service mechanisms that ensure reliable delivery of live and on-demand content. Ever wonder how you are able to watch on-demand TV shows? Those will be stored IPTV in the United Kingdom are BT Vision and Tiscali TV. Broadcast IPTV is when television broadcasters transmit their programming onto the internet for public consumption via personal computers. Many channels are broadcast for free; others will charge a fee for subscribing to their service. One example of Broadcast IPTV is BBC iPlayer. Unfortunately, broadcasters have no control over bandwidth or quality of service. Local IPTV also known as Building IPTV is designed to distribute television and video across building and campus networks over a local area network (LAN), replacing limited traditional analogue distribution systems with a flexible, scalable and cost-effective alternative. Local IPTV does not consume any internet bandwidth as the content is injected directly onto the building LAN. This white paper focuses specifically on the growing demand and benefits of local IPTV.
Version 6.1
WHITE PAPER: text]Introduction to IPTV [Type An
HOW DOES LOCAL IPTV COMPARE TO TRADITIONAL AUDIO/VISUAL (AV) SOLUTIONS? AND WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS?
Recent evidence suggests that the implementation of IPTV is up to 78% more costeffective than that of traditional coaxial TV distribution 1. Below is a comparison of current methods for distributing media via a traditional coaxial TV system versus an IPTV solution.
Traditional AV Video is distributed via individual videotapes or DVDs
Using IPTV
Benefits of IPTV
Video is stored digitally for on-demand viewing; archiving simultaneously available for multiple users manage and transport videotapes or DVDs -demand access helps increase use of resources
from degradation of the videotape or DVD medium Coaxial cable is run throughout a building to send live TV and recorded video; coaxial solutions subject to problems of electrical noise, signal weakening, limited channel capacity DVD quality video and audio is streamed over your existing local area network (LAN)infrastructure infrastructure video network -based solution and video quality simultaneously with no limit to the number of channels In-house news sent by memos or email. Personnel gather to watch broadcast news on shared televisions Live and stored video from inside and outside an organisation is streamed to every desktop -time information information
Data based on recent cost comparison of coaxial TV network versus IPTV implementation by Eurosatellites
4
Version 6.1
WHITE PAPER: text]Introduction to IPTV [Type An
Additional Benefits Using IPTV promotes a rapid rollout of new TV, video and broadband services across the whole organisation Costs are significantly reduced through not having to buy separate TV units or provide a separate satellite/aerial signal distribution system within the building The equipment deployed can utilise the existing network infrastructure, so there is no need for additional cabling to deliver TV at PC terminals; In addition, any PC can be converted easily into a TV with IPTV software that recognises the content on the network The system provides access to live news, entertainment and information channels to any PC, TV or audio/visual device attached to the local IP network Digital terrestrial (DVB-T) and digital satellite (DVB-S) services can be plugged directly into the local area network (LAN) to distribute real-time TV and radio across the whole building or campus network Replacement of analogue Cat5 TV distribution is straightforward Picture and sound quality is superior Compatibility with inherent customer systems Interruption of critical networks can be avoided by utilising a separate video VLAN
Version 6.1
WHITE PAPER: text]Introduction to IPTV [Type An
WHY ORGANISATIONS ARE ADOPTING IPTV
Most organisations already have an IP network covering a building or campus that is capable of supporting a video distribution system. This reduces both the initial cost of implementation and the cost of extending the IPTV network over time. Many organisations are adopting IPTV because: Television and video can easily be supplied to all computers on a network, increasing staff access to news and company information The same infrastructure can be used no matter how many channels or viewing devices are attached to the network. No special wiring or video distribution design is required Consistently high video quality is maintained regardless of the number of people using devices to view a channel Costs can be reduced by converging IPTV with existing data networks to provide services over a single cable infrastructure
Leading organisations regard live and recorded video as essential. It improves their ability to make better-informed decisions and to communicate more effectively with their internal and external stakeholders.
6
Version 6.1
WHITE PAPER: text]Introduction to IPTV [Type An
MARKETS WHERE IPTV IS ALREADY BEING USED
All sorts of organisations can benefit by using an IPTV solution as the platform to deliver quality content over their network. Construction Skip the installation of a coaxial network altogether by integrating AV and broadcast media into the IP network with an IPTV solution. Increase flexibility and scalability for the client while decreasing the cost of the build. Corporate IPTV in businesses large and small enables delivery of real-time news to inform decision makers, broadcasts to staff desktops, distribution of company information in public areas, simple and unified delivery of training, and staff entertainment. Education Educational IPTV provides instant classroom access to a virtually unlimited global archive of instructive material. Teachers no longer have to wait for tapes and discs to be returned to resource centres. Finance Watch current events unfold from around the globe by distributing international and country-specific news channels for content that may affect share dealings and financial markets. Healthcare Patients can receive television, radio and video at their bedsides. Simultaneously, information can be displayed in reception and waiting areas. Record procedures/operations for training and to protect against litigation. Hospitality & Leisure Provide guests with world class in-room entertainment with the latest TV, news, music, films and sport from not only the country where the conference facilities, hotel bars and restaurants. Promote revenue generation by advertising room service, bars and spa/leisure facilities. Manufacturing Use live video feeds from the factory floor for staff supervision and remote quality control inspection. Monitor live workflow to immediately highlight breakdowns and bottlenecks in the manufacturing process.
Version 6.1
WHITE PAPER: text]Introduction to IPTV [Type An
Transport Provide airline, train and bus passengers with departure and arrival times, announcements and information, security procedures, live news and entertainment throughout the transport facility. Venues/Stadiums Stream live coverage directly from the event stage or game pitch to TV screens around the facility so attendees never miss a second of the event. Display third party advertisements, match dates and merchandise information to generate future ticket sales and additional revenue. Provide live TV into hospitality suites.
Version 6.1
WHITE PAPER: text]Introduction to IPTV [Type An
HOW IT WORKS
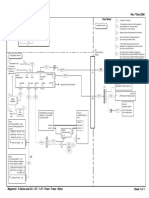
As you read this section, Figure 1 below will help you visually understand how IPTV works. Words coloured in blue below are items you may like to take note of, and many of which you will find represented in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Example of an end-to-end building IPTV solution
An existing network can be turned into a complete IPTV solution and adapted to fit any size organization from a single school, office building or hospital; right up to a geographically dispersed enterprise or college campus with global connections. Within an organization, almost any device with a screen can be turned into a networked television using IPTV technology. Sources of mu headend -end is a collective term for devices that make content available for distribution. It might consist of broadcast media sources such as a digital satellite (DVB-S) or terrestrial (DVB-T) service. These broadcast media are connected to a TV gateway which splits the broadcast signal into separate channels the network can understand.
9
Version 6.1
WHITE PAPER: text]Introduction to IPTV [Type An
Also on the head-end are the non-broadcast AV sources such as a video camera, video conferencing system, a video player, or DVD player. The non-broadcast sources will be connected to an encoder which will convert the content into network-friendly data for transport to various locations. Additionally, organisations can use an IPTV server to deliver Video On-Demand (VoD) services, an Electronic Programme Guide (EPG) and a customisable user interface for accessing all the content. Encoders, TV gateways and IPTV servers are simply connected to the network to make the broadcast media and the non-broadcast AV sources available for consumption. For those curious about the types of encoding used for IPTV, the common formats for streaming broadcast quality content are: MPEG-2, the predominant standard globally for TV transmission and DVDs; and MPEG-4 H.264 which is designed to deliver the same quality at lower bitrates. MPEG-4 H.264 is finding particular application in High Definition (HD) TV broadcasts and High Definition content encoding. Once all this IPTV content is available on the network, it can be received by various IPTV software is used receivers, also known as settop boxes (STBs), are used to decode the content that was sent over the network by the head-end. They convert the encoded data into a format which can be understood by the receiving AV devices. Where a facility requires IPTV, phone, and internet in one place, a -top box would be used. It requires only one network connection. The TV, phone, and PC would all then be connected to the triple-play set-top box. IPTV Management software. This type of software package facilitates the efficient administration of the IPTV system and utilises tools for discovering, configuring, and managing all the IPTV devices such as encoders, TV gateways, and set-top boxes; this includes the ability to filter viewing permissions and track who is watching what content. Many IPTV solutions will integrate with existing AV and IT systems. Examples include control systems that allow channels to be selected from a control panel in an auditorium or integration with an intranet system which requires access rights to varied content.
10
Version 6.1
WHITE PAPER: text]Introduction to IPTV [Type An
For smaller organizations with an existing network, an end-to-end2 IPTV solution can be installed and put into use, in a single day. Larger implementations could require weeks or months. However, so long as the customer configures the installation time should NOT be lengthy.
End-to-end refers to an IPTV solution that includes all the hardware and software needed to run IPTV. Not all IPTV solution providers sell an end-to-end solution. Some will sell only part of a solution such as IPTV set-top boxes.
11
Version 6.1
You might also like
- CCW - Micro800 Is Locked by UserDocument1 pageCCW - Micro800 Is Locked by UserShailesh BangaleNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper An Introduction To IPTVDocument11 pagesWhitepaper An Introduction To IPTVkurianjose2006No ratings yet
- Iptv PPT1Document18 pagesIptv PPT1Ravi AkkiNo ratings yet
- 2011-IPTV Course Notes PDFDocument60 pages2011-IPTV Course Notes PDFLink NguyenNo ratings yet
- IPTV (Internet Protocol Television) Is A SystemDocument6 pagesIPTV (Internet Protocol Television) Is A SystemGP GILLNo ratings yet
- IPTVDocument46 pagesIPTVശ്രീരാഗ് പി എം100% (1)
- Iptv TutorialDocument9 pagesIptv Tutorialapi-3743192100% (8)
- IPTVDocument24 pagesIPTVSanjeev Goutam100% (1)
- Iptv EditedDocument28 pagesIptv EditedSphurthi RaoNo ratings yet
- Internet Protocol TelevisionDocument11 pagesInternet Protocol TelevisionnejavmehtaNo ratings yet
- By: Neeraj Saini (3308412)Document18 pagesBy: Neeraj Saini (3308412)tweetymaniNo ratings yet
- ABCDocument22 pagesABCSanchit GargNo ratings yet
- Internet Protocol Television Seminar ReportDocument34 pagesInternet Protocol Television Seminar Reporttripsabhi08100% (5)
- IPTVPaperDocument6 pagesIPTVPaperHaitham FouratiNo ratings yet
- Internet Protocol TelevisionDocument16 pagesInternet Protocol Televisionharshit_pandey_1No ratings yet
- Tutorial On IPTV and Its Latest Developments: January 2011Document7 pagesTutorial On IPTV and Its Latest Developments: January 2011Prasad RaoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On IPTV and Its Latest Developments: January 2011Document7 pagesTutorial On IPTV and Its Latest Developments: January 2011Andri JunaediNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On IPTV and Its Latest Developments: January 2011Document7 pagesTutorial On IPTV and Its Latest Developments: January 2011Eyob AberaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On IPTV and Its Latest Developments: January 2011Document7 pagesTutorial On IPTV and Its Latest Developments: January 2011Ermin SehicNo ratings yet
- IPTV-Internet Protocol Televsion: December 2011Document62 pagesIPTV-Internet Protocol Televsion: December 2011Ermin SehicNo ratings yet
- Emerging Technology Iptv: Project Report OnDocument16 pagesEmerging Technology Iptv: Project Report OnNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On IPTV and Its Latest Developments: January 2011Document7 pagesTutorial On IPTV and Its Latest Developments: January 2011Demandas SanchezabogadosNo ratings yet
- "Internet Protocol Television": West Bengal University of TechnologyDocument8 pages"Internet Protocol Television": West Bengal University of TechnologyShashi PrakashNo ratings yet
- IPTV New GenerationDocument16 pagesIPTV New Generationmsavasari100% (1)
- The Impact of Internet Protocol Television and Comparison With The Conventional TVDocument5 pagesThe Impact of Internet Protocol Television and Comparison With The Conventional TVElda StefaNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument37 pagesFinal ReportsaranyaeNo ratings yet
- A Dive Into IPTVDocument6 pagesA Dive Into IPTVM-soft solutionsNo ratings yet
- IPTV-Internet Protocol Televsion: December 2011Document62 pagesIPTV-Internet Protocol Televsion: December 2011MarcoBenedettiNo ratings yet
- 05b Chapter 02 An Introduction To IPTV Development of IPTV (Smart TV PTCL)Document20 pages05b Chapter 02 An Introduction To IPTV Development of IPTV (Smart TV PTCL)shahabniaziNo ratings yet
- IPTV PresentationDocument21 pagesIPTV PresentationHiren ChawdaNo ratings yet
- IPTV Service Allows Viewers To Have More Control of Internet Television ServicesDocument14 pagesIPTV Service Allows Viewers To Have More Control of Internet Television ServicesAbhijit PattnaikNo ratings yet
- IPTV-Internet Protocol Televsion: December 2011Document62 pagesIPTV-Internet Protocol Televsion: December 2011Nasida SelimajNo ratings yet
- IPTV RajeshDocument19 pagesIPTV RajeshRajesh RokyNo ratings yet
- 2011 IptvDocument62 pages2011 IptvBacinoni RichardNo ratings yet
- IPTV-Internet Protocol Televsion: December 2011Document62 pagesIPTV-Internet Protocol Televsion: December 2011Khalid KhalidNo ratings yet
- 2011 Iptv PDFDocument62 pages2011 Iptv PDFEyob AberaNo ratings yet
- 2011 Iptv PDFDocument62 pages2011 Iptv PDFEyob AberaNo ratings yet
- Internet Protocol Television (IPTV) Is A System Through WhichDocument15 pagesInternet Protocol Television (IPTV) Is A System Through Whichbprathyusha12No ratings yet
- Iowa Public TelevisionDocument20 pagesIowa Public TelevisionMuhammad TaqiNo ratings yet
- Iptv Basics IecDocument9 pagesIptv Basics IecShadowNo ratings yet
- Rekha Nair Asst - Profes Sor Kvvs It Adoor: Presented byDocument23 pagesRekha Nair Asst - Profes Sor Kvvs It Adoor: Presented byRekha Nair75% (4)
- Report On IPTVDocument19 pagesReport On IPTVVineet KumarNo ratings yet
- Iptvppt 1210502376443368 9Document13 pagesIptvppt 1210502376443368 9Sudeshna RoyNo ratings yet
- Iptvppt 1210502376443368 9Document13 pagesIptvppt 1210502376443368 9Sourav Jyoti DasNo ratings yet
- 452 Internet Protocol TelivisionDocument22 pages452 Internet Protocol TelivisionRam VBITNo ratings yet
- Framework For Delivering IPTV Services Over WiMAX Wireless NetworksDocument6 pagesFramework For Delivering IPTV Services Over WiMAX Wireless NetworksAjay GargNo ratings yet
- Alphaott: Iptv System DesignDocument7 pagesAlphaott: Iptv System DesignAlphaOTTNo ratings yet
- Multicast Streaming For IPTV Content Distribution: A Brief SurveyDocument6 pagesMulticast Streaming For IPTV Content Distribution: A Brief SurveyBelly Yan DewantaraNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report IPTVDocument19 pagesSeminar Report IPTVvaibhavgupta160No ratings yet
- Internet Protocol TV or IPTVDocument3 pagesInternet Protocol TV or IPTVMarjan DraškovićNo ratings yet
- Internet Protocol Television by Deepak RaiDocument31 pagesInternet Protocol Television by Deepak RaiSurya6556No ratings yet
- IPTVDocument11 pagesIPTVvenkateshmukharjiNo ratings yet
- IPTVDocument18 pagesIPTVvaibhavgupta160No ratings yet
- A Presentation ON: Internet Protocol TelevisionDocument25 pagesA Presentation ON: Internet Protocol Televisionpandavas5npspnNo ratings yet
- Linear and Non-Linear Video and TV Applications: Using IPv6 and IPv6 MulticastFrom EverandLinear and Non-Linear Video and TV Applications: Using IPv6 and IPv6 MulticastNo ratings yet
- Digital Video Distribution in Broadband, Television, Mobile and Converged Networks: Trends, Challenges and SolutionsFrom EverandDigital Video Distribution in Broadband, Television, Mobile and Converged Networks: Trends, Challenges and SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Colour Banding: Exploring the Depths of Computer Vision: Unraveling the Mystery of Colour BandingFrom EverandColour Banding: Exploring the Depths of Computer Vision: Unraveling the Mystery of Colour BandingNo ratings yet
- How to Get Rid of Cable TV & Save Money: Watch Digital TV & Live Stream Online MediaFrom EverandHow to Get Rid of Cable TV & Save Money: Watch Digital TV & Live Stream Online MediaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Next Generation IPTV Services and TechnologiesFrom EverandNext Generation IPTV Services and TechnologiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cutting the Cord: A Practical Guide to Alternatives for Expensive Cable TelevisionFrom EverandCutting the Cord: A Practical Guide to Alternatives for Expensive Cable TelevisionNo ratings yet
- Manpower Proposal Template v1.3Document13 pagesManpower Proposal Template v1.3Hytham sa'adeh100% (1)
- PeopleTools Resolved IncidentsDocument15 pagesPeopleTools Resolved IncidentsAnonymous Su10Zrjs3VNo ratings yet
- Programation Deuxieme Annee - OdtDocument4 pagesProgramation Deuxieme Annee - OdtMiguel Clovis KamNo ratings yet
- Xspoc ManualDocument175 pagesXspoc ManualANDEINo ratings yet
- 84-Identify Group Keys On The Keyboard and Their Functions - PPSXDocument29 pages84-Identify Group Keys On The Keyboard and Their Functions - PPSXKapinpilan Endaila Silongan Ces100% (1)
- Oracle Apps Training Program FLYERDocument2 pagesOracle Apps Training Program FLYERkiran_shri1No ratings yet
- 02 Task Performance 18 PDFDocument4 pages02 Task Performance 18 PDFDaves Adamson Nevado SikatNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Agreement Distributed Systems Designs and ConceptDocument63 pagesCoordination and Agreement Distributed Systems Designs and ConceptRitesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- TESC College - Catalog PDFDocument270 pagesTESC College - Catalog PDFwantedfootNo ratings yet
- BM LabI Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesBM LabI Lecture NotesgandurikNo ratings yet
- Complex Engineering Problem Modern Electronics: Submitted To Sir Salman Ahmad Submitted byDocument11 pagesComplex Engineering Problem Modern Electronics: Submitted To Sir Salman Ahmad Submitted bySaad AliKhanNo ratings yet
- Document 2433249.1Document12 pagesDocument 2433249.1khaled_ghrbiaNo ratings yet
- SAS Do ArrayDocument118 pagesSAS Do Arraysarath.annapareddy100% (1)
- Untuk GAME Online: Seting Jalur Games Online, Download, Browsing Pada MikrotikDocument4 pagesUntuk GAME Online: Seting Jalur Games Online, Download, Browsing Pada MikrotikI'mfallingWith MyBrokenwings AndbreakingmydreamzNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Patterns: Part-1Document77 pagesBehavioral Patterns: Part-1birukNo ratings yet
- Epson L365Document2 pagesEpson L365Jimmy G. Díaz VegaNo ratings yet
- Cyber AttackDocument119 pagesCyber Attack2023689774No ratings yet
- Excel Vba To Read PDFDocument2 pagesExcel Vba To Read PDFNicoleNo ratings yet
- Sophos XGS Series Tech Specs - All ModelsDocument3 pagesSophos XGS Series Tech Specs - All ModelsDany MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Alcatel-Lucent 1870 Transport Tera Switch (TTS) : Addressing The Exaflood ChallengeDocument8 pagesAlcatel-Lucent 1870 Transport Tera Switch (TTS) : Addressing The Exaflood ChallengeMarco SurcaNo ratings yet
- Automata Problem Solution UpdatedDocument19 pagesAutomata Problem Solution UpdatedAmrita Pandey100% (1)
- PDFDocument1 pagePDFwicakNo ratings yet
- FactoryIO User Guide en PDFDocument21 pagesFactoryIO User Guide en PDFcarlos.otiniano9811100% (1)
- How To Boot From USB in VirtualBoxDocument20 pagesHow To Boot From USB in VirtualBoxtitusNo ratings yet
- Ubuntu 16.04 Wont Shutdown RestartDocument4 pagesUbuntu 16.04 Wont Shutdown RestartRobinson CruzoeNo ratings yet
- GE Healthcare Technologies Rev 7-Dec-2006: Operator WorkspaceDocument1 pageGE Healthcare Technologies Rev 7-Dec-2006: Operator WorkspaceJongchan Jason MoonNo ratings yet
- CEPAL CyberDocument62 pagesCEPAL CyberEnriqueNo ratings yet
- DataFlex Reports 2014 User GuideDocument189 pagesDataFlex Reports 2014 User Guidestp.vendas2No ratings yet
- Classical ALV Reporting - Overview of ALVDocument54 pagesClassical ALV Reporting - Overview of ALVtopankajsharmaNo ratings yet